How Can Security Issues in an Online Voting System Be Addressed?
Info: 12049 words (48 pages) Dissertation
Published: 9th Dec 2019
Tagged: PoliticsCyber Security
How can security issues in an online voting system be addressed?
Abstract
This report consist of the tools and techniques that can be utilized to minimize electronic online voting from gaining unauthorized access and causing data manipulation. Furthermore, the following paper will provide solutions and reasons why the chosen ideas such as implement stronger safeguards for online registration systems. In this day and age online voting system has started to become a more convenient option to vote therefore it is imperative to implement the right tools to at least minimize online hacking.
Table of Contents
Abstract…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Acknowledgements……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2.1 Security issues with electronic voting?
How can e voting security issues be solved?
What makes a good voting system?
4.2 Artefact research and why this artefact was chosen.
1.0 Introduction
1.1 Academic Question
The academic question has provided the ideal support to answer how the tools and techniques which can be executed on a web application that can potentially help eradicate security issues of electronic online voting. To fully understand this academic question, a set of objectives were made in order to ensure that the research was carried out was relevant to the academic question. After the research was completed an artefact was made which helps voters to vote without any worries through the tools and techniques that cater for these students.
1.2 Objectives
To successfully complete and answering the academic question a set of objectives were implemented in order to fulfill the question.
- Research on ways online hacking can be minimized
- Sketch a web application to visualize its contents.
- Develop a test plan
- Submission of poster
- Hand in literature review
- Develop the web application by using PhP
1.3 Aims
The objectives that were placed would contribute to accomplishing the aims that were also set these were:
- To design and develop a web-based visual voting system.
- To assess the vulnerabilities in the system and explore how these could be improved.
- To implement the necessary safeguards.
- To test and review the artefact
The project was based upon voters who are potentially vulnerable to malicious hacking. Every single individual wants to be safe from these dreadful acts and not be a victim. The reasoning behind the topic choice was because it had always been an interest to the developer since online voting hacking has becoming an issue in today’s online voting it is imperative to have all voter’s sensitive data locked away and away from sight. It is important for each voter to have their info safely secured and hidden away from unauthorized access (data manipulation).
1.4 Artefact
In terms of the artefact being produced, this was a web application which allows users to create an account with added security features, the added security features enhance the overall security to the web application to achieve user satisfaction and to vote with confidence. This web application enables users to select which candidate to choose and the results will be displayed in a form of a donut chart. The artefact had been produced along with the powerful features such as accessibility features for example, the developer made the web application available through different browsers such as
Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Android browser, Internet Explorer 10, 11 and 12, to enhance visibility in the computing area. The two factor authentication (2FA) were implemented on to the web application later down the line this was one of the major tools produced by the developer that was required for users concerning their security. The methodologies that were used to conduct relevant research on the project were resources such as, academic sources. This consisted of e-books/books, e-journals, newspaper articles, online media such as Youtube and academic websites etc. By using a wide range of scholarly sources for research it allowed the researcher to broaden their knowledge on their particular area of the project.
The structure of this report was formed by producing chapters which emphasized on each chapter’s content. By chapters being applied to the report it has allowed to break down the research and would help the reader to easily understand the chapters which would ideally help to understand the information gathered as it will provide a structure flow. With hope, this should help to explain why the chosen artefact was produced. The first chapter consisted of the introduction in which the academic question and the title of the project were mentioned. Furthermore, lists of the aims and objectives for the project have been mentioned along with a description of the artefact that has been produced.
Chapter 2 provided the reader with a fully detailed description in regards to the structure of the report that was produced.
Chapter 3 of the report was a literature review that was carried out which was broken down in sections within itself. These sections helped to distinguish the relative literature that was found and also helped to give a clear approach in regards to the academic question. In addition, comparisons and contrasts were included in the literature review to showa full understanding of the literature provided. The fourth chapter was based on the artefact, full details were provided in this section on how the potential artefact would be developed. This consisted of why the particular artefact was chosen and a methodology; a development life cycle along with a testing plan. In addition, this chapter also covered the academic question as this was answered. This was accomplished by interpreting what was said in the literature review, additional information gathered and also the artefact that was created.
2.0 Literature Review
What is electronic voting?
Electronic voting is a type of voting mechanism which is done through electronically. Electronic voting also known as e-voting has include its technology optical scanning vote systems, punched cards and voting kiosks which contains transmission of ballots and votes via internet or private computer networks and telephone. According to Bravenewballotorg (2018) ‘‘This voting kiosks include a self-contained direct recording electronic voting system also known as DRE’’.
There are two types of electronic voting which can be recognized as; e-voting which is under supervision physically by an independent electoral authorities or government official representatives like the machine at polling stations and remote electronic voting a place where the vote is not physically held under observation by an official or independent representatives like voting from a phone device, personal computer or television via the internet also known as i-voting
According to to Bravenewballotorg (2018) they state that ‘‘ A Voting machine is the combination of electromechanical, mechanical or electronic equipment which includes its software, firmware and the required documentation to program control and support equipment which is used to count and cast votes, defined ballots, to display or report election result and to produce and maintain audit trail information’’.
This machine is fully able to give the voter instant feedback such as possible problem as undervoting or overvoting which can result in a spoiled ballot. This machine has many level of usability, accuracy, efficiency and security. The first ever voting machine was made mechanical. Nowadays, the most common machine use is electronic. Some machines may be more or less accessible for voters. According to Bravenewballotorg (2018) it mentions that ‘‘The Chartists were a political and social reform movement in the United Kingdom. They were the one’s who had made the first proposal for the usage of vote machines in 1838’’.
Figure 2.1: E-Voting System Component Diagram
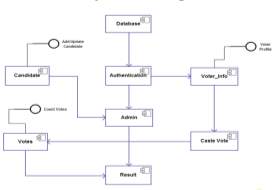
Figure 1. (INFOSEC, 2016a) – Waterfall model
The model proposed is an example of e-voting
Electronic voting (E-voting) systems have become more prominent in the past years as countries such as Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Estonia, France, Germany, India, Italy, Namibia, the Netherlands, Norway, Peru, Romania, Switzerland, the UK, Venezuela, and the Philippines are using online voting for representative democratic systems. . According to e-governance (2015) ‘‘In 2005, Estonia became the first country in the world to hold nation-wide elections using this method, and in 2007, it made headlines as the first country to use i-Voting in parliamentary elections.’’ Since then, it has incorporated online voting as an optional voting mechanism. As internet growth statistics increase it has become an ideal option for voting. As users become more familiar with the internet and its privileges they are more likely to engage with an E-voting system.
Figure 2.2: countries implementing e-voting.
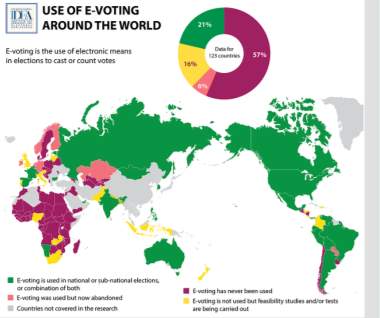 Figure 2. (IDEA. 2015a) – Waterfall model
Figure 2. (IDEA. 2015a) – Waterfall model
2.1 Security issues with electronic voting?
Penny has covered many security issues with electronic voting and also came up with solutions to solve these issues.
According to Penney (2003) ‘‘Electronic voting has been touted as a replacement for paper based voting systems, which are slow and prone to human error and fraud’’. However, electronic voting systems are also vulnerable on receiving the same problems as paper-based systems but just in different ways.
2.2 CODE REVIEW
The officials raise the issue of “certified” electronic
voting systems. The certification process especially in USA or UK is done without any public or third party input, and the results are not released to the public. Individuals refer this to a “security through obscurity”, which means that the source code (and any detailed knowledge of flaws) is kept as a secret. This act could be held as bad practice within the security community.
Penney (2013) states that ‘‘ The authors of [3] also view public access to source code as a necessity, comparing it to the ability to observe all aspects of a paper-based election, except, to preserve the secrecy of their ballots, individuals mark their votes”
The voting system has a big possibility of bias in the creators
of the software. According to Penny (2013) ‘‘ two different professors are
quoted on this issue. One raises concerns over the possibility of programmers being bribed to hide code that modifies the vote count. The other points out that an assumption we have to make is that everyone involved in the election process is a supporter of one side.’’ This demonstrates that the secretive nature of the software, in which we are compelled to put our trust in a small group of people (auditors, the company, both which are private companies) which is unacceptable.
GOVERNMENT STANDARDS
Individuals feel that the issues lies within the government’s electronic voting standards (USA and other countries). According to Penny (2013) ‘‘They say that because the Election Assistance Commission (EAC) standards do not contain a coherent set of requirements, electronic voting systems cannot be designed properly nor meaningfully evaluated by certifiers’’. This points out the core requirements of Election Assistance Commission are incorrect or arbitrarily chosen, and claim that overall the standards seem vague, ad hoc, arbitrary, and even sometimes unreasonable. The election assistance commission (EAC) contains no system or threat model, this means that the electronic voting systems can be in the hand of someone and only them can determine what types of attacks the system should be able to withstand, what the roles of the actors are within the system (and thus what access control systems need to be in place) are, and so forth. Because of these vague and undefined provisions, the vendors and certifiers must make decisions as the intent of The requirements. This makes it difficult to both develop and certify these systems. According to Padmanabhan (2014) ‘‘campaigners for electronic or e-voting say “digital democracy” is on the way in the UK. Although next year’s general election will be run using the traditional system, they predict a different landscape by 2020’’.
AUDITABILITY
A large number of electronic voting systems which are currently in use gives no means of verifying that the vost cast by the voter is indeed the vote registered in the machine. These electronic machines store their records completely within computer memory (hard drive or RAM) and therefore this leads to impossible to dispute the vote count. According to Penny (2013) ‘‘ If there is a fault in thesoftware or the machine and a vote is recorded wrong, there is nothing that can be done. This is a huge problem when coupled with the other problems outlined in this paper’’. If someone decides to tamper with the voting systems there would be no empirical evidence or any records of it happening.
INTERNET VOTING
Internet voting has been showing as a replacement voting system. Individuals describe an internet-based voting protocol which satisfy nine criteria that the individual feel the system is secure and practical to the public; accuracy, privacy, democracy, simplicity, verifiability, efficiency, mobility, scalability and responsibility. Penny (2013) states that ‘‘They examine a number of different protocols, and describe their own protocol which they claim overcomes the shortcomings of previous protocols. However they do not address the fundamental problems with internet-based systems’’.
Internet based electronic voting system has its own vulnerabilities; some which are known to all internet-based applications and even to this day there’s no known fix. Any internet-based system is vulnerable to delivering Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. If one these attacks happen on an election day, it would invalidate the outcome of the election. Similarly, any attempt at election fraud could have a detrimental effect with less effort, compared to co-ordinating attacks on multiple locations in traditional election situations. According to Penny (2013) ‘‘ There is no voter-verifiable paper trail so inaccuracies in the vote count
cannot be corrected. Because the vote can be placed from any internet connected computer, coercion and vote buying can take place easily as there is little or no supervision of
the vote casting environment’’. Home computers are much more vulnerable than corporate machines, so there’s a greater chance of virus infection (and possible vote meddling
on the client side). All these issues may persuade an individual to not engage with an internet voting system. The vulnerability to DDoS attacks, virus infestation, vote buying and coercion, and lack of voter verifiable audit trail are the biggest issues with this type of voting system. This draws a conclusion that internet voting is inherently insecure, and cannot be made secure for use in real elections for the foreseeable future.
Why e voting is important?
Elections are unique. They have the ability to change the destiny of nations, influence participation and activism in politics, and deeply affect the lives and attitudes of citizens. Elections has shown a clear importance in society. Lin and Espinoza (2007) states that ‘‘Accordingly, ethical concerns have become one of the most central elements of the debate surrounding electronic voting. At times, it seems even that the ethics are the most important factor of discussion- influencing technical concerns, et cetera’’. There are obvious concerns about electronic voting machines, however, large companies are seeking ways to develop them and continue to adopt them for election process. there is a large incentive to undertake such risk. Individuals may ask: What are the benefits of electronic voting?
Electronic voting directly affect two parties; the government and the voters. However, in order for electronic voting to be instituted, there has to be a significant advantage (greater than the costs) to one or both of these groups. Ideally, voters gain a better voting experience at the polls, are more confident that their vote will be correct counted, and are able to vote more easily and efficiently. The government is potentially able to increase voter turnout, reduce costs, increase voter confidence, renew interest in the political system (and voting), and ensure the most democratic process possible.
One of the biggest significant benefits of electronic voting system is the possibility for increased efficiency. With electronic voting machines voters can submit their respective votes, and be confident that their vote will count. According to Lin and Espinoza (2007) they state that ‘‘New Electronic Voting Machines can also stop voters from common election faults, such as picking too many or no candidates, also thereby increasing the general effectiveness of voting.’’
Electronic voting via email provides the possibility of making voting easier for citizens who are otherwise geographically isolated from election centers.
Lorrie Faith Cranor, currently an Associate Research Professor in Computer Science and Engineering & Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon University, explained in Crossroads in 1996 that, “Eventually electronic voting may be a viable solution to increasing voter participation in governmental elections.”
This potential to grow voter participation, either from decrease cost, increased accessibility, decreased difficulty, or any other method that clearly has its benefits to the larger community. According to Smartmatic (2018) ‘‘Electronic voting is a term used to describe the act of voting using electronic systems to cast and count votes. Forward-thinking countries and election commissions are keen to explore how it can help them improve their elections.’’.
Electronic voting has the ability to reduce fraud to an extent, by removing the opportunity for ballot meddling, however, if paper ballots are made in copies as a backup in case of a recount necessity, this threat remains.
Michael Shamos of Carnegie Mellon University, who prefers electronic voting but passionately against paper machines, argues that “Paper voting records have shown themselves for the past 250 years to be horribly insecure and easy to manipulate. In practice they have so many flaws that they are as bad as punched-card voting at its worst.” If paper ballots are removed, so is the possibility to distort them as a means of election deception. However, countries like Brazil are in favor of integrating paper printouts into the voting process. Also, electronic voting has the ability to function in the way the voting district needs and prefers. One of the great benefits of electronic voting is that it can come with new developments in mechanical functionality, and software, especially those in favour of privacy, accuracy and verifiability. Hern (2015) states that ‘‘The problems with our current, resolutely 19th-century method of running elections should be obvious. Votes can be miscounted, misread, or even simply misplaced
How can e voting security issues be solved?
It is mentioned that open source development of electronic voting systems could avoid many of these problems from making it into the final product. It has been proposed that the public is to view the source code. This would allow knowledgeable experts to give valuable input on these systems to ensure to build a secure, reliable and ultimately trustworthy electronic voting system is a non-trivial problem. According to Penny (2013) ‘‘All of these methods would result in a better system overall as there will be more people examining the source code for errors and possible vote tampering.’’ A private company in Australia have successfully constructed and implemented an electronic voting system and provided both the draft and finished source code on the internet for the public to see and comment on. This resulted in a number of bugs reported and corrected.
There a few essential requirements that cover the majority of these systems. The system should allow voters to cast one candidate and only one in each race. The voting system should record this vote accurately and allow no modifications to it once a voter cast their vote. Penny (2013) state that the system should prevent a third party from matching votes to the people that cast them, so as to ensure voter anonymity. Penny (2013) further go on to state that Lastly, the results of the election should be verifiable by an attacker could do many things, from voting multiple times to ending the voting process on that machine, effectively disabling it.
An imperative feature of voting is the security of the votes. Votes should not be altered after they have been cast, nor matched to the voter that cast them in order to protect the rights of the voter. Penny (2013) states that Using Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) voting machines which have no paper output for individual votes, insecure systems can lead to votes being changed (p.3). Attacks that achieve this have been shown a number of times on a number of different DRE systems. The main concern with DRE systems is there is no external audit trail that can be implemented in case of election fraud. Internal audit logs can be changed, and a number of attacks can modify the vote count in such a way that any point in the election process it is extremely difficult to determine if the vote counts have been changed. Penny (2013) states that Also, since many of these attacks occur on the voting machines themselves, the errors are propagated to the vote tabulating machines (p.3). The first step in order to fix the issues in these machines to implement a voter verified audit trail. Some time ago, atleast one of the early machine with voter verifiable paper output printed the votes on a continuous roll of paper, which compromises voter anonymity by keeping votes in the order they were made. Cutting the paper after each vote and letting the paper fall into a ballot box would reduce the chance of poll watchers matching voters to their vote. The second step is to ensure to secure the votes on the voting machines. Penny (2013) states that If the machine itself is not recording the votescorrectly then the entire process is subverted, so the software needs to be checked for correctness (p.3). As mentioned earlier, this could be accomplished by allowing the public to see the source code.
After the software on the voting machines are reviewed, check and certified, a tools is needed to identify whether any alterations to the software after it has been certified. This could be achieved by hash of the compiled code, using a known secure cryptographic hashing function. This could provide security against any alterations of the compiled code. A Trusted Computing has a possible application here, securing the platform against uncertified code. Penny (2013) states that the third step is securing the votes once they have left the voting machine (p.3). This goal can be met by encrypting the votes on the transmission medium, authenticating both the source and destination machine, and keeping a document on both of the hash of the vote tally. If the votes were meddled in transit, the the hash on the voting machine will not match the hash on the server. According to Penny (2013) ‘‘ This relies on the hash being secure on the voting machine, which is a weakness in this Solution(p.3). more research needs to be done in this field to determine a secure, robust tool of transmitting votes over a variety of media.
The final step is securing the vote tallying machine. The tallies needs to be in a secure database management system. The vote tallying machine have to be constructed from the ground up to be secure, so that is only operates on code that has been certified as trusted. According to Penny (2013) However as long as the physical output from each step of the voting process is kept, it is possible to rebuild the election results if something does go wrong(p.4.).
What makes a good voting system?
Pete has given three principles which he personally believes if implemented it will provide a better user experience. The following principles that have been created by Pete (2011) are as following:
- Tight focus
- Rich visual experiences
- Rich interactive experiences
- A Tight Focus
A web application needs to have a tight focus which enables people to interact, engage and attain something, rather than passively view content. It doesn’t distract people with content or parts that are orthogonal to the task they’re trying to complete. People integrate it into their daily lives because it feels like a natural extension of the things that they understand and do everyday
- The application is limited to a single, core scenario
- Orthogonal scenarios and tasks are removed from view and not presented to the user
- The primary application components are accessible at all times
- Standard web page content and navigation is minimized and the application controls are the primary focus
- The application looks and behaves consistently across different screens, dialogs, controls and other components
- The application starts immediately and requires no set up or configuration before it’s first use
- When starting the application, the user is taken directly to the application instead of a landing page or marketing page
- The application can be used without registering or signing in, or the sign in/up process is extremely easy
- Rich Visual Experiences
A web application that provides rich visual experiences that will
A web application provides rich visual experiences that will captivate the eye without distracting the mind. It’s vital to provide a positive first impression because it will make users more comfortable, and it assures them that the web application is reliable and professional and compels people to make the product as their own. An exceptional web application puts a premium on aesthetics without sacrificing usability.
- Appropriate fonts and other typographic features are used to enhance readability
- Graphics and illustrations are high quality and look professional
- The application uses all of the screen real estate available to it
- Textures, gradients, and shadows add to the visual appeal of the application
- Controls and graphics convey meaning without requiring additional context
- Controls and graphics offer a manner of realism
- Standard web page content and navigation is minimized
- Animations are used to introduce new content, dialogs, or other items that require attention or interaction from the user
- Window resize events appropriately handle new screen sizes, resized graphics and images
- Messages and information provided to the user is helpful, easy to understand and actionable
- Rich Interactive Experiences
A web application must provide a rich interactive experience that makes technology transparent so people can complete their task confidently without ever having to know or understand what makes the application work.
- The application feels fast and responsive
- The application provides appropriate notifications and information to keep the user informed
- The application follows best practices for building fast web applications
- The application provides a full featured offline experience
- Input from the user is validated before being sent to the server and appropriate input types are used
- Adding or removing data from the application is easy
Web accessibility Law (UK)
Discrimination against people with disabilities is forbidden by law. However, website owners often don’t realize how the law affect websites. According to Taylor (2011) ‘‘ A 2005 study found that as many as 97% of European public service websites failed to provide a minimum level of accessibility.’’
There are clear reasons why that commercial website are more accessible than governmental websites. Developers, web designers and operates need to be more aware of accessibility issues. Even if designers have not intentionally catering disabled users, they could find themselves on the wrong side of the law.
The Equality Act 2010
According to Taylor (2011) ‘‘ Since 2 December 1996 (when the Disability Discrimination Act 1995 came into force) website owners have been obliged to ensure that their websites are accessible to users with disabilities.’’
After ten years in force, the disability discrimination act (DDA) requirements were incorporated into the Equality Act 2010. The Equality Act 2010 Act was to bring clarity to the diversity of previously-extant discrimination legislation. Despite the goal of clarity, the new legislation can be more confusing than the old. Section 29(1) of the 2010 Act says that:
‘‘A person … concerned with the provision of a service to the public or a section of the public (for payment or not) must not discriminate against a person requiring the service by not providing the person with the service.’’
Therefore, intentionally preventing to provide a service to disabled people which is normally provided to other people is considered unlawful discrimination. This applies to commercial web services as much as to traditional services.
Applying the law: an example
Many users visitors use online voting software to help them to deliver their votes, A good number of website have images that contain text as part of the pre-rendered picture file. These images could be unreadable by the software. If the text is not embedded in the image properties (using an alt tag) or alternatively available in text somewhere on the website, this could render the content inaccessible to users, and could therefore be discriminatory for the purposes of the 2010 Act.
Reasonable adjustments
Taylor (2011) states that Sections 20 and 29(7) of the Equality Act create and elaborate a duty for service providers to make “reasonable adjustments” to enable disabled persons to access their services.’’
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), the international organization whose aim is to provide reasonable standards for the web, published a guide which is a good for web developers to comply with to ensure the website are as accessible as possible and in line with the Equality Act 2010. Also, the court could review the guidelines to know what to expect of web developers. At the most basic (“priority 1”) level of compliance, these include suggestions such as:
- Supply text to accompany non-text elements (such as pictures or graphical buttons for navigating).
- Document organisation for sensibly ordered readability without the need for the accompanying style sheets.
- ensure all information conveyed through coloured content can be inferred or is available without colour.
- Clearly and simply labelling the websites content.
- Clearly delineating changes in the natural text of the document to other content, such as captions.
Compliance with both the priority 1 and 2 checklists is recommended. The priority 2 checklist includes:
- Ensuring that both foreground and background colours have enough contrast for those who struggle with differentiating colours.
- Using suitable markup language rather than images to convey information.
- Using header elements to convey structure.
- Using style sheets to control the layout and presentation.
- Clearly identifying the target of each link.
- Providing further information about layout (e.g. a sitemap).
- Using navigation mechanisms in a consistent manner.
- Providing metadata to add semantic information to web pages.
- Dividing large blocks of information into more manageable blocks when possible.
The W3C guidelines have been adopted as the benchmark test in Australia, following the case of Maguire v SOCOG (2000), which concerned a website for the Olympic Games not being adequately useable by visually impaired people. The RNIB offer free accessibility tips to aid with the technical design of your website, with the World Wide Web Consortium standards in mind. The British Standards Institution provides a comprehensive and non-technical code of practice on web accessibility aimed at helping businesses achieve wider digital inclusion when commissioning or designing a website, with the requirements of the Equality Act 2010 in mind. Commercially, many organisations offer web accessibility audits, which can assess the accessibility of a website and give detailed feedback on what changes could be incorporated to achieve greater accessibility. Engaging with disabled users, for instance through online surveys and feedback systems, and is another excellent way of flagging potential accessibility problems.
Accessibility should be addressed at the web design stage, because many fundamental design decisions have an impact on accessibility; but as the EHRC Code of Practice requires, the duty does not end there: many types of change to a website could have accessibility implications. Although it is not a common basis for legal action, website accessibility is important, both from the perspective of legal compliance and because a more accessible website is a website with a greater potential user-base.
3.0 Methodology
Micheal (2018) claims that the core of the Agile methodology was developed by 17 people in 2001 in written form. Their Agile Manifesto of Software Development put forth a groundbreaking mindset on delivering value and collaborating with customers. Agile’s four main values are expressed as – Individuals and interactions over processes and tools,
Working software over comprehensive documentation, Customer collaboration over contract negotiation and Responding to change over following a plan
These four changes can provide opportunities which can lead to good modifications towards a project and how this and an effect on the development of the product; the project had to work in a sequence to manage an agile project, and the way these principles could be amplified. Although other methodologies that are out there may have its uses, agile is the correct method to implement because it focuses on the project team and how it can create a product/ software with a deadline given. On the other hand, a project methodology like Waterfall is generally focuses on getting a project completed in stages. The way that Agile operates is by breaking the work load down within the project. The benefit of this is that it helps the team to observe on what needs to be work on and what it has been completed. So, therefore before starting on new task.
Varner (2014) mentions that ‘‘ While Agile does allow the flexibility to react to changing needs and new developments, there’s also no specific beginning and end to a project. It’s basically done when the client is happy.’’ This methodology is a good approach to follow as it allows a project team to make changes as they wish. However, this methodology is aimed at a group of people however this is a sole project which means this type of methodology (agile) would be impractical. Because the Agile model consist of working in a team and continuously interact with their client to ensure the given requirements are met. Therefore, with the lack of time for the project, this could not possibly be done. With that being said, the research methodology which was strongly emphasized on and applied to the project, it was decided that the Waterfall model would be the suitable approach for the project. The reason for this is because the Waterfall model allows to help producing the artefact and to ensure that it helps the development of the project. During the project’s life cycle, stages were completed in order to make sure that each giving stage was completed to the best of its ability and to ensure the artefact also the artefact also related to the academic question.
4.0 artefact development
The artefact that will be produced is a web application which allows a user to vote. The first page of the web application will have login page where a user inputs his/ her e-mail and password. However, if the user does not have an account there’s a ‘‘sign up’’ page where the voter can proceed to sign up. After the user completes their registration (Sign up ) here then you will see Google authentication code which will be sent on mobile app, once the code is entered the user will enter the given code then will allow for one vote only. Then the user is brought back to the login page and input the details they have used to create the account (e-mail and password used to register). After they have successfully signed in a page will be brought up and it will have five different candidates the user can choose from after a user selects his/her chosen their respective candidate it proceeds to the next page where it displays the results in a form of a donut chart. Each candidate has a distinct color to identify them easily in the donut chart Meier (2018) mentions that ‘‘Contrasting colors help a candidate stand out from competitors. Using color combinations that include a light and a dark color increases visibility. Two diverse but compatible colors are more likely to leave a lasting impression with potential voters. Colors need to work both in print and online.’’ After viewing his/ her results, the user has a ‘log out’ button to return back to the home page (login page). The user is given an option to sign back in to see the results if there’s any updates to the results (donut chart).
Initially, complications did occur in regards to what the artefect would entail as it was very complicated to come up ideas which would answer to the academic question. The commencing idea was to Log IP addresses and prevent voting more than a set number of times from the same address (for example, 5 times the same hour). However, due to complexity and lack of time, it was decided that this was not a good idea to carry out. However, the aim of the project was ‘‘ how can security issues in an online voting be addressed’’. It gives the reader many options to choose from when dealing security issues therefore it was a good idea to implement a Google authentication code which will be sent on mobile app once the code then will allow for one vote only which will tackle multiple votes.
4.2 Artefact research and why this artefact was chosen.
The reason behind the chosen artefact was to grant users a sense of security when a voter cast their respective votes.
The reason the chosen artefact was so it can provide a sense of security when users cast their respective votes. The layout of the website application and the security features that where implemented assist the users with confidence as considerations were taken on board from other web applications, to make sure that the artefact that was created was to ensure that data manipulation does not happen with these voters. Since the UK government emphasis greatly on handling data of people (The Data Protection Act 1998) therefore security issues on e-voting votes must be addressed to avoid breaching any of these laws.
4.21 Website languages
4.2.1 PhP
Suraski (2015) states that the language of PHP ‘‘has been protected from a very big class of potential vulnerabilities.’’ The developers ensure this programming language caters to all needs. PHP is an HTML-embedded scripting language. Much of its syntax comes from other code languages such as Java, Perl and C. PHP has a few unique PHP-specific features thrown in. The aim of PHP is to allow web creators to produce dynamically generated pages quickly. PHP was developed back in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf. According to MacKay (2016) ‘‘As of 2016, PHP comprises more than 80% of the websites on the Internet’’. This shows that even after two decades PHP is still relevant and powerful programming language. Php has gained a huge popularity the reason for this is because PhP is a free programming language to use therefore no licensing fees is required. According to Suehring and Valade (2014) ‘‘The PHP software works with the web server, which is the software that delivers web pages to the world. When you type a URL into your web browser’s address bar, you’re sending a message to the web server at that URL, asking it to send you an HTML file.’’ The web server responds by sending the requested file. A user’s browser reads the HTML file and shows the web page. The user request a file from the web server when they click a link in a web page. In addition, the server processes a file when the user clicks a web page button that submits a form. This process is basically the same when PHP is installed. The user request a file, the web server most like be running PHP, and it send HTML back to the browser. When PHP is installed, the web server is configured to expect certain file extension to contain PHP language statements. According to Suehring and Valade (2014) ‘‘ Often the extension is .php or .phtml, but any extension can be used. When the web server gets a request for a file with the designated extension, it sends the HTML statements as is, but PHP statements are processed by the PHP software before they’re sent to the requester.’’ When PHP statements are processed, the output, or anything seen on the screen is sent by the web server to the web browser. The PHP statements, those that don’t create any output to the screen, are not included in the output sent to the browser, so the PHP code is not normally seen by the user. With this being said about PHP, PHP come along with many pros hence this is why PHP comprises more than 80% of the websites on the internet. Firstly, there are numerous of PHP developers around the world surely with the skills and knowledge the developers have accumulated they wish to share it online and to make it accessible to people who tend to learn PHP and become programmers; by doing this the knowledge will spread among PHP beginners. However, there are cons that come with PHP coding. According to Mah (2009) ‘‘If you haven’t realized it by now, PHP is also called a scripting language for a reason — the codes are not compiled and are accessible as plain text files.’’ Mah explains that with big and more complex projects, you need help or experience from more experience PHP programmer because they are numerous libraries and many ways to make a feature, but a person may not be able to choose the proper one or to find the one they exactly want. So. Therefore. PHP can be difficult this is why training is required for those businesses. It’s essential to have qualified and approved devlopers who will do a wonderful job at handling and securing their website. With this being said, by sending employees on training courses it will use up the company’s money.
4.2.2 HTML5 (check)
According to Shannon (2012) ‘‘HTML is a computer language devised to allow website creation. These websites can then be viewed by anyone else connected to the Internet.’’ This shows that the way HTML webpages are written; it has the capability to display the content of them on web browsers and is saved onto a format which can be fully interpreted by all types of users. HTML 5 is the most recent version of a hypertext markup language is a web language which helps to design webpagesand according to Lawson and Sharp (2011) this recent web design language has been known to be used around the globe. Lawson and Sharp (2011) go on to talk about the advancement of HTML5, and how it has the capability to be compatible with other versions that can also be used to display webpages. One of the benefits of writing in HTML5 when producing a website is that it helps to clean the code that has been written, by adding suitable headings and helps to distinguish the content of the webpage and the styling of the webpage(Cox 2011). The latest version of HTML (HTML5) has the power to add the latest tags of code and has the ability to remove any old tags that are now not in use for example; if an old version of HTML was to be used the <font> tag would have been appropriate to use, however, with HTML5 it requires you to place this particular tag on the CSS styling document. In order to produce the proposed artefact, hypertext up markup language (HTML5) was decided to be used when producing the coding, in relation to the website, since, the developer had come across writing in HTML5 previously before. Furthermore, cascading style sheets (CSS) were also used to format the website in regards to colour, layout of text/pictures, font type and font size. It had been recognized that CSS played a major role whilst creating the website as it assisted with the change of colour schemes of the webpages, to cater those students who are colour blind, and also helped to set out the type of format, text size, background that has to be implemented to cater for pupils needs.
To produce the proposed artefact, it was decided that hypertext up markup language (HTML5) was used when producing the coding, in relation to the website, since, the developer had come across writing in HTML5 previously before. Furthermore, cascading style sheets (CSS) were also used to format the website in regards to colour, layout of text/pictures, font type and font size. It had been recognized that CSS played a major role whilst creating the web application as it assisted with the change of colour schemes of the webpages and also helped to set out the type of format, text size, and background
4.22 Artefact Tools
A good number of tools were seen into in which the developer thought was imperative therefore, as a result there were many tools and techniques that were implemented.
These are as following:
- Colour scheme tool was integrated within the web application the background colour is grey. And the foreground contains a wide range of colours including light grey, blue and yellow, and black text. According to colour psychology (2017) ‘‘ The colours of grey, blue and yellow represent cheerful, fun, honesty, trustworthiness, refined and contemporary’’.
When developing the web application the developer considered using a simple font (Calibri) because these fontd are easier to read. The reason for this because Derek (2015) state that ‘‘I believe that your MAIN font should be a simple font, always to avoid confusion’’. Therefore, this advice was taken on board and the font; Calibri was applied to the content of the web application when it was developed by the developer.
On the candidate page, different colours were used to represent different candidates for easy identification. The developer has used a two factor authentication to deal with multiple votes. This works by every time a voter signs up he/she has to provide their mobile number in order to receive a text message and code will be displayed. The code will be entered in order for them to vote.
A donut chart was implemented to display results after the voter cast their respective votes. The reason why the developer has chosen a donut chart instead of the pie chart Is because it easier to read than pie charts. Robertson (2017) states that ‘‘donut charts are hollowed out, there is no central point to attract your attention. Where do your eyes go instead? If you’re like most people, your eyes travel around the circumference and judge each piece according to its length. As a result, you can also think of a donut chart as being a stacked bar graph that has been curled around on itself.’’
The developer has made use of stored procedures. The reason or this is because it is vital to store SQL code on the server and make it available to application through the use of stored procedures. According to Chapple (2015) ‘‘This limits the range of actions applications may perform on the database and allows for easy, centralized updates if security requirements change in the future.’’
The developer has also decided to not include SQL commands in the web application. The reason is because is it believed that is can create a significant vulnerability if malicious are able to later change the application. According to Chapple (2015) ‘ Don’t let developers have administrative power over users. Security professionals have long practiced the idea of separation of powers.’’ As a developer it is a good idea to ensure that the developer ( who control stored procedures) . are not able to create and/or modify user permissions. This can avoid the developer from succumbing to the temptation of loosening access controls to make a program work “just while we’re testing it.” Accoding to Chapple (2015) ‘‘ I’ve seen all too many cases where those “temporary” solutions have remained in place for years.’’
Furthermore in regards, to why this artefact had been chosen, it had come across
that not many academic web application had not been previously produced before, to cater the needs of voters in terms of security. Thus, the developer considered that creating a web application which fully focuses on voting security would be a good idea to carry out since, the artefact produced was unique and 100% original.
4.23 Screen designs
Appendix 1 shows all of the screen designs that have been produced in order to help the developer to produce their website. By producing the screen designs it will help the developer to have an overview of what the website should entail in terms of layout, content and tools that will need to be implemented. The screen designs also show the developer how the webpages will be interlinked so a visually impaired student can navigate through the website smoothly as possible. Below is an example of the homepagescreen design that has been created.

Login


Login to our site
Enter email and password to log on:
Enter email…
Enter Password…
Sign in!

New User Sign up!
Homepage
The homepage screen design displays the number of techniques and tools that will be implemented within the homepage such as accessibility and appropriate font. When a user decides to sign up he/she will have to provide their personal details (name, email address etc). after an acoount has be made. They will have to provide their mobile number and they will need to use given code in order to cast their respective vote. This give the user a sense of security because French (2014) states that ‘‘improved security: By requiring a second form of identification, SMS-2FA decreases the probability that an attacker can impersonate a user and gain access to computers, accounts or other sensitive resources.’’ This give the voter reassurance because Even if a fraudster gains access to a password, he won’t have the second element required to authenticate. The homepage has keep quit basic in terms of layout. Images have not been included on the homepage, since images should only be used to convey information and are meaningful to the user. The background colour of the homepage is grey this was used throughout the web application because it comes up as less glaring on the screen plus it also allows the designer to use white as a subtle highlight in specific user interactions. According to Brown (2015) ‘Eye fatigue from background glare is reduced’’.
Registration page
The registration page entails the user to input personal information about themselves in order to proceed to vote. Once signed up, the user see Google authentication code which will be sent on mobile app once you will enter code then will allow for one vote only. Two factor authentication (2FA) works by requiring not only a password and username but also something that only, and only, that user has on them, i.e. a piece of information only they should know or have immediately to hand – such as a code. Using a username and password together with a piece of information that only the user knows makes it harder for potential intruders to gain access and steal that person’s personal data or identity.
Voting page
This page displays a list of candidates to choose from. Each candidate has an image of them and a distinct color to identify them . the user has to choose which candidate they wish to choose. After casting their respective votes they know have to click on the ‘Submit’ button in order to have their votes to be accepted.
Candidate result page
After a voter cast their respective votes it will now display in a form of a donut chart with different colors. Each unique color is attached to a candidate for easy identification. Also, the colors on the donut chart is in light colors to make it easier and quicker for users to identify the results. Also, a user can sign back in using an existing account to view any updated results.
Why is internet important for voting?
REFERNCES
https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2015/mar/30/why-electronic-voting-is-not-secure
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/2017/06/07/still-cant-vote-online/
this article is for the main section of the dissertation
http://www.bravenewballot.org/
(what is electronic voting system?)
http://avirubin.com/e-voting.security.pdf
(how to deal with security issues e-voting)
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/4251/c39c413ec0ba29f977ca7f55bbd72dfda95a.pdf
(online voting security issues)
Methodology refercenes
https://www.wrike.com/project-management-guide/methodologies/
Agile methodology
https://blog.trigent.com/the-role-of-qa-in-an-agile-model/
Waterfall methodology
https://castellansystems.com/Waterfall.cshtml
website Law
https://seqlegal.com/blog/website-accessibility-and-equality-act-2010
what makes a good web app?
http://www.petelepage.com/blog/2011/07/what-makes-for-a-great-web-app/
colours
https://classroom.synonym.com/colors-election-campaigns-10634.html
https://crew.co/blog/is-php-still-relevant-in-2017/
http://www.dummies.com/programming/php/how-php-works/
http://www.empower-yourself-with-color-psychology.com/website-colors.html
https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/tip/Five-tips-for-secure-database-development
http://people.ds.cam.ac.uk/ssb22/css/dark.html
https://heimdalsecurity.com/blog/start-using-two-factor-authentication/
https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2015/feb/26/should-britain-introduce-electronic-voting
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Cyber Security"
Cyber security refers to technologies and practices undertaken to protect electronics systems and devices including computers, networks, smartphones, and the data they hold, from malicious damage, theft or exploitation.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




