Fundamentals of Cyber Security
Info: 9161 words (37 pages) Dissertation
Published: 24th Feb 2022
Tagged: Cyber Security
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
LITERATURE REVIEW
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Explain the core information assurance (IA) principles
1) Identify the critical components of cybersecurity network architecture
2) Risk management processes and practices
3) Identify security tools and hardening techniques
4) Different Types of attacks
5) Define types of incidents including categories, responses, and timelines for response
6) New and emerging IT and IS technologies
7) Threats Analysis and risks within the context of the cybersecurity architecture.
8) Appraise cybersecurity incidents to apply appropriate response
9) Evaluate decision-making outcomes of cybersecurity scenarios
10) Access additional external resources to supplement knowledge of cybersecurity
CONCLUSION
References
INTRODUCTION
Cybersecurity also known as information technology security is the technique of protecting systems, programs, and networks from digitally designed attacks. Cyber-attacks are mainly aimed at gaining access to digital data without the knowledge of data owner, destroying digitally stored data, manipulating data, soliciting for money from data owners, and interrupting the normal functionality in the cyber and general information technology field (Singer, 2014). Putting across effective cybersecurity measures has become a complex role in the modern world with many devices than people, and the cybercriminals have largely innovated in the techniques (Singer, 2014).
Cybersecurity is generally the practice of putting into place system control measures to ensure that integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information in the technology world. It enables users to detect, defend and recover from cyber-attack practices hence staying safe from drive failures, virus attacks, and from attacks initiated by adversaries (Singer, 2014). Therefore, it is mainly concerned with the protection of information, systems, programs, and networks from major cyber-threats (Singer, 2014). The threats take many forms, for example; ransomware, exploit kits, phishing, and malware attacks. The complexity has come from the launch of automated and sophisticated attacks by cyber adversaries through the application of the different threats.
The techniques work by developing multiple layers of protection which are spread across the computers, networks, programs, or even data that is to be kept safe and free from the diverse cyber-attacks (Singer, 2014). Due to the complexity that has been reported in the cyber-crime field, keeping pace with the cyber-security against the threats is a great challenge mostly to government and enterprise networks. Cyber-attacks have some attacks which are common in the large technology world which include: Cyberterrorism- this is the use of information and technology by the terrorist in their attacks. Cyberwarfare- a threat which is employed by nation-states through information and technology to disrupt another states’ information technology network. Cyberespionage- is the most applied technique by individuals in the information and technology field to gain access to other people’s data without their permission (Singer, 2014).
LITERATURE REVIEW
Cybersecurity is mainly cyber-risk management mechanisms which access the risks which the information and technology field suffers and comes up with effective mechanisms to prevent and protect user systems, data, network, and programs from damages which are presented by cyber-attacks. In the modern technological world with extensive advancement in technology and its related fields, it is important to have a cyber-security mechanism put in place in both private and public sectors, as well as in organizations. Frequent check on any cyber threat is a considered as an assessment of the risks which the same comes along with (SentinelOne, 2017).
Historically, Bob Thomas in his research project developed that it is possible for a computer program to move across a network, leaving a stream of its impact on all the networks it passes through. He went ahead and designed the program under the name Creeper which he designed to travel between the Tenex terminals on the early ARPANET, with the message “I AM THE CREEPER: CATCH ME IF YOU CAN”.
As the program traveled across systems and computers, it landed to Ray Tomlinson, the guy who founded the email and he liked the idea. He took it over the program and gave it a self-replicating mechanism which identified it as the very first computer worm. From the same idea, he wrote on Reaper, another program which was the first antivirus program to which was to go after Creeper and delete it. Computer security faced threats for much of the 1970s and 1980s with the main threat coming in the form of malicious insiders which stole access to documents which were not theirs. On the other hand, network breaches and malware existed and were used for malicious purposes in the early history of computers (SentinelOne, 2017). Such threat saw the Russians employing cyber power as a weapon to fight against all malicious programs which had been developed. Marcus Hess a Germany computer hacker in 1986 hacked an internet gateway in Berkeley and made a bypass to connect to piggyback on the Arpanet. He successfully hacked 400 military computers and extended to mainframes in Pentagon, with an aim to giving out their secrets to the KGB at a fee. His attempts were detected by Clifford Stoll, an astronaut who employed the honeypot technique through which they were able to catch the intruder of their computers.
Over a long while in the history of cyber security, computer viruses were only known to be academic pranks, but all that was changed as a result of the previous encounter which showcased how they were a threat (SentinelOne, 2017). The same was perpetuated by the growing network connectivity which made it possible for viruses to be passed across networks, programs, and systems effectively. The main virus of the day was the Morris worm which nearly wiped out the early internet and this initiated moves to develop the first antivirus software. In 1988 cybersecurity recorded a viral era with the Morris worm as the main virus which had carried successful attacks. The Morris worm was written by Robert Morris who aimed to gauge the extent covered by the internet. Therefore he wrote the program with the ability to move across networks, the program was able to infiltrate UNIX terminals using a bug then copy itself in the successive attacks.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Technology growth and modernization in the current world is experiencing improvements day in day out hence in every day numerous programs are designed and incorporated into the systems. Such growth and development are significant and central to benefits, wellbeing, and security in the society. The benefits and significance which states can get from their growing digital society have been realized in the UK as a result of its strong research base, supportive government, and history of industrial success. Although the benefits and significances are well known they are under the risk of cyber threats mainly because systems which organizations have in place to fight against the threats lag behind the advancements which are being made by the cyber threats. This has seen the purpose of having systems in place which will enable organizations, public and private institutions, and the government to keep their digital data safe.
Cybersecurity aims at fighting all programs which have been developed to interfere with digital data, and this is ensured through the development of counter programs which will serve fight against the attacking programs to serve the following themes which are mainly in ensuring that the digital data society is secure and stable. The themes are:
i) Verification and assurance; (“Research | Oxford University – Cyber Security Oxford,” 2018) this is aimed at improving trust which the society has on digital data which is key to user satisfaction. Assurance mainly targets risks which relate to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information by digital means.
ii) National, international security, and governance; (“Research | Oxford University – Cyber Security Oxford,” 2018) this mainly addresses how politics, governments, and the international relations maintained by states concerning data society.
iii) Secure systems and technology; (“Research | Oxford University – Cyber Security Oxford,” 2018) this are attempts being made in the data society by building a good technology with the aid of cloud security, cryptography, mobile security, wireless security, trusted platforms, and secure coding paradigms.
iv) Identity, behavior, and ethics; (“Research | Oxford University – Cyber Security Oxford,” 2018) this is an attempt by information technology specialists to design systems which will require authentication while accessing digital data. This is to make sure that cases of data interferences which are resulting from malicious data access are stopped.
v) Operational risk and analytics; (“Research | Oxford University – Cyber Security Oxford,” 2018) this theme is mainly in developing on the risks which result from cyber-attacks and staying prepared for the same with mechanisms which will enable them to stop such attacks as well as staying free from the risks.
Explain the core information assurance (IA) principles
Information assurance applies and defines a collection of standards, policies, methodologies, mechanisms, and services to maintain a mission, respect and integrity to people, processes, information, technology and supporting infrastructure. The main reason for information assurance is that only the authorized people can access particular information at a specific time. The information can either be in storage, processing or transit (Steinberg, 2016). The main principles of information assurance state the fundamental objectives for managing risk. Information assurance can is built on nine core principles namely Confidentiality, integrity, availability, possession, authenticity, utility, privacy, authorized use, and non-repudiation.
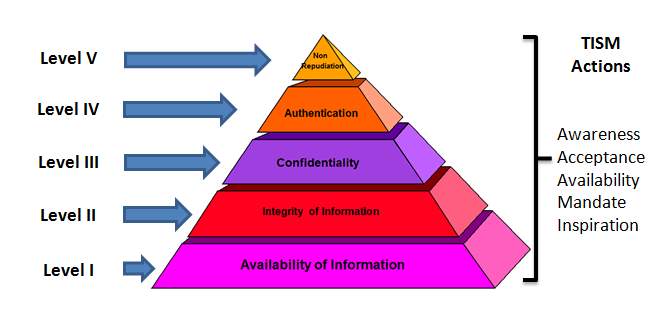
Confidentiality ensures that information is disclosed only to authorized people. One method that can provide privacy of information is encryption. For data at rest or on storage devices, access control can be sued to ensure confidentiality. Data cannot be accessed if the system that contains cannot be located. Integrity is another principle of Information assurance. It ensures that information maintains its originality. In the process of transmission, information can get into wrong hands and thereby get corrupted either inadvertently or for malicious reasons (Willett, 2008). The inadvertent corruption can occur due to errors that occur during transmission. One of the best methods to ensure the integrity of information is cyclical redundancy. Intentional corruption can occur by altering important data on a set of information. Encryption can minimize this.
Availability as a core principle of information assurance ensures that information always ready to use. A denial of service attack may mark an application or a server (Willett, 2008). In case it gets successful it may render the application or server unavailable. This principle, therefore, ensures that any application or server is available when it is needed. Possession mainly safeguards the physical aspect of an asset. With this, information will remain in the custody of an authorized person. Loss of possession occurs due to theft or misplacing a system. Therefore, physical safeguard is the efficient way to guarantee a property.
Authenticity mainly ensures the reality of information. This means that the information in question is not in any way misrepresented or put in a situation that it was not expected to be. To safeguard against falsehood, deception, and imitation, one has to ensure authenticity (Ghosh, 2009). Utility, on the other hand, provides that information or information system continues to be of use. Information may conform to all the principles of all information assurance, but it may not be usable. This implies that information may available, remain in possession of the authorized owner, is confidential but it may be useless. An example is a case where a hard drive is encrypted if the password is forgotten the information on the hard drive cannot be used.
Privacy is another core principle of information assurance. It may be considered as part of confidentiality but taking into consideration its level of sensitivity, it requires its attention. The issue of privacy will continue to be on the rise due to the cases of technology pervasiveness. Authorized use is another principle which safeguards against theft of service (Willett, 2008). This principle ensures that there is the protection of the accessibility of services which can incur a cost to the business. The core principle of information assurance includes non-repudiation due to the increase in legal agreements and online transactions. Nonrepudiation ensures that there are means in which two parties can transact without failure to deny the transaction later. Maintaining the inclusion of non-repudiation in logs is an important part of trust in the online transaction. Therefore, non-repudiation ensures that there is no denial by the service requestor of taking part in a transaction.
1) Identify the critical components of cybersecurity network architecture
Cybersecurity architecture can be described as the unified security design that aims seeks to address the requirements and any potential attacks which can occur in a particular environment or situation. Additionally, it also gives instructions on where and when to use the security controls. A practical and efficient security architecture consists of three components (Buecker, 2011). They include processes, people, and tools which work hand in hand to safeguard the organization assets. For these components to be aligned appropriately, the policy stating management performance expectation should drive the security architecture.
The first component of cyber security architecture is guidance which is aimed at areas of baseline configuration, incident response account creation, and management. The cybersecurity architecture must be developed and applied considering the already established security procedure. This company procedure and policies should be able to note down and communicate the goals and objectives of the management concerning the architecture (Refsdal, 2015). The company should define its response to standards and law. A clear security policy is essential in ensuring the organization can implement the factors that can support architecture.
Identity management is a unified system of companywide processes and policies that enable access for the user to online applications and network resources. As part of the identity management system, a clear security procedure need to be implemented for the users of the company. Inclusion and exclusion is another component of cybersecurity architecture. Cybersecurity architecture should safeguard all the functions of the organization’s IT environment. This ranges from confidential human resources data to publicly accessible web and email servers. To address this issue, it is essential that a reliable architecture is positioned that can account for who is has the authority to access which system (inclusion) and who has no power to access a specified system and data (exclusion).
Another component is the Access and Border Control. Information technology access and organizational resources should be governed by multiple layers. This is from abroad and general level to granular and discrete level. One important thing that helps in access control is preventing the popular of the users at the edge of the network and authorizing only the known business associated and workers to come through. Once in the business environment, restriction of access to the specific area should be done.
Regular training helps empower people and keep security concerns in people minds. It allows people to be updated with the emerging practices, trends, and management expectations. Naturally, people are helpful and look out for performing there efficiently work (Killmeyer, 2006). However, to them, security is a significant hindrance to their work and give minimal attention to the potential risk they face. The hardware and software used to organize, manage, and control the security architecture is the component that is mostly associated with security. However, the security architecture that is purely based on technology and does not consider the processes and people may not work very well. The constant change of technological innovations has got a new solution that is frequently developed to counter the current concerns. In case of technology change, the change effect should be evaluated to determine if any changes need to be done.
2) Risk management processes and practices
International organization for standardization defines risk as an effect of objectives or uncertainty. Risk management is the continuous process of identifying, assessing and responding to risk. To conduct risk management an organization needs to evaluate the likelihood of an event and then to determine the best approach to deal with the fact.
Risk assessment is the first step in the risk management process. Risk can be assessed identifying the vulnerabilities and threats. This is followed by determining the likelihood and impact of each risk. In this case, it is important to designate a team of individuals who understand the company’s mission to assess and manage cybersecurity risks periodically (Refsdal, 2015). Before you determine the risk, it is essential to classify information asset in the company. After categorizing the information asset, the organization needs to identify the threats. A threat is a force, person or organization which has sought to compromise, gain or access information. By determining the nature of the threat, one can assess it. It is important to be aware of the threats to your organization data to prevent unauthorized access. The organization will then identify the vulnerabilities. This is weaknesses in a system that stores or transmits information. The organization will then analyze the risk to information assets.
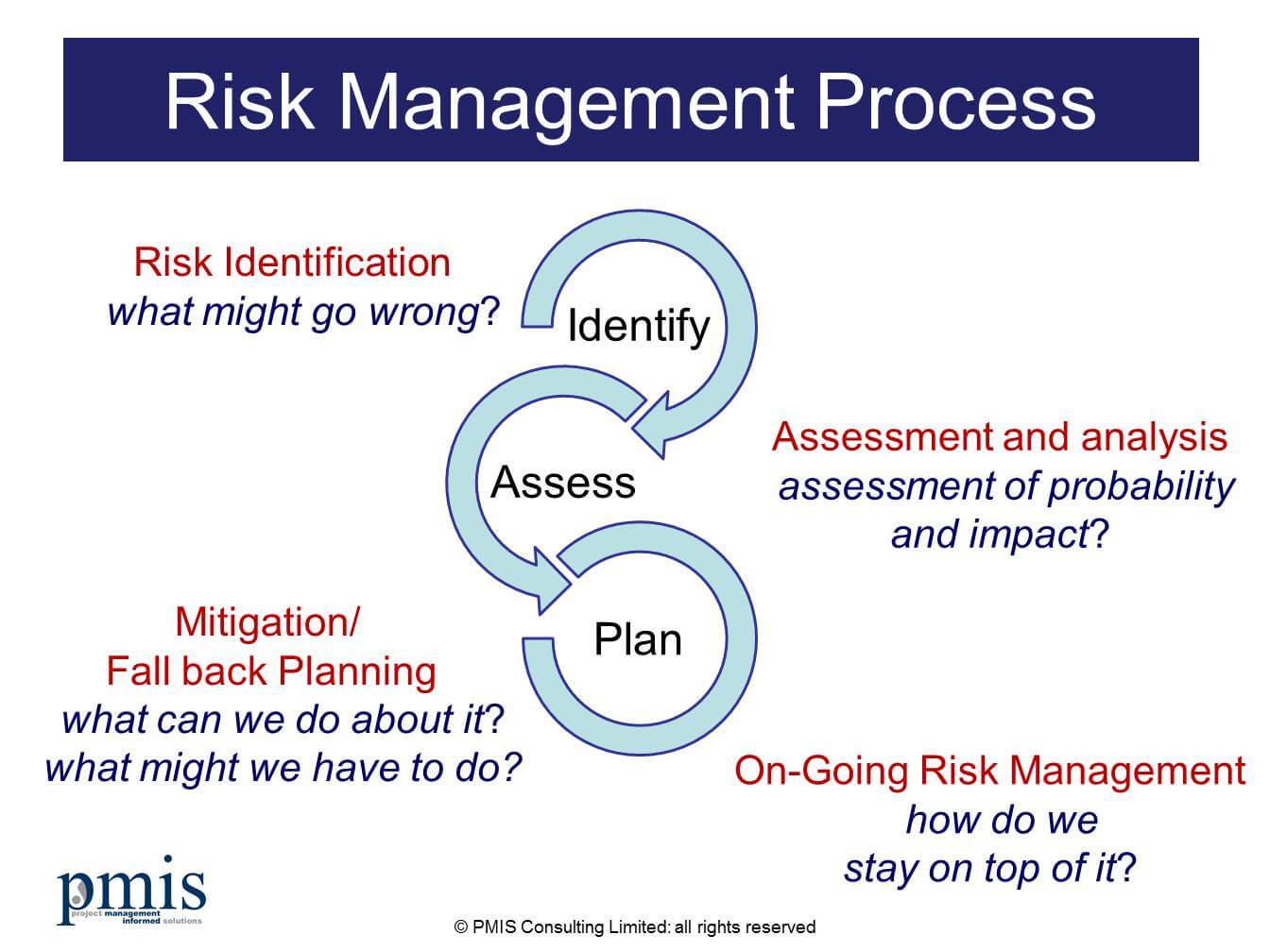
Risk mitigation is the next stage in risk management procedure. Risk mitigation is the process of taking action against the sources are people who want to corrupt and compromise the confidentiality and availability of valued information assets (Wheeler, 2011). One of the steps in risk mitigation is the identify options. Once the risk to information asset has been measured, the organization must decide on how to mitigate the risk. They can choose t to accept, limit, transfer or avoid the risk. Another mitigation effort is implementing the option. This involves putting into practice the choice that was made for mitigating the risk.
The final step in the risk management process is an evaluation. In this case, the team that was designated to carry out a risk assessment and mitigation should ensure that the choice to mitigate the risk for each identified information asset has been put into action. An annual review can be done annually to ensure that the controls put in place are viable and functional in the protection of information asset.
3) Identify security tools and hardening techniques
To minimize the increasing number of dynamically emerging cyber-attacks, information systems need to get hardened. Security hardening is the process of enhancing information systems (Rex, 2016). A proper security hardening procedure will enforce a shied from cyber-attacks and in turn minimize the attacks. Hardening involves the removal of unnecessary process and disables unwanted services. Two of the essential areas that need hardening are services and ports. Hardening activities can be categorized into network, server, application, operating system and database hardening. The default configurations of most operating systems, servers, applications and network are not designed with a focus on security. The default mainly focuses on usability and functionality. Therefore, this means that without hardening, information will run high-security risks.
The primary focus of network hardening is to reduce the cyber-attack surface of the network. When you disable or remove the unused and unneeded software packages or network packages, there is considered the minimal risk that the remaining packages could be compromised in case of an attack (Elleithy, 2010). Some of the techniques in network hardening are installing a firewall between the internet and the network. Access control lists and Network Address Translation need to appropriately used, and the organization should enable the authorized remote access through the use of secure tunnels and virtual private networks. Clock synchronization is an important aspect of network hardening. To harden the network wireless and routers need to be protected with strong passwords. Wireless systems need to be configured to the highest available security level.
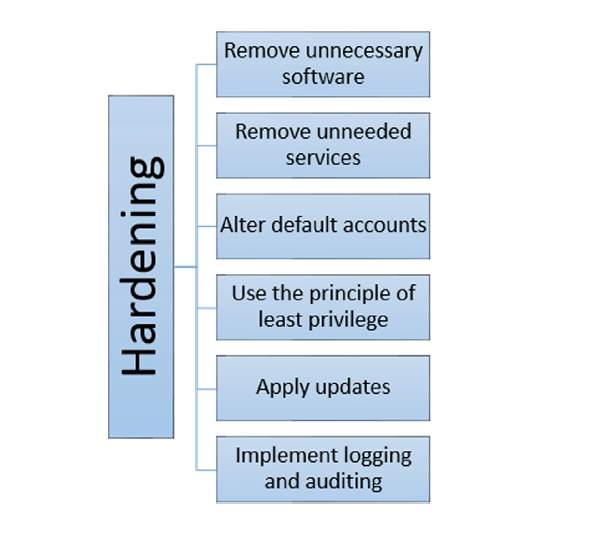
Server hardening involves boosting server protection using a valid and viable means. This is essential in keeping the data and operating environment protected at all times. Server hardening can be done by placing the server in a physically secure location. Just like all the security measures, server hardening becomes understandable when you realize all the risks that are involved (McMillan, 2016). To protect your server, you need to establish a sophisticated and reliable server hardening procedure for all servers located in your premise. Creating a server hardening checklist will likely to be your initial step. Some of the techniques that work well with an organization that is performing server hardening are making sure that Domain Admins are members if the local administrator’s group. It is also important to conduct a periodic penetration test to ensure that vulnerabilities are being minimized fully. It is also essential to avoid installing applications on the server unless they are necessary to the server’s function. For instance, prevent the installation of email clients, utilities, and office productivity tools that are not required by the server to work. It is also essential for you to use network interfaces on the server. One will be for the network, and the other will be for the administrator.
Another category of hardening is the application hardening. This is the process of securing applications against local and Internet-based attacks. Applications hardening can be implemented by elimination the functions or the components that they don’t need. Access can be restricted and applications updated with patches (Elleithy, 2010). Maintaining application security is vital because the applications need to be accessible to users. Some of the proven methods of application hardening involve, avoiding the use of insecure protocols for processing requests, especially those that send passwords in plain text. You can also implement Active directory which allows only one login to several applications servers and data sources.
Databases store critical and sensitive data. Loss of data or incorrect data could negatively affect business operations. Databases can be a target to cause harm to other systems. Some of the proven database hardening techniques involve turning on admin restrictions to ensure specific commands cannot be called remotely (Rex, 2016). User accounts standards can be defined and enforcing password policy. Database hardening can be done by having a TNS listener Password encrypted to prevent unauthorized administration of the Listener.
Operating system hardening is another category of hardening. Hardening the server should start by hardening the operating system. Operating system hardening helps in minimizing the cyber-attack surface of the information systems but disabling functionalities that are not required while maintaining the minimum functionality that is needed. Some of the proven operating system hardening techniques include supporting the operating system updated with the most robust and latest versions. This also provides for the updating of hotfixes and security patches (McMillan, 2016). Periodically. You can also remove unnecessary drivers, disabling non-essential services and delete unnecessary accounts quarterly. Appropriate settings have to be configured for access control on file shares; given authority is set through NFS security features.
4) Different Types of attacks
A cyber-attack can be referred to as an attack on the information system by an external entity. They can be seen to target government, organizations, companies, and individuals. The primary goal of hackers is to compromise or steal sensitive data such as social security numbers, credit cards, and other personal identity information. There are six classes of cyber-attacks. An essential element of cyber security that should be considered is knowing that the threats and networks that they face evolve with time and engage.
Malware and ransomware are one of the most popular classes of cyber-attacks. Malware and ransomware attack computers to steal confidential data. Malware exists in multiple forms. If malware is introduced into the system, it causes the actual damage, and the loss could compromise by erasing all the information that is stored in the hardware. Other malware is a target for individuals who are not in the Information Technology field and may not have sufficient knowledge on the sophisticated level of the attacks or even pay attention. Malware scams unveil by installing software on a system that gives the scammer the authority to access files or monitor what is going on a specific computer. Ransomware is the type of malware limits you access to the data and the network. It then demands ransom money that is paid to the scammer for it to be unlocked. This is never a guarantee. The simple way to safeguard against ransomware and malware is to make sure that all the firewall security is functional and uploaded consistently. Users should also refrain from clicking any suspicious links on the internet.
Phishing and spear phishing are other popular types of cyber-attack. In phishing event, hackers send authentication looking emails and text messages to the target people or organization to steal financial and personal data. The letters often instruct people to validate, inform or confirm an account. The audience of phishing is always indiscriminate and broad. The target of spear-phishing is still private individuals. Small organizations can protect the business against phishing by training their employees on how to recognize the signs and avoid risky behavior on the internet. To curb phishing, understanding the significance of verifying email senders and links is essential. Ignoring genetic looking request for personal data can also combat phishing.
Denial of service DoS attacks is mostly targeted at large corporations. The main aim is ways to shut down the website or system in question. In the DoS, the scammers exploit the weakness of a system and use it to send large amounts of data to the entire system until it cannot function normally. This operation is done from a single computer. When it comes to a distributed denial of service, the scammers use multiple computers. This operation is trying to overcome due to the attacker appearing from many IP addresses around the world altogether. It makes determining the location of the attacker hard. An example is if you flood a website with a significant amount of traffic that it cannot hold. In this case, the website’s server will be overloaded, and it will be impossible even its content of visitors. Compacting DoS and DDoS attacks require the organization to update software regularly. It is also essential in monitoring the flow of data to see if there are any cases of unexplained spikes in traffic. Companies can also purchase bandwidth which can manage traffic spiking or particular that are created for the detection of DDoS attacks.
Man-in-the-Middle MITM attacks occur when hackers impersonate end users to obtain sensitive data. The attacker does this by altering communication between two users and mimicking both of them to manipulate them and gain access to their information. The users are not aware that they are being managed. A good example is when an attacker tries to send customers an email by impersonating the representative of their bank or email the bank by impersonating the customer . This operation can be done by gaining access to both parties through a non-encrypted wireless access point. Therefore, small businesses should be sure to use WAPs, WPA2s for their wireless systems. It is also essential to install intrusion detection system IDS.
Structured query language SQL is a programming language that provides communication with the database. Most of the servers that provides storage for essential data for services and websites make use of SQL to manage the data in their databases. A SQL injection attack mainly targets this kind of servers. It uses malicious codes to get the server to reveal information that is private.
5) Define types of incidents including categories, responses, and timelines for response
A security incident is the warning that there may is a threat to computer system or data. The signal can also say that the threat has already been made. Computer security incident is a threat that aimed at policies which are connected to the computer security (Payne, 2011). There are different categories of security incidences. One of them is the Compromised Computing Resources which defines the user account compromises and system account compromises. Email based abuse spells unsolicited Commercial email which is popularly known as spam. Phishing emails which have sought to have the recipient respond with either user credentials or personal information. Another type of incident is the network and resources abuses which define network scanning activity and denial of service attacks. There are incidents of resource misconfiguration and abuses. It includes aspects of open proxy servers and anonymous ftp servers and the abuse which comes through blog sites and web forms. Some are a misuse of licensed resources.
Incident response is a formally organized approach to dealing with all kinds of security incidents. It always includes an incident response plan (IPR) (Payne, 2011). The IPR lays down the procedure that an organization should take to follow after an incident has occurred. Some of the response to an incident include preparation in which case the company develops a set of policies, communication, response plan and access controls. The nets phase is identification where the organization will detect unusual activity and determine whether it qualifies as a security incident. The next step is containment. Once a situation is considered an incident, the next phase is to contain the incident to prevent more damage. Eradication phase includes the elimination of malicious code and repair any caused damage.
The next response is recovery which occurs after the incident has been eradicated. This involves bringing systems back online gradually taking into consideration measures that will prevent the incident from happening (Payne, 2011). After the systems have become operational, the response team should document the incident and find ways to prevent similar attacks from happening.
6) New and emerging IT and IS technologies
Just like computing, information security is evolving. The building of information security into applications is essential in addressing significant risks. It is also crucial for devices that are interconnected from the very beginning (Elleithy, 2010). Some emerging technologies will boost the security of information systems from being compromised by hackers.
One emerging trend in Information security is the endpoint hardware authentication. It is true that the majority of usernames and passwords of data users are weak. It opens an easy way to for hackers to access the information systems and compromise sensitive data of a business entity or government agency. The proliferation of mobile computing, hardware tokens, removable storage media, and IoT has increased the rate of cyber threats in an attempt of gaining access to user credentials, personally identifiable information intellectual property and other highly sensitive data (Akhgar, 2013). The technology response to this kind of issue comes in for of hardware authentication. In this case, unique identifiers are coded into the hardware itself. With this, it gives each device its digital fingerprint. Tech gurus have created a solution for user authentication process with a core vPro processor that belongs to the sixth generation of processors. The processor can combine multiple hardware components with enhanced factors at the same tin=me for user identity validation purposes. Hardware authentication can be useful when it comes to the Internet of things IoT where the network of connected devices ensures that any device that wants to be connected has the rights for connectivity to that particular network.
Another technology trending is cloud computing. Cloud technology has a significant effect on the transformation of systems security technology. Most organizations and government agencies have adopted cloud technology to store an enormous amount of data that they generate in their daily activities. Securing the clod, in this case, can occur in some levels. At one point, there is an emergence of cloud-based equivalents to the kind of security measures traditionally deployed on-premises (Rex, 2016). Virtualization technology may permit the development of intrusion detection, firewalls, specialist security hardware and prevention systems. It is with options for generating or destroying virtual security cases on a period by period basis. Additionally, there are setting up quality assurance levels and standards for enterprise cloud distributions. Companies such as Information Systems Audit and Control Association provides industry-specific frameworks or certifications which can be allocated to service providers. It allows enterprises a more open view of their security position before they obligate a contribution.
For example, both private and public entities doubled center security by the use if IaaS services such as Firehost and Amazon. Another example is the certified secure enough services that are based on the cloud is the GSA Fed-RAMP. It makes it easier for the small to medium-sized business enterprise to have a data security center that is above average.
Deep learning is another trend in information security. Deep learning incorporates a series of technology such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. Respective of its name, it has a great deal in its security reason (Bhalla, 2017). Similar to behavior analytics, Deep learning has its focus on anomalous behavior. When machine learning systems and Artificial intelligence are fed with the required data regarding potential networks security threats they can make choices on how to avert hacks which depends on the immediate environment without any human input. Entities are scrutinized instead of users that have access to the information system. The newest creation in the machine learning technology and exact business analytics means that we can now be able to analyze the multiple entities that are located in the enterprise at both the micro and macro levels. Organizations and government agencies can be able to stamp out any persistent or advanced cyber-attacks using the artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Almost all successful threat originates from browser and internet chased threats are among the leading source of threats to users (Bhalla, 2017). Information security experts may not top the attack but can contain the damage by dividing enterprise endpoints and networks from end-user internet browsing sessions. Separating the browser function keeps off malware of the end user’s system, and the enterprise has meaningfully minimized the area for attack by shifting the risk of attaching to the server sessions. It can be reset to a known good state on every new browsing session, a tab opened or URL accessed.
7) Threats Analysis and risks within the context of the cybersecurity architecture
What is cybersecurity architecture? Cybersecurity architecture is a type of a unified system which seeks to address the potential threats and risks or necessities which exist in a particular scenario or environment. The system design of cybersecurity architecture is also used to specify when and where to install security controls. In this world of technology and computers, the internet has become part of our day-to-day life. Various activities ranging from online banking, online shopping, sending and receiving emails, social networking, downloading stuff, online businesses and many more are all done on the internet. It leaves us with a question whether it is secure to do all these things on the internet, which is not regulated and that one can get into or out of very quickly without a trace. Using the internet involves many risks and threats to our daily activities and even lives. This raises the alarm about how one can protect himself/herself from these risks. There are many risks involved when it comes to cybersecurity, and these include hacking, phishing, malware attacks, pharming, botnets, spam and fraud, worms, Trojan horses, viruses, spoofing, among many others.
Cybersecurity has been an issue of paramount interest over the course of some years up to date. Companies all over the world are affected by the effect of cybersecurity as everyone is prone to attack by cybercriminals. Large companies face the most significant threat of a cyber-attack mainly because they deal with vast amounts of money. This does not necessarily mean cybercriminals cannot pursue that small companies and individuals. Cybercriminals may attack small businesses mostly because managers do not think that their companies are worth much to be corrupted by cybercriminals. This is the loophole that cybercriminals use to attack small companies and entities mostly. One thing is for sure, that cybercrime is not ending soon but will advance and become more sophisticated and hence the need to install security controls that will help protect businesses. The risks and vulnerabilities involved put the companies’ financial situations in a compromising position yet still endangering the future of these companies.
The risks and threats involved in cybersecurity architecture are many. These risks are explained in the following lines. One of the most vicious risks is hacking. Hacking is a process where a malicious person tries to attain unauthorized access to another person’s computer. Hacking may be successful or not depending on how strong a person’s computer is. The stronger the combination, the longer it might take to crack that combination. Phishing is the use of fake emails, texts, and websites which look like those from authentic companies. These fake websites are used to collect personal details and passwords which help criminals steal financial and personal details about someone or a company.
Malware is an attack carried out by a cybercriminal to try and expose a system’s weaknesses. It can be regarding computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses, spyware and such. A malware attack is meant to infect a computer’s functioning system by deleting files or carrying out commands from a cybercriminal. Spam is a form of unsolicited texts, emails, pornography pictures and all the other junk that is unwanted. They are used to share links useful in phishing or spoofing or even share malware which threatens the privacy of an individual. Another risk that faces companies and most firms is the risk of internal human attack. Employees can aid an attack most likely because they can easily be intimidated or enticed. Managers, therefore, need to be on high alert about the issue of employees facilitating cybercrime to the company. With all these risks and threats, managers of companies and individuals require to take caution and protect themselves and their companies from external or internal attacks. Installing stronger passwords, avoiding clicking unknown links and files can help promote security control over one’s data.
8) Appraise cybersecurity incidents to apply appropriate response
With the advent of cybercrime on companies, installing more measures has become crucial in this era of hacking and technological advancement. Companies must prepare adequately on how to deal with and respond to cases of attempted infiltration into their databases. Managers must be ready to undergo a lot to eliminate, even though not permanently, cybercrime in their companies. A company must select a team that will help in dealing with the cases of cyber-attacks and other cybersecurity incidents. This paper makes an effort to discuss the various types of responses that a company or a small firm can have to help counter and deal with cybersecurity incidences.
The Cybersecurity Incident Management Team of a company helps to monitor the enterprise network of the company and yet dealing with incidences of cybersecurity 24/7. The Cybersecurity Incident Management Team makes an analysis of data and incidents of cybersecurity, performs and prioritizes escalations to the proper stakeholders, performs suppression and mitigation steps and carries out the recording facts throughout the incident (Information Security Policy Templates, 2016). The Cybersecurity Incident Management Team obtains, carries out analysis and acts upon the intelligence about the threat from internal teams of the company and also from external partners (Information Security Policy Templates, 2016). The Cybersecurity Incident Management Team collaborates with the Security Architecture, Information Technology, and Network Administrations, and ensures the Company’s systems and infrastructure fulfill the guidelines and security policies, (Information Security Policy Templates, 2016).
Companies should stay aware of the environment of cyber threats to help in executing the right strategies for mitigation. Companies should access their abilities to handle cases of cybersecurity incidences. Upholding a present security risk management plan for data security systems is authoritative. This security risk management plan aims at reducing the overall risk to organization information systems. The security risk management plan should consist of: assessing main assets and data, recognizing risks evaluated to those assets,
Companies should also carry out training programs to their employees on how to deal with cases of cyber-attacks. These training programs are specifically designed to help equip employees to understand, recognize and react in the best possible way to threats and vulnerabilities of cybersecurity. The training programs emphasize the significance of cybersecurity as a shared responsibility and concentrate on the supply of appropriate data (Information Security Policy Templates, 2016).
Companies should also make use of ethical hacking procedures to help strengthen the security controls of those companies. Ethical hacking is the locating of vulnerabilities and weaknesses in computer systems done by an ethical hacker who tries to bypass the installed security system and look for flaws which can be used by other hackers.
9) Evaluate decision-making outcomes of cybersecurity scenarios
Scenario planning is an essential aspect in the realm of cybersecurity. Cybersecurity scenarios can range from being hacked, spammed with phishing emails and fake website addresses all with the intent to gain some data out of it. Managers of companies have to employ special tactical teams to help deal with the cybersecurity menace. These teams are faced with difficult times when making decisions on how to overcome cybersecurity scenarios yet at the same time improving the company’s security system of controls. The decisions made during cybersecurity scenarios either by the Cybersecurity Incident Response Team or by managers themselves have some outcomes for the company be it financially, or progress-wise. These decisions vary from one company to another and so results will also differ from one company to the other. This paper makes an effort of assessing the outcomes associated with the decision-making process of cybersecurity scenarios.
The outcomes of decision making during cybersecurity scenarios can either be positive or negative. How can decision making have positive results? When the tactical teams deployed to deal with cybersecurity scenarios are faced with difficult choices during a cybersecurity event, the decision that the tactical response team makes can either push the company’s objectives towards the required direction, or the decisions can lead the company backward. Decisions made by the team can be confident in that they propel the company forward. Decisions made during cybersecurity scenarios are important as they can help strengthen a company’s or an individual’s security of their information.
The outcomes of the decisions made during a cybersecurity event can range from improved security system of the company, reduced losses due to theft, protection of customer information, enhanced competition with the company’s rivals, protection of company secrets from outsiders. At the individual level, decision making during a cybersecurity event will help one to protect themselves and their information from malicious attacks from hackers and other cybercriminals. If an individual decides to ignore a possible cyber security scenario, the outcome of this decision may cost that particular individual a lot, and by a lot, I mean the loss of finances, assets and being spied on.
How can decision making have adverse outcomes? When a tactical cybersecurity incident response team decides to ignore a specific threat by rendering it not to be harmful, it leaves a weakness in a company’s security system, and this can be the starting point of a breach into the company’s database. This can lead to a loss regarding profits, customer information and a company’s blueprint for success. A manager should perform check and balance on the decisions made by a company’s incident response team to make sure that they will bring positive outcomes along with them.
10) Access additional external resources to supplement knowledge of cybersecurity
With the recent developments in the cybersecurity scope, companies and individuals must aim at gaining experience and acquiring more and more intelligence on how to deal with the new advancements in cybercrime. There comes the need to access more information, recent news and stories about what is happening related to cybersecurity around the world. Companies, therefore, need additional external sources to assist in gaining more knowledge about cybersecurity. This paper describes the external resources for expertise on cybersecurity that company managers and individuals might get information about cybersecurity from.
The Australian Center for Cyber Security (ACCS) is uniquely crafted research and educational center for cybersecurity. The Australian Center for Cybersecurity aims at providing cutting-edge lasting intelligence in cybersecurity albeit research, engagement, and education.
The Computer Security Resource Center (CRSC) is a part of the Computer Security Division (CSD) and assists in the mass sharing of information tools and practices of security. CRSC is a resource for providing information security guidelines and standards. The Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) was listed as the top global Security, and International Affairs think tank in a 2011 report of ‘The Global Go to Think Tanks.’ The CSIS is a think tank based in the U.S.A., and it focuses on issues relating to global security and international relations. Symantec Security Response is a worldwide team made up of threat analysts, researchers and security engineers who develop a broad scope of content about the latest threats that can have impacts on organizations.
The Information Security Magazine has been listed as the only resource for information which gives instant access to virus alerts, breaking news about cybersecurity, new hacker threats or attacks, webcasts, compliance to security standards, security certification training resources and several others all at no cost. The Information Security Magazine is the best resource dedicated towards the success of IT professionals. The Center for 21st Century Security and Intelligence is another additional resource important in supplementing knowledge of cybersecurity. This research center was established to address the main issues which will help mold security policies over the next coming decades.
CONCLUSION
Cybersecurity is a system that is comprised of controls, processes, and technologies which are developed to stand against cyber-attacks and protect networks, data, and systems from the risks associated with the phenomenon. Hackers and other cyber-attack perpetuators have greatly innovated towards coming up with new mechanisms to launch and spread their attacks as well as extending success and damage. Cyber-attacks are done with diverse purposes which range from deleting, manipulating, accessing, and illegally disclosing digital data, hence breaching the principles which are in place for any information. Such threats may serve to destroy the image of organizations, government units, and important persons.
Cybercriminals employ a number of techniques to carry out their attacks. They include social engineering which is the use of lies and manipulation to drive persons towards revealing their personal information, phishing is an example; Botnet- which is the use of a robot network to spread a malware; skimmers- they are devices mainly employed in the banking industry to steal credit card details; denial of service- a practice which is made by flooding the website to make it inaccessible by its appropriate users. Cybersecurity is continuously innovating at the same phase as cyber-attacks to match their technology since that is the only way it will effectively stop the risks posed by such attacks to digital data users.
Examples of cybersecurity issues
In 2016, Uber Company experienced a breach which exposed 57million personal information of cyber users and 600,000 drivers. The hackers who attacked the systems were able to get in touch with email addresses, names and mobile phone numbers of fifty-seven users of the Uber application. They got driver’s license numbers of over 600.000 drivers. They were not able to get in touch with the social security numbers and credit cards. The company tried to keep the breach secret until a year after when they disclosed the breach. Adobe company also experienced a breach in October 2013 which affected about 38million. The breach was serious that it took the company several weeks to figure out the scale of the breach. The hackers were able to encrypted customer credit cards, login data for an undetermined number of user accounts. Yahoo company also experienced an attack in 2014 which compromised the real names, dates of birth, email address and phone numbers of 500million users. It was later found that the hackers compromised 1 billion yahoo accounts. The passwords were not well protected which created a security vulnerability.
References
Akhgar, a., 2013. Emerging Trends in ICT Security. s.l.: Newnes.
Bhalla, P., 2017. Space Security: Emerging Technologies and Trends. s.l.: KW Publishers Pvt. Limited.
Buecker, A., 2011. IBM Security Solutions Architecture for Network, Server, and Endpoint. s.l.: IBM Redbooks.
Elleithy, K., 2010. Advanced Techniques in Computing Sciences and Software Engineering. s.l.: Khaled Elleithy.
Ghosh, S., 2009. et Centricity and Technological Interoperability in Organizations: Perspectives and Strategies: Perspectives and Strategies. s.l. IGI Global.
Killmeyer, J., 2006. Information Security Architecture: An Integrated Approach to Security in the Organization, Second Edition. s.l. CRC Press.
McMillan, T., 2016. CompTIA Server+ Study Guide: Exam SK0-004. s.l.: Troy McMillan.
Payne, B. K., 2011. White-Collar Crime: A Text/Reader. s.l. Brian K. Payne.
Refsdal, A., 2015. Cyber-Risk Management. s.l.:Springer.
Rex, M. J., 2016. Hardening technique for Enhancing Security in Network. International Journal on applications in Information and Communication Engineering, 2(2), pp. 1-5.
Steinberg, J., 2016. Official (ISC)2® Guide to the ISSMP® CBK®. s.l. CRC Press.
Wheeler, E., 2011. Security Risk Management: Building an Information Security Risk Management Program from the Ground Up. s.l.: Elsevier.
Willett, K. D., 2008. Information Assurance Architecture. s.l.: Keith D. Willett.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Cyber Security"
Cyber security refers to technologies and practices undertaken to protect electronics systems and devices including computers, networks, smartphones, and the data they hold, from malicious damage, theft or exploitation.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




