Role and Impact of Innovation in Hospitality Industry
Info: 9000 words (36 pages) Dissertation
Published: 27th Oct 2022
Tagged: Leisure Management
The role and impact of innovation in Hospitality Industry: A case of the Southeastern Hotel in the Gulf of Thailand
Abstract (250)
The purpose of this research aim to evaluate how lean and six sigma techniques can improve the quality management in term of; problem solving, quality control and quality improvement in order to develop the quality performance of the particular areas in electronic industries of Thailand.
The primary result of this research was collected from the top four of electronic industries in Thailand so as to be a guidance for inefficient electronic industries and be the best strategies for any manufacturing sizes. The result from this investigation showed that even if the top companies, there are also encountered with various problems in their production processes. Therefore, the application of lean and six sigma techniques also aim to help to identify the potential root causes that might affected to the the quality standard performance and, the problem solving in each problem types would be analysed in this research as well.
Table of contents (100)
- Title Page
- Declaration 50 (not included in the word count)
- Abstract 250 (not included in the word count)
- Contents 100 (not included in the word count)
- Introduction 1,200
- Literature Review 3,750
- Methodology 2,550
- Results 2,550
- Discussion 3,250
- Conclusion 1,700
- References
- Bibliography
- Appendices
Chapter 1: Introduction (1,660)
1.1 Introduction
The study on the role of innovation that related to the service quality and business framework of the hotel has been continuously researched in developed countries such as European and North American countries. However, such studies have been less concerned with service, organization, and human resource management (HRM) in the Third world countries (Africa, Latin America, Oceania, especially Asia). Moreover, in a highly competitive environment, the hospitality industry provides a focus on the efficiency and performance effectiveness by creating new ways of innovating. In this era, one of the most important trend is the development and implementation of innovations by enterprises. It can be force for improvement of the hospitality industry.
However, it’s lack of research conductive on this sector in Thailand. This study is looking at the role of innovation in hospitality sector in the gulf of Thailand Hotel. Moreover, this study will explore hospitality innovation and the related area of entrepreneurship. This paper also studies adopting types of innovation in SMEs and Large-sized Hotel. In addition, it will investigate employee perception of the innovation performance in the Southeast-east hotel in Thailand. Eventually, it will study the impact of stakeholders on innovation in the Southeast-east hotel in Thailand. This dissertation seeks to explore the role and impact of innovation in Hospitality Industry in the South-eastern Hotels in Thailand. This chapter is composed of research background, research objectives, research questions, project outcomes, research structure, project management and summary of this chapter.
1.2 Research Background
Over the last three decades, tourism is the fastest growing industries globally, with 4 percent annually over the ten years (OECD,2013). Europe has the highest number of tourists approximately 500 million in 2010. Significantly, the Middle East and Asia had the greatest growth of tourists in the 2010y. Globally, international travelers spent a record 880 million British pounds (approximately 39 billion Thai Baht) in a single year. Tourism industry indicated 10 percent of world GDP. Moreover, the tourism development not only stimulates the growth of the industry but also economic stimulus overall economic growth (Chancharat, 2011). As a result, most developing countries are promoting the tourism industry as the number one priority for economic growth.
The most businesses in Thailand are micro, small, medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), particularly the tourism industry which is the main source of national income in Thailand. Thailand is one of the top destinations for travelers from America, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. According to International Arrivals in Top Wop World Metropolitan Destination (2013), Paris ranked the first place with 18.8 million arrivals, while Bangkok ranked the fourth place with 14.6 arrivals. Excellent shopping and traveling experiences provide multiple choice for visitors. In 2014, the number of oversea travelers visited Bangkok was approximately 15.5 million, the rate decreased in 2014 by 11 % compared with 2013. Therefore, Thailand faced with the biggest challenging in the 2014s, rating of visitor arrival in Thailand approximately 25 million people including full-year total revenue is estimated to be 27 billion British pounds. In 2015, according to Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT) set the target of 28 million people generating an estimated 32 billion British pounds from international travelers (TAT, 2015).
As a service industry, tourism has various tangible and intangible components. Major tangible components, transportation, attraction, restaurant, especially accommodation. In contrast, intangible elements focus on customer experience and customer satisfaction (Albayrak et al., 2010). Accommodation is one of the main sector in travel and tourism which compose with food and beverage, leisure activity, spas, and so forth (Hua and Batra, 2015). All elements of what is now broadly called “Hotel” which can attract more customer and get competitive advantages, hotels need to recover from diverse features. Therefore, the royal Thai Government has concerned the significance of tourism, especially hospitality sector in Thailand (Hua and Batra, 2015). The most importantly, the need to maintain and improve the industry’s performance in the areas of corporate management and competition is the first thing that the royal Thai Government wants hospitality entrepreneurship to consider.
Additionally, the importance of development and training in the hospitality industry are learning about what customer needs and customer satisfactions, especially Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) hotels accelerate improvement their strategy and organization involving with the challenges of a changing world such as both innovation organizational and service. Significantly, innovation is essential for increasing competitive advantage (Nemeth et al., 2013). Moreover, the firm is considered to sustain competitive advantage. The abilities, skills, and knowledges of employees is a crucial part in enhancing the competition advantage. More specifically, improvement service organizations from poor service quality to high service quality is a one culture for innovation performance based on human resource management(HRM) and from a strategic approach to implementation (Cooke,2000).
Furthermore, Fougere (2007) shows that Thailand is the collectivistic country by categorizing from the number of Thai entrepreneurship and SMEs which is presented traditional societies with people moral involvements. In other words, employee tend to respect others as traditional model/hierarchical method (Fougere, 2007). In addition, the rule and regulation in Thailand is flexible rather than strict compared with other developed country (Rupjumlong,2012). Therefore, the different countries and types of company organization are probably differentiated management style in term of innovation organizational and entrepreneurship styles.
The Gulf of Thailand, Thailand has hundreds of islands both in the Southeast Thailand and comprised around 20 provinces. Some of the main attractive destination in the Gulf of Thailand are the islands of Koh-Samui, Koh-Phangan, Koh-Tao, Koh-Nang Yuan, Koh-Angthong, etc. It embraces rich cultures and traditions, a tropical climate and famous hospitality. Moreover, in 2015, the number of international tourist in the Southeast Thailand was around 14.5 million people annually (TAT,2016). It is forecast that international visitor numbers will increase substantially. On the other hand, the number of international tourist in the Southwest of Thailand was around 14 million people annually. Furthermore, the innovative activities and potential drivers of innovation in SMEs and luxury hospitality enterprises in the Southeast destination are poor. Eventually, hospitality entrepreneurship in the Gulf of Thailand needs to improve business system by using type of innovation. This research will give benefits to people who interesting and working on innovation in hospitality Industry, in the Gulf of Thailand.
1.3 Research Aims
This study will explore the role of innovation in Hospitality Industry in the Gulf of Thailand Hotels. The research aims to provide the ways for businesses to innovate and stay competitive in the global market and environment. The tourism sector is a key contributor to nations economy. It is vital to explore the undebatable role that innovation plays in this sector and its impact on businesses and its stakeholders.
1.4 Research Objectives
- Investigate the impact of innovation in transforming processes and services in South-eastern Hotel in Thailand.
- Investigate employee perception of the innovation performance of Hotel in Thailand
- Identify the types of innovation adopted by entrepreneurs in the hospitality industry in South-eastern Thailand.
- Investigate the impact of innovation in gaining competitive advantage
- Investigate the contribution of stakeholders on innovation process in the hospitality industry in South-eastern Thailand.
1.5 Research Questions
Several research studies, journals, and books explain that innovation can improve, manage, and control in hospitality industry and gain competitive advantage. In addition, this research studies in detail the question of ‘How can the role and impact of innovation help hospitality enterprises to change from traditional business to modern business?’ However, the data that the researcher used was collected from the Thai Hospitality industry only.
1.6 Statement of the Problem
The role of innovation and potential drivers of innovation in micro, small and medium, and Five-star hospitality enterprises in the Gulf of Thailand are low quality. The Southeast Hotels are only declarative entities of regional tourism system because there is no a strong connection between them and other entities. Owners and managers of the Southeast hospitality enterprises are not perceived as a part of the hospitality system and don’t have support of a system for their innovation activities. On the other side, owners and managers of SMEs and Five-star hospitality enterprises don’t have knowledge and financial leverage for innovation activities.
1.7 Research Structure
The structure of this dissertation is divided into 7 chapters as follow:
Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter will provide the overview research contained background, aim, objective, research questions of the research to provide more understanding about the idea of working on this research. As well as, in this chapter will provide brief of case study problem statement.
Chapter2: Literature Review
This chapter provide conducted reviews of literature regarding to innovation. This chapter can be divided into three main contents that are including entrepreneurship, innovation, and hospitality and tourism concepts. In each sections will provide the recent research and the critical evaluation between existing studies by other researchers.
Chapter3: Methodology
This Chapter will explain about the step of methodologies which is included in research design, the data collection method, the source of information and data analysis.
Chapter4: Research Result, Analysis and Solution
This chapter presents the research result that was collected not only the interview in four the Gulf Hotels in Thailand and also questionnaires in three sections includes hotel manager, customer, and hotel managers. In addition, it will analyze the finding in the current state, the analysis of problems, the problem solving, the solution and the generic framework to control the quality.
Chapter5: Conclusion and recommendation
This chapter shows the conclusion of this research and the recommendation strategies both short term and long term resolution.
Chapter6: References
This chapter represents all of the references lists which is used in this dissertation to analysis.
1.9 Chapter summary
This chapter described the overview of research including the research aims, objectives, research questions, and research deliverables. It also provided brief summary of all the chapter contained in this research paper. There stared with introduction, literature reviews, research methodology, framework, research result, and conclusion and recommendation respectively. Moreover, this chapter indicated the significance of research and identified research scope that will provide more clear picture of this research.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
A literature review is a critical of information found in the literature associated with particular area of research, especially the research aims to provide a theoretical perspective of the study. This chapter will review the relevant key studies to the research topic. Therefore, the key studies will be explored and these include entrepreneurship, innovation, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), significantly hospitality and tourism.
2.2 Entrepreneurship
2.2.1 Definition of entrepreneurship
Over the past few year, researchers have been developed entrepreneurship (Russel,2015). Researchers (Sheikh 2015 and Mass et al.,2016) define entrepreneur in various ways. Miller and Collier (2010: 85) qualifies entrepreneurship as the process of creating something by adding new value and delivering unique product or service. As Mass et al. (2016) states that “the application of enterprise skills specifically to creating and growing organizations in order to identify and build on opportunities”. In particular, entrepreneurship is a crucial force for economic development (Audretsch,2003). However, they collapsed to present at one universally accepted definition(Skokic,2010). Several scholars have focused on the economic functions of the entrepreneur. This is supported by many researchers (Knight,1921; Schumpeter,1965; Leibenstein,1995; Baumol,1922) focused on risk bearer, market disequilibrium, economic crisis, and societies setting. Afterwards, the definition of entrepreneurship changed to concern with risk-taking and challenges associated with entering new market. In the modern era, the definition of entrepreneurship is based on innovation and creativity which is defined by Schumpeter (Gutterman,2015).
Additionally, many scholars claim that an entrepreneurship achieved by adapting to a several of social economic, historical, and different rules and regulation globally. In recent year, entrepreneurships turned their attention to learning other social science includes psychology, sociology, geography, anthropology, especially, law and regulations (Skokic,2010). Several research studies show their significant disciplinary procedures. This studies created various theories and the way to understanding the definition of entrepreneurship. However, there continues to be a lack of a common conceptual framework for the entrepreneurship.
Nevertheless, Mokaya et al.(2012) considers that the process of entrepreneurship rather than the definition of entrepreneur. The entrepreneurial process connects to the whole activities, functions, especially behavior related to the receiving of opportunities and the establishment of organizations to pursue them. In the modern Western economies, they promoted the role of entrepreneurial activities, particularly which generate managing change and innovation. Including with recognitions to new venture creation, technical progress (process innovation and product innovation), and stimulate economic activity (Amaghouss and Ibourk, 2013). However, this research was not the situation throughout in the world, significantly in the Southeastern Asia.
2.2.2 Types of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship can take an assortment of structures and various scholars (…….)have proposed that it is essential to perceive distinctive sort of business when investigating issues, for example, the characteristics of an entrepreneur from planning, money management, to customer retention, their intentions in picking business enterprise and the commitments of their entrepreneurial exercises to economic growth (Gutterman,2015). Generally, the types of entrepreneurship consist of four types, including Small Medium Enterprise entrepreneurship (SME), Innovation Driven Entrepreneurship(IDE), Large Company Entrepreneurship, and Social Entrepreneurship. However, two of the most popular types are Small-Medium sized Enterprise (SMEs) and Innovation Driven Entrepreneurship (IDE), have distinguishes between ‘addressing’, which includes local and international respectively (Meyers, 2014). Small-Medium sized Enterprise (SMEs), this is a basic level small organization and focused on local and regional markets. This type is not concerned with innovation, nor is competitive advantage. Importantly, most businesses that use this method are family businesses and businesses with low external capital. On the other hand, Innovation Driven Enterprise Entrepreneurship(IDE) has a fundamentally different business. This types is looking for global markets but start a new business by losing money, but if successful will have exponential growth. Therefore, this research failed to address innovation is not focus on innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises, particularly in the tourism and hospitality business (Yuzbasioglu et al., 2014).
Type of Entrepreneurship
Over the course of modern history, innovation has proved fundamental for formal organizations. In the past decades, as market competition intensified and the business environment grew in complexity and uncertainty, innovation became essential not only to an organization’s performance, as several studies have demonstrated, but to its very existence and survival (Han, Kim & Srivastava, 1998). Similarly, a company that fails to innovate and remains blocked in “industry recipes” will eventually lose its competitive advantage (Charitou & Markides, 2003; Sull, 1999, cited by Mattyssens et al., 2006).
2.2.3 Thai Entrepreneurship
2.12. Summary of Chapter 2
This chapter provides part of the academic secondary information which used to support the theoretical and practical techniques. According to the review, there are many techniques and different success factor to accomplish business objectives.
Lean and Six Sigma integration, is appeared to enhance in many aspects; quality improvement, cost reduction, revenue enhancing of Thai Electronic Industries and drive the effective strategy for new implementations.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology (2,330)
3.1 Introduction
A research methodology is a systematic and logical research for solving on specific issue and search for knowledge(Kumar,2014). In other words, it referred to a systematic effort to accept pertinent information on a particular topic, as well as gaining new information (Kothari and Garg, 2016). Indeed, it is an art of scientific investigation. The information may be collecting from several resources such as academic journals, books, discussions, literature surveys, etc. Additionally, descriptive research, it is included surveys and fact situation which is covered business research and social science research (Kothari and Garg, 2016). These researches cannot control the variable, so researchers can only report the result. Alternately, it refers to investigate to find solution for the problem through critical analysis (Sachdeva,2009). However, the explanation of research methodology is the best choice to resolve the issue because it is clearly explanation of the procedure.
Moreover, the research methodology basic concept is not only explicit description but also explicit procedures contribute to powerful project (Purohit and Wagh,2009). Nevertheless, it is important to start the research design because it considers critical analysis and critical research which are the process of work planning and creating the necessary things based on research objective that are essential for scholars (Sachdeva,2009). Consequently, this chapter describes the methodology of research including the research philosophy, research approach, research strategy, research design, data collection and data analysis, especially the conclusion chapter accordingly.
3.2 Research Purpose
This research purpose can classify in four types, including exploratory research,
descriptive research, explanatory research, and predictive research. According to Table 31, it illustrated type of research purpose which this research is exploratory research. Its focus is on the discovery of the type of innovation for transforming process and service in the Southeast Thailand Hotels, collecting statistically accurate data for finding the number of employee perception and competitive advantage.
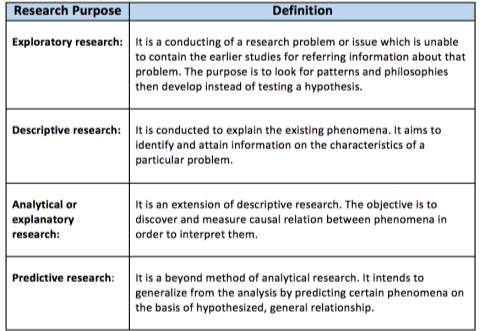
Table 3.1 Type of research purpose (Collis and Hussey, 2014)
3.3 Research Philosophy
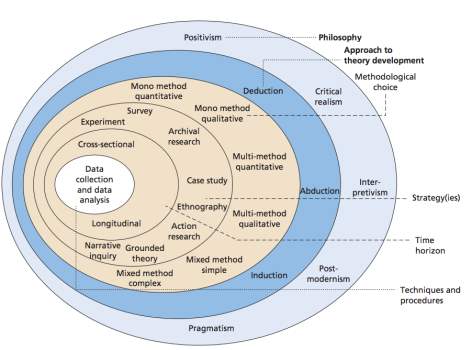
Saunders et al. (2009) discovered that the research onion illustrates the layer of philosophies, approaches, strategies, choices, time horizons, and technique and procedures. The research philosophy is a philosophical and theoretical framework that aims to illustrate strategy for conducting scientific research (Mkansi and Acheampong, 2012). The framework structure is based on the nature of knowledge, humanity, and reality. The researcher has divided into two basic philosophies for learning social phenomenon comprises positivism and interpretivism, it is called phenomenology (Blumberg et al., 2008). This is shown in figure 3.1
Figure 3.1: The Research Onion (Saunders et al. 2009)
3.3.1 Positivism
Clarke (2009) states that Positivism is a research sociology which relevant to scientific manner. The purpose of Positivists is to explore the social world, studying the natural world. It is the search for building fundamental theories which relate to the algorithm and connect to phenomenon. In addition, Positivism apply to statistical analysis by using quantitative method for collecting the data (Hughes,2006).
3.3.2 Interpretivism
Interpretivism is s phenomenologists and anti-positivists (Clarke, 2009). It is philosophy to determine the process of criticism react to positivism. The theory of Interpretivism shows that the society cannot be conducted as science. Collis and Hussey (2014) noted that Interpretivism approaches are not suitable for the study of society because the social world distinguish to the natural world. According to Table 3.2, it illustrated the different between positivism and Interpretivism, the objective of this study is to adopt the role of innovation to improve the quality performance in Hospitality Industry. Consequently, this research will be applied both positivism philosophy and intrepretivism due to suitable with research objectives.
The objective of this study is to adopt the role of innovation to improve the quality performance in Hospitality Industry. Consequently, this research will be applied the positivism and interpretivism philosophy due to suitable with research objectives.
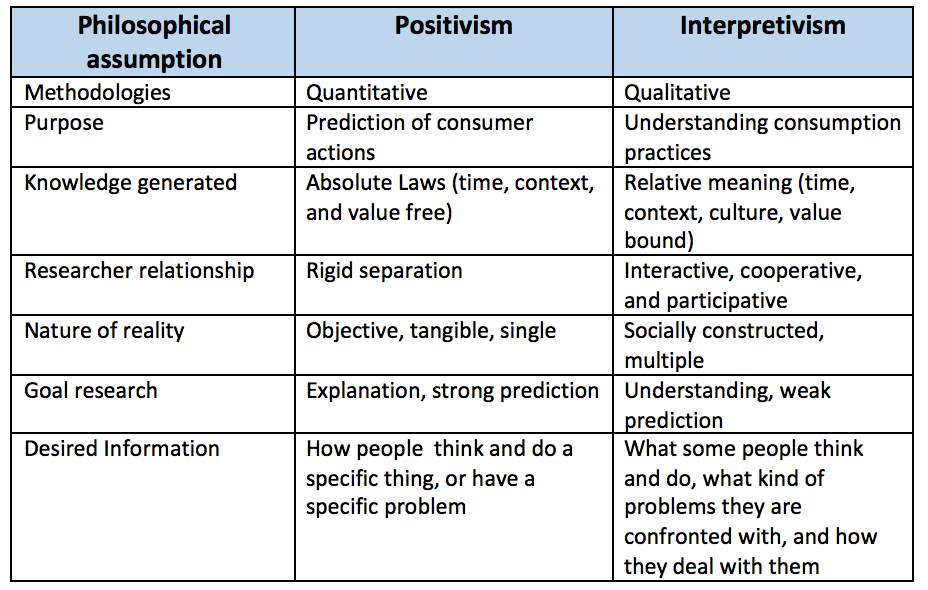
Table 3.2: Positivism versus Interpretivism (Pizam and Mansfeld 2009)
3.4 Research Approach
Saunders et al. (2009) states that research approach consists of two components, deduction and induction. The deductive approach is appropriated for numerous sample project as large numbers of sample are analyzed with low depth. Inn deed, deductive approach is relating to positivism philosophy. In contrast, the inductive approach is appropriated for small sample research because small numbers of sample are small analyzed with greater gravity. In particular, the inductive research is relating to interpretivism philosophy (Weddle, 1984).
3.3.1 Deduction Research Approach: Testing
Deduction research method is a principle investigation depending on the scientific fact with the analysis from theory into the verified data. Creswell and Plano Clark (2007:23) states that “deductive research is works from the ‘top down’, from a theory to hypotheses to data to add to or contradict the theory”. This research is essentially used the data collection of quantitative type. The dissertation with deductive research model is describe as follow;

Figure 3.2: Deductive Process (Singh and Bajpai, 2008)
3.3.2 Induction Research Approach: Building
The inductive research approach does not need to involve hypothesis and the data collection essentially used the qualitative research. Nevertheless, the research model is gaining an understanding of the meaning humans, especially it resembles flexible (Singh and Bajpai, 2008). The dissertation with inductive research model is describe as follow;
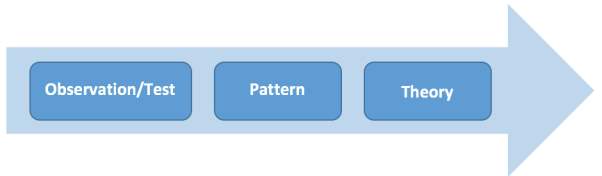
Figure 3.3: Inductive Process (Singh and Bajpai 2008)
This research is adopting the Inductive approach will enable to explain the type of innovation types by creating different necessary aims in the Hospitality in Thailand, especially looking at the different types of innovation can be gaining competitive advantage.
3.4 Type of research
Saunders et al. (2009) note that the type of research method includes qualitative method and quantitative method. According to Table 3.3, it shows the differences between Qualitative Method and Qualitative Method. For Qualitative research, it is explained as a research which emphasizes either quality or in-depth investigation. Qualitative research can get the data from interview. In contrast, quantitative research is explained as a research which focused on amount of quantity. This research is collecting data by using statistical or mathematic analysis tools to evaluate and explain into the data set.
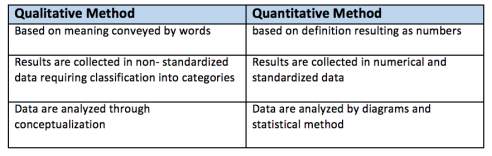
Table 3.3: The Differences between Quantitative Data and Qualitative Data (Saunders et al., 2009)
Therefore, this research is used to collecting data and analyzing by both technique of qualitative method (interview) and quantitative method (close and open questionnaires). Alternately, it is the mixed-method design (Saunders et al., 2009).
3.4.1 Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is focused on scientific approach in social sciences. Blumberg et al. (2008) mentions the scope of qualitative research containing several approaches which are adapted for exploratory surveys of management questions such as in-depth interview, participant observation, an open question, etc.
This research described a qualitative study resulting from video interview performance by using Skype, included in a larger research held in ten small and medium-sized hospitality enterprises and five 3 to 5-star hotels, in the South-east Thailand. The qualitative study was held in fifteen hotels that allowed the researcher to interview the manager in order to identify the role and impact of innovation. More significantly, the first part of the interview form asks manager about demographic detail such as hotel name, ages, period of employment, workplace location, existing system, and the firm primary competitive strategy. The second part is considered the driver for innovation, transforming internal process, and impacts on staff and manager of innovation respectively.
The objective of the interviews is to gain a deeper knowledge for building innovation in hospitality industry. The data collection was focused on understanding, challenges hospitality management, and the perception of employees in terms of innovation organization by their past and present experience. All the interviews used in English Language by recording in personal smartphones for transforming in another process. In this interviews, this study will use a new online communication tools for data collection in qualitative research and simultaneously. This tools use for interviewees and interviewers to interact each other as face-to-face communication. It is easily to use with any device, especially it is cost-free (Bertrand and Bourdeau, 2010). Interviews with hospitality managers indicate that the most critical aspect of innovation in the hospitality sector are their employees (Ottenbacher and Shaw, 2002). Hotels often have the same ‘hardware’ so that employees are the ultimate moderator for differentiating services. This means that when assessing the performance of new services, it is essential to include criteria covering employee management. The relevance of employees in service innovation efforts has been alluded to in previous studies (de Brentani, 1991; Storey and Easingwood, 1998), but not with the intensity they deserve for a highly personalized service offering as hospitality. Korczynski (2002) argues that service management should leave behind the old production line approach and concentrate on the modern application of systematic human resource management. Such a modern application involves careful selection of employees, employee training, empowerment, low formalization, behavior-based evaluation and a strategic approach to human resource management. Unfortunately, if internet is not working, so the interviewer will use telephone interview.
3.4.2 Quantitative Research
The primary aim of quantitative research is to provide a conclusive data in specific area by using statistic techniques to explain the observation. The objective used is aimed to find out the accurate measurement of the target group toward getting the precise numerical answer. This data collection is mostly used in almost final part to explain particularly and clearly picture of information in narrow scope. Quantitative research data can be gathering from surveys, questionnaire or any tools which can be measured and analyse into numerical data collection. Moreover, the data can be mostly presented into statistical graph, table comparison or any formats which can show the number.
The quantitative method has been used in this research and data has been clustered from the hotel and gathered questionnaires from customers who came from the various country, staff perception, especially hotel organization. The survey comprises four parts. The first part investigates demographic profile. The second part investigates Customer View on Technology in the Hospitality Industry. In addition, Employee View on Technology in the Hospitality Industry. Eventually, Entrepreneur view, in terms of Improving the job performance or customer relations
According to this research is aimed to investigate the integration of Lean and Six Sigma techniques which specifically focus on Electronic Industries in Thailand and find out the best strategies approach of integration. Consequently, this research will be adopted qualitative research methodology to achieve research objectives and questions respectively. However, in order to work on quantitative research effectively, (Nalevanko 2016) mentions that there are sevens strategy to achieve qualitative research and it is explained as follow;
- The researchers have to ensure that you have high quality and sufficiently data enough for research.
- List appropriate objectives and research questions which can be measured and assessed the project achievement
- Building the fundamental of your research by focusing on the relevant literature.
- Prepare and design the research methodology before work on it.
- List an observation of empirical research
- List a feasible theoretical used
- Explain a clear picture of research literature
3.5 Research Design
Research Design is a preparation for research project and it is usually taken place after research objectives have been clearly defined. The research design is the most important part for research plan because it can help to conduct research issues such as; what, where, when, who, how and etc. Seltiz, et.al. (2004:303) also stated that “A research design is the arrangement of conditions for collection and analysis of data in a manner that aims to combine relevance to the research purpose with economy in procedure. Therefore, the purpose of research design is to guide the scope and outline of research in order to lead the direction into the same way. Bryman and Bell (2001) note that the consideration factor in research design has to be involved with following;
- The connection and relevant of diversity sources
- The basis summary of each topic
- Understanding particular practise in the context
- Determining the conjunction among various context
The essential steps of effective research design is identified into 6 steps by Collis and Hussey (2014) as follow;
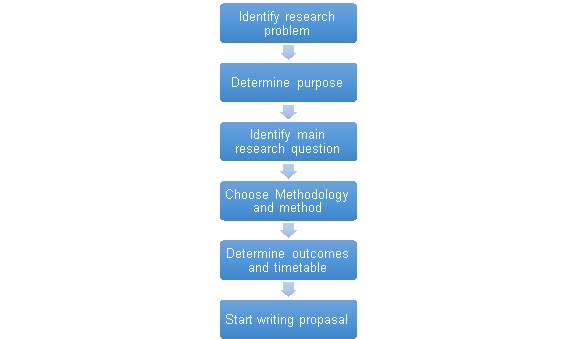
Figure 3.4 The essential steps of research design (Collis and Hussey 2014)
3.6 Research Strategy
According to Saunders et al (2009), research strategy is a methodology to guide the researcher decision direction on which method, techniques appropriate with the project. It is a guidance to broadly indicate project pattern based on research objectives and research questions such as; interview, survey, experiment, case study. Furthermore, he pointed out that there are seven aspects which can be used to combine in strategy toward the satisfy outcome.
- Archival Research
- Action Research
- Survey
- Experiment
- Case studied
- Fundamental Theory
- Ethnography
However, survey will be adopted in this research due to relevant with empirical
investigation. A survey strategy is designed to collect primary or secondary data from a sample in order to analyse the data statistically and generalized the population results (Collis and Hussey 2014). Thomas (2004) believes the purpose of survey strategy is creating generalizations of populations from the sample which has been collected. Likewise he says the various type of survey research such as sampling method, interview, questionnaire, and other quantitative analyses. Therefore, this research will be collected data information through three method called; “literature review, interview & questionnaires and documentary analysis”. Saunders et al (2009) explain that the combination of three techniques called “triangulation” which identified as the application of gathering different data through one single research towards ensuring that the data collection is validity and precision. The process of combine three techniques are explain as follow;
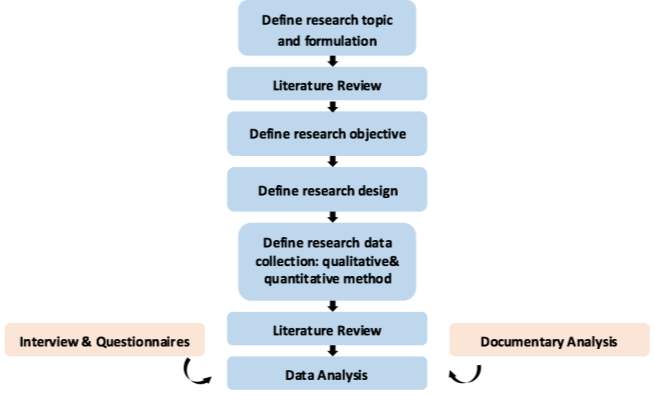
Figure 3.5 The data collection methodology (Saunders et al 2009)
3.7 Data Collection Method
The data collection of this dissertation is collected by used both primary and secondary data. Primary data is mainly collected from the interview by the person, who are currently staying and working in the Gulf Thailand Hotels, including customer, employee, and manager. The interview will be conducted through video interviews on Skype video calls and interpreted into the data collection. The interview questions will be related to the Lean Six Sigma integration framework techniques of company and which strategies they used to approach on the objective. The aim of interview is to analysis in which techniques can be used in practical and appropriate to handle with quality issues over Electronic Industry, understand how to resolve the problem and how the company control the quality performance of products.In contrast, the secondary data collection will be used to support and compare with the primary outcome. It will be collected from books, journals, academic publish papers, case studies and reliable online data based. The collection can be collected from library based and online based as well. According to this research based on the interview as a primary data. It is required the basic skill of the research question and accuracy of There might have both advantages and disadvantages itself.
3.7.1 Strength of Interview
- It can be obtain the validity data in particular of respondent attitudes and opinion.
- It can be approached large and many questions in one time.
- The interview questions are flexible and can be asked in the same way so as to the interviewee can response easily.
- The interviewee is able to explain and clarify the answer in deep details due to the open ended questions. Moreover, the interviewer can fully ensure and make understanding the answer during the interview (Opdenakker 2006).
3.7.2 Limitation of Interview
- The data might not get completely reliability in some point because of it based on attitudes, opinions and knowledge.
- Interviewee are forced to select the alternative answers which the responder asks them.
- Time consuming of data collection and analysis of interview are taken time when comparing with questionnaire which can be easy to compute the result.
- The interviewer has to be familiar with the objective and process of the case study unless, having strong special skill of tendency (Opdenakker 2006).
3.8 Data Analysis
After the data have been collected and interpreted, the data will be classified into purposeful and usable categories toward easily transforming into tabulate and symbol. The coding operation into tabulate generally puts into the table format in computer. Although many types of data and numerous data, it can be interpreted into various templates not only table, but it also can be formulated into any static data such as
bar graph, line graph, pie chart or etc.
In the analysis part, the linking of the differentiation and confliction between the hypothesis and original research data have to be subjected and examined the validity which is needed to identify the conclusion. However, if the data is collected from the different sources, it will give the different mean value and. Accordingly, the conclusion has to clearly show that it comes from the different sample at all but, if the result show different because of chance, the conclusion has to clearly report that it completely belongs to same source.
3.9 Chapter Summary
This chapter presents on the research methodologies of the research in order to determine the suitable method which is adopted in this research. The techniques and method were used in the overall research of overall, are explained with providing caused as the below table 3.2:
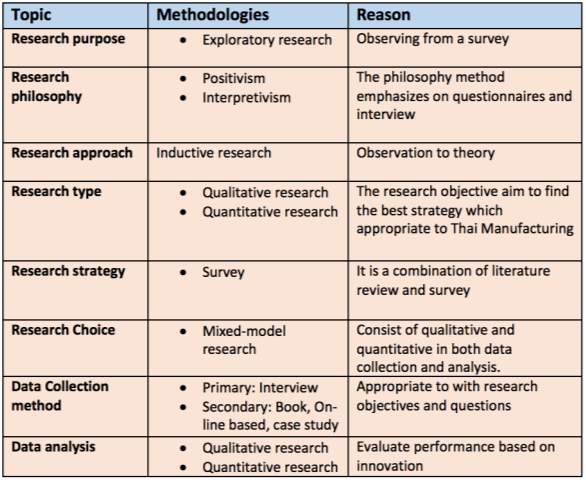
Table 3.2: The summary table of research methodology
References (1,144)
Albliwi, S. and Antony, J. (2013) ‘IMPLEMENTATION OF A LEAN SIX SIGMA APPROACH IN THE MANUFACTURING SECTOR: A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW’. International Conference on Manufacturing Research (ICMR2013) [online] 11. available from
Anbari, F. and Kwak, Y. (2004) ‘Success Factors In Managing Six Sigma Projects’. in 2004 Project Management Institute Research Conference [online] held 2004. The George Washington University. available from
Anderson, M., Anderson, E. and Parker, G. (n.d.) Why Your Operations Management Needs To Focus On Quality – For Dummies [online] available from
Antony, J., Banuelas, R., 2002. Key ingredients for the effective implementation of six sigma program. Measuring Business Excellence 6 (4), 20–27.
Blumberg, B., Cooper, D. R. and Schindler, P. S. (2008) Business Research Method, Second European Edition. 2nd edn. Berkshire: McGraw-Hill Education
BSI group. (n.d.) ISO 9001 Quality Management System Essential Best Practice For Small Businesses [online] United Kingdom: BSI group. available from
Bryman, A. and Bell, E. (2007) Business Research Methods. 2nd edn. Oxford: OxfordUniversity Press
Chiarini, A. (2013) Lean Organization. Milan: Springer
Chiangmai Mail Publishing, (2012) Japanese Firm Ups Investment Near Formerly Flooded Industrial Park [online] available from
Carey, A. (2015) Lean – Seven Wastes – NHS Institute For Innovation And Improvement [online] available from
Chen, J.C., Li, Y., & Shady, B.D. (2010). From value stream mapping toward a lean/sigma continuous improvement process: an industrial case study. International Journal of Production Research, vol. 48, no. 4, p. 1069-1086.
Collis, J. and Hussey, R. (2014) Business Research. Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan
Conner, G. (2001) Lean Manufacturing For The Small Shop. Dearborn, Mich.: Society of Manufacturing Engineers
Dolcemascolo, D. (2015) 7 Wastes Muda Article On The Seven Wastes Of Lean Manufacturing [online] available from
George, M.L. (2002). Lean Six Sigma: Combining Six Sigma quality with Lean speed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hendricks, C. A. and Kelbaugh, R. 1998. Implementing Six Sigma at GE. The Journal of Quality and Participation, Vol. 21, No. 4, 48-53.
Jayaraman, K., Leam Kee, T. and Lin Soh, K. (2012) ‘The Perceptions And Perspectives Of Lean Six Sigma (LSS) Practitioners’. The TQM Journal 24 (5), 433-446
Joon, Y. (2014) Business Process Improvement Methodology- Lean Six Sigma Framework [online] available from
Johnson, A. and Swisher, B. 2003. How Six Sigma Improves R&D. Research Technology Management, Vol. 46, No. 2, 12-15.
Kim, Y. (1997) Technological Capabilities And Samsung Electronics’ International Production Network In Asia’. Australian National University
Lean Entreprise Institute, (2015) What Is Lean? [online] available from
Linton, I. (n.d.) Why Is Quality Important For A Business? [online] available from
Luca Bertolaccini, A. (2015) ‘The Statistical Point Of View Of Quality: The Lean Six Sigma Methodology’. Journal of Thoracic Disease [online] 7 (4), E66. available from
McAdam, R., Lafferty, B. (2004). A multilevel case study critique of Six Sigma: Statistical control or strategic change? International Journal of Operations & Production Management, vol. 24, no. 5, p. 530-549.
Modalisa Technology, (2015) Lean Six Sigma | Modalisa-Technology [online] available from
Monden, Y. (2012) Toyota Production System. Boca Raton: CRC Press
National Occupational Standard, (n.d.) Applying Continuous Improvement Techniques (Kaizen) [online] available from
Nalevanko, C. (2016) Seven Strategies For Publishing Qualitative Research [online] available from
Opdenakker, R. (2006) “Advantages And Disadvantages Of Four Interview Techniques In Qualitative Research”. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research [online] 7 (4). available from
Panasonic, (2015) Panasonic Thailand [online] available from
Paulsen, C. (2015) Guest Post: 5 Reasons You Need To Do A DMAIC | [online] available from
Pena, A. and Ellis, T. (2016) The Benefits Of Using Lean Six Sigma [online] available from
Procera Networks, (n.d.) Panasonic Thailand, One Of South East Asia’s Largest Consumer Electronic Manufacturers, Deploys Multiple Procera Networks’ Packetlogic Appliances | Procera Networks: Empowering Intelligence [online] available from
Rajasekar, S., Philominathan, P. and Chinnathambi, V. (2013) RESEARCH METHODOLOGY [online] available from [1 December 2016]
Redman, L. and Mory, A. (1933) The Romance Of Research. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins Co. in coöperation with the Century of Progress Exposition
Reijns, T. (2010) The Advantages And Limitations Of Lean Six Sigma In Process (Re)Design: Combining Continuous Improvement Methods To Align The Product Characteristics With The Customer’S Requirements. Bachelor’s. Tilburg University
Royal Thai Embassy in Mexico, (n.d.) Thailand’S Electrical And Electronics Industry [online] available from
Salah, S., Rahim, A. and Carretero, J. 2010. The integration of Six Sigma and Lean Management. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 1(3):249-274.
Samsung, (2016) History – Corporate Profile – About Samsung – Samsung [online] available from
Saunders, M., Lewis, P. and Thornhill, A. (2009) Research Methods For Business Students. New York: Prentice Hall
Seagate, (2015) Business Storage 8-Bay Rackmount NAS [online] available from
Sekaran, U. (1992) Research Methods For Business. New York: Wiley
Seltiz, et.al. (2004) “Research Design”. in Research Methodology: Methods And Techniques. 1st edn. ed. by Kothari,, C. New Deli: New Age International (P) Ltd., 303
Sodick, (2015) Sodick Thailand Corporate [online] available from
Smith, G. (2000) Too Many Types Of Quality Problems Categorizing Your Problems In Solution Relevant Ways. [online] available from
Snee, R.D. 2010. Lean Six Sigma – getting better all the time. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 1(1):9-29
Singh, Y. and Bajpai, R. (2008) Research Methodology.
Stegall, M. (2012) Lean And Six Sigma–Comparing And Contrasting The Process Steps [online] available from
Timans, W., Antony, J., Ahaus, K. and Solingen, R. 2012. Implementation of Lean Six Sigma in small and medium – sized manufacturing enterprises in the Netherlands. Journal of Operational Research Society 63:339-353
The British Assessment Bureau, (2010) ISO 9001: Dispelling The Myths | The British Assessment Bureau [online] available from
United Nation (2004) “Research Design”. in Research Methodology: Methods And Techniques. 1st edn. ed. by Kothari,, C. New Deli: New Age International (P) Ltd., 303
United Nation, (2006) Product Quality: A Guide For Small And Medium-Sized Enterprises [online] Vienna: United Nation: Industrial Development Organisation. available from
Waxer, C. (n.d.) Understanding Process Variation [online] available from
Won, J. and Cochran, D. (n.d.) Rationalizing The Design Of The Toyota Production System: A Comparison Of Two Approaches [online] Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology. available from
Zu, X., Fredendall, L.D., & Douglas, T.J. (2008). The evolving theory of quality management: The role of Six Sigma. Journal of Operations Management, vol. 26, no. 5, p. 630-650.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Leisure Management"
Leisure Management involves the planning, organisation, and delivering of leisure and recreational activities, using available resources and facilities.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




