Effectiveness of E-commerce Online Environments
Info: 14239 words (57 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
Tagged: E-commerce
Effectiveness of e-commerce online environments and factors that contribute to the success of such e-commerce websites
Abstract
Technology has helped to create a platform for e-commerce empowerment. Today, e-commerce can make a big contribution to the daily transactions of the Internet by enabling access to a massive population with access to the Internet and looking for a variety of products, information, and services. Since humans have been able to connect to the Internet through a computer, modem, and telephone line, to the Wi-Fi technology we have today, businesses have learned how to make sales possible with a single click.
1 Introduction
Technology has helped us to create a platform for e-commerce empowerment. Today, e-commerce can make a big contribution to the daily transactions of the Internet by enabling access to a massive population with access to the Internet and looking for a variety of products, information, and services. For example, just a few examples of telephone banking services to online trading and the business of Internet businesses – all of which are due to technological advances in the form of communication. Since humans have been able to connect to the Internet through a computer, modem, and telephone line, to the Wi-Fi technology we have today, businesses have learned how to make sales possible with a single click. (Smith-Atakan, 2011)
The system which is going to be build part of this project will be an e-Commerce system, where people can buy and sell cars. This include people provide information about their car and receive information about the value of the car. There will be a forum where potential buyers and sellers could exchange information and discuss about any car deals.
1.1 Background
1.2 Aims
The project aim is to investigate the problems that online businesses face, the effectiveness of e-commerce online environment and the factors that contribute to the success of e-commerce websites. In addition to know user behaviours, needs, motivations through observation and analysis techniques.
1.3 Objectives
2 Literature Review
2.1 Overview
Today, e-commerce can make a big contribution to the daily transactions of the Internet by enabling access to a massive population with access to the Internet and looking for a variety of products, information, and services (Laudon and Traver, 2017). To investigate the problems that online businesses face, the effectiveness of technology used in the e-commerce environment and the factors that contribute to the success of e-commerce websites. To know user behaviours, needs, motivations through observation and analysis techniques.
Access to the internet and e-commerce website which offer products and services has increased rapidly. According to the statistics, growth of the retails sales through the e-commerce website has increased in recent years. Internet access and the smartphone revolution double the company’s presence in e-commerce. As a result, the professional and efficient e-commerce website design is very important, and it is important to create effective websites based on these types of business principles and techniques
Several factors are involved in the success of an e-commerce website
Security is one of the important factors in e-commerce websites, data security and the use of secure payment ports as well as the use of SSL certificates can increase the security and confidence of e-commerce websites.
2.2 E-Commerce
E-Commerce is referred to as the methods provided for the purchase or sale of a product or service through electronic and non-personalized solutions. In many ways, this concept can mean more than just a simple online shopping. Other services such as production, marketing, sales, shipping, service, and payment for a variety of products can also be used as E-Commerce (Khurana, 2017).
E-commerce was first introduced in the 1960s by an Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in Value Added Networks (VANs), due to increased Internet access and the emergence of popular online vendors in the 1990s and early 2000s (Azim-Khan and Brock, 2013).
According to (Rivera, 2017) E-commerce is the electronic data exchange. Electronic data exchange is the production, processing, use and exchange of information and documents in electronic and automatic ways between computer systems based on common language and defined standards and with the lowest human factor interference.
For example, the Amazon website began its work in 1995 in the Jeff Bezos garage as a transport business. Or eBay website that allows consumers to buy and sell online, introduced the online auctions in the world in 1995, and in 1997, with great admiration for Beanie Babies dolls, they found a lot of popularity. By increasing the number of Internet users, many believe that e-commerce will soon become the main way of doing business transactions (Real, 2015).
E-commerce has evolved over the years, like any other digital or consumer-based consumer market.
By using more mobile devices, the mobile business has also found its market. With the advent of sites like Facebook and Pinterest, social networks have become a major factor in e-commerce. For example, according to Paymill.com, since 2014, in sales on the Shopify e-commerce platform, due to advertisements on social networks, in 85% of cases, buyers using Facebook ads on this platform are guided. (Paymill.com, 2014).
Furthermore, according to (Laudon and Traver, 2017) Technology has helped us to create a platform for e-commerce empowerment. Today, e-commerce can make a big contribution to the daily transactions of the Internet by enabling access to a massive population with access to the Internet and looking for a variety of products, information, and services. For example, telephone banking services to online trading and the business of Internet businesses – all of which are due to technological advances in the form of communication. Since humans have been able to connect to the Internet through a computer, modem, and telephone line, to the Wi-Fi technology we have today, businesses have learned how to make sales possible with a single click.
There are so many types of e-commerce that we’ll cover in this article: First-to-business
2.2.1 Business-to-Business (B2b) E-commerce
B2B Business-to-Business is a business deal between businesses or transactions between a company and the other for the transfer of services and products. The possible explanation is that a business involves an online wholesale business where the business sells materials, products, and services to other businesses on sales websites. (B2B) e-commerce is the largest form of e-commerce, used for major sales and purchases where manufacturers selling their product to distributors and wholesalers selling products to retailers. For example, Microsoft Corporation produces highly-used software and offers most of these software to companies.
2.2.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-Commerce
The most commonly used type of e-commerce is B2C or retail. This type of business has grown exponentially with the expansion of the Web, and it is now easy to purchase various types of goods, from cars and computer software, through the Internet. In B2C e-commerce, on the one hand, the manufacturer (seller) of the product and on the other side is the buyer (final consumer).
Business to consumer refers to dealings between a business and its consumer, provides electronic stores that provide information, goods and services between business and consumers. In a retail transaction or one an online business and internet business model that represents a financial transaction or online sale between a business and a consumer.
This model is special for companies that often offer their services to ordinary people. For example: Digi Commodity is one of the companies that uses this model for its business and sells its products on its site. Includes businesses that sell goods to the public through online stores without the need for any interaction with humans.
2.2.3 Consumer-to-Business (C2B) E-commerce
A consumer is the business of transferring services, goods or information from individuals to businesses, or a business model that creates end users of products and services used by companies and institutions. C2B e-commerce, Consumer send out a project with an online budget and companies are proposing for this project. Then the consumer reviews the price suggestions and chooses the company of interest.
2.2.4 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) e-commerce provides a way for consumers to sell to each other, with the help of an online market maker or online platform.
In C2C e-commerce, the consumer prepares the product for the market, sells the product for auction or sale, and easily displays products to market makers e-commerce platform, the platform can provide catalogue, search engine, abilities of transaction clearing and paid for.
This kind of business is done in online classified ads, communities or markets in which people can trade and sell goods together. In this model of e-commerce, sales are made between consumers (ordinary people). Today, people are taking photos of their home appliances, selling them on sites and selling their appliances, which is a common practice today.
2.2.5 Mobile E-Commerce (M-Commerce)
Mobile e-commerce or m-commerce refers to the use of mobile devices to enable online transactions. M-commerce includes the use of mobile and wireless networks to connect to the Internet using devices such as laptops, smartphones, iPads and tablets.
These wireless devices communicate with computer networks that can purchase online merchandise. Mobile commerce allows users to access the internet and buy it without having to find a place to connect. Business-related commerce continues to improve and the phrase includes the sale and sale of a wide range of products and services, online banking, bill payment, delivery of information, etc.
E-commerce or mobile commerce is rapidly growing these days, and people are beginning to buy products using smartphones or other smart devices. Having an e-commerce website that is usable on all devices is important because more and more people are visiting their websites from smartphones and other smart devices. While developing the site, make sure that the site is usable on smartphones and other smart devices. It is important that the business is monitored and up-to-date, and educate customers with useful information on a regular basis so that customers are not tedious and find something new every time they visit the site (Meola, 2016).
2.3 Key Factors Impacting E-Commerce
E-commerce provides many individuals with revenue generating opportunities and a competitive advantage. Every year, the number of people who use e-commerce services, including online shopping, is added. But many sites do not only fail to succeed in this, but quickly overcome the competition with the rest. (Moons, 2017).
In a highly competitive online marketplace, building long-term relationships beyond customer expectations is the only way to become a successful e-commerce brand. Delivering exceptional customer service in a timely manner, driving strong relationships with customers and recognizing them at a more personal level, are important factors in separating the competition.
To have successful e-commerce website If you own an online store, or you plan to have an e-commerce site for you in the future, then go along with the next with 10 major factors that can help you succeed or fail or fail. E-commerce has a role to play, get to know
factors that significantly contribute to the success of e-business are the trust people place in the online businesses and how secure they feel in transacting business on the Internet.
Among these criteria are security and privacy of the store, ease of use, and handling complaints and customer comments.
2.3.1 Accessibility
We all like to use the internet at ease and speed, for most of us, there is no problem to go to this page from this page. Usually, after a few minutes, we will finally find the information we want. But for people who are suffering from disability, the situation does not go well. fortunately, there are many principles and rules that are set up to address the concerns of these individuals and make them accessible on the web (Roggio, 2015).
Accessibility is a kind of thinking in website design that makes the website available to a specific range of people. In general, the website should be scrollable to anyone who visits it and can quickly get the information he needs. Accessibility focuses on creating a website which can be used by people with different disabilities (Smith-Atakan, 2011).
For example, a website should be able to be used by user with disabilities who uses the screen reader to use the website. A user who is deaf should be able to use the contents on the website, if there is a video on the website, video should have subtitle so deaf users can understand what the video is about. Accessibility is one of the important factors e-commerce sites, because revenue opportunities are highly dependent on the activities performed on the site. Issues of access to the e-commerce website have a direct impact on sales.
2.3.2 Usability
Designing an e-commerce site is more serious and more difficult than having an interesting site for the visitor. Although the attractiveness of the site is an important factor, it should be as important as the site’s performance. It seems that many web designers focus on the appearance of the site more than its functionality. But a visitor who is disappointed with the site due to a lack of efficiency will quickly leave the site and will never return. Designing e-commerce sites requires basic information about site design and a bit of experience and training (Rosenzweig, 2015).
When creating an e-commerce website, need to know exactly what expect a customer to enter on website. Pages that do not include products and services should guide through the pages of products and direct the customer and contact to the page are looking for. It should always be noted that the most successful e-commerce websites tell their customers exactly what to do. Never allow customers to be confused at any stage of the purchase or viewing the website, customer should be guided step by step and reach the goal they have (Lynch and Horton, 2016).
Content containing keywords that is purposeful and written in accordance with the principles will increase the ranking of search engines. As the wrong way of typing will drive customers, and the lack of keywords will lower rank in search engines. The style of writing is the first way to influence the visitor who has just visited website, so paying close attention to the content of the site usually leads to more sales.
Pages that slowly appear, pages that are very large or very small, and difficult to navigate on the site, each alone, will make the visitor tired and frustrated. The visitor should never wait for the pages to appear, never must scroll the page up and down to read the information he needs, and never should look for the whole site for information on buying want item. Sites with well-organized, fast and targeted pages are generally more successful in selling (Lebson, 2016).
2.3.2.1 Design Principles
Design principles can guide the designer during the design process and can be used to evaluate and analyse prototype design ideas. A list of high-level design principles from Norman, Nielson and others are listed below. All the principles are encountered in complex ways, affect each other, in some cases they differ and sometimes reinforce each other. they help designer designers with key features of good design and make the designer sensitive to critical issues (Benyon, 2014).
- Visibility: Try to ensure that things are visible so that people cans see what functions are available and what the system is currently doing.
- Consistency: be consistent in the use of design features and be consistent with similar system and standard ways of working. Both conceptual and physical consistency are important.
- Familiarity: Use language and symbols that intended audience will be familiar with. Where this is not possible because the concepts are quite different from those people know about, provide a suitable metaphor to help them transfer similar and related knowledge from a more familiar domain.
- Affordance: Design things so it is clear what they are for, affordance refers to the properties that things have and how these relate to how the things could be used.
- Navigation: Provide support to enable to move around the part of the system: directional signs and information signs.
- Control: Make it clear who or what is in control and allow people to take control. Control is enhanced if there a clear, logical mapping between controls and the effect that they have. Also make clear relationships between what the system does and what will happen outside the system.
- Feedback: Rapidly feedback information from the system to people so that they know what effect their actions have had. Constant and consistent feedback will enhance the feeling of control.
- Recovery: Enable recovery from actions, particularly mistakes and errors, quickly and effectively.
- Constraints: provide constraints so that people do not try to do things that are inappropriate. People should be prevented from making serious errors through properly containing allowable actions and seeking confirmation of dangerous operations.
- Flexibility: Allow multiple ways of doing things to accommodate people with different levels of experience and interest in the system. Provide people with the opportunity to change the way things look or behave so that they can personalise the system.
- Style: Designs should be stylish and attractive.
- Conviviality: Interactive systems should be friendly and generally pleasant. Conviviality also suggests joining in and using interactive technologies to connect and support people.
2.3.3 Security
Security is one of the most important characteristics of any e-commerce business, and security measures should be applied at all levels, this helps to maintain unauthorized access and ensures privacy, confidentiality and data integrity. To build confidence it is very important to protect consumer privacy and personal data (Rybalchenko, 2012).
To run an e-commerce website must stay up-to-date with all security measures to protect customers’ and own data protection. Doing this will help customer have more confidence in business and will make them more likely to purchase product and will be returning to the website.
On the other hand, if security on the site is not continuously updated or a faulty service, there is a great risk and chance of customers’ and company’s own data being stolen. Nothing destroys a business’s credibility faster than a security breach and a serious breach can kill a small business completely (Graham, 2015).
New strategies for processing vast amounts of data, for example, data mining procedures, make it conceivable to distinguish new sorts of buying connections and unordinary affiliations to make factual surmising. While they raise some possibly genuine protection issues, they can likewise be utilized to distinguish fraud, particularly for vast volume, little esteem ecommerce transactions.
The purpose of security is to protect data against unauthorized persons in the process of e-commerce. The Internet is a completely open network and, if the necessary measures to prevent unauthorized persons from accessing information and intervening in them are not available, information may be lost or handcrafted (Mackenzie, 2013).
E-commerce websites must be secure to ensure that the user’s personal information provided to the website is in a safe place and will not be shared sold to anyone else. This issue is important for the website visitors, so any assurance and security of the website will improve sales and attract users. For example, when a credit card is used in a purchase, if a credit card is issued to unauthorized persons, it may cause financial damage to the cardholder by exploiting it, and this is a clear indication for the further protection of electronic transactions in Internet. The main tools for this care are authentication and encryption.
2.3.4 Trust
Trust is of the most important factors in ecommerce website, trust is very useful in helping website to succeed. In the field of e-commerce and online stores, trust is a key factor in the formation of long-lasting and lasting business relationships between the two sides of the deal. The tendency of the two sides to establish long-term relationships rests on the mutual trust of each other. In fact, it is a trustworthy element of the desire for continuity of relationships
One of the ways to gain customer trust is by Providing contact information and location address on website. This will be useful for customer, and will be able to contact you if there is a problem. If refrain from providing contact information and location to customers, it is hard to win their trust (Roggio, 2015).
2.3.5 Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM is used to better understand customers and to better illustrate customer relationship. CRM concepts or new customer relationship management. Today, based on these concepts, they learn how to work and communicate with customers in the long run for more profit and profit. Companies make and invest large investments. The customer is aware of the services he receives and selects it based on his or her experiences and information.
It is a general business strategy that enables companies to effectively manage customer relationships. CRM depicts a general view of the customers of each organization for its members. Based on the concepts of CRM, everyone should focus on customer and customer information. For this purpose, customer information must be fully and completely shared throughout the organization with all customer related elements.
In this regard, the marketing department of each company collects an organized, continuous search of customer information and maintains its information and networking system. Sellers use this information to contact the customer and provide the goods or services they require. Customer services also respond to each customer’s inquiry and request using this information.
Support and production design also uses this information to meet the needs of customers and tailor their activities to these needs. In completing the CRM concepts of each section of the organization, while using the same information about the customer, their performance and relationship with the customer are precisely entered in the same database so that the latest customer calls and comments are available to all organizations.
No part of the organization has the right to maintain confidential and secret information and communication with the client. Rather, the logic of this strategy is that the customer information must be comprehensively, complete and like all the customer-related entities within the organization, and at the same time, this information should not be transferred from the relevant parties to the organization, as the important secrets of the organization.
The need for the development of information technology and especially the global Internet has created an opportunity to improve communication with customers in the face of today’s competitive world. The goal is to turn these communications and interactions into greater profitability by increasing duplicate purchases and reducing customer costs. Client Management is a set of customer-centric processes and strategies supported by a specific software to enhance customer loyalty and, ultimately, increase the company’s profitability, and to satisfy customer requirements (CRM), to create an appropriate, institutionalized offer It is possible to name the best processes, motivate employees and learn about customer care.
2.3.6 Instant Customer Support
With the rapid growth of e-commerce, businesses are working to more actively and more effectively manage their multi-channel environment and link it to their customers at a deeper level. Today’s customers expect businesses to respond faster to their needs and commit themselves to higher levels across different channels. Companies also understand the need for better understanding and management of customer relationships, but they do not have the tools that are tailored to their needs.
Independent polls on the use of the e-commerce site indicate that 27% of customers liked to have an instant messenger box that would help them if they needed to research or buy online. The ability of live chat enables websites to communicate with customers and constantly be available to answer any questions they are posing. Live chat is good for customers because they respond quickly and do not require expensive phone calls for the same application.
Live chat is also a perfect platform for companies to find sales opportunities. After solving the query, the sales representative can immediately inform the customer about the related products or related products, current sales / offers or coupon discounts for the product that the customer has decided to buy. The basket’s retirement rate can be greatly reduced if replicating live chat helps customers complete and send their orders.
2.3.7 Social Media
E-commerce websites need to listen to consumer to better manage their reputation and promote positive speeches in social media platforms. Answering a complaint and accepting error in public operating systems will have a positive impact on target audience. The key here is to be as responsive and active in social media accounts and to respond to the entire query within an hour.
To get feedback from user it is important to add social media icons on website, for user to see them and check website activities on social media websites (Thewebbureau.com, 2016).
Several studies have shown social media has a huge impact on eCommerce. For example, 77% of companies report they acquired customers through Facebook, and shoppers referred by Pinterest are 10% more likely to make a purchase than referrals from other social networks (Delk, 2012).
The impact of social networking on online retailers has been reviewed in a recent report by the BI Intelligence Research Institute. The report says that in recent years, large volumes of electronic purchases have been made through ads posted on social networks such as Facebook and Pinterest. Meanwhile, e-commerce experts and activists believe that the amount of discussion about these advertisements, their average sales price and the frequency of their sharing have been effective factors in increasing the number of referrals from social networks to online e-commerce (Gaitho, 2017).
2.4 Conclusion
The research highlights the most important factors that contributes in success of the e-commerce websites.
As a result, e-commerce is the actual purchase and sale of products through the Internet, but every transaction alone is completed through electronic measurements.
E-commerce websites must be secure and ensure that the visitor’s personal information provided to the site is in a safe place and will not be shared or sold to anyone else. This issue is important for online shoppers, so any assurance and security of the site will improve sales.
3 Research Methodology
The research methodology is a set of valid, reliable and systematic rules, tools and methods for review
In all researches, the researcher should gather information or data to describe or contrast the relationships between phenomena and variables. In collecting data, a method must be used to extract high quality, accurate and reliable data, since the quality and validity of each research largely depends on the information and data collected and the quality of information and Data is also related to their collection. Therefore, accurate data collection, if performed accurately, will usually result in high quality data and findings, and obtaining valid results, and inappropriate ways to invalidate the results.
The method of collecting information is through the inference from theories and the use of related texts, which is using the library. By studying books, articles, and other researches that are of interest to him in the subject area, the researcher can further understand the subject of his research and see its dimensions and clarify the purpose or objectives of his research.
Data can be collected in variety of ways and from different sources. Data collection methods include interviews, Questionnaires and observing people are the three main types of data collection methods.
Interview is one of the methods of collecting data, in which individuals or groups are questioned personally. The important thing is that interview questions have been pre-considered and determined. Interviews are considered as one of the techniques that can be answered more than other methods, because during the interview, it is possible to stimulate the subject to respond, and can be made in the face of ambiguity by explaining the subject (Dawson, 2015).
Data can be obtained from primary or secondary sources. Primary data refer to information obtained first hand by the researcher on the variables of interest for the specific purpose of the research. Secondary data refer to information gather from sources that already exist (Sekaran and Bougie, 2011: 180-184).
Primary data refers to the information gathered by researcher, by conducting interviews, or using questionnaires or used focus groups to gather the data.
Secondary data refer to information gathered by someone other than the researcher conducting the current research. Such data can be internal or external to the organisation accessed through the internet or checking of recorded or published information.
The advantage of seeking secondary data source is saving time and costs of acquiring information. However, secondary data as the sole source of information has the drawbacks of becoming obsolete, and not meeting the specific needs of the situation or setting therefor, it is important to refer to sources that offer current and up-to-date information (Saunders, Lewis and Tornhill, 2016: 318).
Qualitative and quantities research approaches
Qualitative, used numerical data and statics and scientific data
Seven factors emerge from the research
| Factors | Comments | |
| 1 | Accessibility | |
| 2 | Usability | |
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| 3 | Security | |
| Validation | ||
| 4 | Trust | |
| 5 | Customer Support | |
| 6 | Social Media | |
4 Review of Existing Systems
The purpose of this review is to evaluate similar products, which are available in market to gain information about what features and capabilities they offer. Jakob Nielsen’s heuristics will be used to evaluate the current available systems.
| Heuristics | Car Giant | Auto Trader | Rac Cars |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Likert Scale Rating | 3/5 | 2/5 | 2.5/5 |


Shows the user which page they are currently viewing.
Shows the user task or page they are currently are with an icon.
Figure 1 – Car Giant Screentshot
Figure 2 – Auto Trader Screenshot
Figure 3 – Rac Cars Screenshot
4.1 Evaluation using Nielson’s Heuristics
| Heuristics |  |
 |
 |
4.2 Conclusion
5 Analysis
5.1 Stakeholders quadrant
Stakeholders are anyone who has an interest in the project. Project stakeholders are individuals and organizations that are actively involved in the project, or whose interests may be affected because of project execution or project completion. They may also exert influence over the project’s objectives and outcomes (Thompson, 2015).
Each stakeholder is classified according to potential impact. This is shown in the matrix bellow that estimates interest and influence on a simple scale such as low/medium/high. Those with an ability to directly affect the outputs or benefits are sometimes referred to as key stakeholders.
|
LOW Benefits Received HIGH |
Collaborators | Buyers | Compromisers | Developers | |||||
| Private Sellers | Testers | ||||||||
| Trade Sellers | Internal Users | ||||||||
| Business Owner | Trainers | ||||||||
| Accommodators | Admin Team | Resistors | Car Manufacturer | ||||||
| Helpdesk | Car dealers | ||||||||
| Competitors | |||||||||
| LOW Changes Required HIGH | |||||||||
Table 3 – Stakeholders Quadrant
5.2 SWOT Analysis
Swot analysis refers to strength, weakness, opportunities and threats. Opportunities are related to the organization’s internal environment, in which the organization has control. Strengths are areas where the organization is superior to its rivals, while weaknesses are where the organization may be subject to comparative disadvantages (Henery, 2011).
– Customer Loyalty
– 24×7 Available
– Technology
– Brand Name
– Strong Management
– Privacy concerns
– Bad Acquisitions
– Weak Supply Chain
– Customer Services
– Lack of Scale


Weaknesses
Strengths
SWOT


– Government Regulations
– Intense Competition
– Changes in Tastes
– Political Risks
– Substitutes Products
– New Technology
-New Markets
– International Expansion
– Steady future demand
– Increasing Internet and Mobile use
Opportunities
Threats
5.3 PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE Analysis was carried out before the launch of project to identify the external forces that could impact the project. PESTEL Analysis was helpful to effectively monitor and respond to external forces also to single out from the competition and create a competitive advantage. (Henery, 2011)







P
E
E
L
PESTLE
S
T
Political
– The new system affected other firms
– criticized by council for meter rate
Environmental
– eco-friendly cars
– Encouraging to buy Eco
Economic
– Growing Corporate Sector
– Growing Business
– More customers
– Attract more Car Dealers
Legal
– Commercial License
– Government Policies
Technological
– Use of Mobil applications
– Website for all devices
– Elderly Drivers had problem
Social
– Increase demand for transport
– Increased use of Social media
5.4 Development Methodology
The Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) is an agile project delivery framework, primarily used as a software development method. This is the framework that incorporates many current knowledge of project management. DSDM is rooted in the software development community, but the convergence of software development, process engineering, and ports of business development projects has changed the DSDM framework to provide a common framework for complex tasks to solve problems. The DSDM framework can be implemented for fast and traditional development processes (Moira, 2017).
DSDM was the preferred development methodology for the development of Cars4u website, because development results are directly and rapidly visible. In DSDM the users are actively involved in the development of the system, they are more likely to embrace it and take it on.
General features are delivered quickly, with more functionality delivered at regular intervals.
Eliminating barriers for communication between stakeholders.
Due to constant feedback from users, the developed system is more likely to meet the requirements.
Early Indicators on whether the project will work, rather than surprises halfway through development process
System is delivered on time and on budget. The ability of users to influence the direction of the project.
5.5 Functional and None-Functional Requirements
To determine requirements for e-commerce website, different methods were used to gather requirements; such as user questionnaires, evaluating existing systems, to ensure that the requirements were precisely and successfully recognised.
5.5.1 Functional requirements
- User should be able to search for a car using postcode, car make and model also price range.
- User should be able to sell their car by logging in to the website.
- User should be able to value their cars by entering car details.
- User must also be allowed to re-set forgotten passwords.
- User should be able to make enquiry about a car.
- User should be able to contact a seller.
- System should not allow unauthorised users to sell a car.
- User should be able to delete a car once its sold.
- User should be able to add reviews about a seller.
- User should be able to access account and amend their details.
- User should be able to get in touch, using a live chat system.
- User should be able to send email to seller or web admin.
5.5.2 Non-functional requirements
- User should be able to access the website on any device Desktop, Laptop, Mobile or Tablet.
- System should be able to store user’s data and profile details.
- when user register, email should be send to the user email to activate their account.
- User data should be encrypted for security purposes.
- when searching a car, buyer enters details, the system should show available cars.
- The system should be compatible with any Internet Explorer.
- The system should be accessible by different types of users.
5.6 MoSCoW Prioritization
MoSCoW is among the most commonly used prioritization techniques, MoSCoW rules ensure that a critical examination of requirements is made.
5.6.1 High Level Requirements Prioritisation
- User Should be able to register to sell car. Should Have
- Users should be able to value their car by entering car details. Must Have
- User should be able to search for a car of their choice. Must Have
- User Should be able to sell their car by logging in to website. Must Have
- User should be able to make enquiry about a car. Should Have
- User should be able to contact a seller. Must Have
- Website should be responsive to any device. Must Have
- User should be able to add reviews about seller. Should Have
- User should be able to get in touch, using a live chat system. Must Have
- User should be able to access account and amend their details. Should Have
- User should receive email to activate their account. Won’t Have
- User can delete a car once its sold. Could Have
- User Should be allowed to re-set forgotten passwords. Could Have
- System should not allow unauthorised users to sell a car. Must Have
5.6.2 Prioritisation and Time boxing
In time boxing, all must have requirements, at least some of should have requirements and few of could have requirement would be included.
We have a total of 6 months, means we have 24 weeks and if we work 30 hours a week that is going to be a total of are 720-time boxing hours.
Prioritize “Must have” features
Using MoSCoW prioritization, must have hours are 410 hours which 57% of the total time boxing hours.
| No | Requirements | Hours | Prioritisation |
| 1 | User Should be able to register to sell car. | ||
| 2 | Users should be able to value their car by entering car details. | 80 | Must Have |
| 3 | User should be able to search for a car of their choice. | 45 | Must Have |
| 4 | User Should be able to sell their car by logging in to website. | 80 | Must Have |
| 5 | User should be able to make enquiry about a car. | 55 | |
| 6 | User should be able to contact a seller. | 70 | Must Have |
| 7 | Website should be responsive to any device. | 55 | Must Have |
| 8 | User should be able to add reviews about seller. | 60 | |
| 9 | User should be able to get in touch, using a live chat system. | 65 | Must Have |
| 10 | User should be able to access account and amend their details. | 35 | |
| 11 | User should receive email to activate their account. | 30 | |
| 12 | User can delete a car once its sold. | 55 | |
| 13 | User Should be allowed to re-set forgotten passwords. | 65 | |
| 14 | System should not allow unauthorised users to sell a car. | 45 | Must Have |
Prioritize “Should Have” features
Should have hours are 150 hours which is 21% of the total time boxing hours.
| No | Requirements | Hours | Prioritisation |
| 1 | User Should be able to register to sell car. | 25 | Should Have |
| 2 | Users should be able to value their car by entering car details. | 80 | Must Have |
| 3 | User should be able to search for a car of their choice. | 45 | Must Have |
| 4 | User Should be able to sell their car by logging in to website. | 80 | Must Have |
| 5 | User should be able to make enquiry about a car. | 30 | Should Have |
| 6 | User should be able to contact a seller. | 70 | Must Have |
| 7 | Website should be responsive to any device. | 55 | Must Have |
| 8 | User should be able to add reviews about seller. | 60 | Should Have |
| 9 | User should be able to get in touch, using a live chat system. | 65 | Must Have |
| 10 | User should be able to access account and amend their details. | 35 | Should Have |
| 11 | User should receive email to activate their account. | 30 | |
| 12 | User can delete a car once its sold. | 55 | |
| 13 | User Should be allowed to re-set forgotten passwords. | 65 | |
| 14 | System should not allow unauthorised users to sell a car. | 45 | Must Have |
Table 5 – Should Have Features
Prioritize “Could have” features
Could have hours are 95 hours which is 13% of the total time boxing hours.
| No | Requirements | Hours | Prioritisation |
| 1 | User Should be able to register to sell car. | 25 | Should Have |
| 2 | Users should be able to value their car by entering car details. | 80 | Must Have |
| 3 | User should be able to search for a car of their choice. | 45 | Must Have |
| 4 | User Should be able to sell their car by logging in to website. | 80 | Must Have |
| 5 | User should be able to make enquiry about a car. | 30 | Should Have |
| 6 | User should be able to contact a seller. | 70 | Must Have |
| 7 | Website should be responsive to any device. | 55 | Must Have |
| 8 | User should be able to add reviews about seller. | 60 | Should Have |
| 9 | User should be able to get in touch, using a live chat system. | 65 | Must Have |
| 10 | User should be able to access account and amend their details. | 35 | Should Have |
| 11 | User should receive email to activate their account. | 30 | |
| 12 | User can delete a car once its sold. | 55 | Could Have |
| 13 | User Should be allowed to re-set forgotten passwords. | 55 | Could Have |
| 14 | System should not allow unauthorised users to sell a car. | 45 | Must Have |
Prioritize “Won’t have” features
Won’t have hours are 65 hours which is 9% of the total time boxing hours.
| No | Requirements | Hours | Prioritisation |
| 1 | User Should be able to register to sell car. | 25 | Should Have |
| 2 | Users should be able to value their car by entering car details. | 80 | Must Have |
| 3 | User should be able to search for a car of their choice. | 45 | Must Have |
| 4 | User Should be able to sell their car by logging in to website. | 80 | Must Have |
| 5 | User should be able to make enquiry about a car. | 30 | Should Have |
| 6 | User should be able to contact a seller. | 70 | Must Have |
| 7 | Website should be responsive to any device. | 55 | Must Have |
| 8 | User should be able to add reviews about seller. | 60 | Should Have |
| 9 | User should be able to get in touch, using a live chat system. | 65 | Must Have |
| 10 | User should be able to access account and amend their details. | 35 | Should Have |
| 11 | User should receive email to activate their account. | 65 | Won’t Have |
| 12 | User can delete a car once its sold. | 55 | Could Have |
| 13 | User Should be allowed to re-set forgotten passwords. | 55 | Could Have |
| 14 | System should not allow unauthorised users to sell a car. | 45 | Must Have |
Car4u Website has 6 months to complete
| Prioritisation | Hours | % of Hours |
| Must Have | 410 | 57% |
| Should Have | 150 | 21% |
| Could Have | 95 | 13% |
| Won’t Have | 65 | 9% |
| Total Hours | 720 | 100% |
5.7 Use Case Diagram
5.8 Persona
To better understand the user, a persona needs to be developed. User Personas take different forms, ranging from specifications and descriptions of specific users to a fictional character that represents a group of users for a product or system.
5.8.1 Duane Lambert Persona
Duane Lambert is a car dealer, he buys second hand cars and sell the cars in his dealership. Most of the time he is not able to find the right buyer, because he is not able to find buyers. He wants an online platform where he can advertise his cars for less hassle, in addition he can find more buyers by viewing his cars online.
He would also like to use the website find cheap and affordable cars to buy for his dealership to make profit finding cheap cars which are advertised by private sellers, so he can make some profit by buying cheap cars and sell it back for some profit.
5.8.2 Laura Bailey Persona
Laura bailey has recently bought a new car from a dealership, and she still has her older car. She does not have enough space in her drive to store her old car. She wants an online platform where she can advertise her car easily.
She does not know much about cars and car prices or car details she wants an easy option by putting her car registration the website can help her in pricing her vehicle so she can have an idea about her that how much her is worth to put the price for her vehicle.
Figure 8 – Second User Persona
5.8.3 Sarah Davis Persona
Sarah Davis is a floor manager at Tesco, she was using public transport to commute to work and back home. Now she would like to buy an affordable family car to commute to work, in addition she would like to use the car for family vocations. She is a mother of two, she would prefer the car to be affordable and safer for her and her two children.
She would like a SUV with good fuel economy, cheap to buy and less road tax. She has a tight budget, she would to compare many vehicles to find the right one. As she does not know much about cars, she would like to read owner reviews about the cars. She would also like read reviews about the sellers as she wants to buy a vehicle from trust worthy seller.
5.9 Conceptual Diagram
6 Design
Design wireframes for different website pages to start discussing website design and user testing tests
6.1 Logical Diagram
6.2 Class Diagram
6.3 Data Dictionary
Data Dictionary provides complete information about the data, such as definition of data elements, their meanings and suitable values. Data Dictionary offers a tool that enables us to communicate with business stakeholder requirements in such a way that the technical team can more easily design the relational database or data structure to meet those requirements (Brandenburg, 2013).
6.3.1 Seller Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Seller_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| FirstName | Varchar | 50 | Yes | First Name Field |
| Surname | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Sur name Field |
| Varchar | 50 | Yes | Email Field | |
| Phone | Number | 50 | Yes | Phone Number Field |
| Address | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Address field |
| City | Varchar | 50 | Yes | City Field |
| PostCode | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Postcode Field |
| Type | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Seller Type Field |
| Website | Varchar | 50 | No | Seller website |
Table 9 – Seller Data Dictionary
6.3.2 Vehicle Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Vehicle_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| Registration | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Registration Number Field |
| Millage | Number | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Millage Field |
| Reg_Year | Date | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Registration Year Field |
| Manufacturer | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Manufacturer Name Field |
| Price | Number | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Price field |
| Mot | Date | 50 | Yes | Mot Date Field |
Table 10 – Vehicle Data Dictionary
6.3.3 Review Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Review_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| Name | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Name of Reviewer |
| Varchar | 50 | Yes | Email of Reviewer | |
| Comments | Varchar | 250 | Yes | Comments field |
Table 11 – Review Data Dictionary
6.3.4 Make Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Make_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| Fuel | Varchar | 20 | Yes | Vehicle Fuel Type Field |
| Transmission | Varchar | 20 | Yes | Vehicle Transmission Field |
| Colour | Varchar | 20 | Yes | Vehicle Colour Field |
Table 12 – Make Data Dictionary
6.3.5 Admin Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Admin_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| FirstName | Varchar | 50 | Yes | First Name Field |
| Surname | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Surname Field |
| Role | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Admin Role Field |
| Varchar | 50 | Yes | Email Field | |
| Phone | Number | 50 | Yes | Phone Number Field |
| Address | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Address field |
| City | Varchar | 50 | Yes | City Field |
| PostCode | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Postcode Field |
Table 13 – Admin Data Dictionary
6.3.6 Model Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Model_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| Name | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Make Field |
| Type | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Type Field |
| Engine_Size | Number | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Engine Size Field |
Table 14 – Model Data Dictionary
6.3.7 Buyer Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Buyer_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| FirstName | Varchar | 50 | Yes | First Name Field |
| Surname | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Sur name Field |
| Varchar | 50 | Yes | Email Field | |
| Phone | Number | 50 | Yes | Phone Number Field |
| Address | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Address field |
| City | Varchar | 50 | Yes | City Field |
| PostCode | Varchar | 50 | Yes | Postcode Field |
Table 15 – Buyer Data Dictionary
6.3.8 Buyer Vehicle Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Buyer_Vehicle_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| Vehicle_Id_Fk | INT | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Key Foreign Key |
| Buyer_Id_Fk | INT | 50 | Yes | Buyer Key Foreign Key |
Table 16 – Buyer Vehicle Data Dictionary
6.3.9 Seller Vehicle Table Data Dictionary
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Field Length | Required | Description |
| Seller_Vehicle_ID | INT, Autonumber | 50 | Yes | Primary Key Field |
| Vehicle_Id_Fk | INT | 50 | Yes | Vehicle Key Foreign Key |
| Seller_Id_Fk | INT | 50 | Yes | Seller Key Foreign Key |
Table 17 – Seller Vehicle Data Dictionary
6.4 Prototypes
The prototype is a set of frames that are used to simulate a functional application. The prototype is the target model of the program, its flow and its patterns for interaction. A prototype can be low-fidelity, meaning it looks and feels like a sketchbook version of the design; or it can be high fidelity, meaning that it simulates the look and feel of the proposed final design (Allanwood, 2014).
By creating prototypes, we can provide an environment for users to navigate through tasks and identify areas of turmoil or difficulty. Then we can create new samples to solve any problems glitches. The best way to test user interface designs is with real users, the best way to communicate with user interface designs it to implement them. Placing designs in front of users and stakeholders as early as possible means that it is possible to share, test, discuss, identify issues and iterate designs in an efficient and cost-effective way. Involving the whole project team in the creation of a prototype early in the design life cycle is the recommended way to go about it (Lynch and Horton, 2016).
The benefit of low-fidelity wireframes and prototypes are the ability to evaluate a product before it is fully build, saving time and resources early in the development process. A Stakeholders can interact with a prototype themselves; they can experiment with it, explore, review content and data, and add or change contents or data. It is real enough that they can quickly and easily visualise and understand.
6.4.1 Cars4u Low-Fidelity Prototypes
6.4.2 Cars4u High-Fidelity Prototype
7 Development
7.1 Review of Development tools
7.1.1 Web Development tools
Bootstrap was originally designed and written by Mark Otto and Jacob Thornton to create a distinct and consistent appearance framework. Bootstrap is a framework built up of HTML, CSS and JS that is used to develop and design a site-based site. In fact, as you know, with the growing growth in the use of mobile phones and tablets, most people today are doing most of their activities, such as checking websites using these tools. So, it’s very important for your site to be displayed on different pages so that the user does not have to use magnification to read the content or use the elements. For this reason, the design of the site is used to build pages of different sizes, and the best technique and tools are the Bootstrap framework (Chapman, 2014).
Bootstrap plans to eliminate the gap between design and coding and encourage code makers to use default and standard designs. This will provide you with the necessary CSS and jQuery functions so that you can reduce the startup time of a project by significantly reducing the standard startup time using the default commands and compliance principles with the design of Bootstrap (Morales, 2017).
7.1.2 Database Management Systems
7.2 Cars4u Finale Designer
7.2.1 Home Page
7.2.2 Buyer Page
7.2.3 Seller Page
7.2.4 Valuation Page
7.2.5 Car Information Page
7.2.6 Contact us Page
7.2.7 Contact Successful page
Figure 27 – Contact Successful Page

Figure 28 – Car Search Result
8 Testing
Testing is important because it can save money, time and lives altogether for mission critical software systems. Testing is required for effective Web applications. It is important to ensure that the Project should not fail, as it can be very expensive in the future or at a later stage.
Testing is essential to determine the points and errors that are in development. It is imperative to ensure customer confidence and customer satisfaction in the program. It is very important to ensure product quality. A product that is delivered to customers will help their self-esteem.
Testing is required to provide facilities to customers such as high-quality product delivery or software that requires less maintenance and hence the results are more accurate, consistent and reliable. (Portny, 2010).
8.1 Black box testing
8.2 White box testing
8.3 Responsive View
9 Evaluation
9.1 Product Evaluation
9.2 Project Evaluation
9.3 Personal Evaluation
10 Conclusions
10.1 Overview
10.2 Summary of the investigation study
10.3 Findings and recommendations
10.4 Areas for future work
11
12 Appendixes
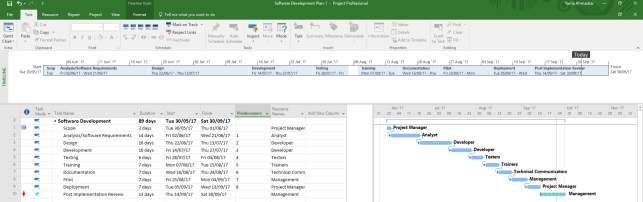
12.1 Gantt Chart
Gantt chart is a tool that project managers can use to collaborate interactively with their project team and stakeholders during planning and execution phase. Identifying the tasks and sequencing the task against a time scale in a way that support the delivery of the project to the specific deadline (Deen, 2015).
Microsoft Project was used to create the Gantt chart for this project. Microsoft Project is a valuable tool for project planning and for project implementation. Using Microsoft project as a tool, it is easy to estimate the duration of a project and we also can view the project timeline. In Microsoft project Gantt chart, we can see the time line of our project, the task name, we can assign duration to a task also able to give a start and finish date.
Create table Buyer(
Buyer_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
FirstName varchar(50) not null,
Surname varchar(50) not null,
Email varchar(50) not null,
Password varchar(50) not null,
Confirm_Password varchar(50),
Phone varchar(50),
Address varchar(50),
City varchar(50),
Post_Code varchar(50),
primary key (Buyer_Id))
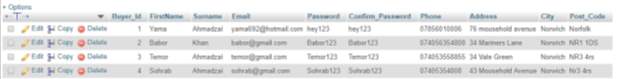
Create table Seller(
Seller_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
Name varchar(50) not null,
Email varchar(50) not null,
Password varchar(50) not null,
Confirm_Password varchar(50),
Phone varchar(50),
Address varchar(50),
City varchar(50),
Post_Code varchar(50),
Type varchar(50) not null,
Website varchar(50) not null,
primary key (Seller_Id))
Create table Review(
Review_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
FirstName varchar(50) not null,
Surname varchar(50) not null,
Email varchar(50) not null,
Rating varchar(50) not null,
Comment varchar(250),
Buyer_Id Int,
primary key (Review_Id))
Create table Vehicle(
Vehicle_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
Registration varchar(50) not null,
Millage varchar(50) not null,
Reg_Year varchar(50) not null,
Manfacturer varchar(50),
Price varchar(50),
Mot DATE,
primary key (Vehicle_Id))
Create table Model(
Model_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
Name varchar(50) not null,
Type varchar(50) not null,
Engine_Size varchar(50) not null,
Vehicle_Id int,
primary key (Model_Id),
FOREIGN KEY (Vehicle_Id) REFERENCES Vehicle(Vehicle_Id))
Create table Make(
Make_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
Colour varchar(50) not null,
Transmission varchar(50) not null,
Fuel varchar(50) not null,
Vehicle_Id int,
primary key (make_Id),
FOREIGN KEY (Vehicle_Id) REFERENCES Vehicle(Vehicle_Id))
Create table Admin(
Admin_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
FirstName varchar(50) not null,
Surname varchar(50) not null,
Email varchar(50) not null,
Password varchar(50) not null,
Confirm_Password varchar(50),
Phone varchar(50),
Address varchar(50),
City varchar(50),
Post_Code varchar(50),
primary key (Admin_Id))
Create table Seller_Vehicle(
Seller_Vehicle_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
Seller_Id Int,
Vehicle_Id Int,
primary key (Seller_Vehicle_Id),
FOREIGN KEY (Seller_Id) REFERENCES Seller(Seller_Id),
FOREIGN KEY (Vehicle_Id) REFERENCES Vehicle(Vehicle_Id))
Figure 38 – Seller Vehicle Table
Create table Buyer_Vehicle(
Buyer_Vehicle_Id int not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
Buyer_Id Int,
Vehicle_Id Int,
primary key (Buyer_Vehicle_Id),
FOREIGN KEY (Buyer_Id) REFERENCES Buyer(Buyer_Id),
FOREIGN KEY (Vehicle_Id) REFERENCES Vehicle(Vehicle_Id))
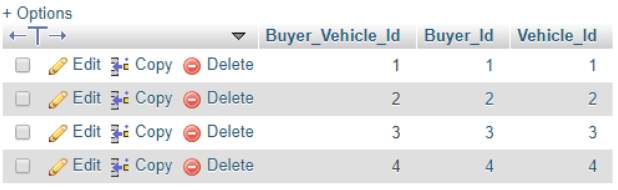
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "E-commerce"
E-commerce is process of buying and selling goods or services online. Some businesses only operate through E-commerce, whilst others have both E-commerce and physical stores to sell their products or services.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




