Literature Review on Learning Theories
Info: 2076 words (8 pages) Example Literature Review
Published: 20th Feb 2025
Tagged: EducationPsychology
Chapter 3: Literature Review
“Education is the passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to those who prepare for it today.” - Malcolm X
3.1 Behavioristic Learning and E-Learning Theories
Learning theory is an organized set of principles which explain how someone can acquire, retain, and remember knowledge. According to Skinner (1974), behaviorists define the mind as a “black box” as a response to a stimulus is observed as quantitative as it ignores the thought processes that are going through the mind [20]. Atkins (1993) [21] discussed four aspects which are linked to realise e-learning courses in consideration to behaviorists in school:
- The learning material should be presented into step-by-step instructions while giving positive examples to reinforce knowledge and understanding and presenting negative examples to demonstrate conceptual boundaries.
- Courses should entail defined instructions using conditional or unconditional branching to different instructing methods such as videos and graphics and this choice should be pre-determined at the time of the course.
- Giving the learner more control over learning the courses by designing and letting them make their choice out of a set of activities. This method will not only maximise the learning efficiency but also to follow a sequence in the learning process.
- Repetition when practicing allows to build proficiency of learning by reviewing and revising the materials with feedback. Furthermore, the instructions should be broken into parts, and specifically for the construction field, it should display the applied skills and procedures that are currently being practiced and in compliance with WorkSafeBC.
The proposed approach of Atkins (1993) suggests a structured and deductive approach on how to design an e-Learning course so as the learners can grasp all the basic concepts and information rapidly. In the case of BCCSA, one of the challenges that the course learners might have in case of switching to e-learning, is that the basic concepts and skills will not be present in an online atmosphere. However, according to Atkins’ (1993) four aspects discussed above, we must use the same basic concepts of behaviorism and make learning an interesting chore, such as including set of activities, and choices. It gives the participant the freedom to think creatively and learn efficiently.
On the other hand, Abas (2003) [22] claimed that there is no best method for e-learning and it just simply provides a different learning experience. It depends on the person whether they are comfortable to learn online or not. One thing he said we can be certain about is that e-learning is a good addition to the pedagogies that are currently available. To support that, Jordan (2017) stressed on the fact that with the increasing offering of online course globally, online modes of study are almost equivalent to an in-class environment when it comes to key outcomes such as the performance of the student. E-learning not only benefits students with the flexibility of learning but it also benefits instructors with professional development in terms of expanding their direct skills (Jordan, 2015).
3.2 E-learning delivery frameworks
It is widely known that there is a need to continuing professional development and lifelong skills learning opportunities. WorkSafeBC recognizes this fact and therefore created the BCCSA to offer construction safety specific courses to the construction industry without them having to pay for the courses.
According to Pew Internet Research Centre (2019), North America has the highest Internet usage in the world and today, 9 in 10 Americans is believed to use the Internet. Figure 2 below shows the demographics from 2008-2019 on the increase of internet usage among adults.
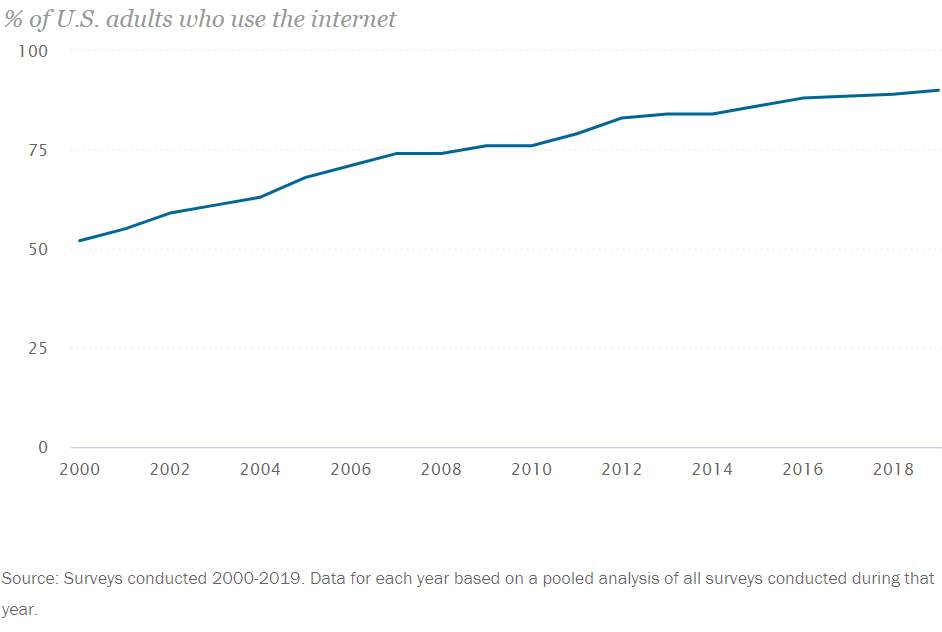
Figure 2: Demographics of Internet and Home Broadband usage
Not only that, the BCCSA only offers to book courses through their website by registering online [1]. So to start with, the construction people must be computer literate to register online for a course, thus it would be easier for them to adopt e-Learning. Of course, there will be blended learning which means there will be both online and in-class safety training courses provided.
There have been many different attempts to build a comprehensive framework for the blended learning approach, and this thesis will apply Badrul Khan’s Octagonal Framework [22] which has been widely used and accepted as a functional framework in the creation of an e-learning environment with eight dimensions.
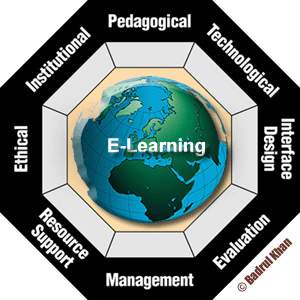
Figure 3: Khan’s Octagonal Framework
Source:
As per Singh (2003) [23], when all the eight dimensions from Figure 3: Khan’s Octagonal Framework is considered, the course creates a meaningful experience for the learners. Below we will emphasize on each of the dimensions:
- Institutional dimension – It consists of the ability of the organization to address issues about the learners adequately.
- Pedagogical dimension – It references to a combination of content, target audience and learning objectives for delivery to our audience in an appropriate strategy.
- Technological dimension – It consists of the suitable tools and systems for the delivery of the courses. It involves any technology, for example use of website or an internet platform to deliver the courses.
- Interface design dimension – It refers to how user friendly is the interface for the learner, the latter should be able to switch back and forth between the contents and it should be easy enough to navigate.
- Evaluation dimension – It refers to a tool which judges and measures the effectiveness of the course contents and online delivery modes.
- Management dimension – It addresses the issues of managing an e-learning/blended program. As a matter of fact, the blended program is much more complicated than the in-class training only, this management dimension considers how the courses are being delivered through multiple content types and any logistical or technological issues that can potentially arise in the future.
- Resource support dimension – It refers to other online or offline support that the learner might need from a counselor or tutor.
- Ethical dimension – It must take in consideration the issues of cultural diversity and localization. (Singh, 2003)
While Khan’s framework may seem to be outdated as it dates from 2003, there have been fewer frameworks for blended or e-learning developed. Among one of the other far-reaching frameworks, there is the ADDIE framework developed by Malamed (2019) [24] which encompasses 5 steps to develop and launch an e-learning platform (Malamed, 2019) [24]. Illustrated below in Figure 4, Malamed’s development model explains the steps to take to launch a successful e-learning platform.

Figure 4: ADDIE Framework
(i) Analysis
In the Analysis phase, the learner’s or audience’s characteristics should be researched and identified, the contents of the materials should be organized and identified how much there is. In additional to that, the learning platform (web-based online platform) and technical specifications such as internet speed, microphone ability of computers, etc. should be taken into consideration. After this, a performance goal can be written.
(ii) Design
The designing of the learning material should be derived from the performance goals developed from the analysis. For example, learning objectives based on existing materials, from interviews with subject matter experts (SMEs) or from gathered data from research. In case of the BCCSA though, the learning content already exists for the in-class courses, so we will just need to convert the in-class materials to an online version. This is also a great opportunity to improve, reorganize and add to the e-learning content.
iii) Development
This phase consists of the transfer of all the developed materials for the course to a web-based platform, see how it will appear on the screen and listen to the audio if it is audible. The visual should grab the viewer’s attention and it should be interactive even though it is not an in-class training. The use of writing story boards and writing test questions can be done in case the course requires a written test. This is also an excellent time to have a sample of co-workers to review the material and provide feedback. This process is known as formative evaluation which may save many revisions in the future.
iv) Production
This phase is when all the visions have been implemented and assembled in a course content which is now viewable online. The graphics, audio, video and text are all produced and ready for further testing or direct launch.
v) Quality assurance
This phase ties into the production phase as it involved testing the online course, the course instructions, navigation between the platforms or pages or the overall e-learning process should work smoothly. Basically, the quality assurance process is to think like the user and walk in their path where they would go during the course and test it. This will allow the tester to log any errors and provide a report for the IT to correct these errors. After the changes have been corrected, it is important to retest again and make sure that there is no further problem. As soon as there is no problem identified, the course is finally ready to launch for your audience. (Malamed, 2019) [24]
3.3 Delivery of course materials
3.3.1 Webinars
According to Gegenfurtner (2019) [25], webinars are far more effective than in-class training. The word webinar is a mixture of the word “web” and “seminar” and in short webinar just means a seminar that is held online. It can be described as online seminars in which the instructor and students communicate live using audio and webcam on the Internet no matter the geographical location of both (Gegenfurtner et al., 2019). This digital learning environment has become popular for higher education and professional training and it is becoming more common to teach and learn through webinars.
As per Ebner (2019), webinars are advantageous over the traditional face-to-face learning and these advantages are listed below:
- Geographical flexibility of both the instructor and the learner.
- Instant attention from the instructor during the webinar. In case the learner does not want to bother the whole class with their question, they can ask the instructor their question privately in a chat.
- This mode allows interaction between participants in the group in real time.
- The course content can be accessed anytime and anywhere, and the online class can be recorded to be viewed again in the future.
Other advantages may include:
- It is cost effective for the training provider.
- It saves the travel time and travel expenses incurred from the instructor and the latter will save on the travel time to the location of the in-class course.
- There is an occupancy limit in every in-class course, however, in a webinar the occupancy limit can be increased to more people.
- Keeping up to date with the new technological advances of the new era.
However, just like two sides of a coin, webinars do have some disadvantages as well. As per Wang and Woo (2007), face-to-face interaction during in-class courses are difficult to replace with asynchronous communication as the immediate feedback is not present and there is an “absence of extensive multilevel interaction between students and lecturers” (Ebner and Gegenfurtner, 2019).
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Psychology"
Psychology is the study of human behaviour and the mind, taking into account external factors, experiences, social influences and other factors. Psychologists set out to understand the mind of humans, exploring how different factors can contribute to behaviour, thoughts, and feelings.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this literature review and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




