Network Infrastructure for Community Teaching and Training Centre
Info: 9759 words (39 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
Tagged: TeachingCommunity Development
Proper and effective Network Management is paramount to every organisation for securing information and data transfer within and outside the organisation. The project is to design a reliable and maintainable network infrastructure for the community training centre that will promote academical achievements and, better resource sharing among students and teachers. Its operating systems, hardware, software and the network operating system being implemented will be a state of art facility.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Factors that influenced decisions for the proposed set-up of the LAN
vii. Subnets and protocol utilized
i. Network configuration issues to enhance performance.
Chapter 3. Network Operating System
i. Operating systems for the Network design.
ii. what are the hardware requirements
iii. explain how you would take these into account in your LAN design.
Chapter 4. Services Provided by Nos to Support Operations and Management on our Network systems.
Chapter 5. Benefits of our network systems
Introduction
The project is to design LAN (Local Area Network) model for franchise campus. The design includes to set up network devices, that are connected to the workstation, multifunctional devises, server’s routers, and other state of the art facility systems. The Client would like to use the proposed network design model to supports the future campus, and have flexibility to add or downgrade the recourses for the proposed design. It must be just one wired LAN that allows all user to have access to the facilities and resources of the learning institution Electronic interactive white boards must be provided in doing so we ensure that the students and lecturers have access to state of the art technology.
Tutors must have access from every classroom to the systems resources such as course content, student information and can manage and update the course content To increase flexibility, hot-desks must be provided in various and relevant areas of the office Apart from hot-desks, adding to the flexibility of the organisation will be the ability to work from home via a secure VPN (virtual private network) Student and lecturers will be encouraged to bring their own devices and the LAN must facilitate such a feature Video conferencing will be available in all teaching rooms and conference rooms Printing facilities must be provided but various environmental and cost effective issues must be considered A disaster plan must be in place to ensure the security and integrity of all data store on the LAN servers
Requirements
The client would like to use the proposed network design model as a model for all the franchise centres. One LAN Design
Electronic interactive white boards
Electronic tutor system
Hot-desk
Working from home
Bring your own devices
Video conferencing
Printing facilities
Disaster recovery plan
Design Assumptions
Wi-Fi access points to facilitate BYOD
The Class can increase in future and network design supports this
All data will be backed up on a server located at headquarters
UPS in case of power cuts
Students and staff will have different levels of access to the resources
Network operating system will be Microsoft Windows 7
One central printer for Students using pay as you go model.
Working from home via VPN
Chapter 1. Factors that influenced the decisions for the proposed set-up LAN
The topology is the physical and logical layout of the network. The physical side will consist of the offices or buildings where the users are located. They are connecting to servers and other offices buildings to remote access. The Logical aspect of the design will be on the VLAN.
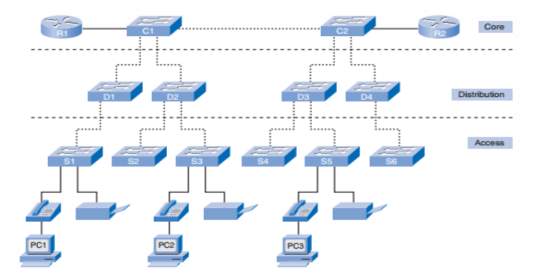
Laying out our logical topology design, there is a security policy in place which decides what our trust model is. Which parts of the network are less trusted, and which are more? Which groups of devices and users should be logically grouped together, and which should be separated? Below is a diagram representing our initial network design which is the Hierarchy topology model;
According to the “OSI model which basically analyses the layers in this model and how different computer networks are connected to each other and it also forms the basis of all interconnections for most of the modern packet switching networks”
Ref: http://catalogue.pearsoned.co.uk/samplechapter/1587132079.pdf |
Building a switched LAN architecture that satisfies the needs of our school project, it will be more successful and reliable based on the importance and what hierarchy model offers. When compared with other network designs, hierarchical is more flexible for expansion and management. Each layer in the design makes clear its function and roles in the overall design.
This is design model is broken into three layers: Access Layer, Distribution Layer, Core Layer
AccessLayer:
Another name for access layer is Interface layer, where there is a direct connection of the devices such as Printers, IP Phones and PCs, to provide access to the rest of the network. A layer that is made up of the routers, switches, bridges, and wireless access points. Generally, this layer connects all this device to network and controlling which devices can communicate on the network.
Distributionlayer:
This layer clumps all the data from the access switches before it is transferred to the core layer for routing to its destination. The distribution layer manages the flow of network traffic using policies and delineates broadcast domains by executing routing purposes amongst virtual LANs (VLANs) distinct at the access layer.
VLANs is a subdivided LAN. it permits segmented traffic flow on a switch into detached sub networks. For instance, in a university it could be possible to separate traffic according to students, guests and faculty. Distribution layer switches are typically high-performance devices that have high availability and redundancy to ensure reliability.
Core Layer:
This is the most important part in the Hierarchy design model, it is a high-speed backbone of internet network. It is a very sensitive layer for interconnectivity between distribution layer devices. It is of utmost importance for the core to be highly available and redundant.
Benefits of Hierarchy topology model;
Scalability – Because of the design, hierarchy networks can be scaled easily with minimal disruption to the organisation. The flexibility of the model permits you to reproduce the project element as the network advances. Because each example of the components is consistent, growth is easy to design and implement.
Redundancy – Hierarchy networks allow redundancy to be designed and built into the networks at key points further increasing the reliability of the network. Availability can be increased through easy redundant implementation in Hierarchy model. For example; Switches in access layer are linked to two separate distribution layer switches to confirm route redundancy. Problem in one of the distribution layer, can let to failing switches.
Performance – Data is moved from the access layer straight into the high-speed distribution layer for forwarding. This dramatically increases performance by moving the traffic on high speed devices.
Security – Security is paramount in today’s networks. The hierarchical model means devices can be identified per layer and appropriately configured for security.
Manageability – Because the network is divided into layers, the function of devices is easily discernible. Devices at each layer can usually be managed in a similar way.
Maintainability – the modular nature of hierarchy networks lends itself well to maintainability. Devices can easily be swapped in the unlikely event they fail or upgraded with minimal disruption to the rest of the network.
MEDIA ACCESS METHOD:
Based on our LAN design, The Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) and the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA). For our wired LAN Ethernet, the assembled data is broadcast (Like a TV programme but occupying the whole frequency) over the media. below are the steps in the transmission.
- Listen to network
- If it’s clear, begin transmission of the frame, continue to listen to the network
- If a collision is heard (two frames colliding with one another), send out a jamming signal
- If the jamming signal is heard, stop transmitting and wait for a random time before retrying.
The main concern with media access is to prevent packets from colliding. There is a collision when two or more computers transmit signals at the same time. By replacing Hubs with multiple layer Switches (which controls the traffic by sending the traffic to each port only the traffic directed to that device on that port) combined with changing from coaxial cable to twisted-pair cabling (with dedicated pairs for sending and receiving data), with the use of optical fibre, shared-medium problem is a thing of the past.
Our LAN design conforms with “802.3 IEEE standard for Ethernet, and both terms are commonly used interchangeably. The terms Ethernet and 802.3 both refer to a family of standards that together define the physical and data link layers of the definitive LAN technology”
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA).
Wireless (WLANs) offers a great flexible alternative to our network, utilising the radio waves as the medium of transmission rather than copper or fibre cabling. They operate in much similar way as conventional Ethernet, but instead of detecting collision, they Avoid collision. They do this by sending a warning signal called Ping, and they wait if there is, before it sends its own.
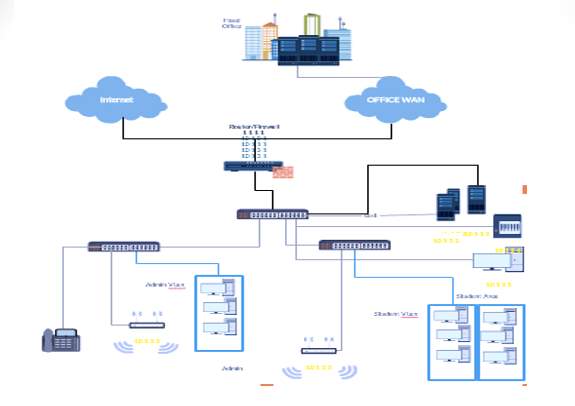
HARDWARE:
LAN Network hardware are range of electronic devices that can be interconnected in such a way as to allow the transmission of communication signals between several workstations. From the visual network design diagram below.
 Ref: from our presentation slide. Ref: from our presentation slide. |
Below is the list of hardware components implemented in our LAN design;
Personal Computers /workstations and Servers, Network Interface Card (NIC), Cables and connectors, for example, coaxial cable and BNC connector, Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and RJ-45 connector, Switch and Router.
| SERVER | SWITCHES (Layer 2) | ROUTER | NIC |
| 1.They are dynamic kind of computers providing a work place with different services ranging from messaging, virus protection, applications and collaboration tools.
2.They operate 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to meet the demands of the work place. 3.Servers are equipped with multiple processors, power supplies and increased memory. |
1.Physically connects computers via ports.
2. Switches provides communication between machines on the same network. 3.Learns which computers are connected to which ports based on Ethernet MAC address. 4.Only sends out one port 5.Fewer Ethernet collisions and Supports Multiple conversations. |
1.Routers send information between two separate IP4 networks
2.They are Based on IP address 3.Sometimes called a gateway |
They are common type of network hardware on all network. Every workstation and server will contain at least one NIC. They contain electronic components that establish and control network communications’ is a principal hardware device that differentiates between a network computer and a stand-alone computer. |
MEDIA CONNECTIONS:
Media connection or network media is the part through which an electric signal travels on from one component to another. choosing the appropriate Ethernet medium is an important part in designing and installing Ethernet. Although there are four major types of media in use today e.g. Thick wire for 10Base5 networks, thin coax for 10Base2 networks, unshielded twisted pair (UTP) for 10Base-T networks and fibre optic for 10Base-FL or Fibber-Optic Inter-Repeater Link networks.
The most common wiring systems are 10Base-T and 100Base-TX, most especially uses unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. It is just like a telephone cable and comes in a different form of grades, with individually higher grade offering excellent performance. For particular applications, fibre-optic, or 10Base-FL
Below is the Connecting medium implemented in the design of our LAN Network
Cat-6 |
Fibre-optic, or 10BASE-FL |
Contains 4 twisted pairs of copper wire terminated by RJ45 connectors. Frequency support is up to 250HzData Rate is about 1000Mbps and network compatibility is 10Base-T, 100Base-TX, 1000Base-T |
For the fact that it does not conduct electricity, fibre-optic cable be of a paramount use in areas expose to strong electromagnetic interference, such as on a industrial floor environment. The Ethernet standard allows for fibre-optic cable segments up to two kilometres long, making fibre-optic Ethernet right for the perfect connections of nodes and buildings that are not able to be connected by the copper media.This is the Backbone Cabling |
Cat 6 cable

Ref: https://www.cableorganizer.com/telecom-datacom/patch-cables-boots-plugs.html |
 Fibre- Optic Ref:https://www.cableorganizer.com/telecom-datacom/patch-cables-boots-plugs.html
Fibre- Optic Ref:https://www.cableorganizer.com/telecom-datacom/patch-cables-boots-plugs.html
EXTERNAL COMMUNICATION:
Basically, external communication is a form of bring your own device system (BYOD). Ethernet and Wi-Fi are two main ways to enable LAN connections. Ethernet is an application that enables computers to communicate with each other. Wi-Fi uses radio waves to connect different machines to LAN. There are other LAN technologies, like the Token Ring, Fibre distributed data interface (FDDI) and ARCNET, they all lost favour as Ethernet and Wi-Fi speeds have increased. The birth of virtualization has given rise to the development of virtual LANs, which allows administrator to logically group computers and partition their networks without the need for major changes to infrastructure.
Ref: http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/local-area-network-LAN |
Fig. BYOD
With the help of a suit application programs kept of the LAN servers. Users who need an application can download and run it from their local device. They can order printing and other materials or application, they can share files and read information. The read and write access is maintained by administrator. LAN server can be used as a web server if caution is in place to make sure that the internal applications and data from outside access are secured.
VLANs (Virtual LAN):
VLAN technology is a by-product of switching technology, allowing a LAN to be subdivided into several virtual LANs. There is no difference in physical structure of the LAN, but the switches deployed are configured to segregate traffic.
In a typical shared LAN; Users are grouped physically based on the network device they are plugged into and routers segment the LAN and provide broadcast domains.
In VLANs; Group users logically by function, department or application and configuration is done through proprietary software. As shown in the diagram fig 1 below;
They work at Layer 2 & 3, control network broadcasts and allow users to be assigned by net admin.
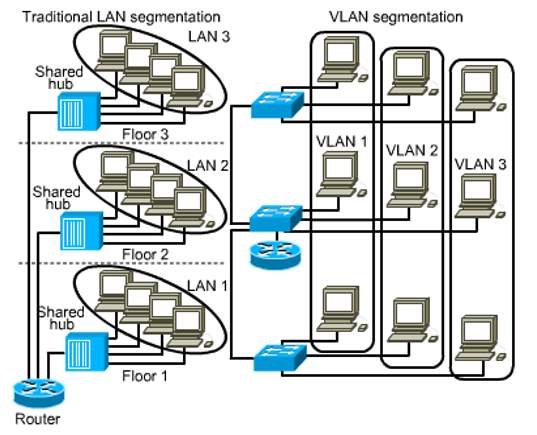
Ref: lecture slides on blackboard |
Fig 1
VLANs can logically segment users into different subnets (broadcast domains)
Broadcast frames are only switched between ports on the switch or switches with the same VLAN ID.
| VLANs Users are logically group via software based on: | Benefits of VLANs to our LAN network |
| Port number
MAC address Protocol being used Application being used |
Increased performance: By the reduction of the Broadcasting domain size, there is an increase in efficiency of network devices.
Manageability Improvement: The network into logical groups of users, applications, or servers allows to mage the network. Physical topology independence: VLANs allows the grouping of users irrespective of their physical position in the campus network. When is an expansion or transfer of a departments to a new area of the network, then VLAN can be transformed on their new ports without creation or alteration of any physical network changes. Increased security: Limitations formed by VLAN over a network LAN, marks the end of logical subnet. For access to other subnets (VLANs), it essential for it to pass through a routed (Layer 3) device. Immediately you send traffic through a router, we have the chance to add filtering decisions (such as access lists) and other security measures. |
SUBNETS AND PROTOCOLS:
Protocols are the TCP/IP protocols. TCP works with a set of instructions to chat messages with other Internet Points at the information packet level. Whereas Internet Protocol (IP)uses some other rules to send and receive messages at Internet address level. Which is (IP) Addressing. Subnet is a portion of a network that shares subnet address.
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol automatically configure our network
We have Implemented the IPv6:
Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) is a network layer protocol (layer 3 of the OSI), that allows information transportations over a packet switched network. Packet switching encompasses the distribution and receipt of information in packets amongst dual nodes in a network. The working standard for the IPv6 protocol was issued by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in 1998. The IETF condition for IPv6 is RFC 2460. IPv6 was proposed to substitute the extensively used Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) that is restrained the backbone of the current Internet. IPv6 is frequently intended to as the “next generation Internet” since of its extended proficiencies and its progress through current great scale distributions. In 2004, Japan and Korea were recognised as having the first public placements of IPv6.
The volatile progress in mobile campaigns with mobile phones, notebook computers, and wireless handheld devices has formed a need for additional blocks of IP addresses. IPv4 presently provisions an all-out of about 4.3 billion exceptional IP addresses. IPv6 upkeeps a theoretical supreme of 2128 addresses
Network Host
!————64bits———-!———–64bits———–!
IPv6 Address: 2001: 0DB8: 0001: 2F00 : 0000 :0000: 0000: 0000
each IPS gets their prefix from IANA
Registry Prefix: 23
+ISP Prefix: 32 (2001:0DB8:)
+ISP assigned Site Prefix: 48 (0001:)
+Site assigned Subnet Prefix: 64 (2F00:)
This is our Network or Subnet information: 2001:0DB8:0001:2F00
1IPV6 Address Abbreviated to: 2001:DB8:1:2F: :/64
The Network Address is the first 48-bits of the address, or since they are convened in 16-bit groupings, efficiently the first 3 groups of numbers elect the network. For the above instance, the Network Address is 2001:0DB8:0001. Most people or organisation receiving their IPv6 addresses from an ISP, the first part of this Network Address will be the same for all the clients of the ISP, which will label the region and ISP
The Subnet Address: is the next 16-bits of the address, or as addresses are grouped in 16-bit groupings, the subsequent group in the IPv6 string. For the above case, that would be 2F00. Instead of a Subnet Mask, in IPv6, you just note the Network Address and the Subnet Address, and that’ll give this address an exact description of the Network that this device is on, and the Subnet that this device is one. This is where I distinguished IPv6 is more effective than IPv4 as each packet has all a router needs to route the information along, instead of taking to add or join routing information, or look to a distinct subnet mask parameter to work backwards into the address.
The Host portion can be dynamically configured, statically configured or the EUI 64 Configured Where it uses the Mac Address to Basically Create an Identifier to Identify the Host.
BENEFITS OF IPv6:
1.The 128-bit span of IPv6 addresses is a substantial increase over the 32-bit length of IPv4 addresses.
2.The extent of the IPv6 address space makes it less susceptible to malicious activities such as IP scanning
3. IPv6 packets can back up a greater payload than IPv4 packets consequential in amplified throughput and transport competence.
4.A key improvement over IPv4 is instinctive care for mobile devices. IPv6 supports the Mobile IPv6 (MIPv6) protocol which enables mobile devices to switch among networks and collect a roaming report irrespective of physical location.
5.MIPv6 is a symbol of the protocol and was specified as a fixed obligation throughout the design of IPv6. The IETF has separate provisions for MIPv6 that detail data structure, messaging, and security requirements.
6.Auto-configuration is another IPv6 improvement that is measured a great advantage to network administrators.
7.An IPv6 router can determine its own IPv6 address using data link layer addressing parameters. The IETF has allotted RFC 2462 to set plans for IPv6 auto-configuration.
8.The IPv6 protocol advances upon IPv4 with improved validation and privacy measures. IPsec security is entrenched into the IPv6 specification to manage encryption and validation between hosts.
9.This built-in security framework allows protected data traffic between hosts that is independent of any applications on either host. In this way, IPv6 provides an effective and complete security background for data transmission at the host or the network level.
Chapter 2. LAN Design
Designing our network, the following methodology was put in place,
Gathering of fact and figures about the organisation and user requirements and expectations.
This part basically we considered the size of the school which is the capacity, status, building plan, numbers of employees, plans for growth and software that will be used, which is part of the operating systems, finally future software requirements. Consideration whether data or software are mission critical and if there are any protocols that need to be supported.
Analysing requirements of the network
The information gathered must then be analysed, particularly we paid much attention to analysing our requirements by considering network availability;
- By measuring Throughput: How much throughput the organisation expects from the network. And Throughput is a measure of how many units of information a system can process in each amount of time
- Response time: The time the users except to wait before the network provides them with the information they require.
- Access to resources: What resources the users expect to have access to, and what the organisation policy is on access to resources. This often must be balanced to provide an effective network.
- Reliability: A realistic expectation of the networks reliability (100% reliability can be expensive to achieved)
Design the structure
Considering the network design structure, network topology and networks cabling must be addressed. The Current EIA/TIA recommendations states; that networks should be implemented using a star topology and should have a minimum of two networking points to every desktop (not all needs to be live). EIA/TIA also requires that a wiring closet (WC) should be placed on each floor to serve nor more than 100m2. Where floor size exceeds this, two or wiring closet should be used. EIA/TIA also specify that a wiring closet should have the following:
- Sufficient heating/cooling to maintain a temperature of 21 degrees when the equipment is in full operation.
- A minimum of two non-switched dedicated AC outlets (positioned every 1.8m along the wall at a height of 150mm above the floor)
- The floor can take the weight of networking equipment.
- Light fixtures should provide 200 lux of brightness and be at least 2.6m above the ground. The switch should be immediately inside the door. If the light used is fluorescent, it should be clear of the cable runs (because of the interference).
- A door 0.9m wide that opens outward with a lock to allow anyone inside the room to exit at any given time. (it may be adjusted in the light of local fire regulations). For the main wiring closet (the one that will provide any external connections), it is recommended that the telecoms provider’s is used.
- Where their cable enters the building (this entering point is known as the Point of Presence (POP). The wiring closet is known as the Main Distribution Facility (MDF); the others are known as Intermediate Distribution Facilities (IDFs) EIA/TIA also recommends that the cabling is a minimum of category 6 enhanced (cat 6) to the desktop and either fibre or copper between the wiring closets (vertical cabling).
Minimise the network delay in traffic traversing the network (network diameter)
As data passes through networking device, a delay is introduced; this is known as latency and its effects are cumulative. Therefore, the more devices the data must pass through between source and destination, the greater the delay. Good design practice must be implemented in our LAN to reduce latency and optimise data speed. And this is achieved by reducing the number of devices the traffic needs to pass through.
Network diameter is a measure of the number of network devices the traffic needs to pass through between sources and destination.
Because network performance and network technologies are constantly changing, we decided to make sure that our LAN design can accommodate these changes and that performance is maximised by carefully positioning of critical components. Designing a LAN, for a high-speed technologies and multimedia-based applications certain criteria must be addressed.
1. Function and positioning of Servers/broadcast control:
Positioning of servers fall in two distinct classes:
Organisational servers (such as email servers; organisational-wide application or database or DNS); and workgroup servers (data and application)
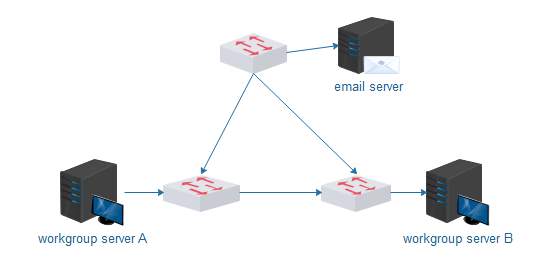 Ref: www.edraw.com Ref: www.edraw.com |
Fig.1
Diagram above shows a well-structured designed network All three switches design structure. By structuring the network in this way, the machines connected to switch A can use server A without having to use the network backbone (through the organisational level switch close to the email server), which helps to keep traffic on the backbone to a minimum. If the machines need access to email, they will not cause excess traffic on the machines connected to switch B while accessing the organisational server (for email). Access to server B from the machines connected to switch A is possible but should not be used often. This type of design is called Two-Layer network design. Which is suitable for small enterprise.
But the diagram above could create a broadcasting problems, because there are no routers. And a broadcast by any machine will traverse the whole network, hence wasting bandwidth. To adopt a better and well-structured design we have decided to replace the organisational switch close to the email server with a router which will divide the network into three broadcast domains.
From the diagram below you can see that, a router is added to the top switch to avoid broadcast issues.
Ref:www.edraw.com (self drawn)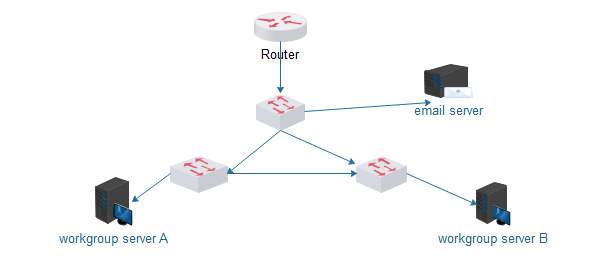 |
Fig.2
2. Collision containment/segmentation:
Collision can be a real problem with Ethernet networks. Indeed, during heavy loads collisions can reduce the available bandwidth. This is because the nodes contend with one another for access to the network. So, we have designed Ethernet in such a way to reduce access contention and the number of collisions on the network. Hence that the reason for the three switches, the switch virtually eliminates collisions on each network (A and B) and on the organisational backbone, the process is known as segmentation. While the router help divides the network into three broadcast domains.
Chapter 3. Network Operating System
Network Operating System: Is software that supply’s network with multi-user and multitasking capabilities. NOS help facilitates communications and resource sharing, providing the basic framework for the operation of LAN. And there are two types of network Operating system, which is the peer-to-peer network operating system and the client/server network operating system.
In our LAN design, we have followed the procedure of the Client/Server Network Operating system. Where by system is based on the Client/Server architecture where a server enables multiple clients to share resources. It permits the network to integrate functions and applications in one or further dedicated file servers. The Server is the core of the systems, permitting access to resources and establishing security. Below is our operating system;
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 is what we have implemented as our Network operating system because of the following reason;
- Server Deployment: Previously there was a restriction in installing windows server 2012, because you might only install the windows as the only domain manager on a small office network. It can now be installed in a domain server of any size. Currently you can install Window Server 2012 essentials on a Physical Server, Virtual Server, and on a Member Server in a domain of any size already in existence. when installing as Member Server, you can have more than one running Server essentials in your domain.
- Client Deployment: Connecting a computer to your domain from a remote location is possible. This means other users mobile computer can join your network even when they are not your corporate network. When a new employee is directed to CONNECT virtual directory of Essentials, the Remote Access Website launches a simple wizard that request four pieces of information; Username and Password for domain, ask if the computer is for personal or public use, instruct you to type “TechRepublic Windows 8.1 Tablet”, if you want the computer to perform backups when its running.
- Pre-configured auto-VPN dialling: There is an access to on premise network resources, because there is a pre-configured VPN client, as shown below diagram. It prompts the user with dialogue box immediately after linking nodes to the network over internet. client can willingly trigger auto-VPN dialling so they are connected to the workplace.
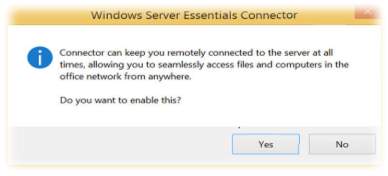
Ref: http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/10-things/10-cool-new-features-in-windows-server-2012-r2-essentials/ |
- Server storage: Most often shared folder is created as a user home folder on a secondary server on the network. Users can also receive an alert when a server folder grows past its limits or its defined quota.
- Health Report: Health Report is unified with Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials and does not need to be installed as an added software or as an add-in. Based on the commercial needs, the system health reports can be modified to show items that you wish to monitor. It’s also shows every day health report that can be observed from even a mobile device. This is an instant and easy way of keeping pulse on the health of a small network like ours.
- Branch Cache: This a kind of application where by the BranchCache is switched on to advance data access if the server running window server 2012 R2 Essentials is situated offsite. It duplicates its content from the head office or hosted cloud content servers and caches the content at branch office locations, permitting client computers at branch offices to access the content within.
- Office 365 integration: The subsequent new structures in office 365 have been combined with Windows Server 2012 R2, SharePoint Library management and office 365 Distribution Groups management, small and medium size business that want to accelerate their cloud Journey.
- Remote Web Access: The Remote web Access can be updated and optimised for touch devices and enhanced functionality with rich HTML5 support. It displays a standardised looking interface.
- Mobile Device Management:
- Client Full System Restore:
Hardware requirements for the Network Operating System in line with our LAN design;
| Item | Minimum Requirement | Recommendation |
| Cable | Cat-6 UTP | Cat-6 UTP |
| Network Adapters | Ethernet 100Base-TX | Ethernet 1000Base-T |
| Switches and Routers | 100 Megabit Hub | 1.0 Gigabit Switch |
| Printers | Windows Compatible | HP2100, 4050 |
| Power | Surge Protector | Surge Protector & UPS |
| Servers
IP Phones WorkStation IP Camera’s |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2Ghz processor or better. Dual processors recommended
4 GB RAM Configured in an Active Directory Domain (Server) |
| There is an Anti-infringement system formed by Microsoft that imposes online authentication of the licensing of several recent Microsoft Windows Operating systems when going through different services, such a Windows Update, and downloading windows components from the Microsoft Download Centre.
In Windows 7, WGA is retitled Windows Activation Technologies. [1] WGA consists of two components: an installable component called WGA Notifications that hooks into Win logon and validates the Windows license upon each logon and an ActiveX control that checks the validity of the Windows license when downloading certain updates from the Microsoft Download Centre or Windows Update. WGA Notifications covers Windows XP and later, with the exception of Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional x64 Edition. The ActiveX control checks Windows 2000 Professional licenses as well. [2] Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_Genuine_Advantage |
Chapter 4. Services Provided by Nos to Support Operations and Management our Network systems.
The Network Operating systems we implemented is meant to cover the wide area management of our systems in terms of; Security, Performance and Reliability. Below are basic services provided by the Network Operating Systems in place; Directory Services, Telecommunication Services, File Services, Application Services
Directory Services: These are software application or systems that stores, provide access to and organise information which is in directory. Directory services can be applied for many things such authentication management, account management, active directory and DNS.
- Active Directory: This is a very important part of the directory services as it supplies different and all other directory services such as, account administration and authentication administration for clients and users in the same network. The account is managed by the Server through active directory which is very important for users as it will help them to run their accounts in which it does not limit users from primary functions. It works in a way that, before student could get access through login on, they would need a username and password which after they put their credentials in the server, which would now check their details to see whether they match with the details that are on server. If they are same with the details on the school network server, it will allow the user to have access to the account, however if they are different it will deny user access. Education for all server divided up into different groups, such as staff and student. Users can also make changes to their network domains, they can even add, delete and modify a network by the help of account management application. Although is handled by Group policies which are the rules of what user can do, such as, changing settings and what webpages they can access. Account management is split with active directory and it also pacts with password encryption. Its encryption is using a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). STM servers have its own given name; makes it easy instead of IP addresses , this is what the DNS server does.
- Authentication management: Members of staff and students that must have access to our Education for all Network systems from any workstation must have their own username and password. This method or process is called Authentication. The teachers have more access to webpages while students are restricted when they login from some websites such as, game sites. Yet, it is not just restricted to this as there could be much firmer questions that is yet to be answered such as, date of birth, email address, your first school attended or your first vehicle as this would help to improve a secured network.
- Domain Name Server (DNS): This is a kind of facility on the internet that interprets domain names into IP addresses because the internet is only actually built on IP addresses. STM servers are termed because it is easy to remember instead of IP addresses. It works in a way that, it has a list of all the IP addresses and from this you can name each device. On the server, all devices will see the device by the name given to it instead of their IP addresses. It is like database for the IP addresses. Most times users use a domain name, a DNS service will interpret the name into an IP address. DNS is a database system and so if one DNS server fails to translate a domain name then it would go on to another one and ask that until the correct IP address is retrieved.
Telecommunication Services: It is a facility or communication process where users can interconnect with one another using different servers and devices. Telecom services have several examples such as emails, internet relay chat (IRC), discussion boards, remote access, remote desktop and social networking.
- Communication: Common way of communication via network system is through emails, which is a medium where users can send and receive messages electronically to each other, and it is not time consuming. Services of this kind, is most especially for computers to basically send and receive messages to each other in which its frequently done by LAN networks and WAN networks as this will involve users send and receiving emails from around the world. A critical sample is shown in the below diagram. How emailing works as SMTP protocol post messages that users are sending, while the POP protocol let users to move the emails from their mail server to their computer, lastly the IMAP protocol will permit users to control their email messages which are in the server.
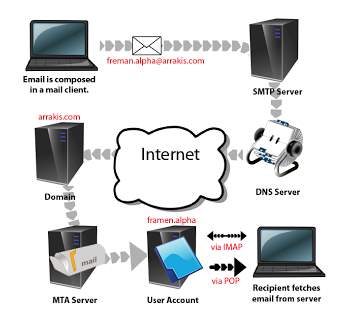
Ref: http://arunnighah.blogspot.co.uk/ |
- Internet Relay Chat (IRC): It is an easy chat service that accepts users to connect to an IRC server using a software program or web service to interconnect with each other. It is a text based service that is on the internet where real-time chats take place amongst users. A typical example is MSN.
File Services: the type of technology that allows server to share data internally in an organisation. Example are File Transfer and File sharing.
Application Services: An application that manages software based across a wide area network. E.g. Storage space, web, Proxy, Voice over IP(VoIP) and Mobile working.
Chapter 5. Benefits of our network systems
Managing a Network is as extremely important as building the network. Because we have designed and built a state of art facility and ensure there is a flexibility to add or downgrade the recourses for the proposed design. Below are some of the Potential Benefits the Network System Offers in terms of Information Transfer, Efficiency and Management.
Information Transfer:
- Added IT security: Most Part of our network application devices, including routers, have been mostly designed with built-in security qualities like firewalls that makes users getting online safer. Furthermore, with backups implementation over the network can progress the dimension of data security, and servers that are in secured location, can’t be stolen or otherwise accessed. In accordance, with
“The Computer Misuse Act (1990) recognized the following new offenses: Unauthorised access to computer material, Unauthorised entry with intent to commit or facilitate a crime, Unauthorised modification of computer material. Making, supplying or obtaining anything which can be used in computer misuse offences.”
“Computer Misuse Act 1990″. Legislation.gov.uk. N.p., 2017. Web. 1 May 2017.
- Creating users and groups: User accounts is a major level of entry control to a network. It is important that only authorised personnel are given user accounts and they are used in accordance with the organisation policy. Below are some of the policies in place;
- How users can interact with the network (including acceptable use)
- Detailed procedure for the creation, amendment and suspension of accounts.
- Penalties for Breach
- Length of password, acceptable password character
- Password ageing.
.
Efficiency:
- Better performance: Our System Servers are designed to support network by enhancing them for better performance, which is particularly useful for Web servers and email servers. fully enhanced servers can be used for file or database servers, also they can increase application and data accessibility, eventually producing a more prolific employees.
- Universal access to business applications: Our networking systems gives all our users access, even if they work in the main office, a remote office or from home, we have put in place a universal access to the same business applications and company information. This network is designed to also have open up advanced communications applications, like VoIP or video conferencing.
Management:
- Centralized backups: Supporting a data over a network can be centrally managed and scheduled, which is more reliable (not to mention more likely to happen on a regular basis). Data can also be saved to an off-site location. Which means that your backups are protected and harmless from any downtime or disasters at your office. As identified by The
Disaster recovery strategies, ISO/IEC 27031, the world-wide standard for IT disaster recovery, states, “Strategies should outline the approaches to implement the mandatory resilience so that the principles of incident prevention, detection, response, recovery and restoration are put in place.” Strategies define what you plan to do when responding to an incident, while plans describe how you will do it.
SECURITY:
Safeguarding and Protecting network systems, data and traffic is one of the greatest challenges for enterprises today. Securing your network infrastructure is key to preventing attacks, keeping out malware, and protecting your enterprise data from unauthorized access and loss. Meeting these demands is essential. Therefore, it is critical to identity your users and your network assets, because remote access, wireless networks, different sites and distributed systems are a reality of Enterprise Resource Planning.
To be effective in carrying Proper security checks and measures, there must be a planned and co-ordinated effort based on risk assessment with various tools and techniques put together to help secure the organisation. Carrying out this processes and techniques, we must follow the elements of good practice which states; it is paramount that network security is viewed as a continuous process, -new threats emerge daily and you must test to determine the effectiveness of your security. Which is based on policy.
Here are major steps we have followed to set our network security; The security Wheel
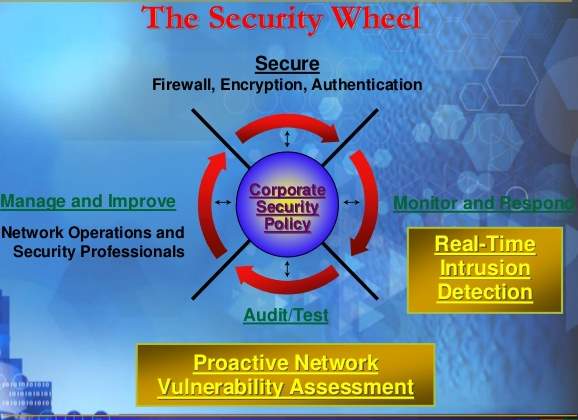
Ref: https://www.slideshare.net/laonap166/eximbank-security-presentation |
Embarking on the security wheel, we have policies in place that comply with the ISO/IEC code of practice (ISO/IEC 27002) that assist with information security management and drafting policies. Which states organisation must assess their own information risks, clarify their control objectives and apply important control measures using the (ISO/IEC 27002) standard for guidance.
Below are some of the major threats to a computer system that we have addressed in our networks design.
- Misuse of computer systems:
It has been proven that must of the computer misuse is committed by the employees of the organisation. Common sources of misuse include creating (and Paying) bogus employees, creating dummy purchase orders and paying invoices, etc. and for the fact that most of this misuse are caused by the clients there needs to be policy in place to help tackle this issue. These policies will make it difficult such activities to take place. Physical separation of duties will help a great deal. Employees needs to be educated not to share their IDs and passwords. Finally, before creating an employee on a payroll system, request must be received from HR Dept.
- Attacks on Networks:
Various surveys by the Computer Security Institute (CSI) found that 70% of most of the organisations said their network security defences had been breach, and sixty percent of the breaches came from within the organisation, confirmation again the internal threat is greater than the external threat. Below are some of the necessary counter measures we have implemented in our LAN Network system.
Physical disconnection: By switching off most of the computers after use and also locking down the computer rooms and also security access card to access the rooms where the computers are kept.
User Account: There should be password in every users account in the school, all students and staff should have username and password to be able to access their account, once an account is being shared by two users and there is fraud detected how would one know who committed the fraud. So, it’s a paramount for every student and staff member to have their own personal access.
Access Control List on a router (ACLS): Access Control List on a router are means by which traffic can be controlled based upon IP addresses. Traffic can be filtered on source address, destination address and port, giving network managers the ability to prevent unauthorised traffic from our network systems. As you can see from the diagram below, with the help of ACL students cannot access the finance server.
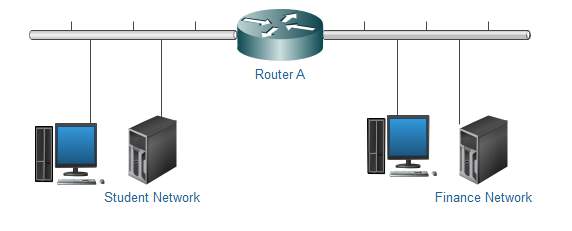
Ref: Self drawn |
Hardware Firewall (Routed Firewall): Firewallsare piece of software appliances often built into a border router itself (Adaptive security appliance. ASA). Function of a firewall is to examine packets (both sourced from internal and external addresses) and to apply pre-configured security policies to them. It prevents hackers and harmful data from entering the organisation. It protects the entire networks because it’s been implemented on the router.
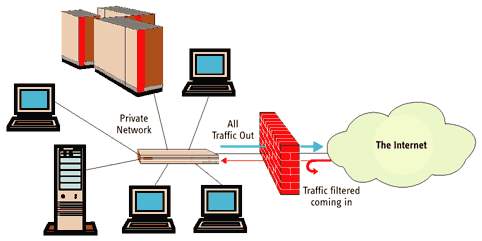
Ref: https://www.online-sciences.com/computer/software-firewalls-and-hardware-firewalls-advantages-and-disadvantages/ |
Software Firewall: Compare to hardware cousins, software firewalls are very important for single users or small productions that have dial-up or broadband Internet networks. Instead of using a custom (and often expensive) piece of hardware, a software firewall installs on an individual’s PC, notebook, or workgroup server.
Even if an organization has hardware firewalls in place, it is of paramount interest for individuals to use software firewalls on their own systems. The core reason: software firewalls are particularly suitable for mobile staffs who wants digital security when working separately of the corporate network. Since the entire security solution is just a single application running in one’s devices. Another key advantage, software firewalls are effortlessly upgraded. Users basically download this software from firewall provider’s web site, or the provider guides these enhancements through the Internet. E.g. McAfee® for Consumer
VLANS: Boundaries created by VLAN over a network LAN, marks the end of logical subnet. For access to other subnets (VLANs), then it must pass through a routed (Layer 3) device. Any time you send traffic through a router, we can add filtering options (such as access lists) and other security measures.
Virus Protection: Computer viruses is another major threat to networks and systems. The development of networks and emails means viruses can spread easily and quickly. But we have put in place a security policy to check and deal with the threat of computer viruses, which could let to either denial of services or can be used to open a back door into the system. Protecting the systems from viruses, the staff and students will be educated of the necessity to be aware of the risks of computer viruses and the way in which they can spread. Our policy has been aimed to minimize the threat of viruses. Some of our policies below;
- Regulate the use of portable media, such as floppy disk, memory stick and CDs and DVDs.
- Controlling of sending and receiving email attachments
- Control downloads from the web
- Control the installation of software
- Ensure that every machine has an up-to-date Virus checker
- Ensure each machine is regularly updated with the latest version of anti-virus software.
Data backup and Recovery:
1.The immediate measures that get operations up and running again temporarily, but the disaster recovery effort is not finished until the organization is completely back to normal operations.
2.Initial Response following an Emergency disruption to an Organisation is designed to:
Contain the damage caused by the disaster.
– Recover whatever capabilities that can be immediately restored. Include a variety of activities depending upon the nature of the disaster and may include activating an alternate processing facility, containing physical damage or calling in contractors to begin an emergency response.
3.During a disaster recovery effort, the focus of most of the organization shifts from normal business activity to a concentrated effort to restore operations as quickly as possible.
But before we go into detailed recovery plan, we need to consider risk assessment (RA) and business impact analysis (BIA) to identify the IT services that support the academy critical business activities. Which we will then establish the recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs).
Conclusion:
The tactics used in our services outlined above are some of the enhancements we have put in place to improve most importantly the security and management services of our Network systems. It is vital to recognize that, while it’s better late than never, security measures decrease in their effectiveness the longer you wait to implement them. Security cannot be an afterthought and must be implemented from the start alongside the services and applications you are providing. The facilities we have put in place in our Network design model is a state of art facility that conform with durability and flexibility in case of expansion in the future.
References:
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Community Development"
Community development is defined by the UN as "a process where community members come together to take collective action and generate solutions to common problems".
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




