Priorities and Approaches to the Provision of Services for People with Disease or Illness
Info: 7759 words (31 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
Tagged: NursingHealth and Social Care
Introduction:
Using the scientific method depending on the type of disease to determine which type of treatment and direct approaches to treat this disease, below are the approaches to use Prevention, Treatment, Palliative care and Remedial.
PREVENTION: Disease prevention, understood as specific, population founding and individual based involvement for primary and secondary [early detection] prevention, aiming to lessen the burden of disease and associated risk factors. The Primary Prevention refers to actions meant to avoid appearance of a disease such as the provision of information on behavioural and medical health risks, nutrition and food supplementation, oral and dental hygiene education, clinical preventive services such as Immunization and vaccination of children, adult and the elderly as well as vaccination or post exposure prophylaxis for people exposed to a communicable disease.
Secondary Prevention: deals with early detection when this improve the possibilities for positive health results, it comprises of screening programs for early detection of diseases or for prevention of inherited malformations and preventive drug therapies which shows effectiveness when dispensed at an early stage of the disease. Provision of maternal and child health programmes. Provision of chemo-prophylactic agents to control risk factors like hypertension. (WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2017)
TREATMENT: This is about getting care when you are already infected, getting a good care not o spread the disease further than it is, using of Antibiotics in fighting the bacterial infections, it either kills bacterial or stop them from reproduce, allowing the body’s natural defences to eliminate he pathogens. When used properly it saves lives, taking Antibiotics as guided even after symptoms disappear is the key to curing an infection and preventing the development of resistant bacterial. (National Centre for Biotechnology Information)
REMEDIAL: Is about what to do in preventing getting more sick, in confirming that a person is sick, it has to be diagnosed firs, and when this is done, and the person is sick but can still prevent it from getting worse, this where REMEDIAL comes in, or there is a traces of a disease but it has not being well determined, the person cam be asked to come back for check-up in 3 months’ time, what you do to prevent against it coming to materialised is called REMEDIAL.
PREVENTION OF CANCER: Tobacco use is directly associated with one third of cancers, not smoking and avoiding exposure to Tobacco smoke can greatly reduce the risk of lung, kidney, bladder, and head and neck cancer. Using of smokeless Tobacco [snuff or chew] lessen the risk of cancer of the mouth and tongue. Early detection of cancerous growth can save life by having test carry out on time. TREATMENT: when the diagnosis is of cancer is first made, the main objectives is to remove it the cancer if possible through a single treatment or a combination of surgery and radiation treatment and chemotherapy- is the only treatment if it has grown beyond expectation. Uses of chemotherapy drugs may also help reducing the original cancer and at the same time eliminate the cells elsewhere in the body. Some people turn to alternative medicine [REMEDIAL] such as herbs, this has not been proven to be working much because they may contain toxic and may interact with standard treatment such as chemotherapy thus reducing its effectiveness. (MERCK AND MERCK MANUALS, 2017)
PALLIATIVE CARE: This is a support for people who are in the last months or years of their life, when an illness cannot be cured, Palliative care or End of life makes them comfortable as possible by managing their pain and other distressing symptoms, also involves the psychological, social and spiritual support them and their family or carers, it is also called HOLISTIC approach, because it deals with them as a person. Palliative care is not only an End of Life, its being also relate to the care one gets from the GP or community nurses in our daily care. (NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES, 2015)
In conclusion Public health helps people to live longer and healthier by reducing preventable deaths and free burden of ill health associated to smoking, high blood pressure, obesity, poor diet, poor mental health, insufficient exercise and alcohol.
2.2 Some Factors to consider in Planning for Health and Social Care.
FACILITIES: This is one of the things to consider when planning Health and Care setting, it comprises of;
Building and Estates: When thinking of public health, you consider enough money to build the Hospital or care centre, it’s also how to go about planning, materials, the Equipment’s, and Machineries such as Vehicles: Using of vehicles to take service users and the health professionals.
Also about Upgrading and Replacement: to upgrade some of the equipment and if it is old and rustic, how to go about in getting a new and improve one. Servicing and Maintenance is also very important when considering planning for health and social care setting, this is about checking if the machineries are still in good condition, when this service are performed, a date of service will be put on it and when next it is due for next inspection.
Capital Intensive is also one of the factors to consider, getting more money into the project to make it materialised. Hence FUNDING is a major consideration in planning the project, getting enough funding by checking if three is enough and where to get it from.
- UK Health and Social Care is a state funded, but this still need planning.
- NHS England is the world’s largest public funded health services. NHS employs more than 1.7million people, their annual budget of £109 billion for 2012/13 funded through Taxation.
Health and Care Regulations
Regulations are needed in setting the standard of the organizations, this tells people what to do and not to do, what is expected of you as a health provider. Examples of those organizations are;
- Nursing and Midwifery Council
- General Medical Council
- Health and Care Professionals Council
- Health watch England
- Coe of Practice for Social Care Workers.
CARE QUALITY COMMISSION: make sure health and social care services provide people with safe, effective, compassionate, high quality care and encourage care services to improve.
ROLES OF CQC
They register care providers, monitor inspect and rate services, their inspection follow a specialist, and expert and risk based approach that allows tm to get at the heart of what really matters to service users and the public. They act to protect people who use service, and regulate the HS Trusts, independent acute hospitals and treatment centres, ambulance services and community health care services. CQC speak with an independent voice, publishes their view on major quality issues in health and social care. Their work is to protect the right of vulnerable people, including those restricted under the mental health Act. The new regulations allow CQC to implement action when identifying issues that were previously unable to act against. This allow them to prosecute directly when the regulations are breached as it constitute a criminal offence without serving a warning notice hence holding the provider of care to account.
- Need to consent
- Safe care and treatment
- Safeguarding service users from abuse
- Meeting nutritional needs
- Duty of candour
- Display of ratings. (CARE QUALITY COMMISSION, 2017)
CODES OF PRACTICE FOR SOCIAL CARE WORKERS
This is a set of standards expected of social care workers, it outlines the behaviour and attitudes that is expected by the people from the social care workers, it gives the reassurance that you are providing safe and compassionate care of high standard, and the confidence to challenge others who are not. The code is voluntary, but it is assign of best practice, guidance to help us understand or implement the code of conduct are also available.
- As a social worker we should be accountable by making sure we can answer for our actions or omissions.
- We should be able to communicate in an open and effective way to promote the health, safety, and wellbeing of people who use health ad car services and their carer.
- As a social worker we should respect a person’s right to confidentiality.
- We should strive to improve the quality of healthcare, care and support through continuing professional development.
- We should uphold and promote equality ad inclusion.
- As a social worker we should work in collaboration with our colleagues in ensuring the delivery of high quality safe and Compassionate healthcare and support. (SKILLS FOR CARE , 2013)
Factors to also think about is Partnership Working this comprises of Internal Stakeholder
- Proprietors and owner [Shareholders]
- Staff and Employers
- Residents
- Service users
- Carer and services.
The Stakeholders have a right to know what is going on and what is to happen in future they have the rights to be informed with the ongoing activities in working partnership context is developed
by NHS in which the individual comes together, when groups come together it make them strong than working individually. Working towards an objective to arrive to a one goal, it was started in 1992 till date. This is when an organisation works together by informing other of a plan in progress and thereby is not been duplicated by another organization. They also compare works together and solve a problem when need arise for an Expertise to be consulted, it increases effectiveness and efficiency.
In conclusion all service providers, Doctors, Nurses, carer, support workers, social workers, professionals, care quality commission, Training and CPD, all working in partnership to arrive in one goal which is core meaning of health and social care in providing service to the service users by caring for them in achieving a disease free live and cater for their wellbeing mentally and physically.
2.3 Impact of current Lifestyle Choices on future needs for Health and Social Care Services.
What is LIFESTYLE?
Lifestyle can be defined as a set of attitude habits in which person live and act according to their tastes and values that may enlarge or reduce the possibility of injury or disease. The lifestyle can be a healthy or unhealthy based on your food choices, activity level and behaviour, a positive lifestyle can bring you happiness, while negative lifestyle can lead to sadness, illness and depression.
There is different type of Lifestyle; (LIVESTRONG- Nutrition, Fitness and Lifestyle Choices, 2017[A])
- DIET: This refers to the nutrition that individuals assume in their daily lifestyle, healthy food choices helps in living a disease-free lifestyle. Good hydration is part of healthy living, since we are always passing water out from our bodies via urine and sweat, the health authorities recommend 8-ounce glasses which equals 2litres or half a gallon per day. There are some studies that says if a person hydrate well it helps the energy levels and brain to function properly, also burn the fat in the body system. (HEALTHLINE- NUTRITION, 2005-2017).
Lack of appetite is common during cancer treatment, some patients even says that it makes food taste unpleasant, its then advisable for the cancer patients to eat well during treatment to help them getting better and responding to their treatment, hence balance diet is recommended for them, and plenty of fluid preferably fruit or vegetable juices. (WEBMD HEALTH SERVICES, 2005-2017).
Why Five a Day? Fruit and vegetables are part of a healthy, balance diet and can help us stay healthy, its important that we eat plenty of them. Here is an evident that shows advantages of eating a least five 80g portions of different fruit and vegetables every day., this count as five portions of fruit and vegetable in total.
Five reasons to eat five portions of fruit and vegetable.
- Fruit and vegetables area good basis of vitamins and minerals including vitamin C and potassium.
- Exceptional source of dietary fibre which can help to uphold a healthy gut and stop constipation and other ingestion problems, it also reduces risk of bowel cancer.
- It helps reduce risk f stroke, heart disease and other type of cancers.
- Fruit and vegetable contribute to a healthy balance diet.
- Fruit and vegetables palates and there are varieties. (NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES-YOUR HEALTH, YOUR CHOICES, 2017[A])

(NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES-YOUR HEALTH, YOUR CHOICES, 2017[B])

EATWELL BALANCE PLATE. Balance plate: what we eat should come from each food group to achieve a healthy, balanced diet.
- SUBSTANCE USE: This is when a person uses alcohol or drugs, it does not necessarily an addiction, occasion drinking is good, even red wine is recommended as a good source of balance diet an extreme is when it leads to addiction hence substance misuse. It can also be a misuse of drug, when dependency is high, and a person cannot live without taking it every day. We are not talking about those that needs their prescribed medication as treatment for an ongoing illness or to cure an illness, the misused is talking about those that have taken this type of drugs and discover it gives a sort of high to hide them from reality of what is happening in their life instead of getting a psychology helps to get them through the difficult times, such drug can be Cocaine, Heroine or prescribed tablets that excessive can cause damaged to the liver with long time usage. Alcohol is a poison to the body, it makes the body and brain waste away with excessive drinking, the body metabolism breaks it down in the Liver, and with heavy drinker the Liver gets worn out, it then put a hole in the brain which make it to work faster than normal thus make them react to incidents irrationally or misjudge an incident. When a patient is on a very strong medication or any continuous medication at all, drinking too much alcohol is not good for them or they might be instructed
not to drink any until the course treatment is complete. (Study.com for Schools- Alcohol Abuse problems: effect and treatment , 2003-2017)
- EXCERCISE: A higher physique can lead to greater self-confidence and motivation to live a healthier lifestyle, it advisable to incorporated at least 20minutes of exercise into one’s way of life, take a walk, plan a hike with friends, exercise class like GYM or Swimming. (LIVESTRONG- Nutrition, Fitness and Lifestyle Choices, 2017[B])
- RELAXATION: Sleep is also recommended for a good source of energy, when a patient is recovering from an illness sleeping helps them with speed recovery. Eight hours of sleep is recommended.
- WORK PATTERN: Good working environment is also paramount in day to day life, if a patient does not like the environment where they are being hospitalised or rehabilitate, it can slow down their recovery if they feel depressed or sadden with their environment.
Health care, Environment, Human biology all this contribute to the economic burden in our society, so also is the lifestyle which link together which is 51% in people that smoke, obese, stress, blood pressure substance uses they all needs health care and when too many people have poor health it tends to cause strain on the health services. Populace needs to stop bad eating habits and way of life in excessive drinking or too much tobacco usage.
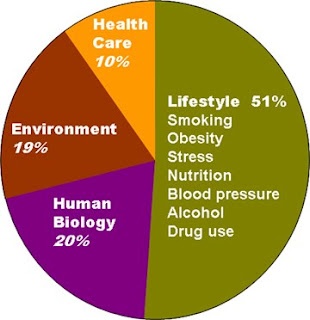
3.1
What is Health? Health as defined by World health organisation is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. (WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2014)
SOCIAL DETERMINANTS OF HEALTH: It’s one of the conditions that affects health in which people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a range of health functioning and quality of life outcomes and risks.
- Employment/Income: the most important factors that shape populace’ social position is employment and working conditions. Employment circumstances’ knowledge network[EMCONET] developed and measures to explain how different types of jobs, conditions of underemployment and the threat of becoming unemployed affect workers’ health. The working conditions affecting workers and families can be improved by having fair access to employment and other dimensions of decent work. (WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION- EMPLOYMENT CONDITIONS, 2017)
- HOUSING: Housing quality and suitability is major determinants of health and wellbeing and hence impacts on request for NHS services, older adults are the main users of both hospital and primary area and their homes are a particular important factor in maintaining physical and mental health addressing health inequalities. Suitable houses for older adult can reduce costs of health care, it can decrease GP appointments by older people with chronic disease such as stroke, heart disease, arthritis respiratory, some of this disease might be happening due to poor state of their house or if they don’t have good heating system in their homes. Poor heating in a home where there is an Asthma child might stop them having a proper growth because of ill health. (THE HOUSING AND AGEING ALLIANCE , 2013) people squatting together in an overcrowded household are likely to inflict disease on each other by passing it around, say if person have communicable disease like Tuberculosis, and use each other’s cutleries or cough continuously in an humid area, this is going to be pass around.
- ENVIROMENT: As asocial determinants depend on the area that is not over crowded, take for example people living in Westminster that the area is more sophisticated and well-lit area will more likely enjoy good health than people living in overcrowded area like Peckham or Woolwich. The way in which food are display in the area is important as well, the food is displayed openly on the street, this is going to cause food poisoning which does not promote good healthy living.
SOCIAL EXCLUSION: There are 3 types of exclusion – POLITICAL can include the denial of citizenship rights such as political participation and the right to organise, also personal security, the regulation of law, freedom of expression and equal opportunities. And sometimes discriminate between social groups when there is a society that dominate a place. ECONOMIC exclusion this may be lack of access to capital assets, or access to labour markets or credit amenities. Social exclusion may be in forms of several things like discrimination, either, gender, ethnicity, age which reduce the opportunities of some groups to have access to social services and their participation in labour market. CULTURAL exclusion is the extent which diverse value, rules and ways of living are recognised and appreciated. The relationship between the three are interrelate and coinciding by complications of influence on individua People might be excluded deliberately by others, in the form of an employer or colleagues or society which might not be a deliberate action on their part or even by people’s choice. More of the exclusion leads to poverty, suffering or
- deaths which attributed to unequal power relation. (GSDRC- APPLIED KNOWLEDGE SESERVICES, 2015)

This visual representation of health determinants shows that many opportunities for action t improve heal and to reduce inequalities [Dahlgren et al., 1991].
Determinants of health is a concept used to describe what influence our health status and general wellbeing, which are Agriculture and Food production where we get our source of balance diet from. Education which have impact in the growth o a country in which we are enlighten in what to do in life and the growth in terms of technology and infrastructural. Work and Environment deals with how we live and working conditions. Housing, healthcare and water sanitation they all interlocked in our wellbeing.
WELLBEING is the psychology of our body systems and risk of disease especially cancer, heart disease and diabetes.
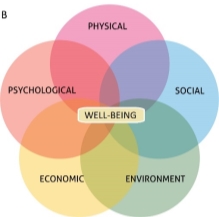
These are all factors influencing the health and Wellbeing of individuals: Physical health- exercise, nutrition, sleep, alcohol, drugs and weight management. Psychological- mental health- learning, stress management and mental disorders. Social health- public health, relationship, peer relationship.
3.2 STRATEGIES, SYSTEM AND POLICIES.
There are lot of strategies applies in a health and social care settings, these are few from Government that is effective and ongoing:
- CHANGE FOR LIFE Basic for this is to eat well and engaged in activities, helps eat a healthy balance diet by showing individual different type of food and drink to consume as a part in improving the nation’s health and wellbeing by encouraging everyone to eat well, move more and live longer. This includes the NHS, local businesses, charities, schools, families, community leaders with food and drink we should consume. It’s all about improving your lifestyle and live longer. It was aimed at parents with children and offers support to make the changes need to a healthier lifestyle. Adapt a healthy behavior, watch the salt intake, cut on fatty food and drinks, most especially eat five a day.
- SURE, START Is a government programmed which provides a range of support services for parents and children under the age of four who lives in disadvantages areas across Northern Island, it aims to support parents from pregnancy and to give children the best start in life.
- Drug, Abuse, Resistance Education[DARE] is an education program campaign that seeks to prevent use of controlled drugs, membership in gangs and violent behavior. It was founded in Los-Angeles in 1983. This centralized-on control Drugs such as morphine, antibiotics, if you are given the control drugs in a hospital, two people had to co-sign it and is always locked away in a coded cabinet. Therefore, people are being educate on how to use drugs at home, not to be addicted to it.
- VACCINATION PROGRAMMES Is given to prevent getting disease such as Flu jab for cold, Tetanus injection for preventing infections like MEASLES vaccine from birth so also is POLIO, YELLOW FEVER, CHICKEN POX, HEPATITIS B. Vaccination is a biological preparation to improve immunity to a disease, it contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the micro, its toxins or one of its surface proteins.
- EVERY CHILD MATTERS: Children Act 2003- it is every adult’s responsibility to protect children from any sort of abuse, especially children in Needs such as protection, basic needs in life, food, shelter, clothing etc. This is UK government initiative for England and Wales that was launched in 2003 at least partly in response to the death of Victoria Climbie, it covers young adults and children up to age of 19 or 24 years for those with disabilities.
- ANTI-SMOKING CAMPAIGN: Government developed a campaign that is smoke free which is for the smokers to reduce their excessive habits of smoking. There are so many disease and illness because of smoking for example lung cancer. Government has developed many strategies to stop or reduce smoking in the society such as;
- Advertisement by way of Television advert or poster that says cigarette are dangerous
- Increasing the cost of cigarettes, the pack has been increased rom pack of 10 to 20
- Vapor
- E-cigarettes
- Smoking free zone in most public places, especially hospitals premises are now smoke free zones.
3.3
Changes that could be made to improve the health and wellbeing of individuals in a health and social care setting.
Healthy Lifestyle.
For many it takes ill health to force them to finally overhaul their life, some people knew already that the lifestyle they are leaving is bad, but they are not doing anything to work towards correcting the bad habits, it takes illness or chronic disease to make them change their way of living. Health is something we all want but we don’t think about it until it disappears, we can improve our health by implementing all this 9 keys to a healthy lifestyle:
Implementing and sustaining to changes by thinking positive and focus on benefits;
- Create urgency
- Form a powerful coalition
- Create a vision
- Communicate the vision for changes
- Communicate the vision
- Empower action
- Create quick ways
- Build on the changes
- Make it stick
To make a change – first make a plan on what to do in improving your wellbeing then make a consultation with the people that are giver of health and discuss changes with them, some will resist, some will support and try to find a medium ground for everyone.
1. Improving the health and wellbeing of people with high blood pressure- Cardiovascular disease [CVD] affects around seven million people in the UK and is the most important cause of preventable, early disability and death, affecting individuals, their families and communities. It contributes to half of all strokes and heart attacks, millions of people are living with undiagnosed and untreated high blood pressure which increases risk of developing heart attack and stroke and heart failure, including kidney disease and dementia. CVD is one of the disease associated to with health inequalities, the death is three times higher among the deprived communities than those from affluent society CVD is also reaching ethnic groups with higher rate of having an heart tack or stroke. The NHS Health Check Programme offers opportunity to impact on health inequalities. Department of health estimates that each year the NHS Health Checks offers the potential to prevent 1,600 heart attacks an stroke, it also supports GPs and the wider primary care workforce. Among the attendees of the checks 50% more new cases of hypertension were diagnosed compared to non-attendees. The benefits of the checks is the reduction from CVD in the past 20years, and still remains the second highest cause of death and ill health in England. (GOV.UK, 2017)
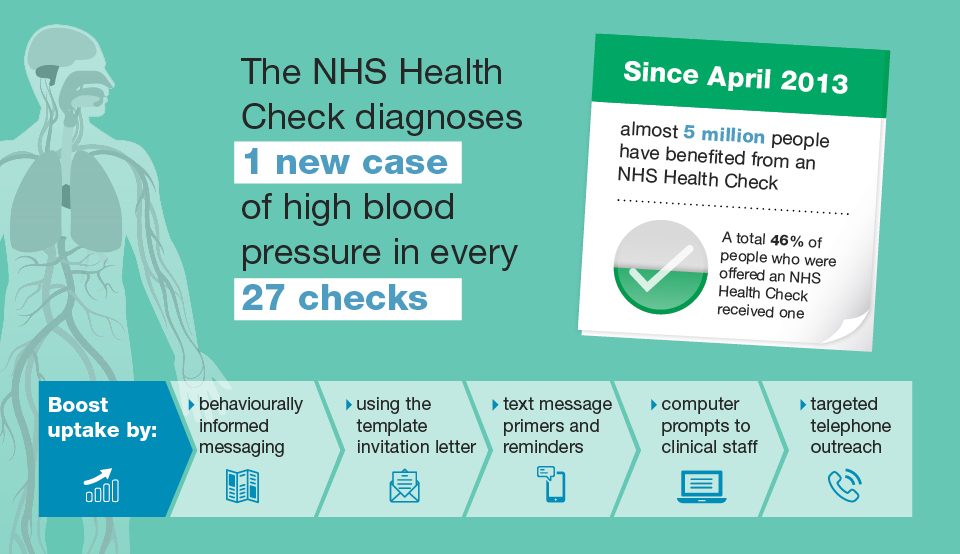
This diagram shows that the NHS checks programme diagnoses 1 new cases of high blood pressure in every 27 checks. Since April 2013 about 5 million people have benefited from an NHS Health Check, a total of 46% who were offered one received it. The NHS supply Boost uptake by: making behaviourally informed messaging, using the template invitation letter, text message primers and reminders, computer prompts to clinical staff, targeted telephone outreach.
Thousands more people could live healthy for longer, because early stage disease is detected during a check, we can do to increase the number of people having a check and endure they gain access to the appropriate clinical or lifestyle support.
2.Engaging and enabling the Organisation [the Stakeholders] let the organisations that the CVD is everyone’s business by consulting with them and set additional ways to tackle the rate death through stroke and heart attack with thee ethnic area and under privilege area.
3. Think about who are your partners, thin about those eateries, work with them to prepare healthy food because too much fatty food can cause heart attack or obesity, think about kebab, McDonalds be in partnership with them in how to deal with the problem and the ways to tackle safety that the potential changes in exercising as well.
4. Dealing with it.
5. The utmost goal is to cut down on bad habit that is causing high blood pressure.
There should be element of training if people are going to change their behaviour by enlighten them or train themselves in building their abilities on how to monitor their blood pressure by getting the blood pressure monitor or go for check-up regularly. And training staff and update their learning.
For local Authorities:
- Work with local partners to create and manage more safe spaces.
- Address concerns around safety, crime.
- Making routes, cycles parking and area maps.
- Make streets cleaner.
3.4 To evaluate an activity that has been implemented to encourage behavior change.
There are lot of activities that has been implemented o encourage behavior changes. Such as Sure start, Change 4 Life, DARE, CQUIN;
Commissioning for quality and innovation [CQUIN] The system was introduced in 2009 to make a proportion of healthcare providers’ income conditional on demonstrating improvements in quality and innovation in specified areas of patient.
Approaches to evaluation: Quantitative and Qualitative approaches.
Quantitative relating to measuring or count, this can be amount of, or what proportions the thing is or how often.
Quantitative Evaluation – there are study use to evaluate impact of health communication interventions;
Observational is a type of study which individuals are observed, or certain outcomes are measured.
- Cross sectional is a type of observational study that analysis transversal study, prevalence study, such as data collection from a populace or a representative sub category at a specific point in time.
- Cohort are type of research used to investigate the causes of diseases, establishing links between risk factor and health outcomes.
Qualitative is a primarily explanatory research , it is used to gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinion and motivations, thus provides insight into the problem and helps to develop ideas or hypothesis for potential quantitative.
Qualitative methods- examples-
- Focus group discussions: facilitator guides group: participants have similar characteristics.
- Interviews: in depth: guided by the respondent : semi-structured: loose set of questions
- Ethnographic observation: immersion in another’s culture: this is by learning about another ethnic culture in solving a problem and learn how to approaches and the way to improve their wellbeing by so doing learn why they do what they are practicing in.
Bibliography
Guide to health gains from structural funds, 2009-2010. Health determinants- guide to health gains from structural funds. [Online]
Available at: http://www.healthgain.eu/determinants-health
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
age uk, 2017. benefit calculator. [Online]
Available at: https://www.ageuk.org.uk/information-advice/money-legal/benefits-entitlements/benefits-calculator/
[Accessed 27 october 2017].
age uk, 2017. health and wellbein. [Online]
Available at: https://www.ageuk.org.uk/information-advice/health-wellbeing/health-services/health-tests-that-could-save-your-life/
[Accessed 2017 october 2017].
Anon., n.d. nhs england. [Online]
Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/about/about-nhs-england/
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
Bracknel forest JSNA, n.d. Comunicable Disease-Bracknel forest council. [Online]
Available at: https://www.google.co.uk/search?q=tuberculosis+incidence+uk&rlz=1C1CHBF_en-GBGB765GB765&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjS_aPKr-vXAhXS1qQKHbLkD_4Q_AUICigB&biw=1920&bih=974#imgrc=nWWmG88dxrwz3M:
[Accessed 27 november 2017].
CARE QUALITY COMMISSION, 2017. WHO WE ARE- CARE QUALITY COMMISION. [Online]
Available at: http://www.cqc.org.uk/about-us
[Accessed 02 DECEMBER 2017].
google.uk, n.d. google.uk. [Online]
Available at: https://www.google.co.uk/search?q=graphs+on+cervical+cancer2017&rlz=1C1CHBF_en-GBGB765GB765&tbm=isch&tbo=u&source=univ&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiun4qQ-ZbXAhWBTRoKHQiLCa8Q7AkINQ&biw=1920&bih=974#imgdii=Z1cJNfblL822SM:&imgrc=kez420YmS-Zl9M:
[Accessed 29 october 2017].
gov.uk, 2015. nhs constitution of england. [Online]
Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-nhs-constitution-for-england/the-nhs-constitution-for-england
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
GOV.UK, 2017. Health matters- Combating the High Blood Pressure. [Online]
Available at: https://publichealthmatters.blog.gov.uk/2017/01/24/health-matters-combating-high-blood-pressure-with-the-nhs-health-check/
[Accessed 09 December 2017].
gov.uk, n.d. nhs england our work. [Online]
Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/mental-health/
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
GSDRC- APPLIED KNOWLEDGE SERVICES, 2015. SOCIAL EXCLUSION-TOPIC GUIDE. [Online]
Available at: http://www.gsdrc.org/topic-guides/social-exclusion/causes/causes-and-forms-of-social-exclusion/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
Gynaehealth , n.d. Cervical cancer prognosis and survival rates. [Online]
Available at: https://www.gynaehealthuk.com/cervical-cancer-information/cervical-cancer-prognosis-and-survival-rates
[Accessed 23 October 2017].
HEALTHLINE- NUTRITION, 2005-2017. AUTHORITY NUTRITION-HOW MUCH WATER SHOULD I DRINK PER DAY. [Online]
Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/how-much-water-should-I-drink
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
LIVESTRONG- Nutrition, Fitness and Lifestyle Choices, 2017. Nutrition, Fitness, and Lifestyle Choices for cold and Flu- LIVESTRONG. [Online]
Available at: https://www.livestrong.com/article/1011714-nutrition-fitness-lifestyle-choices-cold-flu/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
medicins sans frontieres, 2017. about medicins sans frontieers. [Online]
Available at: http://www.msf.org/en/about-msf
[Accessed 27 october 2017].
MERCK AND MERCK MANUALS, 2017. Prevention of Cancer and Treatment of Cancer-MERCK AND THE MERCK MANUALS. [Online]
Available at: http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/cancer/prevention-and-treatment-of-cancer/prevention-of-cancer
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
National Centre for Biotechnology Information, n.d. PREVENTION AND TREATMENT-National Centre for Biotechnology Infrormation. [Online]
Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209704
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES, 2015. END OF LIFE CARE- NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES. [Online]
Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/Planners/end-of-life-care/Pages/what-it-involves-and-when-it-starts.aspx
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES-YOUR HEALTH, YOUR CHOICES, 2017. NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES CHOICES-YOUR HEALTH, YOUR CHOICES. [Online]
Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/Livewell/5ADAY/Pages/Why5ADAY.aspx
[Accessed 03 DECEMBER 2017].
SKILLS FOR CARE , 2013. CODE CONDUCT FOR HEALTHCARE SUPPORT WORKERS AND ADULT SOCIAL CARE WORKERS IN ENGLAND. [Online]
Available at: http://www.skillsforhealth.org.uk/standards/item/217-code-of-conduct
[Accessed 02 DECEMBER 2017].
Study.com for Schools- Alcohol Abuse problems: effect and treatment , 2003-2017. Alcohol Abuse Problems- Fundamentals of counselling. [Online]
Available at: https://study.com/academy/lesson/alcohol-abuse-problems-rates-effects-treatment.html
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
THE HOUSING AND AGEING ALLIANCE , 2013. POLICY PAPER: HEALTH, HOUSING AND AGEING. [Online]
Available at: https://www.housinglin.org.uk/_assets/Resources/Housing/HAA/HAAllianceTopic_Statements_Health.pdf
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WEBMD HEALTH SERVICES, 2005-2017. Eating Well During Cancer Treatment. [Online]
Available at: https://www.webmd.com/cancer/features/eating-treatment#1
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WHO, n.d. World health organisation. [Online]
Available at: https://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=%2FWHO_HQ_Reports%2FG2%2FPROD%2FEXT%2FTBCountryProfile&ISO2=NG&LAN=EN&outtype=html
[Accessed 29 october 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION , n.d. Communicable disease-WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION. [Online]
Available at: www.who.int/tdr/publications/document/seb
[Accessed 17 november 2017].
world health organisation, 2017. about who. [Online]
Available at: http://www.who.int/about/en/
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION- EMPLOYMENT CONDITIONS, 2017. Social Determinants of health. [Online]
Available at: http://www.who.int/social_determinants/themes/en/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2014. Mental health: a state of wellbeing. [Online]
Available at: http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/mental_health/en/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2017. HEALTH PROMOTION AND DISEASE PREVENTION- WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. [Online]
Available at: http://www.emro.who.int/about-who/public-health-functions/health-promotion-disease-prevention.html
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
Bibliography
Guide to health gains from structural funds, 2009-2010. Health determinants- guide to health gains from structural funds. [Online]
Available at: http://www.healthgain.eu/determinants-health
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
age uk, 2017. benefit calculator. [Online]
Available at: https://www.ageuk.org.uk/information-advice/money-legal/benefits-entitlements/benefits-calculator/
[Accessed 27 october 2017].
age uk, 2017. health and wellbein. [Online]
Available at: https://www.ageuk.org.uk/information-advice/health-wellbeing/health-services/health-tests-that-could-save-your-life/
[Accessed 2017 october 2017].
Anon., n.d. nhs england. [Online]
Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/about/about-nhs-england/
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
Bracknel forest JSNA, n.d. Comunicable Disease-Bracknel forest council. [Online]
Available at: https://www.google.co.uk/search?q=tuberculosis+incidence+uk&rlz=1C1CHBF_en-GBGB765GB765&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjS_aPKr-vXAhXS1qQKHbLkD_4Q_AUICigB&biw=1920&bih=974#imgrc=nWWmG88dxrwz3M:
[Accessed 27 november 2017].
CARE QUALITY COMMISSION, 2017. WHO WE ARE- CARE QUALITY COMMISION. [Online]
Available at: http://www.cqc.org.uk/about-us
[Accessed 02 DECEMBER 2017].
google.uk, n.d. google.uk. [Online]
Available at: https://www.google.co.uk/search?q=graphs+on+cervical+cancer2017&rlz=1C1CHBF_en-GBGB765GB765&tbm=isch&tbo=u&source=univ&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiun4qQ-ZbXAhWBTRoKHQiLCa8Q7AkINQ&biw=1920&bih=974#imgdii=Z1cJNfblL822SM:&imgrc=kez420YmS-Zl9M:
[Accessed 29 october 2017].
gov.uk, 2015. nhs constitution of england. [Online]
Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-nhs-constitution-for-england/the-nhs-constitution-for-england
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
GOV.UK, 2017. Health matters- Combating the High Blood Pressure. [Online]
Available at: https://publichealthmatters.blog.gov.uk/2017/01/24/health-matters-combating-high-blood-pressure-with-the-nhs-health-check/
[Accessed 09 December 2017].
gov.uk, n.d. nhs england our work. [Online]
Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/mental-health/
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
GSDRC- APPLIED KNOWLEDGE SERVICES, 2015. SOCIAL EXCLUSION-TOPIC GUIDE. [Online]
Available at: http://www.gsdrc.org/topic-guides/social-exclusion/causes/causes-and-forms-of-social-exclusion/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
Gynaehealth , n.d. Cervical cancer prognosis and survival rates. [Online]
Available at: https://www.gynaehealthuk.com/cervical-cancer-information/cervical-cancer-prognosis-and-survival-rates
[Accessed 23 October 2017].
HEALTHLINE- NUTRITION, 2005-2017. AUTHORITY NUTRITION-HOW MUCH WATER SHOULD I DRINK PER DAY. [Online]
Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/how-much-water-should-I-drink
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
LIVESTRONG- Nutrition, Fitness and Lifestyle Choices, 2017. Nutrition, Fitness, and Lifestyle Choices for cold and Flu- LIVESTRONG. [Online]
Available at: https://www.livestrong.com/article/1011714-nutrition-fitness-lifestyle-choices-cold-flu/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
medicins sans frontieres, 2017. about medicins sans frontieers. [Online]
Available at: http://www.msf.org/en/about-msf
[Accessed 27 october 2017].
MERCK AND MERCK MANUALS, 2017. Prevention of Cancer and Treatment of Cancer-MERCK AND THE MERCK MANUALS. [Online]
Available at: http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/cancer/prevention-and-treatment-of-cancer/prevention-of-cancer
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
National Centre for Biotechnology Information, n.d. PREVENTION AND TREATMENT-National Centre for Biotechnology Infrormation. [Online]
Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209704
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES, 2015. END OF LIFE CARE- NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES. [Online]
Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/Planners/end-of-life-care/Pages/what-it-involves-and-when-it-starts.aspx
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES-YOUR HEALTH, YOUR CHOICES, 2017. NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES CHOICES-YOUR HEALTH, YOUR CHOICES. [Online]
Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/Livewell/5ADAY/Pages/Why5ADAY.aspx
[Accessed 03 DECEMBER 2017].
SKILLS FOR CARE , 2013. CODE CONDUCT FOR HEALTHCARE SUPPORT WORKERS AND ADULT SOCIAL CARE WORKERS IN ENGLAND. [Online]
Available at: http://www.skillsforhealth.org.uk/standards/item/217-code-of-conduct
[Accessed 02 DECEMBER 2017].
Study.com for Schools- Alcohol Abuse problems: effect and treatment , 2003-2017. Alcohol Abuse Problems- Fundamentals of counselling. [Online]
Available at: https://study.com/academy/lesson/alcohol-abuse-problems-rates-effects-treatment.html
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
THE HOUSING AND AGEING ALLIANCE , 2013. POLICY PAPER: HEALTH, HOUSING AND AGEING. [Online]
Available at: https://www.housinglin.org.uk/_assets/Resources/Housing/HAA/HAAllianceTopic_Statements_Health.pdf
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WEBMD HEALTH SERVICES, 2005-2017. Eating Well During Cancer Treatment. [Online]
Available at: https://www.webmd.com/cancer/features/eating-treatment#1
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WHO, n.d. World health organisation. [Online]
Available at: https://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=%2FWHO_HQ_Reports%2FG2%2FPROD%2FEXT%2FTBCountryProfile&ISO2=NG&LAN=EN&outtype=html
[Accessed 29 october 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION , n.d. Communicable disease-WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION. [Online]
Available at: www.who.int/tdr/publications/document/seb
[Accessed 17 november 2017].
world health organisation, 2017. about who. [Online]
Available at: http://www.who.int/about/en/
[Accessed 26 october 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION- EMPLOYMENT CONDITIONS, 2017. Social Determinants of health. [Online]
Available at: http://www.who.int/social_determinants/themes/en/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2014. Mental health: a state of wellbeing. [Online]
Available at: http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/mental_health/en/
[Accessed 03 December 2017].
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2017. HEALTH PROMOTION AND DISEASE PREVENTION- WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. [Online]
Available at: http://www.emro.who.int/about-who/public-health-functions/health-promotion-disease-prevention.html
[Accessed 02 December 2017].
(world health organisation, 2017)
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Health and Social Care"
Health and Social Care is the term used to describe care given to vulnerable people and those with medical conditions or suffering from ill health. Health and Social Care can be provided within the community, hospitals, and other related settings such as health centres.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




