Effectiveness of the Existing Cloud Forensic Practices
Info: 8151 words (33 pages) Dissertation
Published: 11th Dec 2019
Tagged: Forensic ScienceCyber Security
CHAPTER 4: DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS
4.1 Introduction
Through this chapter, the data collection, analysis and interpretation of the results is outlined. As mentioned in the previous sections, the researcher has conducted systematic literature review on the secondary information sources for obtaining detailed knowledge on the effectiveness of the existing cloud forensic practices. The existing studies available on the research topic were identified using a search strategy and the relevant studies were identified using inclusion/exclusion criteria. The researcher with the help of the inductive approach could identify the similar patterns occurring in the systematic literature review and further it enabled in meeting the objectives of the study in an effective manner. Based on the findings emerging from the systematic literature review the chapter discusses the contradictions and similarities found during the examination in existing knowledge available on cloud forensics. Through cross examining the findings of the systematic literature review the researcher also outlines the inferences of the research findings.
4.2 Plan of Analysis
The studies relevant to the research topic were identified and these studies are critically evaluated in the systematic literature review. The methods used in the existing studies are critically evaluated along with the findings of these studies. The contributions made by the selected studies to existing knowledge on digital forensics were also assessed in the systematic literature review. Based on the review of findings of systematic literature review, the effectiveness of digital forensics practices used in cloud computing was identified along with the emerging challenges in cloud forensics.
4.3 Systematic literature review
One of the key studies which focussed on digital forensics was carried out by Sang (2013). The study focussed on developing a log-based forensic-friendly cloud computing model. Sang (2013) noted that the main deficiency of existing SaaS (Software as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service) models of cloud computing was the absence of a local log for the activities carried out in the cloud. Due to this, these existing models of cloud computing are not forensic-friendly as digital forensics rely on the log file information and other volatile information in the system. Moreover, existing SaaS and PasS services store user log files in a co-located manner while some services store the information across a range of devices. Due to this cloud forensics is very difficult in existing cloud services. Sang (2013) outlines log-based cloud computing model as a forensic-friendly alternative to existing SaaS and PaaS models. In this new model, a local log of the activities is retained in the user’s system and this log is synchronised with the log file of the Cloud Service Provider (CSP). This helps in reducing the challenge of cloud forensics as forensic agents can retrieve log information without consulting CSP’s. The main benefit of this proposed log-based model is that it can easily be integrated with PaaS and SaaS models.
The study of Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013) also focussed on facilitating efficient log retrieval in cloud setting for forensic investigators. The study outlined that cloud forensics was a challenging affair due to the multi-tenant nature of the existing cloud-models and black-box nature of cloud. Moreover, multiple users utilise the same processing and networking infrastructure at the same time making the retrieval of logs (process logs and network logs) an arduous task. Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013) note that some of the proposed strategies such as log API and cloud management console does not address the challenges associated with user privacy in cloud environment. Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013) proposes Secure-Logging-as-a-Service (SecLaaS) as an alternate approach to facilitating log retrieval in cloud environment. In this approach, CSP’s collaborate with forensic investigators to facilitate the retrieval of cloud logs without compromising the user privacy. Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013) tested the Secure-Logging-as-a-Service (SecLaaS) approach in Openstack which is an open source cloud computing platform and the results revealed that SecLaaS was practically feasible approach to resolving log retrieval challenge in cloud infrastructure. However, the practicality and feasibility of SecLaaS need to be further tested before adopting this as a standard cloud forensic tool. But the results of the preliminary test carried out by Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013) offers promising results regarding the efficacy of this approach.
The study of Zawoad and Hasan (2013) focussed on the challenges faced in cloud forensics. The study used meta-analysis approach to identify the main challenges faced by forensic investigators in cloud environment. The study identified that main challenges of cloud forensics involved lack of physical inaccessibility, CSP dependence, multi-tenancy, log decentralisation and inaccessibility of logs. The main challenges summarised in the study are given in the below table.
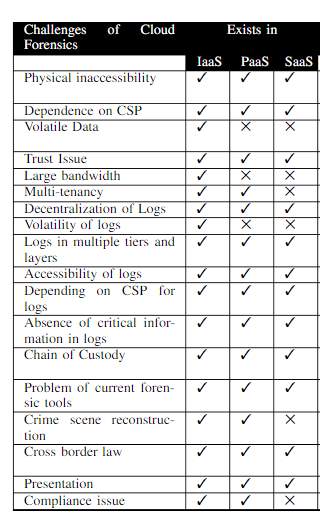
Figure 2 Cloud forensics challenges
Source: Zawoad and Hasan (2013)
The findings of Zawoad and Hasan (2013) revealed that majority of the cloud forensic challenges emerged from the physical inaccessibility and lack of log accessibility in cloud environment. Apart from these challenges that can be linked to the distributed nature of cloud infrastructure, cloud forensics also faces challenge regarding cross border laws. The user privacy and digital laws across the world lack harmony and hence forensic investigators face challenge in investigating cybercrimes that have international scope. Zawoad and Hasan (2013) have succeeded in summarising the main challenges in cloud forensics in an effective manner.
To identify the Digital Forensics Challenges associated with cloud computing, Lopez, Moon and Park (2016) conducted a literature study. The studies of Lopez, Moon and Park (2016) identified cloud computing as best in offering significant advantages to corporate bodies, and this included efficient allocation of the data in more reliable location, the accomplishment of business coordination, elimination of capital expenditure, accessibility to data from around the world etc. From the studies of Lopez, Moon and Park (2016) it was identified that the challenges faced by the cloud computing in the initial stages has been ruled out. However, as the cloud computing field is an emerging field the cyber criminals manage to exploit the challenges faced by it. Moreover, higher preferences of the firms to consider cloud computing for storing data were found as more favourable channels for the cyber criminals to gain access to the highly private and confidential data. The studies of Lopez, Moon and Park (2016) also identified that the operations of traditional computer forensics were largely limited to the detection and prevention of IT triggered frauds and thus fails to deal with the cyber-crimes occurring in the cloud computing units. The researchers have further found that dealing with the cloud computing issues was huge and challenging issues to the forensic investigators. According to the authors, some of the major issues confronted by the Forensic teams while dealing with the cloud computing frauds included difficulty in dealing with the personal resource allocation at various locations, limited domain, various legal issues in different countries, ineptness of forensic tools, high cost of operations etc.
Burney, Asif and Abbas (2016) conducted a research study to ascertain the digital forensic challenges in cloud computing. From the research studies of Burney, Asif and Abbas (2016) it was identified that the forensic investigation was highly challenged by legal, technical and architectural constraints. While summarizing the studies of Burney, Asif and Abbas (2016) it was found that the cloud service providers enable the firms to keep abundant of data in the network and this seems to be a desirable opportunity for the cyber criminals to hack the privacy and the confidentiality of stored data. It was identified from the studies that the cyber criminals may conduct scams and spread malware into the cloud platform for destroying the data and information. From the hypothetical case scenario of Burney, Asif and Abbas (2016) it was identified that mobile forensics, network forensics, cyber forensics, data forensics, email forensics, cyber forensics, web forensics and system forensics were the various forms of forensics investigations carried out to scrutinize the cyber-crime in the cloud computing units. From the study, it was also identified that lagging law and administrative issues were one of the main challenge confronted by digital forensics when dealing with the cloud computing issues. It was also identified from the studies of Burney, Asif and Abbas (2016) that, stenography and encryption were the major challenges faced by digital investigators from the technical view point.
Ghanam, Ferreira and Maurer (2012) has conducted a research study to identify emerging issues and challenges in cloud computing. According to the authors, the application of cloud computing has gained significant momentum in the IT industry particularly in managing the data more effectively. The cloud computing has offered promising benefits to the firms particularly in terms of reliability, security, complexity, costs, regulations, performances etc. However, through the research study, Ghanam, Ferreira and Maurer (2012) identified that the cloud computing currently has been facing a high rate of fraudulent issues which were highly intensive in destructing the privacy and confidentiality of the data. The study has identified that most of the critical issues associated with the cloud computing start when the user loses control over data. In the study of Ghanam, Ferreira and Maurer (2012) an extensive in-depth interview with the experts was conducted to gain a detailed understanding of issues associated with data management, data security and confidentiality in the cloud computing units. From the research study, it was found that the issues emerging from the cloud computing have increased over the past five years starting from 2007-2012. In the study, the researcher has classified the main cloud computing issues into twelve, and they were interoperability, security and privacy, learning and education, infrastructure, data management, economy, legal, trust, change management, software and service management. It can be concluded from the study that migrating legacy systems and Interoperability which demonstrates the lack of standard interfaces and service deployment interface were the main challenges in cloud computing.
The study of Zargari and Benford (2012) was focussed on the cloud forensic concept, the issues and the challenges that the concept might face during the performance. The study identified that cloud forensics had confronted certain issues like evidence trace in the multi-jurisdiction, multi replicas of stored information, the reliability and ownership of evidence and the maintenance of chain of custody all along the investigation. Zargari and Benford (2012) emphasised more on the security issues of cloud computing defining the multi-location issues and the gap in Service Level Agreement (SLA). The study has underlined the technical and legal dimensions depicting research and technical challenges in the cloud forensics such as loss of data, limited access to network routers and firewall installations, log analysis and accessibility challenges, information deletion and the malicious insider. Zargari and Benford (2012) noted the importance of cloud forensic tools interpreting that E-discovery tool could be used to locate, sought and secure evidence, utilising for legal and civil cases. The study has also mentioned that the current tools deemed to mobile cloud forensics are inefficient to extract data from cloud applications like Dropbox and Gmail.
Pichan, Lazarescu and Soh (2015) investigation of the cloud forensic concept outlined that cloud computing market is expected to achieve a growth rate of 30% in 2020 fuelled by the cost savings characteristics. The study has mainly concentrated in listing the major challenges in the cloud forensic process and significant solutions for the issues. The study entailed interpreted different digital forensic models such as Digital Investigative Process (DIP), McKemmish model, NIST Forensic model, Integrated Digital Forensic Process Model (IDFPM) etc. The study has referred the challenges and recommended solutions in various phases of the process including identification phase, preservation phase, collection phase, examination and analysis phase and reporting and presentation phase. Pichan, Lazarescu and Soh (2015) mentioned that ensuring the cloud evidence trust remained to be the biggest concern for cloud forensics along with challenges like a collection of deleted and encrypted information. The provision of comprehensive log management system was proposed as a solution for mitigating lack of log framework. Whereas the cloud key management infrastructure, AWS cloud trail supports aggregation of log files, security information and event management (SIEM) as solutions to encrypted data and evidence data integration.
The study of Ruan et al. (2013) entailed the cloud forensic capability related to the results of the survey. The survey was performedon international digital forensic experts and practitioners producing 257 responses. The survey has underlined the questions related to the definition of concepts like cloud computing and forensics, challenges and opportunities in the cloud forensics. In response majority of participants has mentioned the ineffectiveness of encryption management and the single points of failure. The study spotlight that survey respondents outlined vital challenges as the jurisdiction, international collaboration limitation, lack of a cross-nation legislative mechanism in data access and exchange and the challenges in cloud provider external chain dependencies. The study of Ruan et al. (2013) indicated that significant participants have agreed to the opportunities such as establishing policies and standards for forensics that can evolve with the technology and forensic as a service. Although, it was identified that more participants remained neutral towards the opportunity metric which was only able to collect 106 response.Moreover, the study outlined the need for cloud investigation tool kits and procedures and indicated the importance of staffing, agreement and policy facets in the cloud forensics.
Veeramachaneni (2015) conducted a study to evaluate the security issues associated with cloud computing and countermeasures in cloud computing environment. It is founded on this study that the cloud computing has great flexibility, low level of information technology overhead for the end users and low rate of total ownership costs. Veeramachaneni (2015) noted that the distributed resources are shared by cloud computing through the network in the open environment and which enhances the chances of occurring security issues. Cloud computing outsource the key services to a third party and which enhanced the level of security risks in the organisations like difficulty to maintain privacy and security of data, demonstrate compliance, service availability and support data. Veeramachaneni (2015) also mentioned that the main types of such security concerns are availability, confidentiality, data protection, software isolation, identity management, architecture and trust. The inefficiency of the cloud computing to attain these security concerns generate different threats on a cloud like session hijacking, denial of service attack, network intrusion, eavesdropping, misuse of cloud infrastructure, authentication, etc. Moreover, another key challenge associated with cloud security is Cloud Forensic.
The study of Badiye, Kapoor and Shelke (2013) mainly focusing on evaluating the major security and forensic issues of cloud computing. By reviewing this study, the researcher understood that cloud computing is highly helpful for accessing different varieties of applications from any system anywhere in the world at affordable costs. However, in cloud computing, users heavily depend on the provider, and the users have only limited control over their software. Insecurity of the stored information is another key disadvantage of cloud computing, and this created constrain for the users to recreate the stored information if the server goes out of service (Badiye, Kapoor and Shelke, 2013). The author mentioned that the cloud computing also generated issues for the users to transfer a high amount of information when migrating from one provider to another. From the study of Badiye, Kapoor and Shelke (2013), it is also clear that the main challenges associated with cloud computing are lack of relevant legal experience and forensic expertise. Moreover, cloud models have many easy-to-use features and which adversely affect the registration system and increases the chances of occurring abuses in the system. Thus, the cloud criminals can easily conceal their information and thereby generate constrain for tracing the criminals.
The study of Jain and Rana (2014) mainly focus on assessing the main challenges and issues associated with cloud forensics. The sudden rise of the offline and online users with various devices, most of the users choose cloud computing for storing users’ information. Due to the efficiency of the cloud computing for storing a large amount of information and low level of computing resources problems, usage of cloud computing in the organisations are increasing. According to Jain and Rana (2014), the increasing usage of cloud computing also leads to rise in the cyber-crimes associated with cloud. Hypervisor-level exploration, velocity of attacking, difficulty to access to large firewall, malicious nodes, difficulty to analyse the log of cloud applications, etc. are the main issues faced to complete mapping of events within the cloud computing environment.
The study of Grispos, Storer, and Glisson (2012) provided a detailed analysis regarding the challenges of cloud computing in digital forensics. The study outlined that cloud computing was a rapidly evolving information technology that provided the organisations with potential benefits. It highly played a crucial role in reducing fixed capital commitments, minimising the cost of IT services, reducing support requirements, eliminating redundant computing power and storage, etc. Further, it was also noted that various challenges were also faced while using the cloud computing. And almost all the organisations were highly concerned about the security of confidential corporate and private data and the cyber-crimes. Grispos, Storer, and Glisson (2012) also pointed out that cloud computing platforms were already a targeted area for malicious activities and evidence such as compromise of the Gmail email service by (alleged) Chinese hackers, Botnet attacks on Amazon’s cloud infrastructure etc. prove this fact. And the findings of the study also postulated that these challenges have highly led to the demand for digital forensic investigations and data retention and privacy laws. Thus, this paper with respect to the existing digital forensic investigation models also analyses the challenges emerged due to cloud computing.
The study conducted by Chaudhary and Siddique (2017) elucidated the various security issues and challenges encountered while investigating forensic cloud computing. The study also has revealed the numerous characteristic features of cloud computing such as resource pooling, virtualisation, scalability, customizability etc. The numerous applications of cloud computing such as e-learning, e-governance and cloud ERP along with various services offered through these applications was also highlighted in this study of Chaudhary and Siddique (2017). The service offerings include the Email simulation, customer relation management, supply chain vendors, employee management system, file broad casting and sharing etc. The study of Chaudhary and Siddique (2017) also showed that the different service models SaaS, PaaS and IaaS underwent certain security issues. The user control over the security was minimum for SaaS model and partially controllable for PaaS model and fully controlled for IaaS model. The various security issues and bugs were identified in the applications, and the security problems were identified with data encryption and backup in SaaS model. The security issues in an end to end reporting and logging, data leakage and infrastructure hardening were observed with IaaS model and the PaaS model encountered with security issues in the web hosting developmental tools and third-party web services. The forensic challenges occurring during the cloud computing investigation are concerned with the control of the physical evidence involving data gathering, validation and preservation.
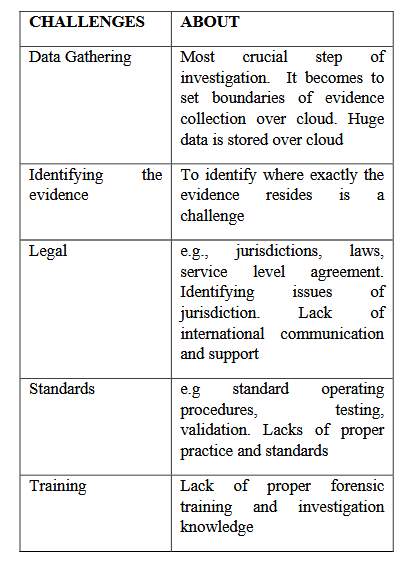
Figure 3 Challenges during cloud forensic investigation
Source: Chaudhary and Siddique (2017)
The study conducted by Reilly, Wren and Berry (2011) focussed on evaluating the pros and cons for computer forensic investigations with respect to cloud computing. It was found from the study that cloud computing helped organisations to migrate their data to the cloud thereby providing high speed access. The study also revealed that computer forensics was mainly employed by law enforcement agencies for attaining digital evidences related with the cybercrimes. As per the observation of the authors the centralised data and virtualisation was the major advantage of cloud computing and virtualisation highly enabled to share the same resources among multiple users. Further the study also identified that the major drawbacks of cloud computing was data acquisition and loss of important artefacts. Also, the lack of tool support and legal aspect of computer forensics also created issues. Reilly, Wren and Berry (2011) also noted in the study that Association of Chief Police Officers (ACPO) guidelines for the computer investigations and electronic evidences highly aided in computer forensic investigations.
4.4 Analysis and interpretation
The premier objective of the current study was to identify the forensic and security challenges of cloud computing which were outlined majority of the studies that have illustrated in the systematic literature review. Examining the thoughts of authors Zawoad and Hasan (2013) study has concentrated on the challenges and used a meta-analysis data for identifying the forensic investigation challenges. The physical in accessibility, multi-tenancy, CSP dependence and log inaccessibility and decentralisation. The author has summarised the main challenges representing in a table and pointed out the challenges from cross border laws. The studies of Lopez, Moon and Park (2016) showcased that the company’s higher reliance on cloud computing has created a channel for cyber criminals in gaining access to the confidential information. The authors have also mentioned the difficulties faced by the forensic investigators in dealing with such cyber-crimes. Burney, Asif and Abbas (2016) study on the notion has also reflected the challenge metric is underlining legal, architectural and technical as the pivotal constraints to the investigation. The authors have also noted the lagging of law and administrative constraints as critical challenges to the cloud forensic investigation corroborating the facts of Lopez, Moon and Park (2016) study.
Examining the study of Zargari and Benford (2012), it could be interpreted that the study has also focused on the challenges faced during cloud forensic performance. The issues noted by the authors were evidence trace, multi-jurisdiction and presence of multiple replications of stored information. Zargari and Benford (2012) views reflected the multi-location, security issues and service level agreement gap as more important challenges for the concept. Thus, the study has allayed with the previous authors in the technological and legal challenges. Zargari and Benford (2012) study has also outlined various other challenges such as access limitation to the firewall and network routers, challenges in log analysis and malicious insider. Analysing the study of Ruan et al. (2013) which entailed the result of a survey performed on digital forensic experts indicated that jurisdiction, limitations in international collaboration and cross-nation legislation and accessing of data as the key challenges for cloud forensics. The studies of Rana (2014) also mentioned the difficulties in firewall access and malicious nodes thus support the thoughts of Ruan et al. (2013). Whereas the views of Grispos, Storer, and Glisson (2012) purported the malicious challenge in the notion and Chaudhary and Siddique (2017) underpinned the security challenges.
Hence the study analysis in understanding the challenges to cloud forensic implies that the log management, accessibility issues in the firewall, jurisdiction issues precisely in the cross-nation data collection are the major issues in practice.
By reviewing the study of Sang (2013), it was identified that lack of local log for the activities undertake in the cloud is the main reason for the deficiency of existing PaaS (Platform as a Service) and SaaS (Software as a Service) models of cloud computing. Digital forensics depends on the log file data and other volatile information in the system, and thus SaaS and PaaS models of cloud computing are not forensic-friendly. The log- based cloud computing model, is a forensic-friendly alternative to existing SaaS and PaaS models. In this model, a local log of the activities is retained in the user’s system, and this log is synchronised with the log file of the Cloud Service Provider (CSP). This assists in minimising the challenge of cloud forensics. By reviewing the study of Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013), the researcher identified that Secure-Logging- as-a- Service (SecLaaS) is an alternate approach to facilitating log retrieval in a cloud environment. It was also understood from the study of Zawoad and Hasan (2013) that, lack of physical inaccessibility, CSP dependence, multi-b tenancy, log decentralisation and inaccessibility of logs are the main challenges of cloud forensics.
In the light of challenge analysis, it was identified physical accessibility is a vital facet in the cloud forensics, and Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013) has mentioned the use of efficient log retrieval cloud settings. The study outlines the previous methods like log API and cloud management console utilised to achieve the outcome and alleged that the models were not able to address the challenges related to the cloud environment and user privacy. The study has also proposed Secure-Logging-as-a-Service (SecLaaS) approach for successful retrieval of log in a cloud environment. The approach also emphasises on the collaboration of CSP with the forensic investigators facilitating the log details without compromising the user privacy. Zargari and Benford (2012) mentioned the E-discovery tool for evidence seeking, locating and securing however argued that current tools used in the mobile cloud forensics are not efficient enough to tackle the challenges posed by the cyber criminals. On the other hand, Pichan, Lazarescu and Soh (2015) outlined certain solutions for mitigating the lack of log framework such as the introduction of comprehensive log management system, AWS cloud trail supports aggregation of log files and security information for efficient data encryption and event management (SIEM) for evidence integration. Hence the analysis indicates the scope for improvement in the cloud forensic tools.
CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
5.1 Introduction
Through this concluding chapter of the dissertation, the researcher delivers the evaluation of the different interpretations of the findings attained through this study. This section primarily reviews whether the systematic literature review performed on the effectiveness of the prevailing cloud forensic practices has able to meet the formulated objectives of the research. The identified issues learned from the analysis assists the investigator to provide recommendations to enhance the cloud computing practices are also elucidated in the final portion of this chapter. The constraints encountered during the conduct of the research problem as well as suggestions to the prospective researchers to perform the study with more efficacy will also are elucidated in the study.
5.2 Conclusions
By collecting adequate and reliable secondary information, the researcher has summarized the main findings of the research study based on research objectives.
Objective 1: To evaluate the key security and forensic challenges related to cloud computing
By critically evaluating the studies of Veeramachaneni (2015), Badiye, Kapoor and Shelke (2013) and Jain and Rana (2014), the researcher understood that, in cloud computing, the computing resources problems are comparatively very low and it is highly helpful for storing a large amount of information. It was noted that the cost-effective nature of cloud computing, great flexibility, low level of information technology overhead for the end users, etc. increases the usage of cloud computing; however, it also results to rise in the cyber-crimes associated with cloud. By reviewing the studies of Veeramachaneni (2015), it was identified that session hijacking, denial of service attack, network intrusion, eavesdropping, misuse of cloud infrastructure, authentication, etc. were the main security issues associated with cloud computing. The researcher also understood that, in cloud computing, the users have only limited control over their software. Moreover, cloud computing does not ensure the security of the stored documents and which generate barrier for effectively handling the data and for recreating it when the server is down. It was also found that, while migrating from one provider to another, the users face constrains to transfer the huge amount of information (Badiye, Kapoor and Shelke, 2013). Similarly, from the literature review analysis, it was identified that difficulty to ensure data integrity and confidentiality, legal constraints, difficult to recover data, etc. are the key security and forensic challenges related to cloud computing (Ruan et al., 2013; Xu, 2012; Rittinghouse and Ransome, 2016; and Zawoadand Hasan, 2013). By identifying the correlation between the various literature findings, the researcher successfully attained this objective of the study.
Objective 2: To analyze how digital forensics has evolved to tackle the security challenges posed by cloud computing
The second objective of the current study was to analyse how digital forensics has evolved to tackle the security challenges posed by cloud computing. It was understood by the researcher from the systematic literature review that the major security challenges posed by the cloud computing include difficulty in dealing with the cloud computing frauds, in handling personal resource allocation, various legal issues in different countries, insecure APIs, Malware Injection, abuse of Cloud Services etc. The studies by Zargari and Benford (2012) noted that cloud forensic tools could be used locate, sought and secure evidence, utilising for legal and civil cases. Similar findings were observed from the literature studies. Russ (2015) pointed out in the literature studies that cloud computing practices could be used in facilitating the events associated with the forensic investigation such as for legal and civil cases. It was seen from the studies of Sang (2013) that digital forensics relies on the log file information rather than volatile information in the system. Similar findings were observed from the literature studies. It was reviewed the studies of Rittinghouse and Ransome (2016) that digital forensics should make use of system and application logs for identifying the pieces of evidence. He also added that for making this possible suitable logging mechanism must be used. In line with this observation Sang (2013) pointed out a new cloud computing model named log-based forensic friendly cloud computing model that enables to retrieve log information without consulting the CSP’S. Also, it was observed from the studies that existing cloud computing models such as the SaaS (Software as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service) models failed to rely on the log file information. The studies by Zawoad, Dutta and Hasan (2013) also pointed out a model named Secure-Logging-as-a-Service model to tackle the security challenges posed by cloud computing. Thus, it can be said that the researcher has successfully met the second objective of the study.
Objective 3: To assess the effectiveness of existing cloud forensic practices
The purpose of the third objective was to assess the effectiveness of prevailing cloud forensic practices. From analysing the various systemic literature review performed, the researcher observed that the study of Lopez, Moon and Park (2016) revealed that cloud computing provided prominent advantages to companies for effective data allocation trustworthy location, minimising of the capital expense, data accessibility throughout the world. By examining the study of Asif and Abbas (2016), it was comprehended that cloud services benefited the organisations to maintain a huge collection of information in the network. Similarly, from the study of Ghanam, Ferreira and Maurer (2012), it was identified that cloud computing had presented various advantages to the companies particularly IT firms regarding reliability, complexity, security, performance and cost efficient. The study conducted by Chaudhary and Siddique (2017) showed that cloud computing at present are widely employed and preferred as it would minimise the labour cost about 50% in maintenance and monitoring, improves the utilisation effectiveness through virtualisation, lowers the completion time as well as would make the project cost low. It was also analysed from the literature study of Rittinghouse and Ransome (2016) showed that cloud computing is effective and beneficial in offering virtualisations and thus uphold the potential to reshape the IT procedures. It was also found in the study that cloud computing ensures trouble free scalability, cost savings and greater availability. Therefore, it was observed that the systematic literature findings have similarities with the existing literature study indicating that the researcher could meet the third objective.
5.3 Recommendations
- To adopt Secure-Logging-as-a-Service (SecLaaS)
It has been found from the study that the same processing and networking infrastructure was utilised by multiple consumers at the same time making the retrieval of logs as a difficult task. Thus, for facilitating log retrieval in the cloud environment, all organisations are highly recommended to adopt Secure-Logging-as-a-Service (SecLaaS) as an alternate approach. This practically feasible approach will highly aid firms to resolve the log retrieval challenge in the cloud infrastructure.
- To enhance CSP collaboration
The studies also revealed that the physical inaccessibility was the main challenge faced by forensic investigators in the cloud environment. Thus, to overcome this challenge, it is highly suggested to organisations to enhance the collaboration between the cloud service providers and forensic investigators. The collaboration with the forensic investigators would also highly facilitate the retrieval of cloud logs without compromising the privacy of the users.
5.4 Limitations of this study
The current topic for examining the effectiveness of existing forensic cloud computing practices has solely relied upon the numerous secondary resources and has not incorporated any primary data gathering techniques like survey or interview which could deliver more reliable and credible findings on the topic. The researcher faced some restriction in availing more information on the forensic cloud computing practices and diverse security challenges concerned with it due to the insufficiency of prevailing studies on this topic. The researcher also confronted with limited time by which the researcher could utilise only about 15 cases on this topic to conduct systematic literature study. The inadequacy of money also created an obstacle to access some significant journals and articles on the topic.
5.5 Recommendations for future works
The future researchers performing research on this topic could make utilise of primary information gathering methods like interview or survey to attain more reliable facts on the forensic cloud computing practices. The researchers may also avail more number of studies to do a comprehensive systematic literature review which enables them to obtain more valid conclusions for the research. The researcher by availing greater financial resources could incorporate more number of journals and articles demanding payments regarding the forensic cloud computing practices. It is suggested that upcoming researchers should make the best utilisation of time management so that the more number of systematic literature studies could be reviewed for enhancing the knowledge on forensic cloud computing practices.
5.6 Global applicability
The use of cloud has increased exponentially across the globe and the cloud services offered across the globe varies depending in the information technology infrastructure of the country. Most developed countries have advanced security and forensics features in the cloud whereas the developing and under developed nations still uses the older security features which creates vulnerability to the cloud in those regions and the cyber- criminals uses this vulnerability and they exploit the cloud services. The competition between CSP in these countries are very high and to capture the vast market most of the CSP does not focus more in the security features so that they can provide economical services to the individual users. The recommendations made in this research plays a vital role in the global context as these recommendations are more essential for the developing nations than the developed countries. The feature of SecLaaS plays a key role in the developing countries as they are more vulnerable to more cyber attacks.
References
Ab Rahman, N.H. and Choo, K.K.R. (2015) A survey of information security incident handling in the cloud. Computers & Security, 49, pp.45-69.
Ali, M., Khan, S.U. and Vasilakos, A.V. (2015) Security in cloud computing: Opportunities and challenges. Information Sciences, 305, pp.357-383.
Babatunde, Y. and Low, S.P. (2015) Research Design and Methodology. In Cross-Cultural Management and Quality Performance (pp. 93-113). New Jersey: Springer.
Babbie, E. (2010) The practice of social research.12th ed. Belmont: Wadsworth.
Badiye, A., Kapoor, N. and Shelke, P. (2013) Some forensic & security issues of cloud computing. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 3(10), pp.91-96.
Burney, A., Asif, M. and Abbas, Z. (2016) ‘Forensics issues in cloud computing’, Journal of Computer and Communications, 4, pp.63-69.
Chaudhary, O. and Siddique, A. S. (2017) Cloud computing application: its security issues and challenges faced during cloud forensics and investigation. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science, 8(2), pp. 12-15.
Chen, D. and Zhao, H. (2012) March. Data security and privacy protection issues in cloud computing. In Computer Science and Electronics Engineering (ICCSEE), 2012 International Conference on (Vol. 1, pp. 647-651). IEEE.
Chen, Z., Han, F., Cao, J., Jiang, X. and Chen, S. (2013) Cloud computing-based forensic analysis for collaborative network security management system. Tsinghua science and technology, 18(1), pp.40-50.
Columbus, L. (2017) 2017 state of cloud adoption and security. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/louiscolumbus/2017/04/23/2017-state-of-cloud-adoption-and-security/#513a3ef41848 (Accessed: 11 August 2017).
Daniel, L.E. (2012) Digital Forensics for Legal Professionals: Understanding Digital Evidence from the Warrant to the Courtroom. New York: Syngress.
Daryabar, F. and Dehghantanha, A. (2014) A review on impacts of cloud computing and digital forensics. International Journal of Cyber-Security and Digital Forensics (IJCSDF), 3(4), pp.183-199.
Dawson, C. (2009) Introduction to research methods: a practical guide for any undertaking research project. 4th ed. London: Sage Publications.
Edson, M.C., Henning, P.B. and Sankaran, S. eds. (2016) A guide to systems research: Philosophy, processes and practice (Vol. 10). New York: Springer.
Enisa (2016) Exploring Cloud Incidents. [ebook] TLP GREEN, pp.1-14. Available at: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/exploring-cloud-incidents/at_download/fullReport (Accessed: 07 September 2017).
Ennajah, H. andChow, E. (2016) Cloud Forensics. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology Research. 4(2). pp. 47-58.
Ghanam, Y., Ferreira,J. and Maurer, F. (2012) ‘Emerging issues & challenges in cloud computing—a hybrid approach’, Journal of Software Engineering and Applications, 5, pp.923-937.
Grant, M.J. and Booth, A. (2009) A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26(2), pp.91-108.
Grispos, G., Storer, T. and Glisson, W, B. (2012) Calm before the storm: the challenges of cloud computing in digital forensics. International Journal of Digital Crime and Forensics, 4(2), pp. 28-48.
Ho, A.T.S. and Li, S. (2015) Handbook of Digital Forensics of Multimedia Data and Devices. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Jain, S. and Rana, T. (2014) A review of cloud forensics issues & challenges. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science & Technology, 2(3), pp.55-57.
Ketchen, D. and Bergh, D. (2009) Research methodology in strategy and management. Bingley, U.K: Emerald.
Kumar, R. (2010) Research methodology, a step by step method for the beginner. London: Sage.
Lopez, E.M., Moon, S.Y. and Park, J.H. (2016) ‘Scenario-based digital forensics challenges in cloud computing’, Symmetry, 8(107), pp.2-20.
Madsen, T.L. and Walker, G., (2015) Modern competitive strategy. New York:McGraw Hill.
Maltby, J., Williams, G., McGarry, J. and Day, L. (2014) Research methods for nursing and healthcare. Abington: Routledge.
Maxwell, J.A. (2012) Qualitative research design: An interactive approach(Vol. 41). Sage.
McCafe, (2016) Building Trust in a Cloudy Sky-The state of cloud adoption and security. Available at: https://www.mcafee.com/us/solutions/lp/cloud-security-report.html (Accessed: 11 August 2017).
Myers, J.L., Well, A. and Lorch, R.F. (2010) Research design and statistical analysis. London: Routledge.
NIST (2014) NISTCloud Computing Forensic Science Challenges. Available at: http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/drafts/nistir-8006/draft_nistir_8006.pdf (Accessed: 07 September 2017)
Pichan, A., Lazarescu, M. and Soh, S.T. (2015) Cloud forensics: Technical challenges, solutions and comparative analysis. Digital Investigation, 13, pp.38-57.
Pluye, P., Gagnon, M.P., Griffiths, F. and Johnson-Lafleur, J. (2009) A scoring system for appraising mixed methods research, and concomitantly appraising qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods primary studies in Mixed Studies Reviews. International journal of nursing studies, 46(4), pp.529-546.
Punch, K.F. (2013) Introduction to social research: Quantitative and qualitative approaches. London : Sage.
Quick, D. and Choo, K.K.R. (2014) Data reduction and data mining framework for digital forensic evidence: storage, intelligence, review and archive.
Reilly, D., Wren, C. and Berry, T. (2011) Cloud computing: pros and cons for computer forensic investigations. International Journal Multimedia and Image Processing (IJMIP), 1(1), pp. 26-34.
Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., Nicholls, C.M. and Ormston, R. eds. (2013) Qualitative research practice: A guide for social science students and researchers. London: Sage.
Rittinghouse, J.W. and Ransome, J.F. (2016) Cloud computing: implementation, management, and security. CRC press.
Ruan, K. (2012) Cybercrime and Cloud Forensics: Applications for Investigation Processes. London: IGI.
Ruan, K., Carthy, J., Kechadi, T. and Baggili, I. (2013) Cloud forensics definitions and critical criteria for cloud forensic capability: An overview of survey results. Digital Investigation, 10(1), pp.34-43.
Russ, J.C. (2015) Forensic uses of digital imaging. CRC Press.
Sammons, J. (2014) The Basics of Digital Forensics: The Primer for Getting Started in Digital Forensics. 2nd ed. New York: Syngress.
Sammons, J. (2014) The Basics of Digital Forensics: The Primer for Getting Started in Digital Forensics. Waltham: Syngress.
Sang, T. (2013) A log based approach to make digital forensics easier on cloud computing. In: Intelligent System Design and Engineering Applications (ISDEA), 2013 Third International Conference, pp. 91-94. May, IEEE.
Sareen, P. (2013) Cloud computing: types, architecture, applications, concerns, virtualization and role of it governance in cloud. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 3(3).
Veeramachaneni, V.K. (2015) Security Issues and Countermeasures in Cloud Computing Environment. International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology (IJESIT), 4(5), pp.82-93.
Walliman, N. (2010) Research methods: the basics. Abington: Routledge.
Weinman, J. (2015) Digital Disciplines: Attaining Market Leadership via the Cloud, Big Data, Social, Mobile, and the Internet of Things. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Xu, X. (2012) From cloud computing to cloud manufacturing. Robotics and computer-integrated manufacturing, 28(1), pp.75-86.
Zargari, S. and Benford, D. (2012) Cloud forensics: concepts, issues, and challenges. In Emerging Intelligent Data and Web Technologies (EIDWT), 2012 Third International Conference on (pp. 236-243). IEEE.
Zawoad, S. and Hasan, R. (2013) Cloud forensics: a meta-study of challenges, approaches, and open problems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1302.6312.
Zawoad, S., Dutta, A.K. and Hasan, R. (2013) SecLaaS: secure logging-as-a-service for cloud forensics. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGSAC symposium on Information, computer and communications security, pp.219-230. ACM.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Cyber Security"
Cyber security refers to technologies and practices undertaken to protect electronics systems and devices including computers, networks, smartphones, and the data they hold, from malicious damage, theft or exploitation.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




