Mobile Application for Shopping
Info: 9368 words (37 pages) Dissertation
Published: 19th Oct 2021
Tagged: Information SystemsTechnology
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION
CHAPTER 8: CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 3.1: Iterative Waterfall model
Figure 3.2: Gantt chart for communication
Figure 3.3: Gantt chart for planning
Figure 3.4: Gantt chart for modeling
Figure 3.5: Gantt chart for Construction
Figure 3.6 Gantt chart for Deployment
Figure 5.4: Activity Diagram for customer
Figure 5.5: Activity diagram for shopkeeper
Figure 5.6: Activity diagram for admin
Figure 5.9: DFD level 1 for login
Figure 5.10: DFD level 1 for registration
Figure 5.11: DFD level 1 for manage category
Figure 5.12: DFD level 1 for manage subcategory
Figure 5.13: DFD level 1 for product detail
Figure 5.14: DFD level 1 for cart
Figure 5.15: DFD level 1 for order
Figure 5.16: DFD level 1 for bill
Figure 5.17: DFD level 2 for category
Figure 5.18: DFD level 2 for subcategory
Figure 5.19: DFD level 2 for product
Figure 5.20: DFD level 2 for cart
Figure 6.1: Database of slimzon
Figure 7.4: Admin manage shop page
Figure 7.6: Manage category and subcategory
Figure 7.17: Registration form
Figure 7.19: product search on category
Figure 7.21: Product detail select size
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1: Comparison of existing system
Table 2.2: Comparison with existing system
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Project summary
Slimzon is meant at promoting shopping methods and make people life easier in terms of shopping in mall; we built this mobile application that could play a significant task in the shopping at mall as a whole. The practice of slimzon is to help the users to find desired item efficiently and buy both online and offline mode.
1.2 Purpose
The main purpose of our project is to make shopping of mall items easier and less tiring. The user will easily get the desired item by providing filters like price categories etc. The user can even check total bill of products by qr scanning feature. Even the user can but online or generate bill and give offline payment.
1.3 Scope
This application is used mainly by the customers who can be any human being like student, teenager, rich people, old people, teacher, businessman, housewife etc to view and buy items online as well as offline through application
1.4 Report Outline
Chapter 1 is the basic introduction of project. In gives overview of the project and purpose & scope of the project.
Chapter 2 is the information about the technology which is use for the implementing to this project.
Chapter 3 is the gives information about planning and scheduling of this project. It includes different techniques for planning & scheduling. These techniques are work break down structure, pert chart & Gantt chart.
Chapter 4 is the gives information about software requirement specification of this project. It include functional and non-functional requirement of this project.
Chapter 5 includes the analysis of the system develop by the system developer. In that include the feasibility study of this system. Also include the diagrams like E-R diagram, UML diagram & USECASE diagram of the system which shows the behavioral aspect of the system.
Chapter 6 includes the schema designs of the project. This is use for store the data in database.
Chapter 7 shows the implementation part of this system. It gives the GUI design of the project and testing process of system.
Chapter 8 contains the conclusion of the project and remaining future work of this project or system.
CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW
A fine deal of work has been directed toward mall shopping tools. The literature shows that grave efforts have been put in order to come up with a successful mall shopping mall navigator. Authors developed a communication robot for use in a shopping mall to provide shopping information and give direction to customers when desirable. The authors faced difficulties in sensing human behaviors, conversation in a noisy environment, and the needs of unpredicted miscellaneous information in the conversation. The robot was designed to avoid the speech recognition problem by using radiofrequency identification (RFID).
The author of reference tried to improve entertainment experience which represents a very significant role in shopping mall competitive edge. In his research, he depended on both theoretical and empirical studies which provide several strategies principles for mall manager. He planned and empirically investigated the premises of the ‘Holistic Entertainment Experience for Wooing Shoppers’ (HEE-WS) model which is illustrative for mall managers to pursue seamless alignment between the creation of holistic entertainment experience and the creation of perceived satisfaction in mall attributes. This kind of alignment is crucial in predicting policies to elevate the effectiveness of shopping mall management.
In a study carried by, the authors examined the effect of gender and work status on Shopping Center Patronage, and they improved what other researches recommend that there are important differences between men and women models as well as between women who work outside a home as opposed to the ones that don’t. Social presence influence on perceived security. Conceptual model was built to represent virtual malls where behavior of users was enhanced to provide more intensive view of virtual reality. In a study showed that pre 1994, low income earners depend on small and informal businesses represented as retail landscapes, which provide very limited choices and services to the customer, therefore shopping outside town appeared and known as “out shopping”. Moreover in 1994 the income growth rapidly resulted in “in-bound shopping”, which forms the last retail in South Africa. After that the shopping malls appeared on small townships which reduced the market share of retailer [5]. According to reference [6], in 2002, as a result of the increasing number of small-sized online malls, the number of customers who depend on online shopping is increasing. However, these online shopping malls won’t exist for a long time since the shortage in Customer Relationship Management (CRM) strategies imply their needs. The CRM strategies can be improved by making some analysis on transaction data of a certain shop. Some types of analysis can be made by using some data mining techniques, decision tree, association rules and sequential patterns based on data about VIP customers.
Table 2.1: Comparison of existing system
| Existing System
|
Advantages | Limitations of Existing System
|
Solution |
| a communication robot | The robot helped the customer to give information about mall |
|
The robot was designed to avoid the speech recognition problem by using radiofrequency identification (RFID). |
| A Static device | No need of sensing human behavior or language |
|
Lot of static device where placed in mall |
Table 2.2: Comparison with existing system
| Existing System | Technique of existing System | Use of your technique in project | Justification |
| S-mall, Robinsons, lullu mall etc | Just search shops ; alert you about events | Can also search on the basis of items | Malls are basically for buying items so if they will be able to search their item (considering its color, price and reviews) within the app this will save their time and money. |
CHAPTER 3: PROJECT MANAGEMENT
3.1 Project Planning and Scheduling
3.1.1 Project Development Approach
Our project is developed using specific software development lifecycle. Software Development approach is best suited for the project depends on the requirement and other factors. A process model is a development strategy that is used to achieve a goal that satisfies the requirements abiding by the constraints.
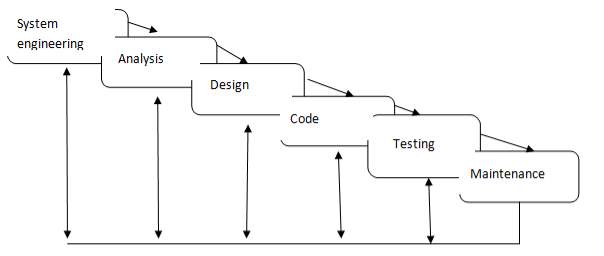
Figure 3.1: Iterative Waterfall model
An iterative life cycle model does not attempt to start with a full specification of requirements. Instead, development begins by specifying and implementing just part of the software, which can then be reviewed in order to identify further requirements. This process is then repeated, producing a new version of the software for each cycle of the model.
System Engineering:
Analysis:
The aim of the requirement analysis is to understand the exact requirements of the customer and to document them properly.
Requirement gathering and analysis:
This activity consists of first gathering the requirement and then analyzing the gathered requirement.
Requirement Specification:
The customer requirement identified during the requirement gathering and analysis activity are organized into a software requirements specification (SRS).
Design
The goal of the design phase is to transform the requirements specified in the SRS document into a structure that is suitable for implementation in some programming language. In technical, during the design phase the software architecture is derived from the SRS document.
Traditional Design Approach:
The traditional design technique is based on the data flow oriented design approach. While using this technique the design phase consists of two important activities: first a structured analysis of the requirement specification is carried out where the detailed structure of the problem is examined.
Object-oriented design approach:
Object-oriented design approach (OOD) is a relatively new technique. In this technique, various objects that occur in the problem domain and the solution domain are first identified and the different relationships that exist among these objects are identified.
Code
The purpose of the coding of software development is to translate the software design into source code. The coding phase is also sometimes called the implementation phase since the design is implemented into a workable solution in this phase. Each component of the design is implemented as a program module. The end-product of this phase is a set of program modules that have been individually tested. To enable the engineers to write good quality program, every software development organization normally formulates its own coding standards that suits itself. A coding standard addresses issues such as the standard ways of laying out the program code, the template for laying out the function and module headers, commenting guidelines, variables and function naming conventions, the maximum number of source lines permitted in each module, etc.
Testing
System testing is normally carried out in a planned manner according to a system test plan document.
Maintenance
Maintenance of a typical software product requires much more effort than the effort necessary to develop the product itself. Maintenance effort is roughly in 40:60 ratios.
Advantages of Iterative Waterfall Model
- In iterative model we can only create a high-level design of the application before we actually begin to build the product and define the design solution for the entire product. Later on we can design and built a skeleton version of that, and then evolved the design based on what had been built.
- In iterative model we are building and improving the product step by step. Hence we can track the defects at early stages. This avoids the downward flow of the defects.
- Iterative model we can get the reliable user feedback. When presenting sketches and Blue prints of the product to users for their feedback, we are effectively asking them to imagine how the product will work.
- In iterative model less time is spent on documenting and more time is given for designing.
3.1.2 Project Plan
In this part we plan the project.
We have six modules in our project, which are as follows:
- Registration Module: Customer can register on their own. Shop registration are dome by admin.
- Product Search module: Customer search Desired Items Categories, Item Name.
- QR code scanning module: QR code will be scanned by customer while buying items at the mall to calculate total bill amount..
- Payment module: Customer can pay bill online as well as offline.
- Order Management Module: Order are basically managed by shop admin
- Report System module: Report are generated giving statistical analysis
3.1.3 Schedule Representation
| Start date | Days to complete | |||
| Communication | ||||
| Training | 13-jul-16 | 10 | ||
| Requirement Gathering | 23-Jul-16 | 20 | ||
| Milestone: project definition completed | ||||
| Planning | ||||
| Project estimation | 13-Aug-16 | 15 | ||
| Project Scheduling | 28-Aug-16 | 6 | ||
| Milestone: project planned | ||||
| Modeling | ||||
| requirement analysis | 13-Sep-16 | 15 | ||
| design | 18-Sep-16 | 20 | ||
| canvas making | 08-Oct-16 | 15 | ||
| Milestone: project achieved | ||||
| #Construction | ||||
| coding of basic website | 23-oct-16 | 60 | ||
| testing of basic website | 23-Dec-16 | 15 | ||
| coding of basic Android Application | 7-Jan-17 | 50 | ||
| testing of basic Android Application | 27-Feb-17 | 15 | ||
| Milestone is in progress | ||||
| *Deployment | ||||
| Verification by faculty | 14-Mar | 15 | ||
| Documentation and submission of report | 01-Apr | 12 | ||
| Milestone: not yet achieved | ||||
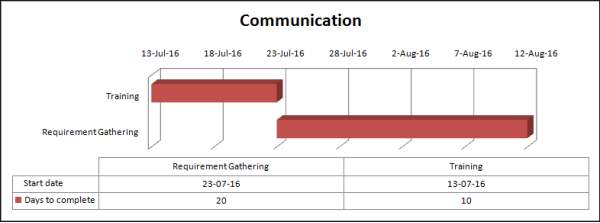
Figure 3.2: Gantt chart for communication
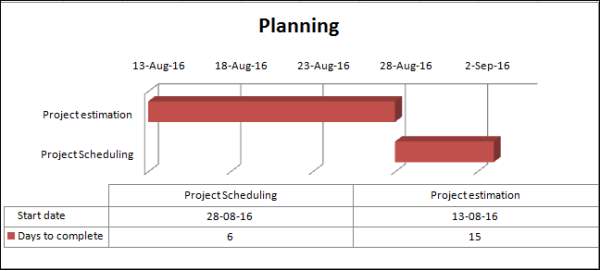 Figure 3.3: Gantt chart for planning
Figure 3.3: Gantt chart for planning
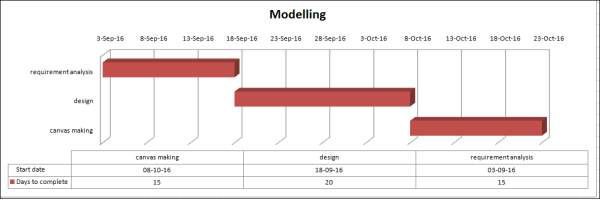
Figure 3.4: Gantt chart for modeling
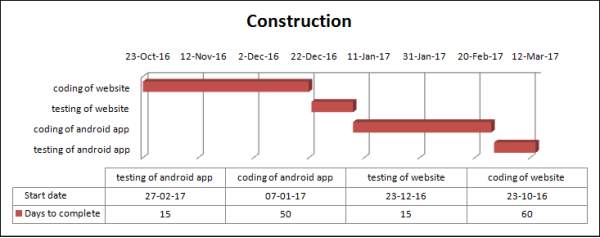
Figure 3.5: Gantt chart for Construction
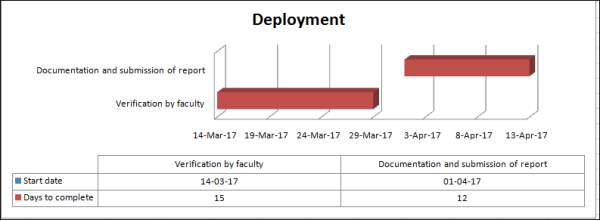
Figure 3.6 Gantt chart for Deployment
CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION
Introduction
Purpose
The main purpose for preparing this document is to give a general insight into the analysis and requirements of the existing system or situation and for determining the operating characteristics of the system.
Overview
This system provides an easy to solution customer’s to buy the product without go to the mall and to search their desired items in mall easily.
4.1 User Characteristics
There are four user groups for the slimzon:
Admin can:
- Register for shop admin
- Manage(add and update) category and sub category
- Manage ( add and update) shop in the mall
- View report prepared by shop admin
Shop admin can:
- Manage product
- Approve order
- Dispatch order
Customer can:
- Search items
- Buying items
- Order products
- Payment online/offline
- Scan QR-code
General public can
- Search items
- Scan QR code
Functional Requirement
R.1 Registration
Description: If customer wants to buy the product then he/she must be registered, unregistered user can’t go to the shopping cart, they can only search and view items. Shopkeepers are registered by mall admin, only registered shop admin can perform activity of shop admin.
Input: details of user. (Name, Address, City, State, Mobile No., Email ID, Password, Confirm Password)
Output: Account created
R.2 Login
Customer/ shop admin/mall admin logins to the system by entering valid user id and password.
Input: username and password
Output: Home page
R.3 Manage category and sub category
Description: Mall admin can add, update and delete category and sub category.
R.4 Manage Products
Description: Shop admin can add and update the product details and related offers
R.5.Search/Browse product
Description: The user can search their desired item by name or browse item through filter and options
Input: product related name
Output: list of products
R.6 QR Scanning
Description: The customer scans the qr object to calculate bill amount
Input: QR code
Output: Total amount
R.7 Manage order
R.7.1 Changes to Cart
Changes to cart means the customer after login or registration can make order of the product from the shopping cart.
R.8 Payment
For customer there are many type of secure billing will be prepaid as debit or credit card, post paid. The security will provide by the third party like Pay-Pal etc.
Input: bank account details, debit/credit card details
Output: Bill Generated .
R.9 Report Generation
After all transaction the system can generate report on the admin side giving various statistical analyses
Input: Report aspects on which need to analysis
Output: Report
4.2 Hardware and Software Requirements
Developer side
Hardware
- Processor: AMD A4-4000 APU with Radeon™ HD Graphics 3.00GHz
- RAM: 4GB min
- Display: 1024 × 768 or higher resolution monitor
Software
- OS: Microsoft Windows 7 Professional(64 bit)
- WampServer 2.4
- SQL Server 2005 Express
- Google chrome
- Notepad ++
- E-draw 8.0
- Microsoft Office Excel 2007
- Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007
- Microsoft Office Word 2007
- Android studio 2.2
- Android SDK
- Android version – 4.1(jellybean) to 6.0(Marshmallow)
- JAVA SE Development Kit 7 Update 75
- Web browser: Microsoft Internet Explorer 7.0 and above, Mozilla Firefox 3.5 and above, Apple Safari 5.0 and above, Google Chrome 1.0 and above
User side
- Android version – 4.1(jellybean) to 6.0(Marshmallow)
- Web browser: Microsoft Internet Explorer 7.0 and above, Mozilla Firefox 3.5 and above, Apple Safari 5.0 and above, Google Chrome 1.0 and above
- Network: faster connection between client computers and server
CHAPTER 5: SYSTEM ANALYSIS
5.1 Feasibility Study
Feasibility is the measure of how beneficial or practical the development of information system will be to an organization.
The feasibility study involves following main criteria:
- Whether the identified user needs may be satisfied using current software and hardware technologies ?
- The study will decide if the proposed site will be cost-effective and if it can be developed given existing budgetary constraints
- Feasibility study should be cheap and quick
- The result should inform the decision of whether to go ahead with a more detailed analysis.
5.1.1 Technical Feasibility
It is a measure of the practicality of specific technical solution and the availability of technical resources and expertise. Technical feasibility is computer oriented.
- Is the project feasibility within the limits of current technology?
- Does the technology exist at all?
- Is it available within given resource constraints (i.e., budget, schedule )
5.1.2 Economical Feasibility
It is a measure of the cost-effectiveness of a project or solution. This is often called a cost-benefit analysis. Economic feasibility deals with the costs and benefits of the information system.
5.1.3 Operational Feasibility
It is a measure of how well the solution will work in the organization. It is also a measure of how people feel about the system/process. Operational feasibility is people oriented.
Is there sufficient support for the management from the users?
- Will the system be used and work properly if it is being developed and implemented?
- Will there be any resistance from the user that will undermine the possible application benefits?
5.2 Function of System
5.2.1 Use Case Diagram
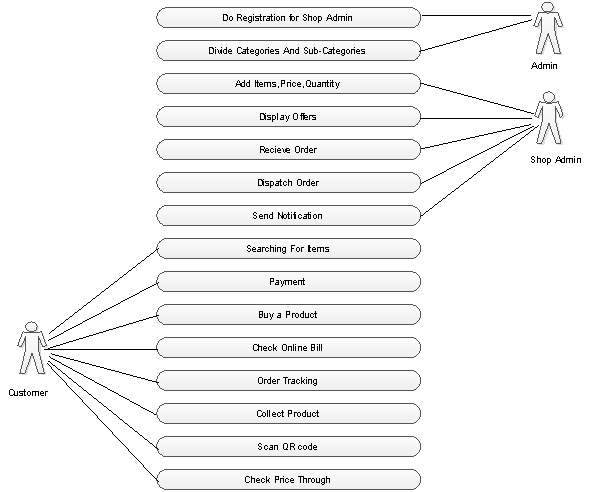
5.3 Data Modeling
5.3.1 Class Diagram
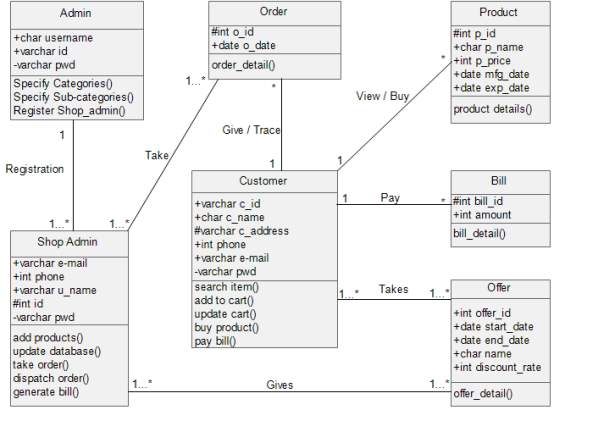
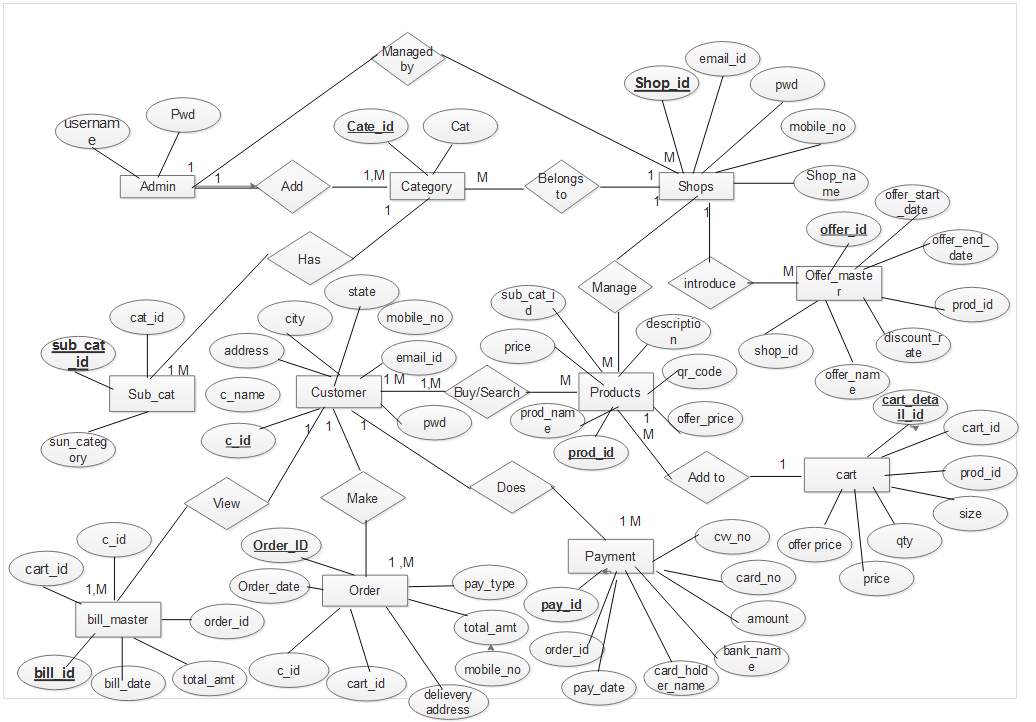
5.3.2 E-R Diagram
5.3.3 Activity Diagram
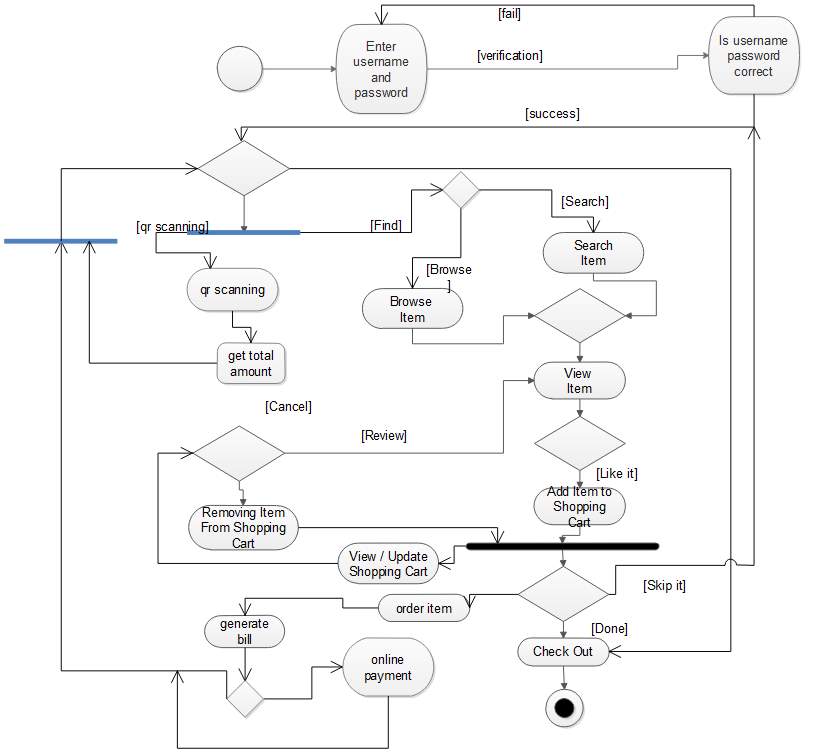
Figure 5.4: Activity Diagram for customer
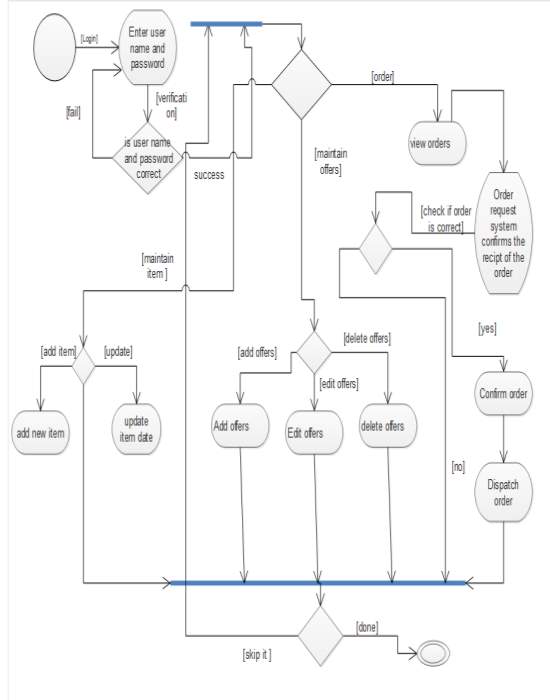
Figure 5.5: Activity diagram for shopkeeper
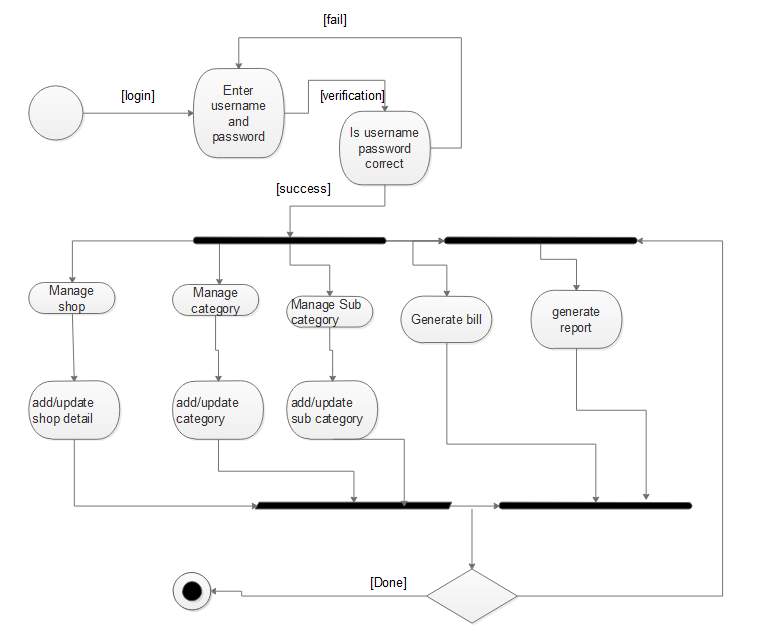
Figure 5.6: Activity diagram for admin
5.3.4 Sequence Diagram
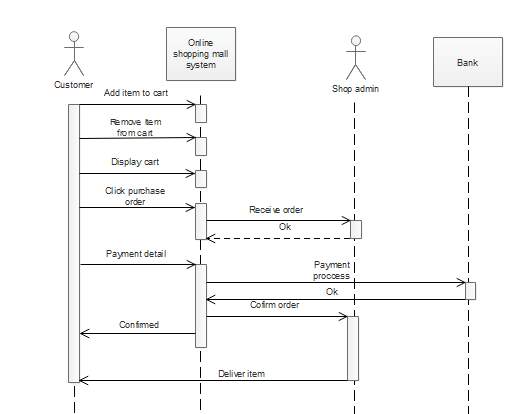
5.4 Functional and Behavioral Modeling
5.4.1 Data Flow Diagram
Level 0- context Level
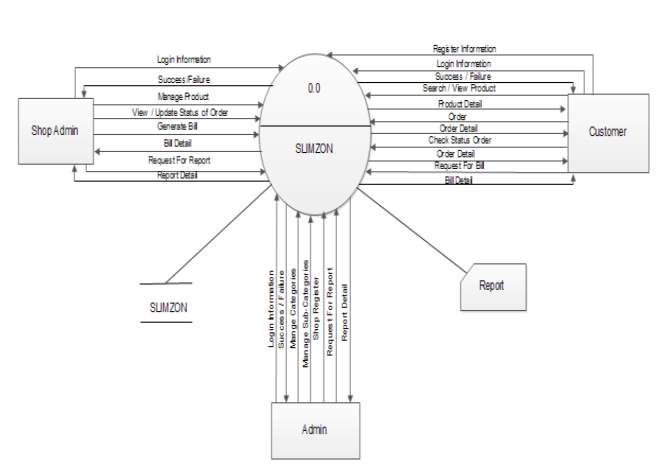
Level-1
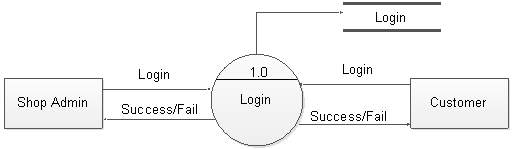
Figure 5.9: DFD level 1 for login
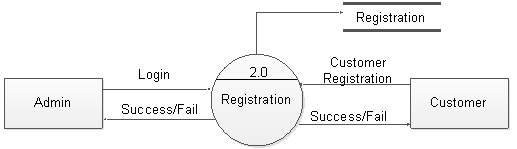
Figure 5.10: DFD level 1 for registration
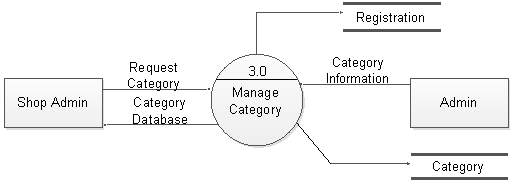
Figure 5.11: DFD level 1 for manage category
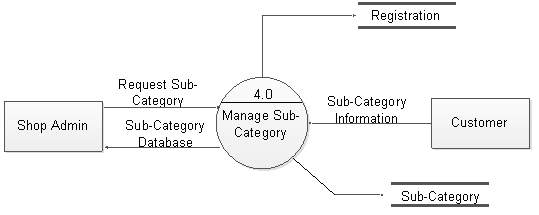
Figure 5.12: DFD level 1 for manage subcategory
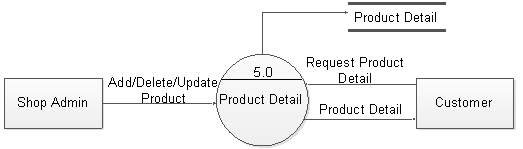
Figure 5.13: DFD level 1 for product detail
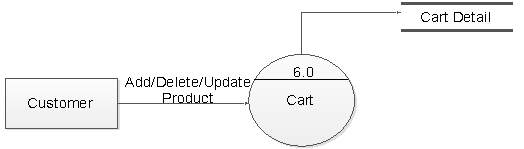
Figure 5.14: DFD level 1 for cart
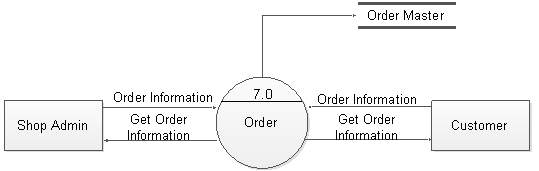
Figure 5.15: DFD level 1 for order
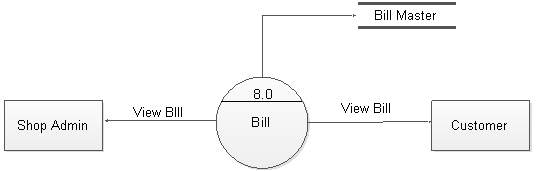
Figure 5.16: DFD level 1 for bill
Level-2
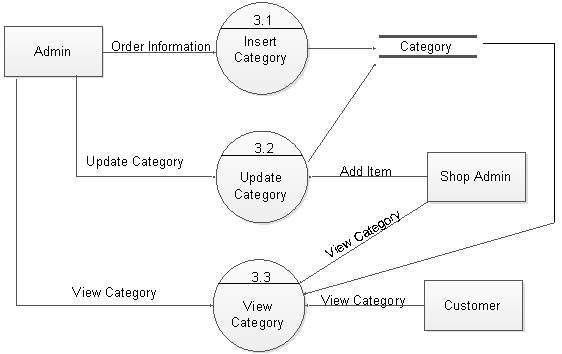
Figure 5.17: DFD level 2 for category
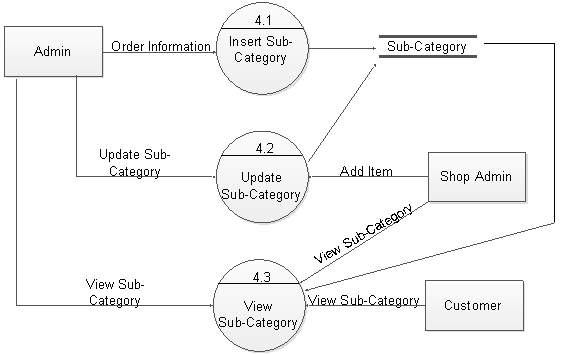
Figure 5.18: DFD level 2 for subcategory
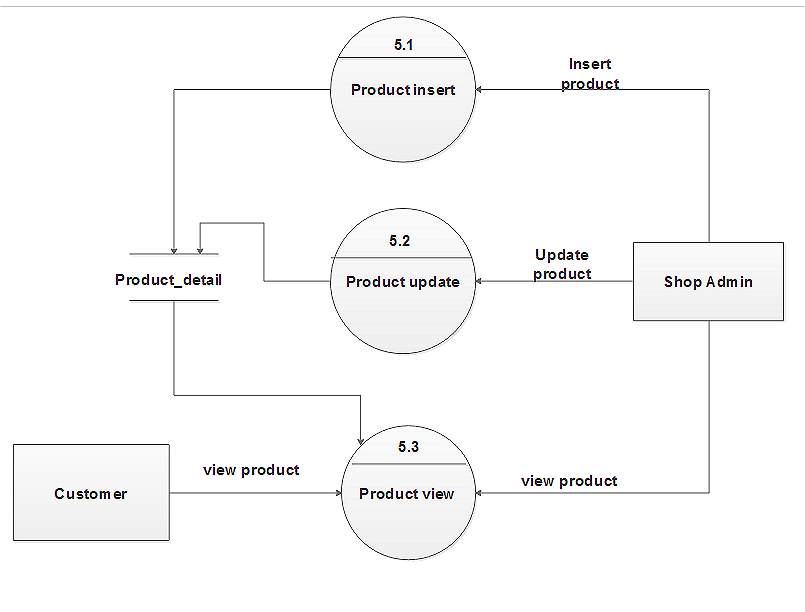
Figure 5.19: DFD level 2 for product
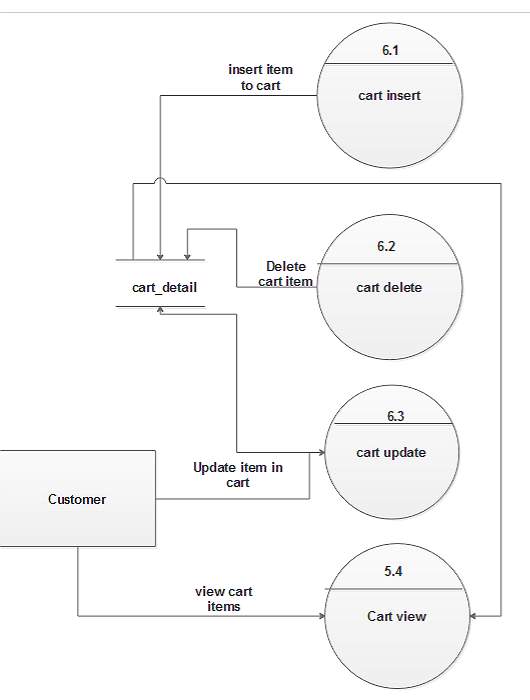
Figure 5.20: DFD level 2 for cart
CHAPTER 6: SYSTEM DESIGN
6.1 Database Schema Design
Database design is the process of specifying the logical and/or physical parts of a database. The goal of database design is to make a representation of some “universe of discourse”- the type of facts, business rules and other requirement that the database is intended to model.
A description of the structure of the database including the structure of the tables, column, constraints, view, etc that makes up the database.
The schema describes the complete blueprint for the database, defining everything about the database except that data itself.
Database Name: SLIMZON
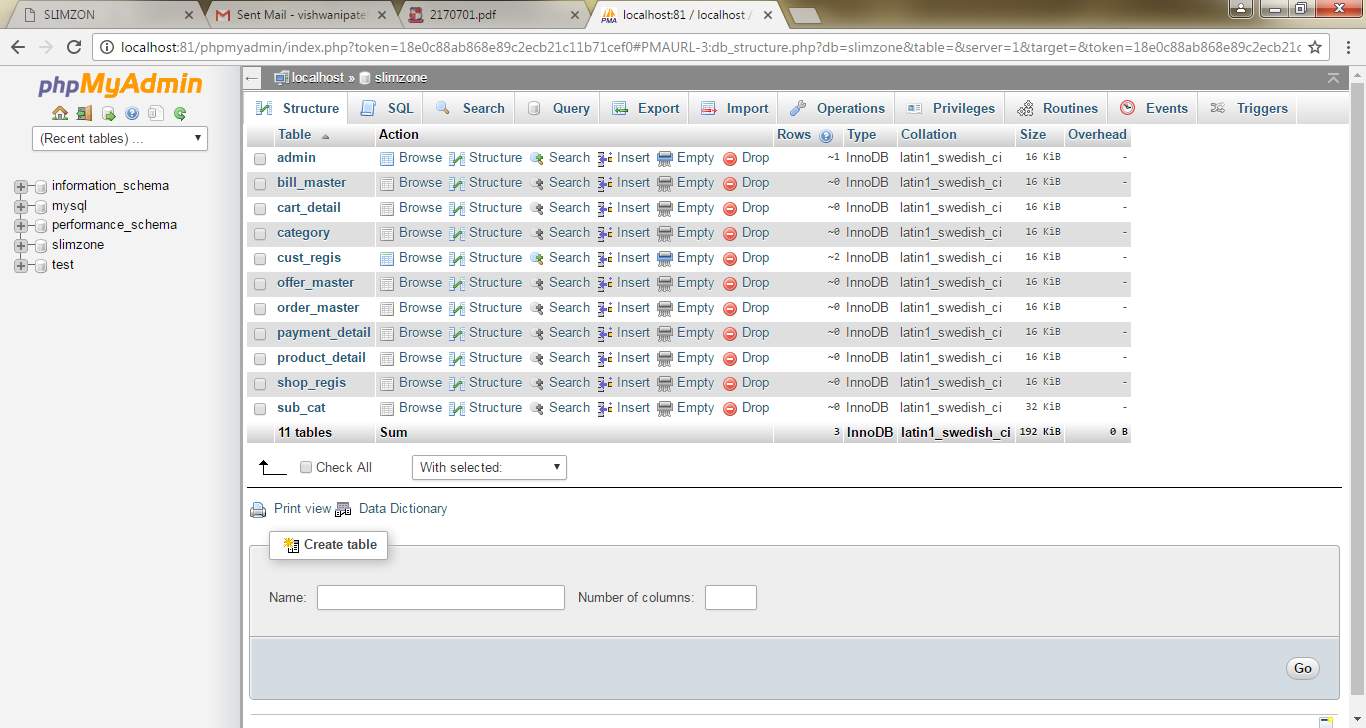
Figure 6.1: Database of slimzon
This database stores all the information related to the online Shopping Mall system.
Table Name: Admin
This table contains the information about the Admin that are registered to the web application.
Admin
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| username | varchar(50) | No | ||
| pwd | varchar(10) | No |
Table Name: Bill_master
This table will show the information about the Bill_master that are registered on the web application.
bill_master
Table comments: bill_master
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| bill_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| bill_date | date | No | ||
| order_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| c_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| cart_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| total_amt | int(10) | No |
Table name: cart_detail
This table will show the information about the cart_detaill for the web application.
cart_detail
Table comments: cart_detail
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| cart_detail_id | int(10) | No | ||
| cart_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| prod_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| size | varchar(10) | No | ||
| qty | int(10) | No | ||
| price | int(10) | No | ||
| offer_price | int(10) | No | ||
| discount_rate | int(2) | No |
Table name: Category
This table shows all the Category details of items.
category
Table comments: category
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| cat_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| cat | varchar(50) | No |
Table name: Cust_regis
This table will show the information about Customer Registration.
cust_regis
Table comments: cust_regis
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| c_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| c_name | varchar(50) | No | ||
| address | varchar(255) | No | ||
| city | varchar(50) | No | ||
| state | varchar(50) | No | ||
| mobile_no | varchar(10) | No | ||
| email_id | varchar(50) | No | Foreign key | |
| pwd | varchar(10) | No | ||
| r_date | date | No |
Table name: offer_master
This table will show the information about Offers.
offer_master
Table comments: offer_master
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| offer_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| offer_start_date | date | No | ||
| offer_end_date | date | No | ||
| prod_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| discount_rate | int(2) | No | ||
| offer_name | varchar(50) | No | ||
| shop_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key |
Table name: Order_master
This table shows the information about Order.
Table comments: order_master
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| order_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| order_date | date | No | ||
| cart_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| c_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| delievery_address | varchar(255) | No | ||
| mobile_no | varchar(10) | No | ||
| total_amt | int(10) | No | ||
| Status | int(1) | No | ||
| pay_type | varchar(10) | No |
Table name: payment_detail
This shows the information about payment.
Table comments: payment_detail
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| pay_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| order_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| pay_date | date | No | ||
| card_holder_name | varchar(50) | No | ||
| bank_name | varchar(50) | No | ||
| card_type | varchar(10) | No | ||
| card_no | varchar(16) | No | ||
| cvv_no | int(3) | No | ||
| expiry_date | varchar(10) | No | ||
| Amount | int(10) | No |
Table name: product_detail
This table shows the information about the details of product.
Table comments: product_detail
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| prod_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| prod_name | varchar(50) | No | ||
| cat_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| sub_cat_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| Description | varchar(255) | No | ||
| company_name | varchar(50) | No | ||
| Price | int(10) | No | ||
| offer_price | int(10) | No | ||
| qr_code | varchar(10) | No | ||
| prod_img | varchar(50) | No | ||
| shop_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key |
Table name: shop_regis
This shows the information about the shop registration.
Table comments: shop_regis
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| shop_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| shop_name | varchar(50) | No | ||
| email_id | varchar(50) | No | ||
| pwd | varchar(10) | No | ||
| mobile_no | varchar(10) | No |
Table name: sub_cat
This shows the information about the sub category of product.
Table comments: sub_cat
| Column | Type | Null | Default | Comments |
| sub_cat_id | int(10) | No | Primary key | |
| cat_id | int(10) | No | Foreign key | |
| sub_category | varchar(50) | No |
CHAPTER 7: IMPLEMENTATION
Home page
Home page is the main page a visitor navigating to a website from a web search engine will see, and it may also serve as a landing page to attract visitors. The home page is used to facilitate navigation to other pages on the site by providing links to prioritized and recent articles and pages.
Registration Page
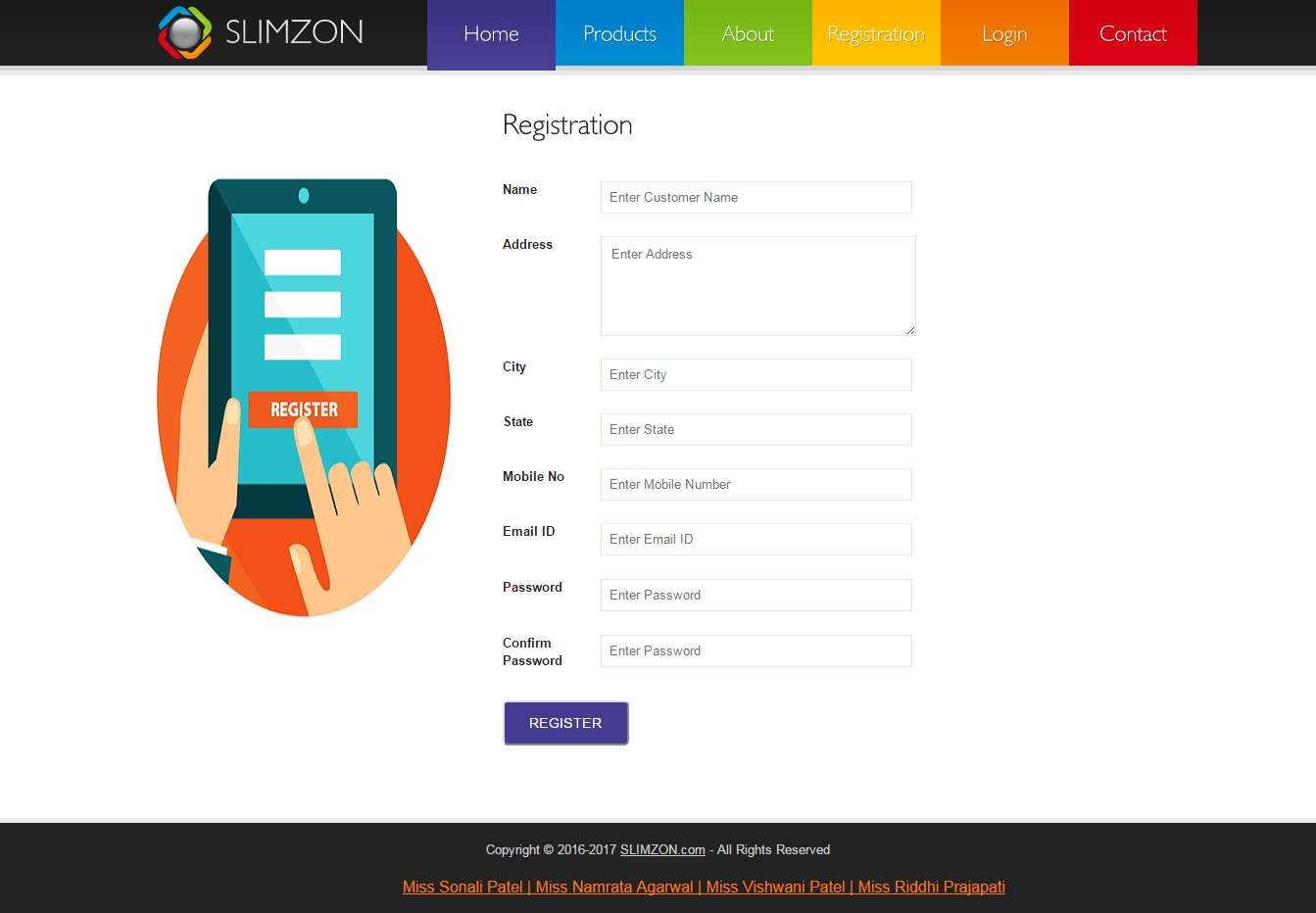
Registration page will register the customer. In our page we have kept fields and all are compulsory to fill.
The fields are
Name: only validates alphabet, no numeric and special characters are allowed
Address: all are valid
City: only validates alphabet, no numeric and special characters are allowed
State: only validates alphabet, no numeric and special characters are allowed
Mobile no. : should be 10 digit number.
Email id: should be a proper email-id
Password: should be more than 6 char and less than 10 char
Confirm password: should be same as password
Login Page
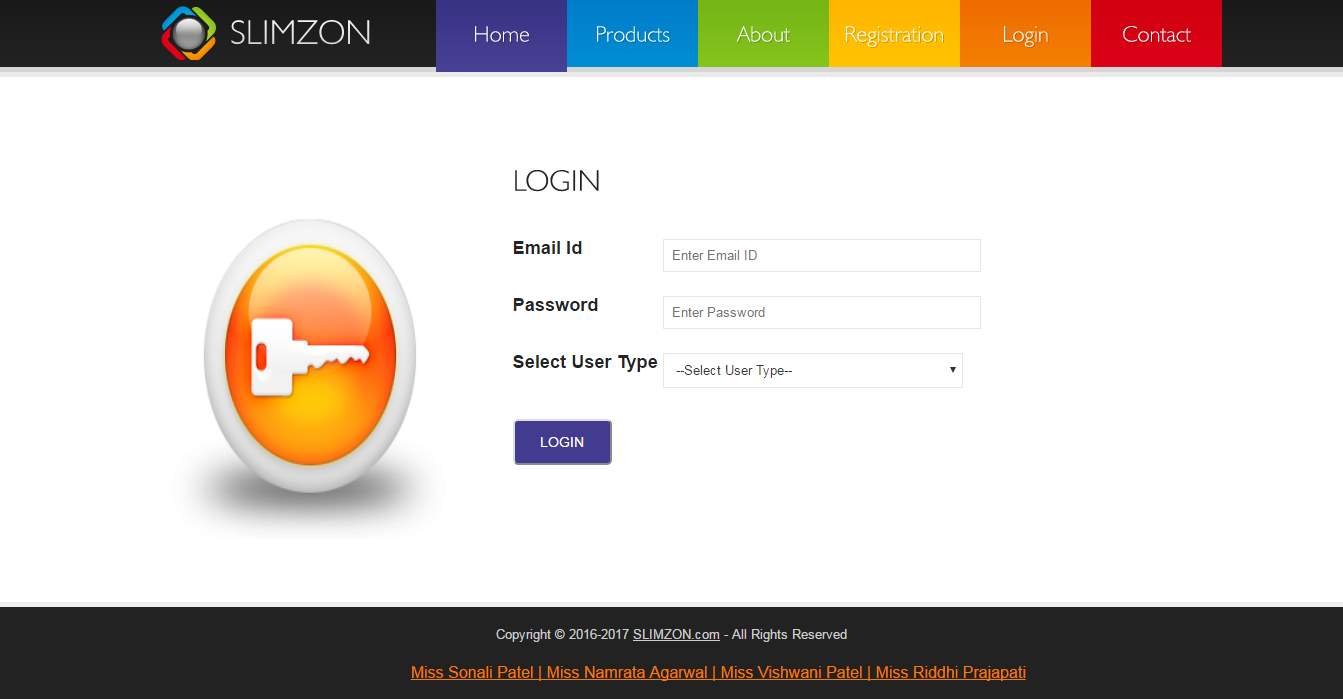
Login page for all three user customer, shop admin and admin; contain two fields to login that is email id and password, and even we have had added a separate field to select whether the user is customer or shopkeeper.
Manage shop page (Admin)
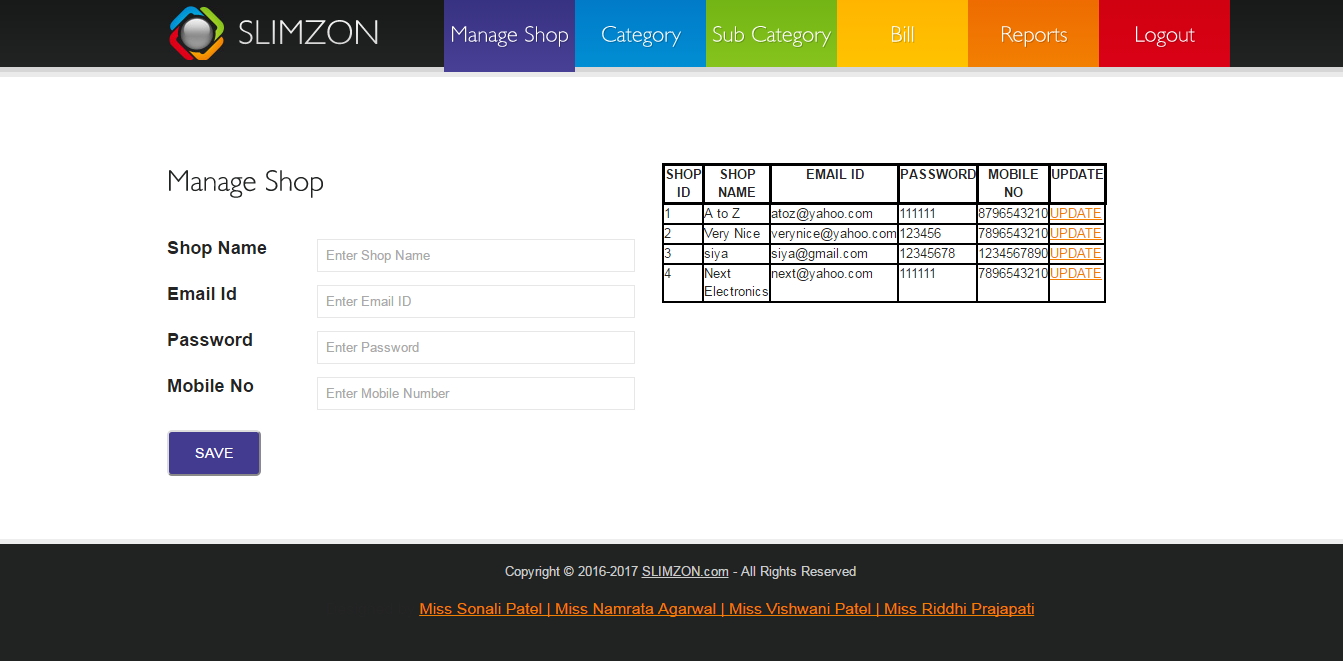
Figure 7.4: Admin manage shop page
Admin here can add new shops in the database and update the existing shop detail
Manage category and subcategory
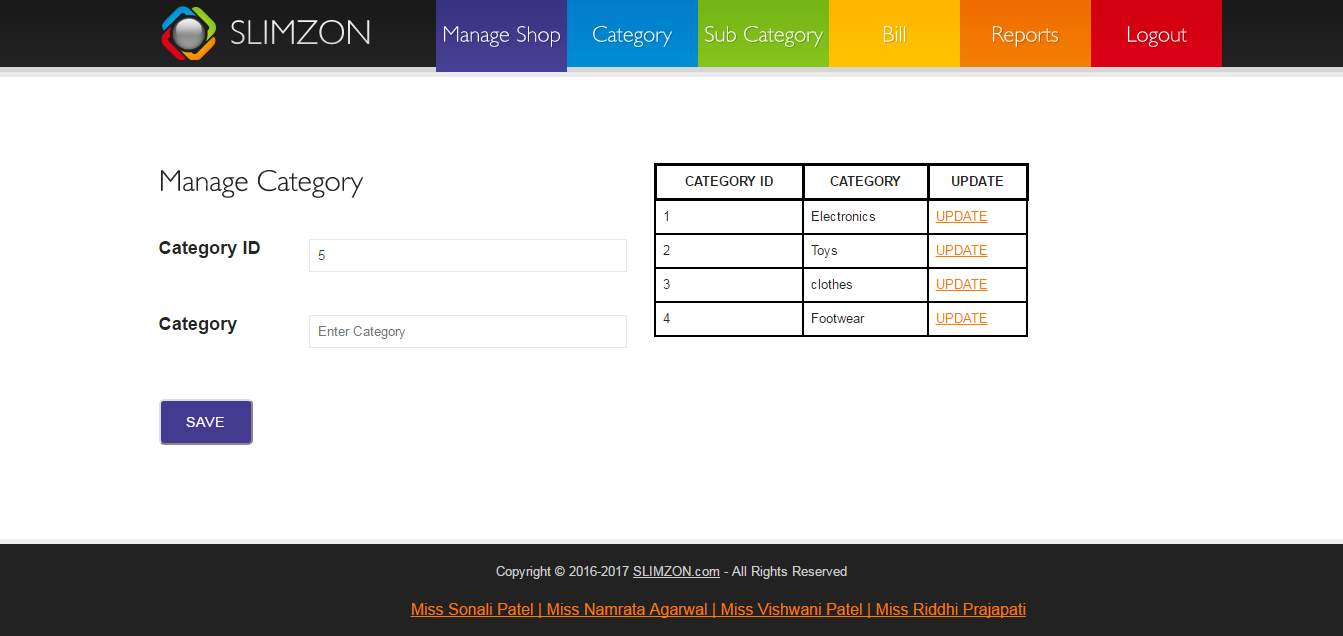
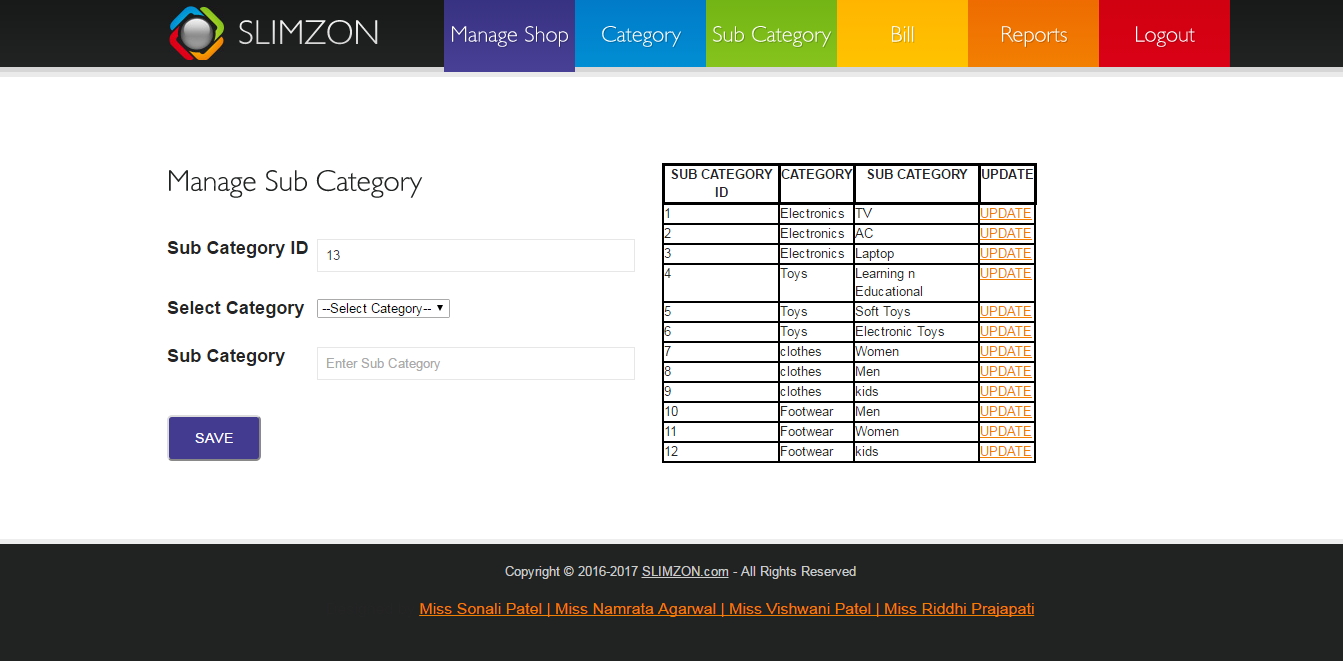
Figure 7.6: Manage category and subcategory
Admin can add new category and related subcategory of item and update them.
Report (Admin)

Admin can generate report on basis of Shop Wise Product Detail Reports, Order Detail Report, Bill Detail Report, and Product Wise Selling Report.
Manage product (Shop Admin)

Shop admin can add new product details of their shop and update them.
Manage offer (Admin)
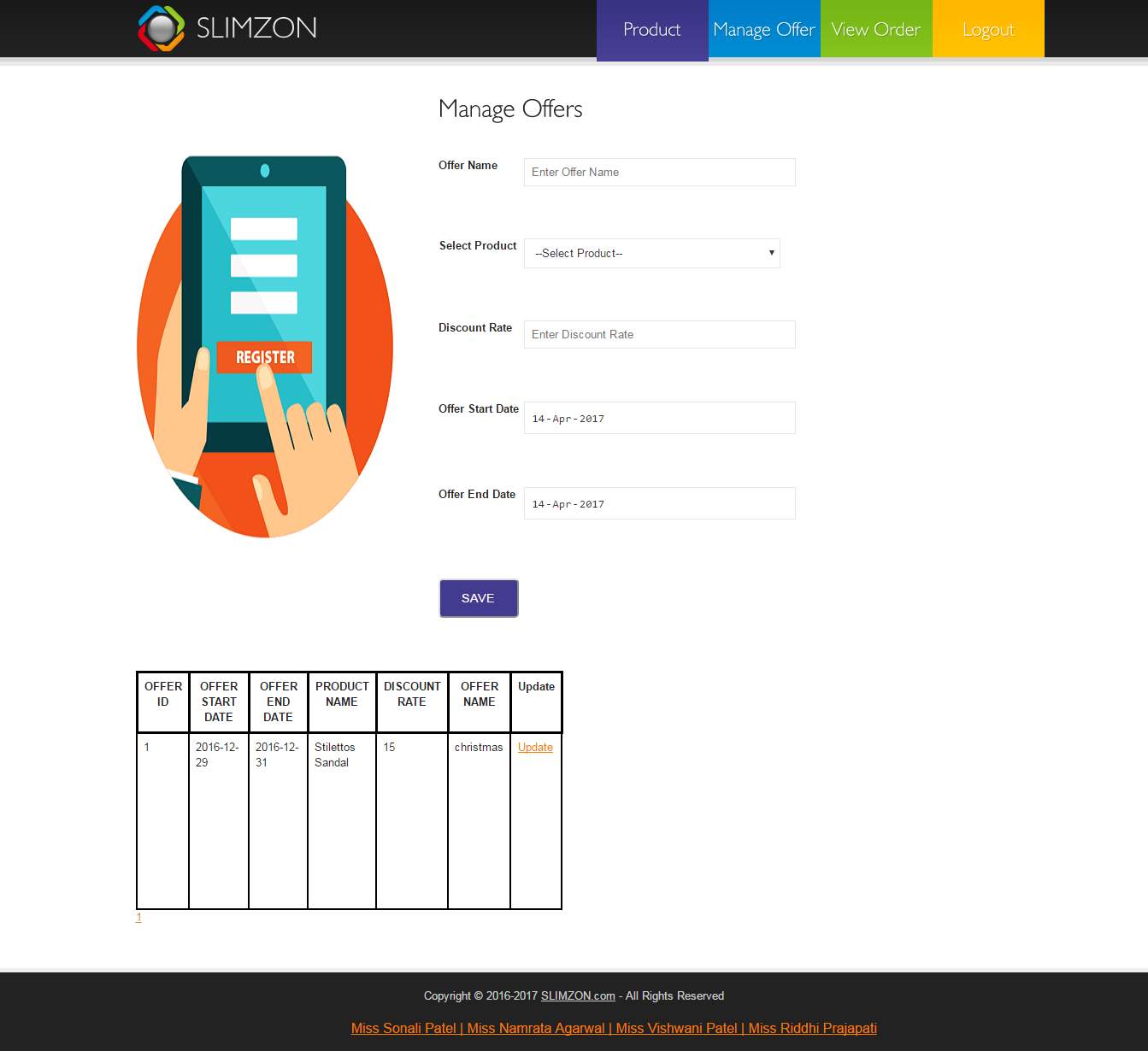
Shop admin can add new offers to particular product and update them
Shopping (Customer)
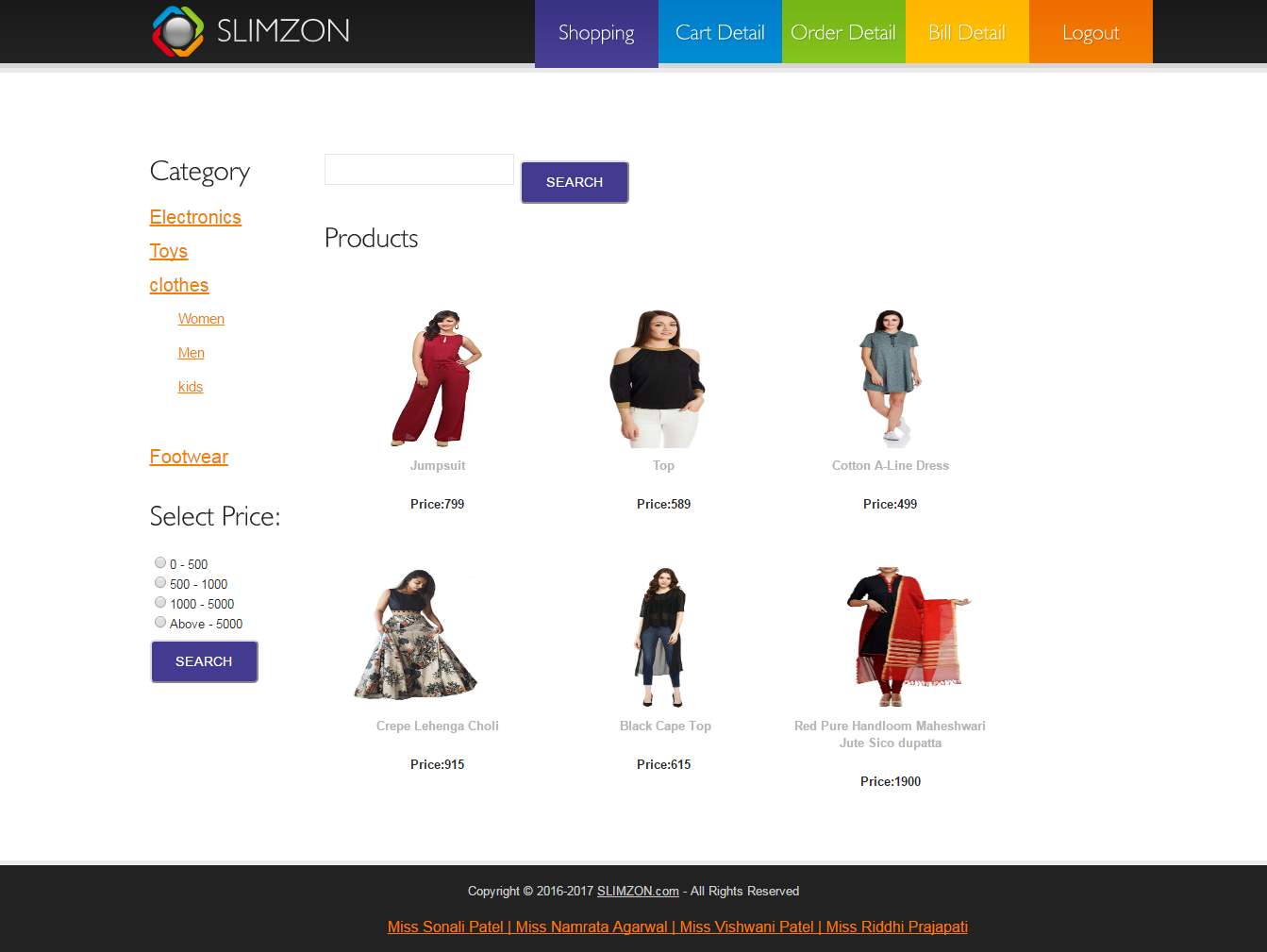
Customer can browse product on basis of category and sub category, can use filter on basis of price and can search by entering similar name of the product and get their desired product
Product detail (Customer)
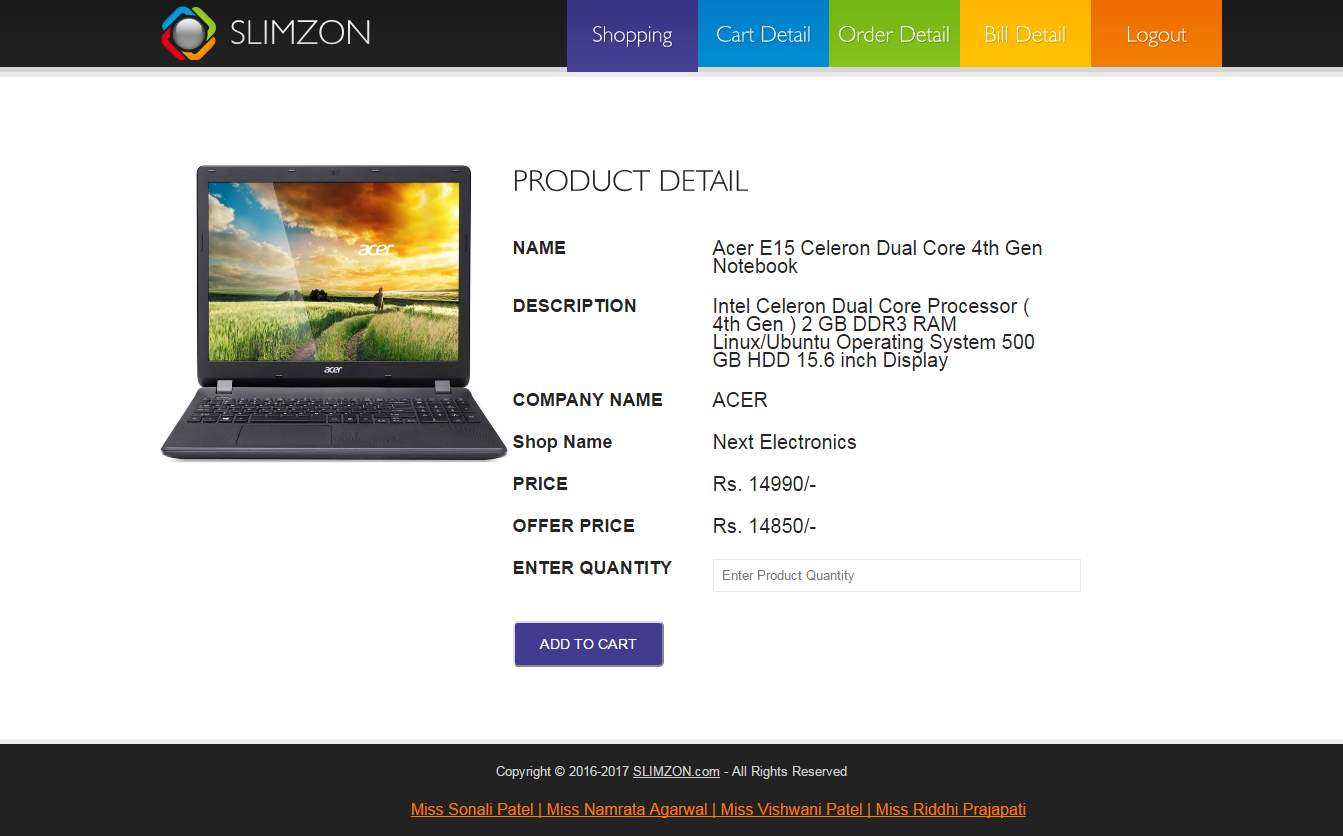
Customer can view product detail and add item to the cart if they want
Cart Detail (Customer)
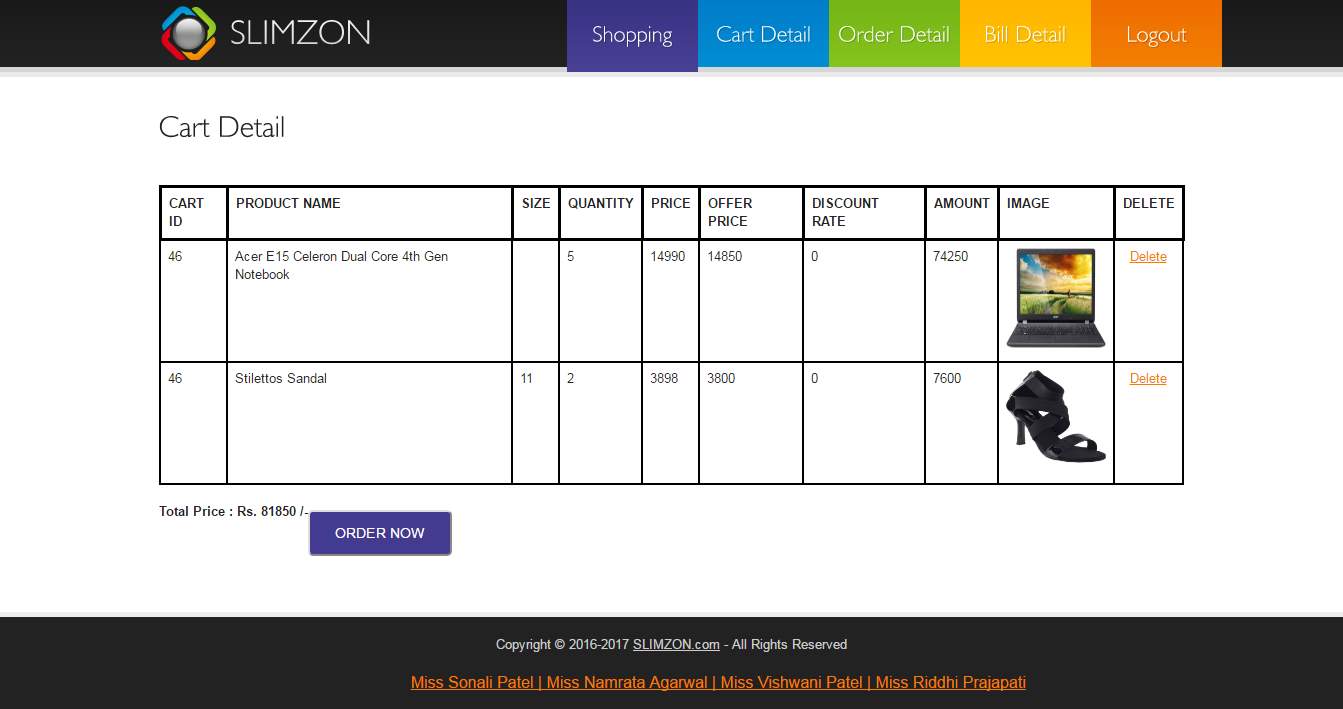
Cart detail gives the detail of items added to cart and we can delete the item from the cart. From this page we can order the cart items.
Payment form
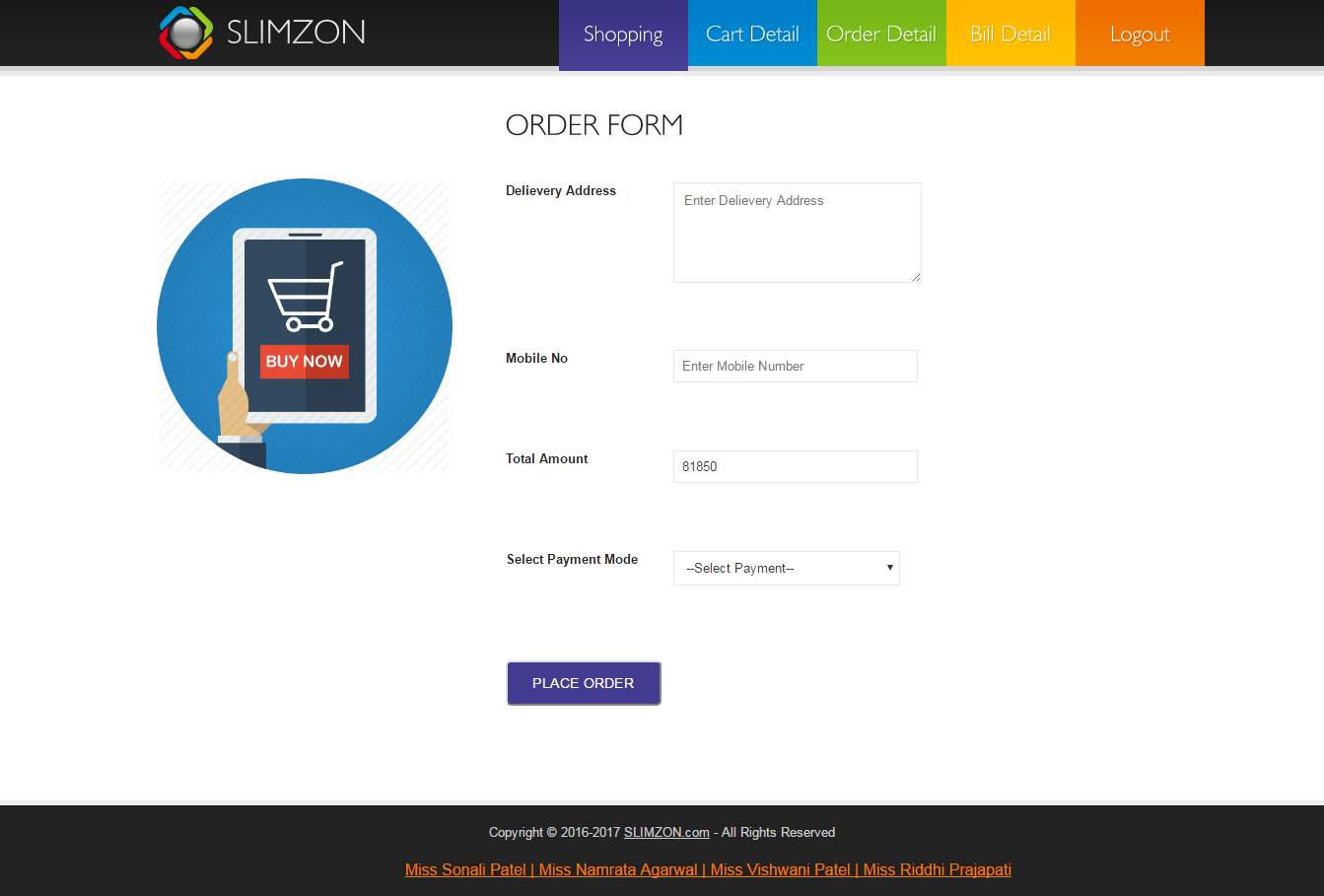
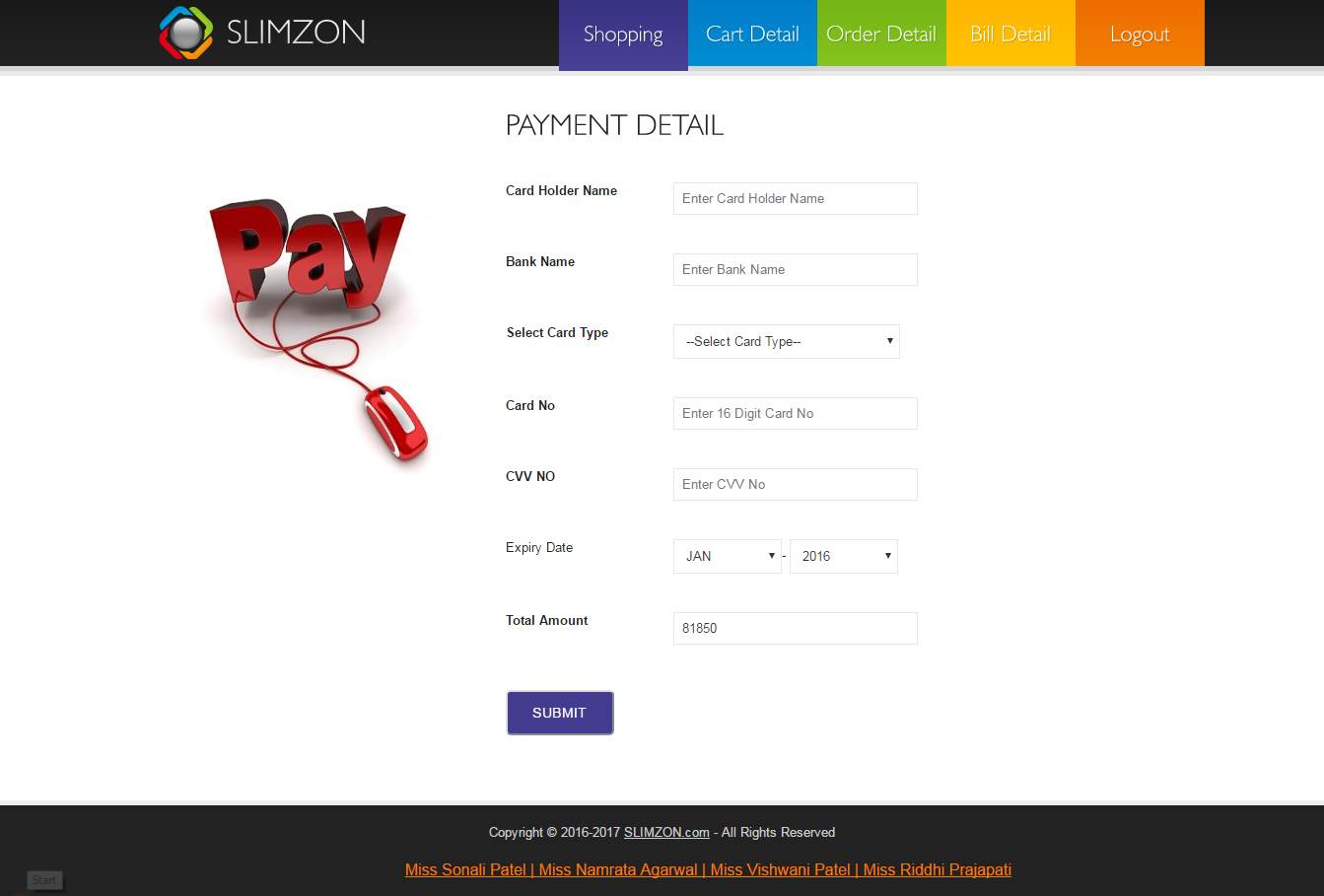
Payment can be done by both online and offline mode. By adding respective details
Android application

Login Page
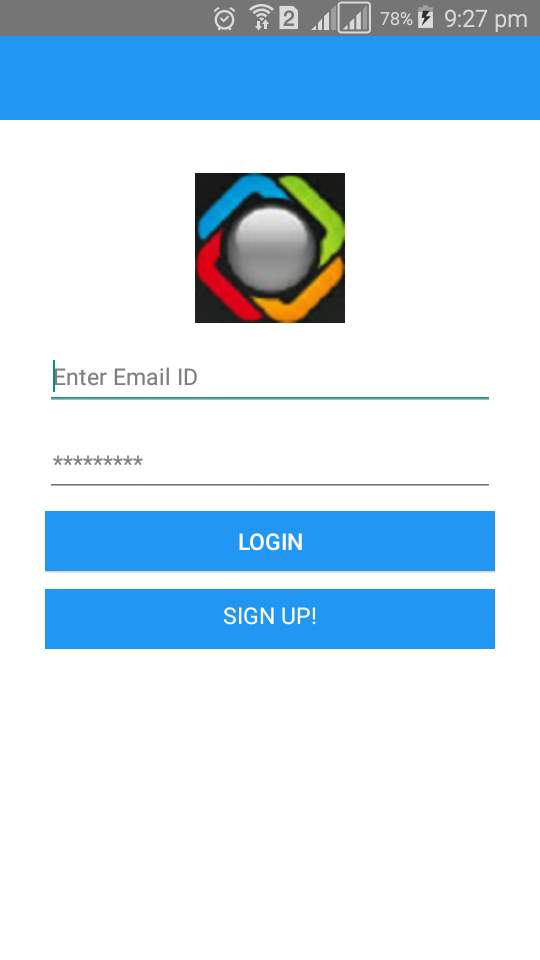
Login page for customer to login entering valid email id and password
Registration form
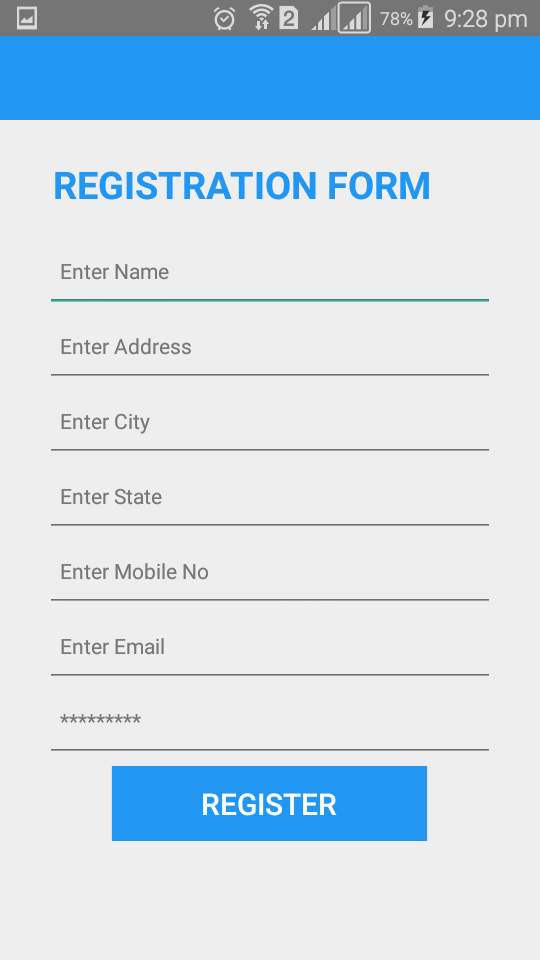
Figure 7.17: Registration form
Registration form for customer to register by entering all details which mandatory.
Product
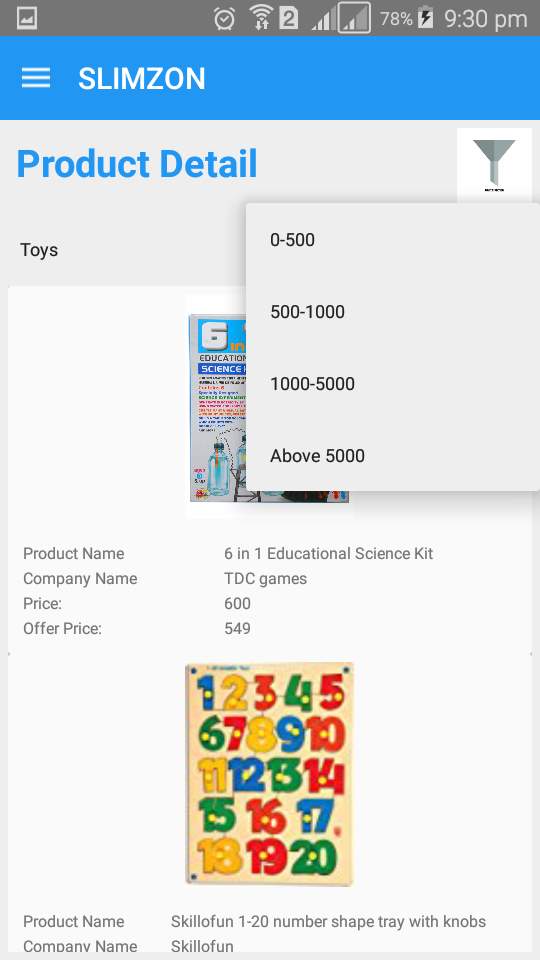
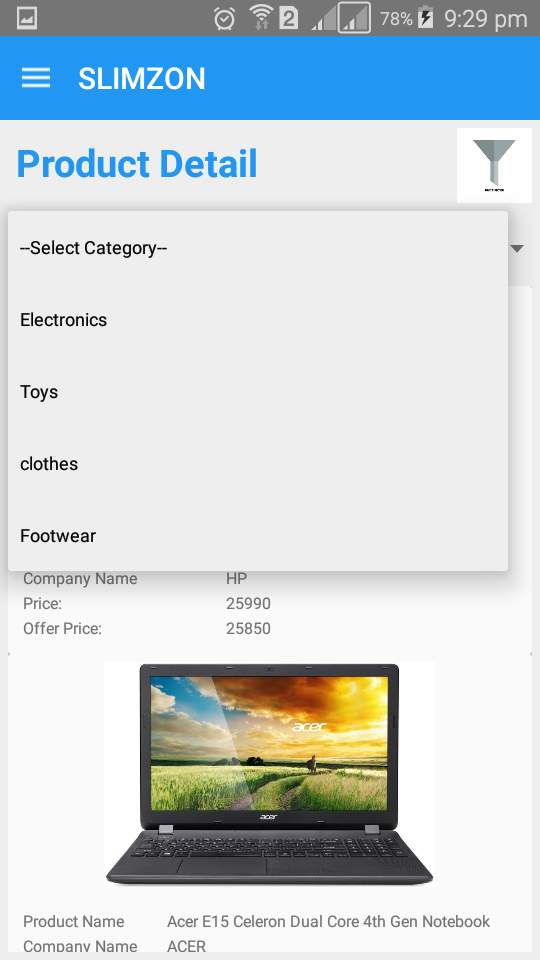
Figure 7.19: prroduct search on category
Item can be searched on the bases of categories and filter like price are provided to search more conveniently.
Product detail
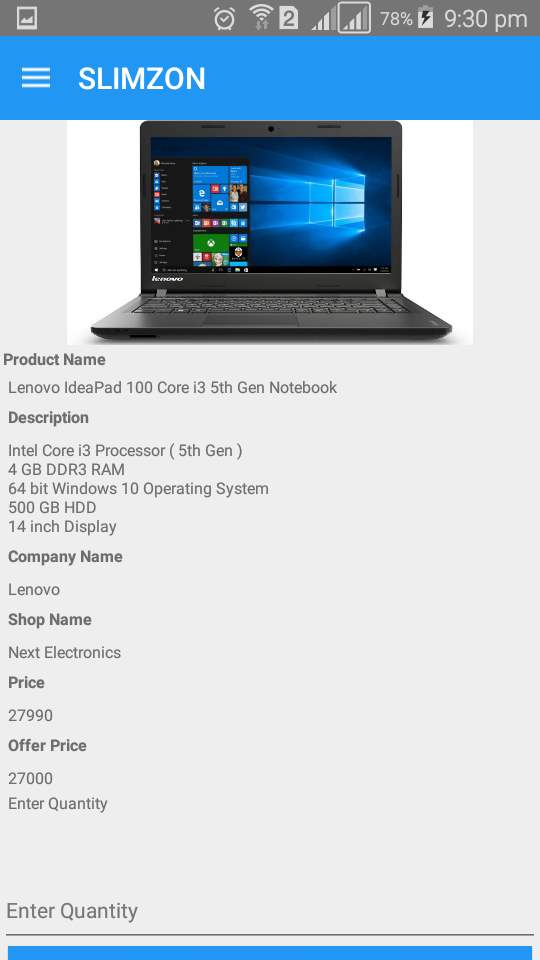
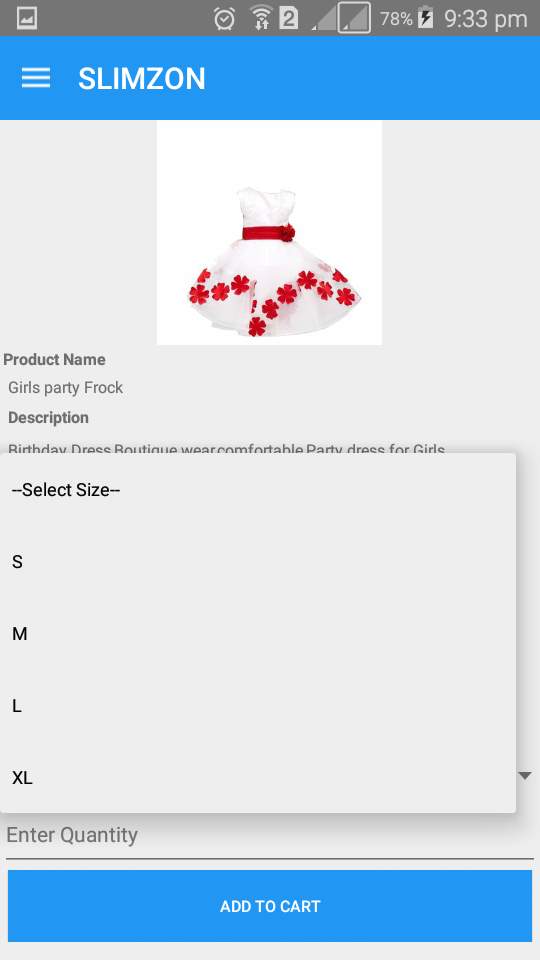
Figure 7.21: Product detail select size
Product detail which gives detail of the product and allow item to be added into the cart
Qr scan
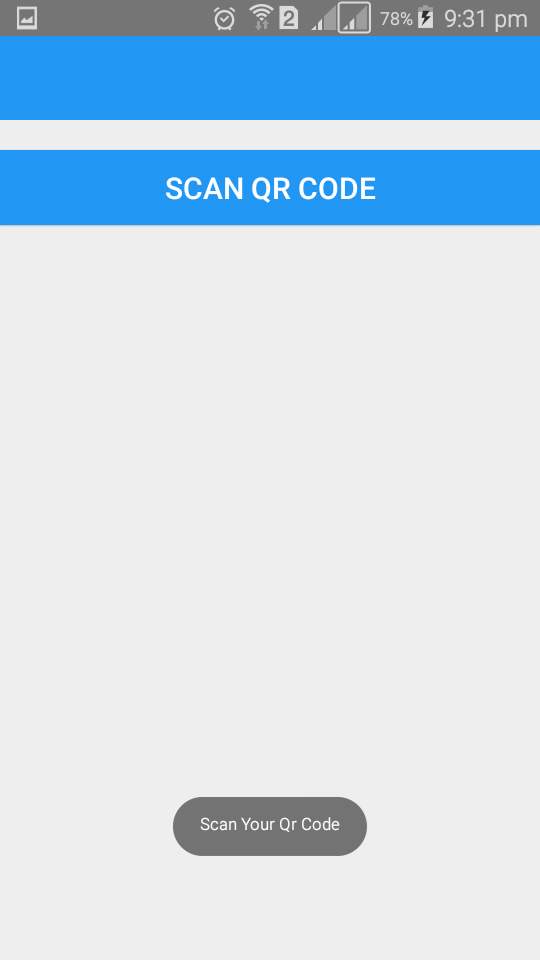
Customer can scan qr of various product and get the total amount of scanned products
Cart Detail
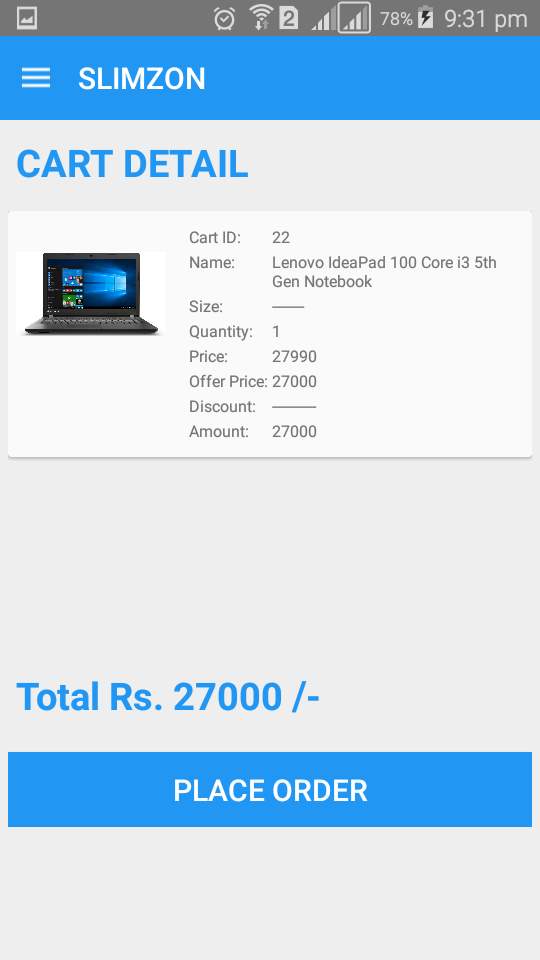
Cart detail gives the detail of items added to cart and we can delete the item from the cart. From this page we can order the cart items.
Order detail
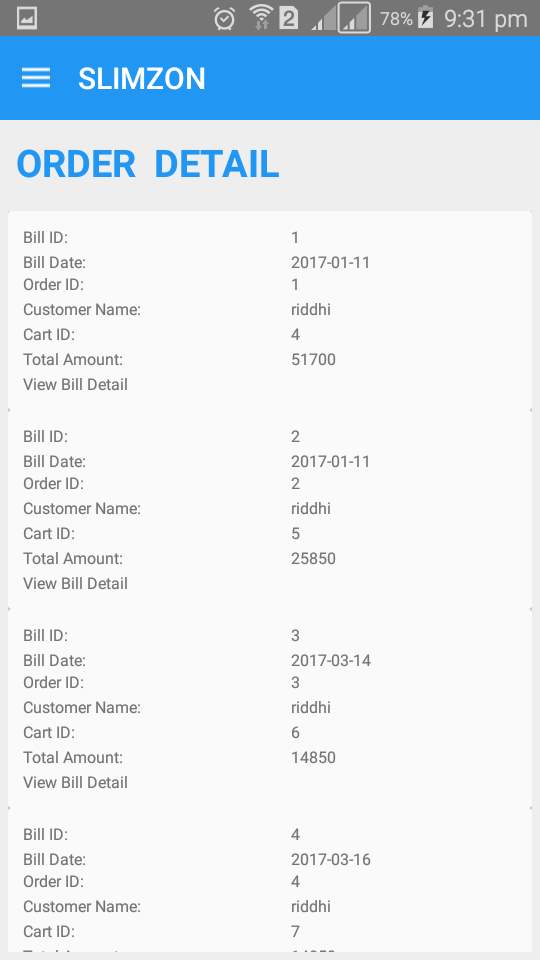
Order detail gives detail of all ordered products by the login customer.
Order Form
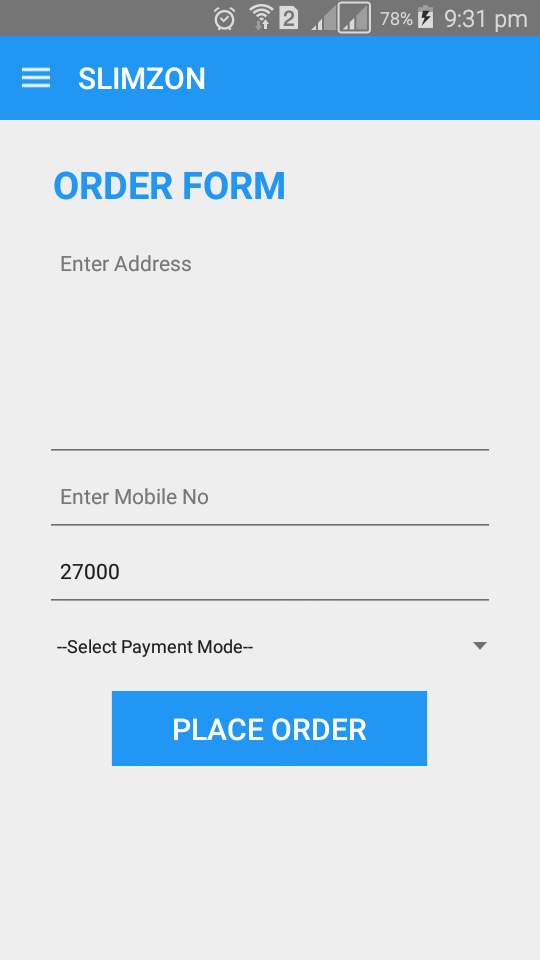
Payment can be done by both online and offline mode. By adding respective details
CHAPTER 8: CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
Conclusion
It intends to promote shopping methods and make save time for people; we built this mobile application that could play an important role in the Indian malls as a whole. For major shopping complexes Indian who are always on the go, we believe that application is feasible and very practical and have met most of our expectations and proved to have positive feedback from its users who tried it. We realize that not everything is perfect; therefore we plan to improve our application so that it can carry more weight with this vastly changing era.
Future Work
Area of improvement include: Downloading of Application automatically while entering in the mall the customers automatically download our application instead of initially doing it manually when entering the mall, introducing videos, increase search criterion for example searching by brand, color etc, and GPS system, which helps identifying the customer’s position and generates a path to their required shop.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Technology"
Technology can be described as the use of scientific and advanced knowledge to meet the requirements of humans. Technology is continuously developing, and is used in almost all aspects of life.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




