Enablers and Barriers to Business Start-up: Comparison of Business Sizes
Info: 8390 words (34 pages) Dissertation
Published: 9th Dec 2019
Tagged: Business
TABLE OF CONTENT
| CONTENT | PAGE No. |
| TITLE | 1 |
| TABLE CONTENT | 2/2 |
| INTRODUCTION | 3/3 |
| P1 | 3/8 |
| P2 | 8/11 |
| M1 | 11/15 |
| D1 | 15/19 |
| P3 |
19/21 |
| P4 | 21/23 |
| M2 | 23/25 |
| D2 | 25/26 |
| P5 | 26/29 |
| P6 | 29/32 |
| M3 | 32/34 |
| D3 | 34/34 |
| P7 | 34/36 |
| M4 | 36/38 |
| D4 | 38/38 |
| BIBLIOGRAPHY | 39/39 |
Introduction:
In this Unit 9, we will be talking about three enterprises with three different sizes.
The three enterprises are: The Body shop (large size), Debenhams (medium size) and Southern Business Technologies Ltd (small size).
This topic is about the understanding of the definition and scope of entrepreneurship and an understanding of the enablers and barriers to business start-up.
The personal characteristics of entrepreneurs and the impact of personal situational factors, including education and background influence the national culture and economy on entrepreneurship.
The understanding of the role and importance of small firms and social enterprise to the economy.
Learning about the risk to start a new business; as well as to be able to identify the characteristics of entrepreneurial ventures.
P1
Entrepreneurship
It is the ability and desire to plan, develop, organise and manage the company venture along with any of its risks in order to make a profit. The starting of new businesses is an example of entrepreneurship.
The entrepreneurial activity refers to human action in pursuing of the generation of value, to create or to expand the economic activity, by identifying and exploiting new products, processes or markets. On the other hand it helps identify opportunities within the economic system (Hartman, 1959)
Where there are entrepreneurs or enterprise there will always be entrepreneurial activity but the latter is not dependent of the existence of the former. People within The Body Shop Company may demonstrate an entrepreneurial activity without compulsory having a stake in the company. The entrepreneurial activity is the process of creation, change and innovation of the regional economic development (Reynolds at al., 2001)
According to Legazkue, 2004, through entrepreneurial activity a modern industrial society can turn into a knowledge society.
Example of entrepreneurial activities from 1984 to 2002 by Kohler Stefan
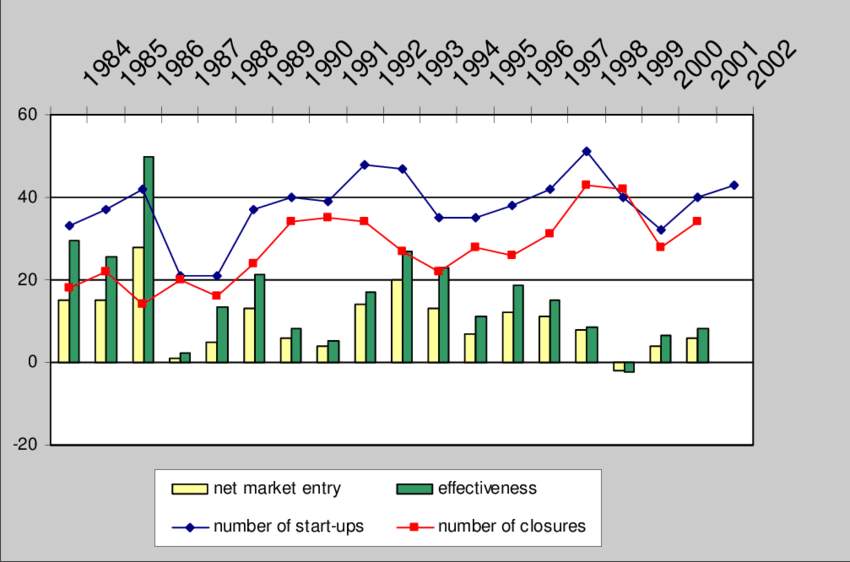
Entrepreneurial venture
Innovation and opportunism are part of any organisation in order to produce economic and social value.
There are different types as described by Steve Blank in 2011, which are:
- Small Business Entrepreneurship is an independently owned and operated company that is limited in size and in revenue depending on the industry. A local bakery that employs 10 people is an example of a small business. A manufacturing facility that employees less than 500 people is an example of a small business.
Example: Southern Business Technologies Ltd (Communications).
- A business with 100 or fewer employees is small but with 100-999 employees is considered medium-sized. Matthias F., 2009
Example: Debenhams retail company (clothing and goods retailers)
- Large Company Entrepreneurship is big than the medium-sized business and has 250 or more employees.
Example: The Body Shop Company (Beauty products)
- Micro Entrepreneurship it is a small enterprise that employs fewer than 10 people and can operate in providing goods and services locally. Example: Local pizza Shop.
In terms of private and public sector; both have similarity but the only difference is on entrepreneurial profit.
Private sector: the management has the decision making to control the higher cost of the capital and the stakeholders need profit.
Public sector: the transactions provide moneybut the management has limited incompatibility between autonomy and the cost of capital.
In contrast, private sector provides the desired trade-off within calibrated contracting, but creates illiquid ownership.
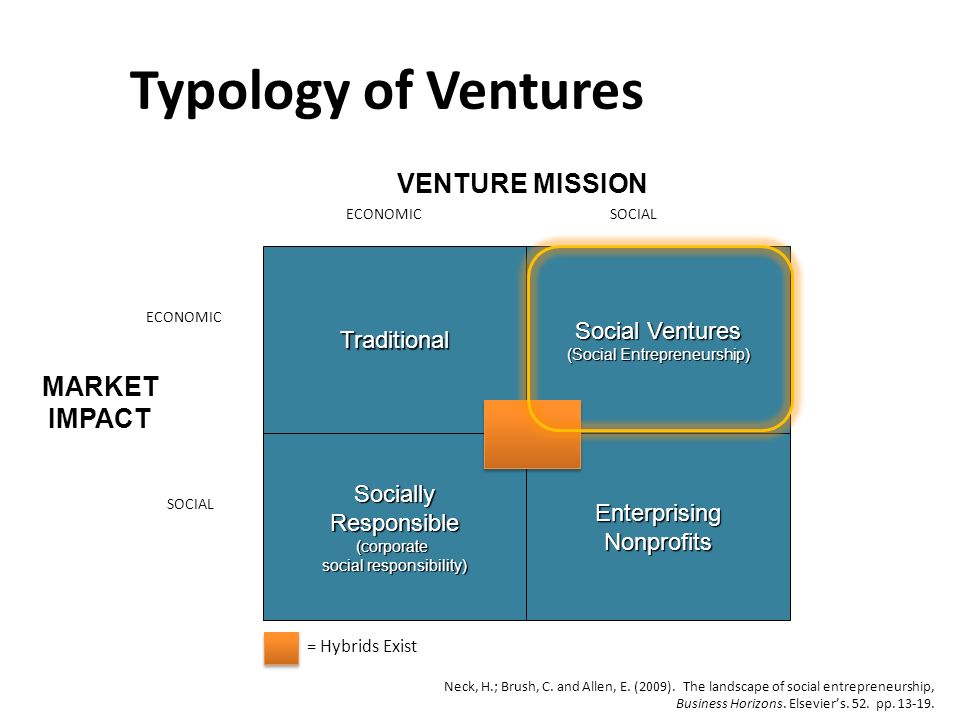
The entrepreneurial typology employs two dimensions, high versus low entrepreneurial alertness and internal versus the external attributional styles that helps understand why entrepreneurs start new businesses. The typology identifies 4 entrepreneur types based on two dimensions: believer, clueless, practical, and reluctant.
In the other hand some need achievement, risk-taking, and commitment providing support for typology validity.
The typology of entrepreneurship it is also important to stipulate that, generally speaking, types are studied within a predetermined category, usually a professional category. In entrepreneurship it is possible to establish and study different types within separate entrepreneurial categories, such as entrepreneurs, family business owner-managers, small business owner-managers, the self-employed, micro-enterprise owner-managers, entrepreneurs in general and entrepreneurs divided into more specific categories, such as technopreneurs (technological entrepreneurs), social entrepreneurs and collective or cooperative entrepreneurs. (Louis Jacques F, 2000)
One of the first typologies to be developed, that of Smith (1967), has since gone on to become a classic. Smith established the distinction between the craftsman entrepreneur and the opportunist or business entrepreneur.
These typologies were developed from types of strategies, organisations or decision-making styles. According to Miller (1996), their value lies in the fact that they show how and why the attributes of each type relate to one another. Pitcher (1995) suggests three types of leaders in organisations, namely artists, craftsmen and technocrats.
Most of the criteria used to develop entrepreneurial typologies are related basically to human behaviour. The types should be able to comply with universal laws and be reproduced unchanged in almost all social contexts. The typologies can be used to help understand the nature of a relationship between a type and its subject, or between a type and its object. The typologies can also be useful in identifying the competencies required by each type for its professional application. Each type have a set of criteria used to make decisions affecting the process of identity, self-awareness and future progress, as well as action.
Typologies are also useful in improving the efficiency, effectiveness and performance of actors and the organisation in which they work. They can help in decision-making criteria and enable actors to target things they want to achieve.
In some way, they allow for the introduction of more appropriate tools for the achievement of goals and objectives and they become basic management, educational and training tools, for time and resource management.
P2
- Scalable Start-ups Entrepreneurship is a business that employs a small number of workers and does not have a high volume of sales. Sometimes called a small business or a small-scale enterprise. The legal definition varies by industry and country (JustPark in app & software development, revenue of £1.7 million/year, 33 employees)
- Social Entrepreneurship is a proper business that makes its money in a socially responsible way. These ventures are not necessarily formed to invest all profits into the communities (Barnsley Community Build delivers training and employment in the construction industry for young people without work or education )
- Lifestyle Business for freelancer sole employee with freedom to do what you want to do (Lauren Razavi freelancer on writing, teaching and managing a band)
- Micro-enterprise which is generally defined as a small business employing nine people or fewer (Wiser, creative and recruitment company, https/wearewiser.com)
- Second Stage Company which is viable independent.
This research study shows similarities and differences in entrepreneurial activities and process of corporate new ventures and independent new ventures. Hereby, the leading theme is the theory of causation and effectuation. By analysing four different cases, findings suggest that both, effectuation and causation are determinants in the entrepreneurial process in corporate and independent new ventures. While independent ventures show more effectual reasoning by establishing strategic alliances, focus on personal affordable loss and means-based actions, they also show causal elements by conducing competitive analyses and focusing on expected returns.
In contrast, although corporate ventures often have to focus on expected returns and goals, they like to experiment with ideas, build partnerships, and exploit contingencies within and outside their core business. Hereby, they are restricted in their entrepreneurial activities and face organisational challenges. Therefore, findings indicate the importance of an organisational environment welcoming entrepreneurial activities and innovation. Besides theoretical contribution in the field of entrepreneurship, the study also has practical relevance and gives managerial implications. (Na MI N, 2013)
- Amount and speed of wealth creation, risk tolerance, and innovation.
- Different mind-sets, different passions and different way of doing things.
But all making a difference.
The entrepreneur never want things to stay as they are – looking for actions and more energy.
The entrepreneur does things not because of passion or opportunity rather than strictly profit and want to change the world.
The small business owner if often happy with how things are, content to make profit.
The small business owner does things others are doing.
The small business owner is more sentimental and sees his business as part of the community.
The small business owner wants to make a living, and often serve his local community first.
The entrepreneur is the innovator who takes financial risks in the hope to make profit.
The serial Entrepreneur starts and leads one business after another or, multiple business at the same time. But an entrepreneur leads only a single business and runs it until exit or retirement. (Chris G., 2013)
The intrapreneur is a manager who is given the authority to create or promote innovative product development (marketing).
The owner-manager is a person who owns and manages at the same time his business.
But all of them share some of the same characteristics (passion, flexible, self-motivation, etc.) and all of them are concerned with business growth and success.
But some differences exist when it comes to the basic traits of each:
Managers plays an entirely different role than an entrepreneur – unless, of course, an entrepreneur is managing his own business. In that case, the entrepreneur takes on some the traits of a manager out of necessity.
The entrepreneur is at the beginning and the end of the business in all aspects but intrapreneur is a facet of this broader vision as well he is an important asset of the company. Jared L., 2017
M1
All small, medium-size, and large businesses are of critical importance to the performance and growth of the economy.
However there is a distinction between entrepreneurial ventures and individual and corporate entrepreneurship since they serve different economic functions and their potentials for innovation and growth are different. Also the differences are in terms of size, resources and turnover. LK Gumdy, 2001
Rob H., 2017 has stated that:
- Independent “Main Street” Business:
- The small business such Southern Business Technologies Ltd (Communications) can generate payroll taxes and jobs. They provide services that are necessary parts of a city’s infrastructure. Growth into a log-term business that is profitable and sustainable of eventual sale to employee or hand over to family member.
- A business with 100 or fewer employees is small but with 100-999 employees is considered medium-sized such Debenhams (clothing and goods retailers)
- The lifestyle business (freelancers and micro-enterprises) is for self-employed individuals enjoying a lifestyle, one-person firm with small operations.
- The Micro Business is a small business that employs a small number of employees, and will operate with fewer than 10 people and is starts with a small capital. Most of them are specialised in providing goods or services for
their local areas.
- Large Company Entrepreneurship it is an organisation that grown beyond the limits of a medium-sized business and has 250 or more employees.
Example: The Body Shop Company (Beauty products)
- Social Good Enterprises:
The socio good business is about to solve global health issues, non-profits with a philanthropic mission. Can run the entire capital and improve lives.
- The Established Companies:
The large business it is a corporation with revenue, tax credits and subsidiaries. It is a significant employer in the community with reputation and community presence (500 employees or more)
- High Growth Companies:
- The scalable start-up focus to create and innovate. Built to generate wealth for founder and investors when the sales increases.
- Second Stage Company that moved one step up from start-up and willing to grow.
The public sector organisation is part of a country’s economy which is controlled or supported financially by the government. It consists of national and local governments, their agencies, and their chartered bodies.
The public sector provides free services to people. Example, the public school system is open to all children and their parent’s income is not considered. But the difference between these two sectors in private they have to pay a fee.
The potential role of entrepreneurship is to build cultural competitiveness in organisations which is to detect and fill gaps between the market desires and what is currently offered (Anderson, J.C. 1987)
It outlines research that investigates whether those factors, which the literature describes as stimulating corporate entrepreneurship in the private sector, apply to the public sector. It concluded that entrepreneurship is a strategic phenomenon and, as a consequence, the unique environmental influences on public sector bodies generate stimulants and constraints to corporate entrepreneurship, which vary from those applicable to the private sector. (Robert J Sadler, 2000)
D1
To get growth and expansion; the businesses need to focus on selling to the new market and applying for a loan to expand operations if necessary.
The geographic expansion, foreign markets, and expansion through the development of new products and technologies may help the organisation to achieve its mission and goals and brings growth (Austin J., 2006)
The entrepreneurs are so important and can change the way we live and work. Their innovations may improve people standard of living if they are successful. In addition to creating wealth from their entrepreneurial ventures, they also create jobs and the conditions for a prosperous society.
JR Baum, 2004 has stated the following:
- Entrepreneurs create new business
Path breaking offerings by entrepreneurs, in form of new goods & services, result in new employment, which can produce a cascading effect or virtuous circle in the economy. The stimulation of related businesses or sectors that support the new venture add to further economic development.
Businesses in associated industries, like call centre operations, network maintenance companies and hardware providers, flourished. Education and training institutes developed a new class of IT workers offering better, high-paying jobs. The infrastructure development organisations and even real estate companies capitalised on this growth as workers migrated to employment hubs seeking new improved lives – the entrepreneurs enable benefits across a broad spectrum of the economy.
- Entrepreneurs add to national income
The established or existing businesses may remain confined to the scope of existing markets and may hit the glass ceiling in terms of income. Entrepreneurial ventures generate wealth, also the new markets developed.
The cascading effect of increased employment and higher earnings contribute to better national income in form of higher tax revenue and higher government spending. This revenue can be used by the government to invest in other, struggling sectors. The government can use the surplus to save people job.
- Entrepreneurs also create social change
Overall, this result in an improved quality of life, greater morale and economic freedom.
The people can work without worrying about what else to do because more time working means economic growth.
The globalisation of tech means entrepreneur in lesser-developed countries have access to the same tools as their counterparts in richer countries. They also have the advantage of a lower cost of living, so a young entrepreneur from an underdeveloped country can take on the might of the multi-million pound existing product from a developed country.
- Community development
Entrepreneurs regularly develop entrepreneurial ventures by other like-minded individuals. They invest in the community projects and provide financial support to local charities. This enables further development beyond their own ventures.
- The other side of entrepreneurs
The negative impact on the growth can be found for example with Italy, where high levels of self-employment have proved to be inefficient for economic development.
- The role of states
The regulations play a crucial role in nurturing entrepreneurship, but regulation requires a fine balancing act on the part of the regulating authority.
Unregulated entrepreneurship may lead to unwanted social outcomes including unfair market practices, pervasive corruption, financial crisis and even criminal activity.
High number of entrepreneurs may lead to fierce competition and loss of career choices for individuals; and levels of aspirations usually rise.
The scenario of having too many entrepreneurs in a successful entrepreneurial venture may lead to income inequalities, making people more – not less – unhappy.
- The bottom line
The interesting interaction of entrepreneurship and economic development has vital inputs and inferences for policy makers, development institutes, business owners, change agents and charitable donors. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks, a balanced approach to nurturing entrepreneurship will result in a positive impact on economy and society.
Social entrepreneurship to Socio economic
Chanakyaiacademy.com
Conclusion:
Social entrepreneurship can help to embrace socio-economic development in an inclusive and sustainable way.
P3
Micro-enterprise is defined as a small business with nine or fewer people and with a turnover less than a certain amount (e.g. £1.7 million)
Small business is define as an independently owned and operated business, limited in size and in revenue depending on the industry (10 people and less than 50 people and turnover under 10 million). Gov.uk, 2017
In such advanced technology and increasing demand of the market; more innovative ideas in the corporate world shaped many individuals to become entrepreneurs. More innovative ideas help to gain profit which lead to the increase in new businesses. The entrepreneurs become more creative by coming up with innovative ideas, idea development for the market which make a huge impact on the expansion of the corporate world in practical situations.
SMEs hired people in the UK last year and the gross value stands at £1.8 trillion, which represents 47% of UK economy (turnover)
SMEs are job creation, introducing new markets and contributing to the UK economy.
The Small Businesses are the backbone of the UK economy, driving growth, opening new market and creating jobs. Their contribution is vital, they encourage competition, and innovation and bring new ideas that challenge the status quo (represent 99.9% of businesses).
The SMEs triumph over their large counterparts in terms of growth. They are the key drivers of innovation, competition and growth. SMEs played a big role by helping UK to come out of the recession in 2008.
The Small and Micro – Businesses: They add diversity nationally, regionally and locally as well they play a big role in the community and customers.
But the micro-businesses such sole traders who work independently are not employers. They are vital to the economy in the UK and there numbers still increase with 96% of UK businesses classified as micro.
UK has an entrepreneurial spirit and its economy relies hugely on businesses.
| Name | Size | Profit | Rate/Growth | Innovation | Sustainability | Adaptability | turnover |
| The Body Shop
(Global, national, regional and local) |
Large Business | € 4.54 billion | +0.6% | Range of three star products of the year | Enriching people and the planet with biodiversity and resources | 3,082 stores worldwide. Three new in Chile | 47.64% Consumer products.
12.97% Professional products. |
| Debenhams
(Global, national, regional and local) |
Medium-Size Business | £2.5 billion | +2% | Innovation in mobile and delivery-Internet Retailing | Reducing the impact on the environment and complying with all mandatory requirements | 240 stores worldwide | £65m |
| Southern Business Technologies Ltd
(National, regional and local) |
Small Business | £5m | +3.5% | Innovation in multiple business telecoms offerings | Customers retention and keep eye on the environment | Have made eight acquisitions and new customers (6,600 in UK) | £10.4m (2010/2011) growing to £36.2m (2016/2017) |
P4
Social economy is the branch of economics that focuses on the relationship between social behaviour and economics. This shows that social norms, ethics and other social philosophies influence the consumer behaviour, shape the economy and use history, politics and other social sciences to examine potential results from changes to society or the economy.
Social Economy Businesses are: Charitable Organisation, Cooperative Society, Non-profit Organisation and Social enterprises (Susan W, 2017)
The business start-ups is with innovation focused to create a new market or change the existing market and generate wealth for founder and investors and create revenue, job and economic impact.
Most start – ups don’t define success in monetary terms, but in terms of community. Many of them are turning to foundations for start – ups money (Westphal, 2008) and operating as not-for-profit.
But the disadvantage is that the challenge of being the start-ups business in the market is that when working late hours during the initial phase of the business and when facing the extensive and dynamic competition it is really difficult to pave it way to the top in the corporate world.
The official figures show that most of start-ups are opportunity driven. Biz C., 2016
The small and medium business:
Small business may not produce as much money as large corporates but it is a critical component of and major contributor to the strength of local economies by bringing growth and innovation to the community in which the business is established as well providing employment opportunities. Larger businesses also often benefit from small businesses within the same local community and for completion of various business functions through outsourcing.
Small businesses give money back to the local community when they are patronised by the local consumers. Local business will generate high levels of revenue, which means that the business will pay higher tax, including local taxes. Then the money collected will be used for local police, fire brigade and schools, etc.
Small businesses can create and grow to become large corporations and as well can become major players nationally and internationally. Also can employs people who are not employable by larger corporations. Must train and attract new people to develop innovative products for the sake of the community. (SM Beheiry, 2006)
The challenge is that gaining access to the funding is difficult with banks and building societies becoming choosy over who to lend the money. It is difficult for SMEs – particularly start-ups and micro-firms – to prove they are not at risk.
For this reason they choose alternative lenders and loan firms in order to fund themselves. Susan W, 2017
M2
Businesses are all different in terms of profit, growth, turnover, size, innovation and sustainability (Aarno A, 2017)
- An example of one of a small business:
Southern Business Technologies Ltd Turnover that illustrate how the company is doing well
| 2016/2017 | 2015/2016 | 2014/2015 | 2013/2014 | 2012/2013 | 2011/2012 |
| £36.2 | £30.8 | £22.8 | £16.7 | £14.5 | £12.4 |
| 2010/2011 | 2009/2010 | 2008/2009 | 2007/2008 | 2006/2007 | 2005/2006 |
| £10.4m | £10m | £9m | £7m | £4.3m | £2.9m |
The company’s turnover started from £2.9 million to £36.2 million.
It is an active and private limited Company, specialised in wired telecommunications activities.
The management buyout was in 2002, since then the company is taking innovative advantage of new telecoms markets and has evolved dramatically from the original core product – phone systems, to multiple business telecoms offerings.
They provide the customers with full range of data products, business mobile and cloud based services.
In 2016, they were listed for the second consecutive year in Megabuyte50 Top 50 best performing privately owned technology companies in the UK mid-market.
- An example of one of a successful medium business:
Debenhams Plc
It is one of the longest clothing and goods retailers operating company in the UK. Founded in 1778, the company has 100 department stores in England alone and the annual sales of more than £1.3 billion in the British market – It is among the country’s top five retailers.
The Company has built a strong reputation among its customers for many generations and has restructured to play always the leading role by embracing the global market since 1998 (Rovnick N., 2018)
Debenhams as a British heritage, has a portfolio of over 100 successful designer and own brands; and has 82 stores in 26 countries outside the UK and Ireland (Sarah Butler, 2017)
They struggled a lot during 2017 and planned to cut jobs and close some of the stores.
The Company has changed the strategy to social shopping than the traditional one – With mobile the unifying platform for interacting with the customer as a new tool.
They have also refreshed and remerchandised to raise the profitability.
Sir Ian Cheshire, the chairman has said that “this is a strategy about growth and efficiency not job losses, and that the plans should lead to the creation of more jobs” (BBC NEWS)
The Body Shop (large size business) is founded in 1976 by the late British environmental and human rights campaigner Dame Anita Roddick, The Body Shop started life as a small outfit in Brighton selling just 25 products (2,500 stores around the world and more than 300 products). In 2006,
Roddick sold her company to L’Oréal for £652m. The same L’Oréal that is part part-owned by Nestle and continues to test new ingredients to animals. Roddick had never been a stereotypical beauty entrepreneur and when questioned about the selling of her company; she replied that The Body Shop would act like “Trojan Horse” or virus that could influence the huge business from the inside.
Sadnely, she died in 2007 leaving some nostalgia among women. (Anna C., 2011)
L’Oréal to sell Body Shop to Brazil’s Natura in €1bn (£877m) deal, and operates in 66 countries and has more 3,000 outlets, 133 of them in Brazil.
D2
The small business contribute to the strength of local economies (local venture) and present new employment opportunities by inducing innovation and growth.
Example: The small business can become large corporation, such as Nike is a major player in national (national venture) and international marketplace.
Nike was first manufactured nationally (USA) but now it is manufactured in Asia countries.
P5
The entrepreneurs are not born.
The entrepreneurs can be successful by harnessing crucial attributes. They can emerge at any stage of the life and from any realm, and they come in all personality types and with any grade point average.
Not all the entrepreneurs are created from the same blueprint. They come from different geographic, location, income brackets and social classes, as well as education levels.
You don’t need to be “type A” student to be successful in business because “type C” student can do better.
Focus on comparing yesterday to today to see what you have achieved – motivation
Create a network, collaborative bonds and emotional connections – strong ties to others (family, friends and colleagues).
Take care for the body and the mind; on the other hand tend to the body and spirit to be successful in your life – exercises, wall, sport or gym
The characteristics needed:
- The entrepreneurs are goal-oriented: setting goal and trying to achieve them.
- They are committed to their business: failure is an opportunity for future success.
- They are hand-on: inherently procreative
- Willing to take risks: not ask if they will succeed
- Trust in and respect for the team
The traits needed:
- They are passionate and full of positivity: passion is the most important trait for a successful entrepreneurial
- Resilience: from one failure to another with no loss of enthusiasm
- Strong Sense of self in terms of confidence.
- Flexibility in terms of time management.
- Vision in achieving objectives and goals.
The Skills needed:
- Focus: in terms of direction to follow and monitoring.
- Invest in long-term: to achieve the objectives and goals
- Find and manage people: the right people and use them effectively.
- Learn: learning the news products or services in the markets.
- Sell: put in place strategies to help sell the products or services.
However, the best entrepreneurs do share a collection of characteristics, from tenacity to the ability to tolerate risk, that are crucial to a successful venture.
The entrepreneurs have different personality traits than corporate managers, scoring far higher on traits such as openness to experience (curiosity, innovation) and conscientiousness (self-discipline, motivation) and considerably lower on neuroticism, which allows them to better tolerate stress.
The managers and the entrepreneurs play an important role in the business community.
But all of them share some of the same characteristics (passion, flexible, self-motivation, etc.) and both of them are concerned with business growth and success.
- Entrepreneurs are innovators in the industry, whereas managers will rely upon tried and true methods for running a business. Managers can be innovators, but they do not start new business or open new markets.
Entrepreneurs are inherent risk-takers whereas managers are not.
- Entrepreneurs tend to be visionaries. They turn their vision into reality. A manager has to concern himself with the vision of someone else.
P6
Personal entrepreneurial tendency
Most entrepreneurs have a natural tendency toward innovation and responsiveness.
They are hard-wired to challenge the status-quo in the society and in the minds of their target market (Gillaspie D, 2014)
The personality type are the traits and characteristics of your personality that blend with the needs of your business.
The education is very important to facilitate the new business motivation; as well to gain knowledge and skills.
The entrepreneurs have distinctive personality traits, motivation and values. The culture background, demographics and personal features all have link to the concept of entrepreneurial personality.
The personality traits which can link to business success according to Rauch, 2009 (extroversion, emotional stability, openness to experience, agreeableness and conscientiousness).
The research results have shown that student in developing countries are likely imagine becoming an entrepreneur in future and are more positive toward entrepreneurship than student in industrialised countries.
Entrepreneurs with higher motivation will show higher levels of risk-taking tendency due to their desire to fulfil their needs for self-actualisation even if the situation is full of uncertainty or unpredictability.
The role model in work place to whom all people will get inspiration is very important.
Individuals are different according to their gender, social-cultural background or their education, we can observe a difference in motivations for entrepreneurship or/and a difference in skills and behaviours. All society is composed of social and cultural groups.
There are diversity or variety in terms of race, religious belief, and political belief, gender, sexual orientation, nationality, etc. – will stimulate innovation (Hampen – Turner et al., 2010) and can influence the entrepreneurship.
When born in wealth family, there is a big chance those people can achieve their goal by becoming entrepreneurs due to the help from the family – positive mind set
The conclusion is that the personality has a positive impact on entrepreneurial motivation.
The entrepreneur’s personality profile is based on these 9 points (Darrell Z, 2016)
- The Advisor: provide high level of assistance and advice to customers. Customers are right and we must please them.
- The Visionary: will set up plans to avoid the landmines, and future vision.
- The Analyst: focus on fixing problems in a systematic way (computer firms, science and engineering)
Some example of mind-sets to help achieve the goal are:
- Learning is a continuous journey: learning many new skills.
- Love your business, but be objective: love doing long hours for the interest of the business.
- Start Now: start shifting your mind-set while you’re employed.
The entrepreneurs must take action, not get scare in any situation, be resourceful, obsess of cash flow, don’t ask permission, be fearless, welcome any change, love challenge, recover quickly when in difficult situations, listen to ideas that aren’t yours and focus on what matters.
The motivation is the key for the entrepreneurial behaviour to overcome difficulties and pressures. Dejun (2005)
The entrepreneurial motivation is the result by an individual variable factors and environment factors, management skills, management of resources, market conditions, business culture and policy support have an impact on entrepreneurial motivation. Suzuki et al. (2002)
M3
As explained above (P5), the entrepreneurs are not born.
The entrepreneurs can be successful by harnessing crucial attributes. They can emerge at any stage of the life and from any realm, and they come in all personality types and with any grade point average.
Not all the entrepreneurs are created from the same blueprint. They come from different geographic, location, income brackets and social classes, as well as education levels.
You don’t need to be “type A” student to be successful in business because “type C” student can do better.
As explained above (P6), the culture background, demographics and personal features all have link to the concept of entrepreneurial personality.
The personality traits which can link to business success according to Rauch, 2009 (extroversion, emotional stability, openness to experience, agreeableness and conscientiousness).
The research results have shown that student in developing countries are likely imagine becoming an entrepreneur in future and are more positive toward entrepreneurship than student in industrialised countries.
Entrepreneurs with higher motivation will show higher levels of risk-taking tendency due to their desire to fulfil their needs for self-actualisation even if the situation is full of uncertainty or unpredictability.
The role model in work place to whom all people will get inspiration is very important.
There are diversity or variety in terms of race, religious belief, and political belief, gender, sexual orientation, nationality, etc. – will stimulate innovation (Hampen – Turner et al., 2010) and can influence the entrepreneurship.
When born in wealth family, there is a big chance those people can achieve their goal by becoming entrepreneurs due to the help from the family – positive mind set
The conclusion is that the personality has a positive impact on entrepreneurial motivation.
There are characteristics needed and to be combined to start a business.
- Motivation: Are optimistic, enthusiastic and future-oriented. They are willing to risk their resources in pursuit of profit.
- Creativity and Persuasiveness: Creative capacity to recognise and pursue opportunities. They possess strong selling skills and are both persuasive and persistent.
- Superb Business Skills: They are focused on cash flow, sales and revenue at all times.
- Risk Tolerance: It is a risky venture but to reduce the risk you can do it by researching your business concept, industry and market.
- Drive: Be proactive in the approaches to everything.
- Vision: Know where the business should go in right direction.
An entrepreneur is responsible for several things. The risks associated with adopting and implementing new and innovative ideas may sometimes result in failure. Keeping this in mind, the success or the downfall of a company depends on the entrepreneur and therefore, it is a highly challenging task to always make the right decision.
D3
With reference and as explained in P5, P6 and M3, the entrepreneurs must be prepared of risk-taking and confident. The Body Shop is one of the best large successful Business.
P7
The business and entrepreneurship skills and experience affect the propensity of individuals to become entrepreneurs and the likelihood of their success.
The issue of business and entrepreneurship skills and competencies is closely related to broader questions related to skilled labour, migration and attitudes toward entrepreneurship. Suitable education programmes to help develop entrepreneurial mind-sets and company training in entrepreneurship skills are considered critical.
The main differences are:
- Difficulty to raise money: getting Bank loan is hard.
- Poor R&D and education investment: This makes it impossible for people to have a good will that will give a differentiating factor to their venture.
- Culture: People are naturally adverse to change and to risk.
The result of this is an over-demand of small businesses such hair salons, restaurants and grocery stores. There are third-world country companies targeting continental and global markets for sure; but because of what I mentioned previously, entrepreneurship is hindered.
Also lack of resources, lack of education, lack of customers, lack of access, lack of utilities and lack of security and corruption are the main issues that need to be sort it out in first place.
There are several risks that may come along with entrepreneurship. An entrepreneur is responsible for several things. The risks associated with adopting and implementing new and innovative ideas may sometimes result in failure. Keeping this in mind, the success or the downfall of a company depends on the entrepreneur and therefore, it is a highly challenging task to always make the right decision.
The risks are part of the game, without risks you cannot achieve your goals or get your business succeed.
Entrepreneurs with higher motivation will show higher levels of risk-taking tendency due to their desire to fulfil their needs for self-actualisation even if the situation is full of uncertainty or unpredictability.
The rewards are such the earning is limitless; you controlling your own financial destiny, there is opportunity to set up product pricing, set own salary and of employees and make decision in terms of investment and expansion.
But in developed countries with huge potential opportunities to study, to create employment, to have better social life, to communicate and the enforcement of the law to protect people whatever their background; it is quite ease to become an entrepreneur.
M4
The entrepreneur is someone who possesses a unique cocktail of traits, skills and characteristics that enable them to beat the odds and go after their dreams full throttle.
There are three categories of skills: basic, advanced and converging.
The basic skills are generic and routine skills present in most industries and organisations.
The advanced skills require more knowledge. They can refer to specific language and cultural skills that are of growing importance in certain multicultural working environments.
The converging skills it is a combination of basic and advanced skills, such as entrepreneurship skills (OECD, 2010).
But the disadvantage is that the challenge of being the start-ups business in the market because of working hard during the initial phase of the business. When facing the extensive and dynamic competition it is really difficult to pave it way to the top in the corporate world.
The advantage of having maximum control on the work you do can often help you gain maximum benefit.
Getting in the overall functioning of the host country can be challenging.
But through education policies, skills and experiences the entrepreneurs should overcome the challenge and be successful.
- The best example of Mohamed Al Fayed, Egyptian Business Magnate (Former Harrods owner, 2010).
He was ambitious and committed because he put huge amount of money for the success of his business; Mohamed Al Fayed, former Harrods’s owner illustrated how from a different background in the host country, he succeeded considerably.
He tried his best to achieve what it has achieved despite many problems surrounding his business.
He was a true leader with passion and risk-taker.
He sold it because of some government pension trustee constraints but he made huge profit (£1.5 billion).
- The Pierre Omidyar Way in 1995, French born, Iranian-American, a computer programmer started auctioning stuff on his personal website, made it a business Internet account after a while then started charging fees – Now the site is eBay and is successful.
D4
As explained in task 4 regarding background and experience and their impacts, the difference is huge in terms of adaptation in foreign country with many barriers compare to the national entrepreneurs.
Example of former Harrods boss, he was refused British citizen despite the huge work done through charities, sport and the economy in general. The British government by doing so, they had destroyed his ambitious and willingness to help – he sold the Foot-ball team (Fulham) and Harrods.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Hisrich R. D., 2009. Public and Private Sector Entrepreneurship. Glendale. USA
Kearney C., 2009. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, Vol: 16 Issue: ROI
Boot W. A., 2006. The entrepreneur’s choice between private and public ownership. The journal of finance. Vol: LXI, No 2
Tang J., 2000. Developing an Entrepreneurial Typology. Saint Louis University. USA
Kirby D. A., 2005. The international Entrepreneurship and Management Journal. Canada.
Miber J. B., 2000. The Journal of applied Behavioural Science. Journals. Sagepub.com
Mathias F., 2009. The Entrepreneurship. Germany
Gillaspie D., Entrepreneurs. Lover of Entrepreneurship. UK
Miller, D. (1996) Configurations Revisited. Strategic Management Journal, Vol.17: 505-512.
Ireland, Covin & Kuratko, 2009; Morris & Jones, 1999
Currie, Ucbasaran & McManus 2008, Kim, 2010
Drucker, 1985, Stevenson & Jarillo, 1990. Ney York
Mintzberg & Waters, 1985. The Entrepreneurs. USA
Robert J Sadler, 2000. The entrepreneurship and Business. Kentucky
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Business"
The term Business relates to commercial or industrial activities undertaken to realise a profit including producing or trading in products (goods or services). A general business studies degree could cover subjects such as accounting, finance, management and increasingly, entrepreneurship.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




