Oracle, MySQL and MongoDB Databases Performance
Info: 11038 words (44 pages) Dissertation
Published: 16th Dec 2019
- INTRODUCTION
| Requirement ID | Priority | Requirement |
| REQ 01 | Mandatory | 1. Read/Insert/Delete Function for oracle Input : Required value and table name Output: Time in milliseconds taken to read/insert/delete data from the given oracle table. Processing: Open the given table and read/insert/delete the data from table and calculate the read/insert/delete time in milliseconds. |
| REQ 02 | Mandatory | 2. Read/Insert/Delete Function for MongoDB Input : Required value and table name Output: Time in milliseconds taken to read/insert/delete data from the given MongoDB table. Processing: Open the given document and read/insert/delete the data from that document and calculate the time in milliseconds. |
| REQ 03 | Mandatory | 3.Read/Insert/Delete Function for MySQL Input: Required value and table name Output: Time in milliseconds taken to read/insert/delete data from the given MySQL table. Processing: Open the given table and read/insert/delete the data from table and calculate the time in milliseconds. |
| REQ 04 | Mandatory | 4. Graph Generation Input : Calculated time Output: Graph for comparing Read/Insert/Delete operations between Oracle, MySQL and MongoDB. Processing: Take the calculated time from table and generate graph. |
- Hardware Requirements
- System : Pentium IV with minimum 1.60GHz.
- Hard Disk : 80 GB
- Monitor : 14” Color Monitor
- Mouse : Optical Mouse
- Ram : 2 GB.
- Software Requirements
- Windows Operating System
- Java
- Servlet API
- Oracle 10G Express Edition
- MySQL
- MongoDB
- MySQL WorkBench
- RoboMongo
- Ojdbc API
- Mongo-java-driver API
- Mysql-connector-java API
- Block/Architectural Design:
- Analysis Diagrams
UML remains for Unified Modeling Language. This question situated arrangement of documentation has advanced from the work of Grady Booch, James Rumbaugh, Ivar Jacobson, and the Rational Software Corporation. These eminent PC researchers combined their particular advances into a solitary, institutionalized model. Today, UML is acknowledged by the Object Management Group (OMG) as the standard for displaying object situated projects.
Types of UML Diagrams
- Use Case Diagram

Use Cases
 Use Case Diagram:
Use Case Diagram:
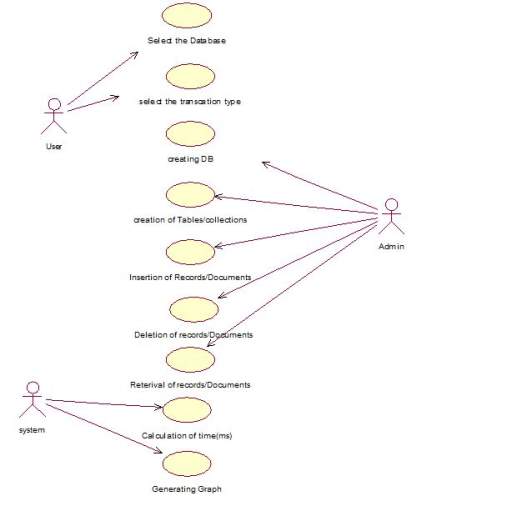 Fig. 3.1 Use Case Diagram
Fig. 3.1 Use Case Diagram
- Sequence Diagram
- Identify objects.
- Identify actor.
- Add messages to the diagram.
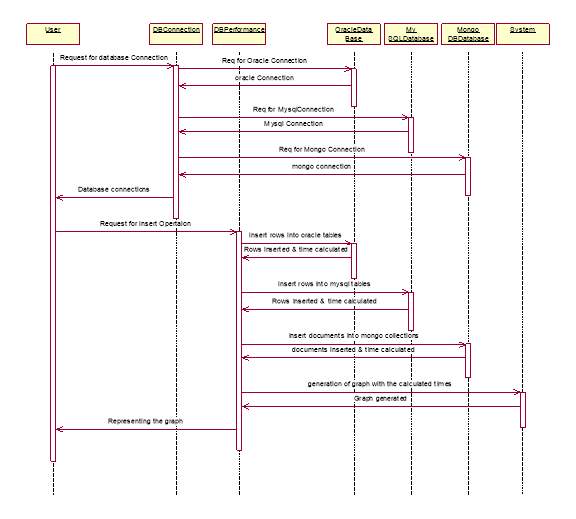 Fig. 3.1.2.1 Sequence diagram for inserting the data into the databases
Fig. 3.1.2.1 Sequence diagram for inserting the data into the databases
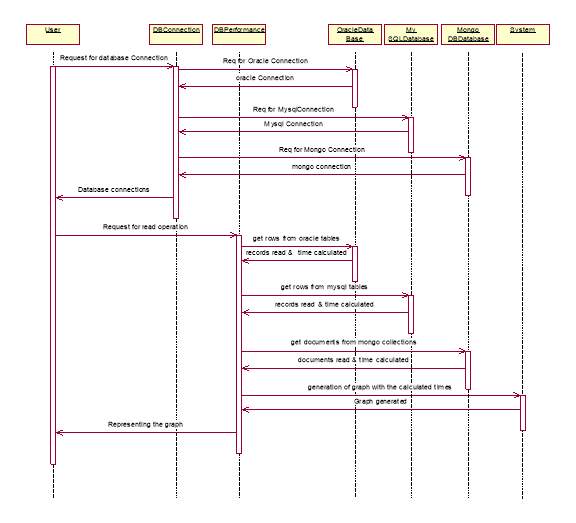 3.1.2.2 Sequence diagram for reading data from the databases
3.1.2.2 Sequence diagram for reading data from the databases
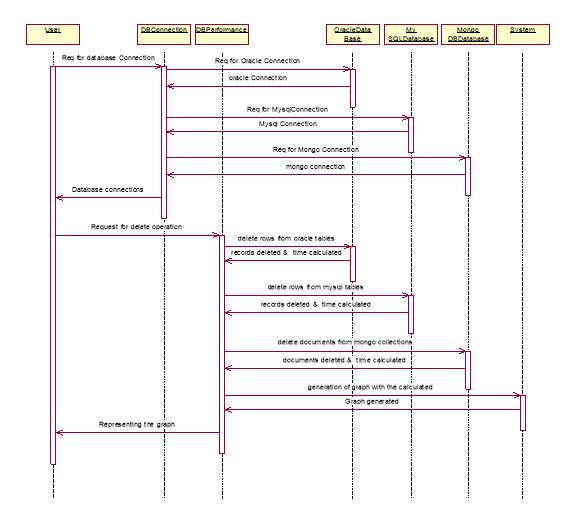 Fig. 3.1.2.3 Sequence diagram for deleting the data from the databases
Fig. 3.1.2.3 Sequence diagram for deleting the data from the databases
- Data Design:
- A class is a description of a group of objects with common properties (attributes), common behavior (operations), common relationships to other objects (associations and aggregations), and common semantics.
- A class is shown using the following notation:
 Class Diagram:
Class Diagram:
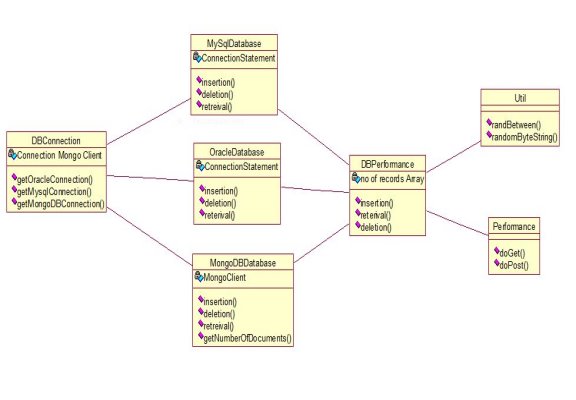 Fig. 3.2.1 Class Diagram
Fig. 3.2.1 Class Diagram
- Implementation Design:

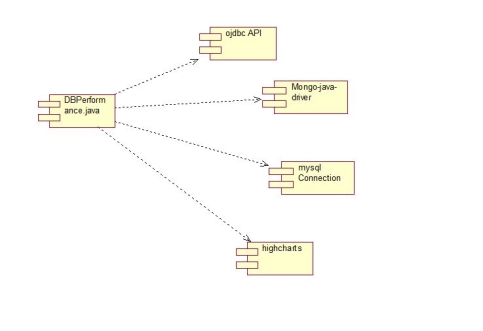 Fig. 3.3.1Component Diagram
Fig. 3.3.1Component Diagram
- Deployment Diagram:
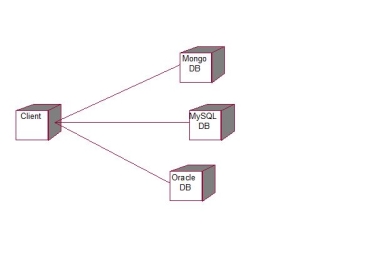
Fig. 3.3.2 Deployment Diagram
4. IMPLEMENTATION
Modules
4.1 Installation of databases
4.1.1 Installation of Oracle Database: Oracle 10g installation is done via Oracle Universal Installer. Enter the database name and password.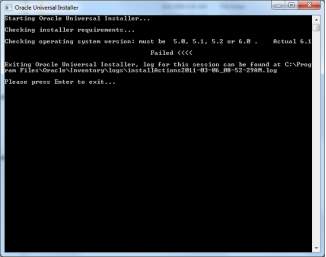
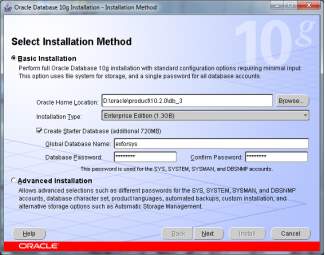
- In this screen, the Source and Destination locations must be selected. The Source path should reflect either your the directory in which you unzipped the source files. For the Destination, leave the Oracle Home named oraDb10g_home as the default. Choose a hard disk drive that has at least 6 gigabytes of free space.
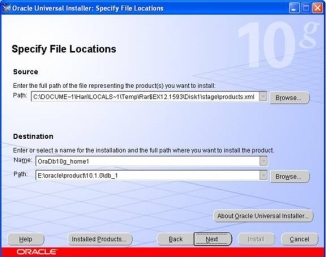
- Click on the Next button to select installation type. This may take up to 2 minutes. Once the product information has been read, the following 3 "Available Products" options are presented. After selecting the type click on the next button to get the screen:
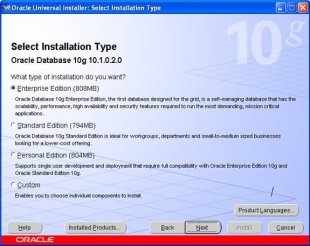
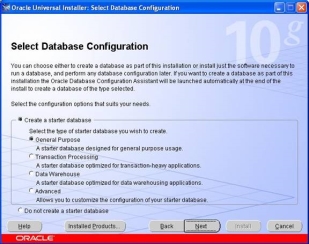
- For this installation, we choose the "General Purpose" Database option. Click on the Next button to continue. The next step is to identify the database using the Global database name
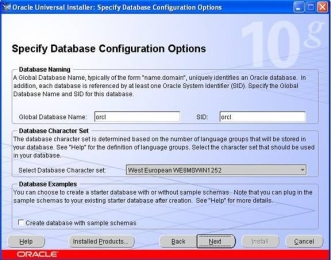
- In this step, we need to select where the Oracle data files should be located. We typically keep the data files on a separate disk , however, for this install, keep the default storage. Click on the Next button to move to the "Summary" screen:
- In this screen (shown above), the products and files that will be installed are summarized. If everything looks OK at this point, click on the Install button to begin the installation. During the install, you will notice various Oracle products being copied over to the hard disk. Once the installation is completed, the next step will be to configure the various additional services and the database.
- Click on the next button .The Oracle Database Configuration Assistant will appear for some time while the default database is created and opened. Once the default database has been installed, the second screen will appear.
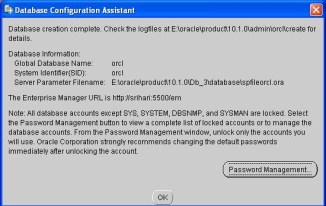
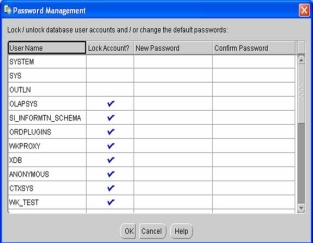
- Click on the Password Management button and change the default passwords for the SYS, SYSTEM, SCOTT and DBSNMP accounts as shown below:
- Click the OK button to complete the installation. The following screen will be appears.
- After completion of installation reboot your computer.
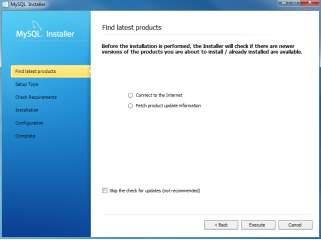
- Windows configures MySQL Installer and A welcome screen provides several options. Choose the first option: Install MySQL Products
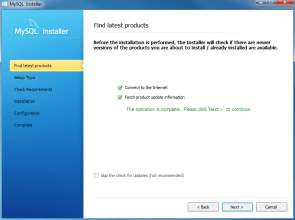
- Download the latest MySQL products : MySQL installer checks and downloads the latest MySQL products including MySQL server, MySQL Workbench,etc. Click Next button to continue
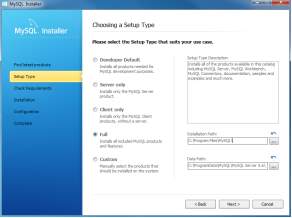
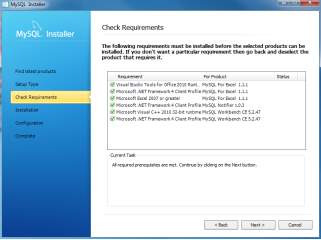
- There are several setup types available. Choose the Full option to install all MySQL products and features. Checking Requirements
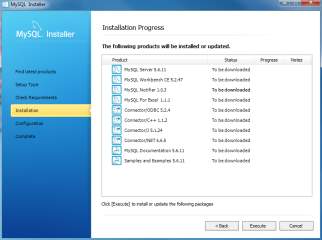 MySQL Installer downloads all selected products. It will take a while, depending on which products that you selected and the speed of your internet connection.
MySQL Installer downloads all selected products. It will take a while, depending on which products that you selected and the speed of your internet connection.
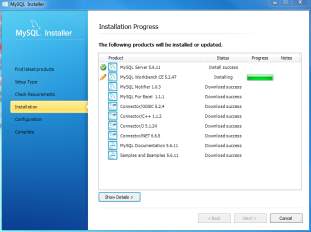
- Once download complete click Next button to continue…. Choose Configuration Type and MySQL port (3306 by default) and click Next button to continue configure MySQL Database Server
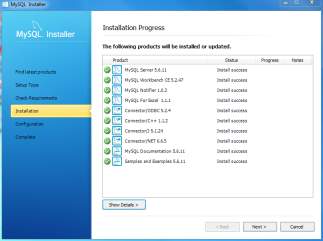
- Choose a password for the root account. Choose Windows service details including Windows Service Name and account type, then click Next button to continue.
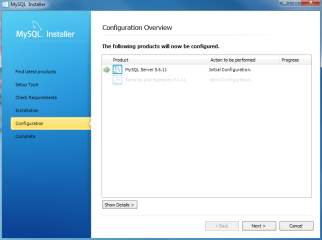
- MySQL Installer is configuring MySQL database server. Wait until it is done and click Next button to continue.
- Once MySQL Server Configuration done. Click the Next button to continue. MySQL Installer installs sample databases and sample models.
- Click finish button to close the installation wizard and launch the MySQL Workbench.
- one for Newer OS, Windows server 2008 and Windows 7, Server 2012 (download link Big Green button)
- other for Older OS, Windows Server 2003,2008 and Vista (Download link, 64-bit legacy )
- After you download, you will get zip archive in follwing format- mongodb—.zip
 Setup up configuration parameters and start/stop MongoDB
For starting and stopping the MongoDB server, we need only the bin/mongod.exe, which is the daemon process executable for MongoDB. In short, it is the executable which starts up the MongoDB Server.
For starting up, we need to provide the parameters for executable as config parameters or params. We can setup the config parameters using the two ways
Setup up configuration parameters and start/stop MongoDB
For starting and stopping the MongoDB server, we need only the bin/mongod.exe, which is the daemon process executable for MongoDB. In short, it is the executable which starts up the MongoDB Server.
For starting up, we need to provide the parameters for executable as config parameters or params. We can setup the config parameters using the two ways
- Using command line options or
- Using config file
- Use the following commands to start the server process
- Change to bin directory
- cd I:\Servers\mongodb\bin
- mangod to start the mongod process
- mongod --dbpath I:\Servers\data --port 27017
- While starting, Windows firewall may block the process as shown as follows
- Click “Allow access” to proceed. After successful execution of command, it will show logging info in standard console itself as shown follows:
- $> mongod --dbpath D:\Servers\data --port 27017
- If you specify the logpath option, then logging will direct to that log file instead of showing up on standard console
- $> mongod --dbpath D:\Servers\data --port 27017 --logpath D:\Servers\logs\mongod.log.
4.2 Creation of Tables
4.2.1 Table creation in Oracle: create table student"+number+" (ROLL_NO Number ,NAMEVarchar2(32),FATHER_NAME Varchar2(32),"+ "YEAR Varchar2(10),SEMISTER Varchar2(10),DOBDate,PHONE, Varchar2(12),PERCENTAGE Number,BRANCH_NAME Varchar2(12))" 4.2.2 Table creation in MySQL: create table student"+number+" (ROLL_NO int(11),NAME Varchar(32),FATHER_NAME Varchar(32),"+"YEAR Varchar(10),SEMISTER Varchar(10),DOB Date, PHONE Varchar(12),PERCENTAGE int(3),BRANCH_NAME Varchar(12)) 4.2.3 Creation of a document in MongoDB: Insert Intostudent"+number+"(ROLL_NO,NAME,FATHER_NAME,YEAR,SEMISTER,DOB,PHONE,PERCENTAGE,BRANCH_NAME) values("+i+",'"+randomByteString()+"','"+randomByteString()+"','"+YEARS.values()[r.nextInt(4)]+"','"+SEM.values()[r.nextInt(2)]+"','"+date+"','"+phoneNO+"',"+r.nextInt(100)+",'"+BRANCHES.values()[r.nextInt(6)]+"4.3 Designing the Web Application

4.4 Performing operations on databases
Operations performed on the databases are insertion, deletion and reterival of data from the tables /documents. 4.4.1 Queries performed in MongoDB for transaction insertion ,deletion and reterival of document BasicDBObject document = new BasicDBObject(); document.put("ROLL_NO", i); document.put("NAME", Util.randomByteString()); document.put("FATHER_NAME", Util.randomByteString()); document.put("YEAR", YEARS.values()[r.nextInt(4)]+""); document.put("SEMISTER",SEM.values()[r.nextInt(2)]+""); document.put("DOB",date); document.put("PHONE",phoneNO); document.put("PERCENTAGE",r.nextInt(100)); document.put("BRANCH_NAME",BRANCHES. values()[r.nextInt(6)]+""); table.insert(document); table.drop(); 4.4.2 Queries performed in MySQL for transaction insertion ,deletion and reterival of document- “Insertinto student"+number+"(ROLL_NO,NAME,FATHER_NAME,YEAR,SEMISTER,DOB,PHONE,PERCENTAGE,BRANCH_NAME) values("+i+",'"+Util.randomByteString()+"','"+Util.randomByteString()+"','"+YEARS.values()[r.nextInt(4)]+"','"+SEM.values()[r.nextInt(2)]+"','"+date+"','"+phoneNO+"',"+r.nextInt(100)+",'"+BRANCHES.values()[r.nextInt(6)]+"'
- “delete from student"+number
- “select * from student”+number
- “insert into student"+number+"(ROLL_NO,NAME,FATHER_NAME,YEAR,SEMISTER,DOB,PHONE,PERCENTAGE,BRANCH_NAME) values("+i+",'"+Util.randomByteString()+"','"+Util.randomByteString()+"','"+YEARS.values()[r.nextInt(4)]+"','"+SEM.values()[r.nextInt(2)]+"','"+date+"','"+phoneNO+"',"+r.nextInt(100)+",'"+BRANCHES.values()[r.nextInt(6)]+"'
- "delete from student"+number
- “select * from student"+number
Module 5: Generation of Graph
 5. CODING
DBPerformance.java
package com.db.performance;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DBPerformance {
int numbersArray[] = new int[] { 100, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000,
3500, 4000, 4500, 5000};
public Map<String,Object> insertion(String db1,String db2){
long db1Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
long db2Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
switch (db1) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0)
odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
db1Timings[i] = odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0){
mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber>0){
mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
switch (db2) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0)
odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
db2Timings[i] = odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0){
mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber>0){
mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("type", "Insert");
map.put("db1Name", db1);
map.put("db2Name", db2);
map.put("db1Timings", db1Timings);
map.put("db2Timings", db2Timings);
return map;
}
public Map<String, Object> deletion(String db1,String db2){
long db1Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
long db2Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
switch (db1) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0)
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
db1Timings[i] = odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
switch (db2) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0)
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
db2Timings[i] = odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("type", "Delete");
map.put("db1Name", db1);
map.put("db2Name", db2);
map.put("db1Timings", db1Timings);
map.put("db2Timings", db2Timings);
return map;
}
public Map<String,Object> retreival(String db1, String db2) {
long db1Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
long db2Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
switch (db1) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = odb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mydb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mdb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
switch (db2) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = odb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mydb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mdb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("type", "Read");
map.put("db1Name", db1);
map.put("db2Name", db2);
map.put("db1Timings", db1Timings);
map.put("db2Timings", db2Timings);
return map;
}
public List<Map<String,Object>> recordsInsertion() {
int tableArray[] = new int[]{100,500,1000,1500,2000};
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
int noOfRecords[] = new int[] { 1, 10, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500};
long timeArray[] = new long[3];
for (int number : noOfRecords) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
timeArray[0] = odb.addingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[1] = mydb.addingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[2] = mdb.addingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
map.put("rows", number);
map.put("oracleTime", timeArray[0]);
map.put("mysqlTime", timeArray[1]);
map.put("mongoDBTime", timeArray[2]);
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
public List<Map<String,Object>> recordsDeletion() {
int tableArray[] = new int[]{100,500,1000,1500,2000};
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
int noOfRecords[] = new int[] { 1, 10, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500};
long timeArray[] = new long[3];
for (int number : noOfRecords) {
if(number <=tableArray[4]){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
timeArray[0] = odb.removingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[1] = mydb.removingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[2] = mdb.removingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
map.put("rows", number);
map.put("oracleTime", timeArray[0]);
map.put("mysqlTime", timeArray[1]);
map.put("mongoDBTime", timeArray[2]);
list.add(map);
}
}
return list;
}
}
Util.java
package com.db.performance;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Random;
public class Util {
static Random r = new Random();
public static int randBetween(int start, int end) {
return start + (int)Math.round(Math.random() * (end - start));
}
public static String randomByteString() {
char[] chars = "abcdefghijklmnop/qrstuvwxyz".toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int length = r.nextInt(32);
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = chars[r.nextInt(chars.length)];
sb.append(c);
}
String word=sb.toString().replaceAll("/"," ");
return word;
}
public static int getMaxStudentId(int number){
DBConnections dbc = new DBConnections();
int studentId = 0;
try {
Connection con = dbc.getOracleConnection();
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
String sql = "select MAX(ROLL_NO) ID from student"+number;
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
studentId = rs.getInt("ID");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return studentId;
}
public static int getMaxStudentIdFromMySQL(int number) {
DBConnections dbc = new DBConnections();
int studentId = 0;
try {
Connection con = dbc.getMysqlConnection();
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
String sql = "select MAX(ROLL_NO) ID from student"+number;
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
studentId = rs.getInt("ID");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return studentId;
}
}
Hello.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<link href="css/application.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<title>home</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1
style="text-align: center; margin-top: 2%; font-family: MyHelvetica; font-size: 50px;">Database
Performance Analysis</h1>
<form
style="padding: 20px; border: 1px solid black; border-radius: 10px; width: 400px; background-color: #b3ccff; margin-left: 35%"
name="performanceForm" action="/DBPerformanceAnalysis/Performance"
method="post">
<table cellpadding="15" align="center">
<tr>
<th colspan=4>Transaction Type <select name="operationType"
class="wrapper-dropdown-3">
<option value="">---select---</option>
<option>Insert</option>
<option>Read</option>
<option>Delete</option>
</select>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Database 1</th>
<td><select name="database1" class="wrapper-dropdown-3">
<option value="">---select---</option>
<option>Oracle</option>
<option>MySQL</option>
<option>MongoDB</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Database 2</th>
<td><select name="database2" class="wrapper-dropdown-3">
<option value="">---select---</option>
<option>Oracle</option>
<option>MySQL</option>
<option>MongoDB</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
</table>
<br /> <input type="submit" value="Analyse" class="buttons"
style="cursor: pointer; height: 50px; background-color: rgba(242, 242, 242, 0.4); width: 200px; font-family: RIKY2vamp; font-size: 30px; border-radius: 8px;">
<br /> <br />
<a href="/DBPerformanceAnalysis/Performance">ClickHere</a> to analyse More.
<br/>
<a href="/DBPerformanceAnalysis/DBAnalysis">Analyse</a>
</form>
</div>
<div id="footer">
<img class="logos" loading="lazy" src="./images/oracle_logo.png" id="oracle"
alt="oracle_logo"> <img class="logos"
src="./images/mysql_logo.png" id="mysql" alt="mysql_logo"> <img class="logos" loading="lazy" src="./images/mongoDB_logo.png" id="mongoDB"
alt="mongoDB_logo">
</div>
</body>
</html>
5. INTERFACE
5. CODING
DBPerformance.java
package com.db.performance;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DBPerformance {
int numbersArray[] = new int[] { 100, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000,
3500, 4000, 4500, 5000};
public Map<String,Object> insertion(String db1,String db2){
long db1Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
long db2Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
switch (db1) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0)
odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
db1Timings[i] = odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0){
mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber>0){
mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
switch (db2) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0)
odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
db2Timings[i] = odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength>0){
mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber>0){
mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("type", "Insert");
map.put("db1Name", db1);
map.put("db2Name", db2);
map.put("db1Timings", db1Timings);
map.put("db2Timings", db2Timings);
return map;
}
public Map<String, Object> deletion(String db1,String db2){
long db1Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
long db2Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
switch (db1) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0)
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
db1Timings[i] = odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
switch (db2) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0)
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
db2Timings[i] = odb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mydb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mdb.deletion(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("type", "Delete");
map.put("db1Name", db1);
map.put("db2Name", db2);
map.put("db1Timings", db1Timings);
map.put("db2Timings", db2Timings);
return map;
}
public Map<String,Object> retreival(String db1, String db2) {
long db1Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
long db2Timings[] = new long[numbersArray.length];
switch (db1) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = odb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mydb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db1Timings[i] = mdb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
switch (db2) {
case "Oracle": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
int rowsLength = odb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
odb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = odb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MySQL": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
int rowsLength = mydb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(rowsLength==0){
mydb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mydb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
case "MongoDB": {
for (int i = 0; i < numbersArray.length; i++) {
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
int documentsNumber = mdb.getNumberofRecords(numbersArray[i]);
if(documentsNumber==0){
mdb.insertion(numbersArray[i]);
}
db2Timings[i] = mdb.retrieval(numbersArray[i]);
}
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("type", "Read");
map.put("db1Name", db1);
map.put("db2Name", db2);
map.put("db1Timings", db1Timings);
map.put("db2Timings", db2Timings);
return map;
}
public List<Map<String,Object>> recordsInsertion() {
int tableArray[] = new int[]{100,500,1000,1500,2000};
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
int noOfRecords[] = new int[] { 1, 10, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500};
long timeArray[] = new long[3];
for (int number : noOfRecords) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
timeArray[0] = odb.addingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[1] = mydb.addingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[2] = mdb.addingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
map.put("rows", number);
map.put("oracleTime", timeArray[0]);
map.put("mysqlTime", timeArray[1]);
map.put("mongoDBTime", timeArray[2]);
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
public List<Map<String,Object>> recordsDeletion() {
int tableArray[] = new int[]{100,500,1000,1500,2000};
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
int noOfRecords[] = new int[] { 1, 10, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500};
long timeArray[] = new long[3];
for (int number : noOfRecords) {
if(number <=tableArray[4]){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
OracleDatabase odb = new OracleDatabase();
MySQLDatabase mydb = new MySQLDatabase();
MongoDBDatabase mdb = new MongoDBDatabase();
timeArray[0] = odb.removingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[1] = mydb.removingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
timeArray[2] = mdb.removingRecordsToExisting(number,tableArray[4]);
map.put("rows", number);
map.put("oracleTime", timeArray[0]);
map.put("mysqlTime", timeArray[1]);
map.put("mongoDBTime", timeArray[2]);
list.add(map);
}
}
return list;
}
}
Util.java
package com.db.performance;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Random;
public class Util {
static Random r = new Random();
public static int randBetween(int start, int end) {
return start + (int)Math.round(Math.random() * (end - start));
}
public static String randomByteString() {
char[] chars = "abcdefghijklmnop/qrstuvwxyz".toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int length = r.nextInt(32);
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = chars[r.nextInt(chars.length)];
sb.append(c);
}
String word=sb.toString().replaceAll("/"," ");
return word;
}
public static int getMaxStudentId(int number){
DBConnections dbc = new DBConnections();
int studentId = 0;
try {
Connection con = dbc.getOracleConnection();
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
String sql = "select MAX(ROLL_NO) ID from student"+number;
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
studentId = rs.getInt("ID");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return studentId;
}
public static int getMaxStudentIdFromMySQL(int number) {
DBConnections dbc = new DBConnections();
int studentId = 0;
try {
Connection con = dbc.getMysqlConnection();
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
String sql = "select MAX(ROLL_NO) ID from student"+number;
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
studentId = rs.getInt("ID");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return studentId;
}
}
Hello.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<link href="css/application.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<title>home</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1
style="text-align: center; margin-top: 2%; font-family: MyHelvetica; font-size: 50px;">Database
Performance Analysis</h1>
<form
style="padding: 20px; border: 1px solid black; border-radius: 10px; width: 400px; background-color: #b3ccff; margin-left: 35%"
name="performanceForm" action="/DBPerformanceAnalysis/Performance"
method="post">
<table cellpadding="15" align="center">
<tr>
<th colspan=4>Transaction Type <select name="operationType"
class="wrapper-dropdown-3">
<option value="">---select---</option>
<option>Insert</option>
<option>Read</option>
<option>Delete</option>
</select>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Database 1</th>
<td><select name="database1" class="wrapper-dropdown-3">
<option value="">---select---</option>
<option>Oracle</option>
<option>MySQL</option>
<option>MongoDB</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Database 2</th>
<td><select name="database2" class="wrapper-dropdown-3">
<option value="">---select---</option>
<option>Oracle</option>
<option>MySQL</option>
<option>MongoDB</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
</table>
<br /> <input type="submit" value="Analyse" class="buttons"
style="cursor: pointer; height: 50px; background-color: rgba(242, 242, 242, 0.4); width: 200px; font-family: RIKY2vamp; font-size: 30px; border-radius: 8px;">
<br /> <br />
<a href="/DBPerformanceAnalysis/Performance">ClickHere</a> to analyse More.
<br/>
<a href="/DBPerformanceAnalysis/DBAnalysis">Analyse</a>
</form>
</div>
<div id="footer">
<img class="logos" loading="lazy" src="./images/oracle_logo.png" id="oracle"
alt="oracle_logo"> <img class="logos"
src="./images/mysql_logo.png" id="mysql" alt="mysql_logo"> <img class="logos" loading="lazy" src="./images/mongoDB_logo.png" id="mongoDB"
alt="mongoDB_logo">
</div>
</body>
</html>
5. INTERFACE
5.1 Screen Shots: Interface Design
 5.1.1Getting started for database performance analysis
5.1.1Getting started for database performance analysis
 5.1.2 Selecting transaction type(insertion/retrieval/deletion)
5.1.2 Selecting transaction type(insertion/retrieval/deletion)
 5.1.3 Selecting transaction type(insertion/retrieval/deletion)
5.1.3 Selecting transaction type(insertion/retrieval/deletion)
 5.1.4 selecting the databases to analyse
5.1.4 selecting the databases to analyse
5.2 Screen Shots: Graph Generation Module
Transaction type: Insert
| Number of records | Oracle: Time taken in ms | MongoDB: Time taken in ms |
| 100 | 4652 | 563 |
| 500 | 25326 | 629 |
| 1000 | 52328 | 1099 |
| 1500 | 79852 | 940 |
| 2000 | 115444 | 1484 |
| 2500 | 120304 | 2921 |
| 3000 | 150277 | 2058 |
| 3500 | 183788 | 3215 |
| 4000 | 187444 | 4954 |
| 4500 | 210028 | 4142 |
| 5000 | 210976 | 5028 |
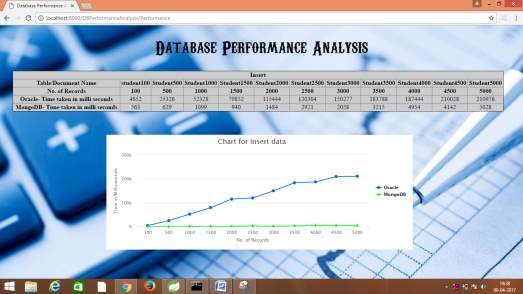 5.2.1 Graph generated by the above results for insertion
Transaction type: Read
5.2.1 Graph generated by the above results for insertion
Transaction type: Read
| Number of records | MySQL : Time taken in ms | MongoDB : Time taken in ms |
| 100 | 2 | 0 |
| 500 | 4 | 1 |
| 1000 | 6 | 0 |
| 1500 | 9 | 0 |
| 2000 | 11 | 0 |
| 2500 | 14 | 0 |
| 3000 | 17 | 0 |
| 3500 | 20 | 0 |
| 4000 | 23 | 0 |
| 4500 | 25 | 0 |
| 5000 | 27 | 0 |
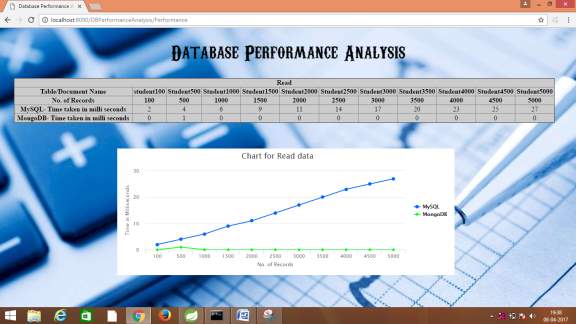 5.2.2 Graph generated by the above results for retrieval
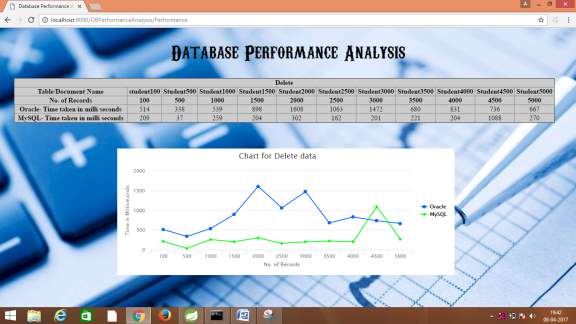
Transaction type: Delete
5.2.2 Graph generated by the above results for retrieval
Transaction type: Delete
| Number of records | Oracle: Time taken in ms | MySQL: Time taken in ms |
| 100 | 514 | 209 |
| 500 | 338 | 37 |
| 1000 | 539 | 259 |
| 1500 | 898 | 204 |
| 2000 | 1608 | 302 |
| 2500 | 1063 | 162 |
| 3000 | 1472 | 201 |
| 3500 | 680 | 221 |
| 4000 | 831 | 204 |
| 4500 | 736 | 1088 |
| 5000 | 667 | 270 |
 5.2.3 Graph generated by the above results for deletion
Transaction type: Insert
5.2.3 Graph generated by the above results for deletion
Transaction type: Insert
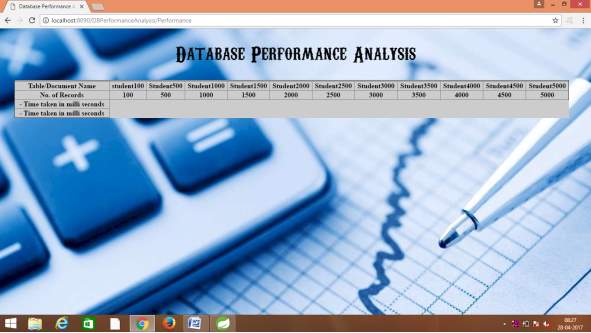
| Table/Document Name | No of records | Time taken in milli seconds | ||
| Oracle | MySQL | MondoDB | ||
| Student100 | 100 | 4317 | 4056 | 459 |
| Student500 | 500 | 13393 | 21792 | 923 |
| Student1000 | 1000 | 19741 | 39529 | 1160 |
| Student1500 | 1500 | 23579 | 58908 | 993 |
| Student2000 | 2000 | 22346 | 82410 | 1342 |
| Student2500 | 2500 | 19979 | 162919 | 1332 |
| Student3000 | 3000 | 6993 | 115927 | 2297 |
| Student3500 | 3500 | 8645 | 142075 | 2227 |
| Student4000 | 4000 | 11481 | 165914 | 2437 |
| Student4500 | 4500 | 1295 | 194406 | 5128 |
| Student5000 | 5000 | 15200 | 20542 | 3426 |
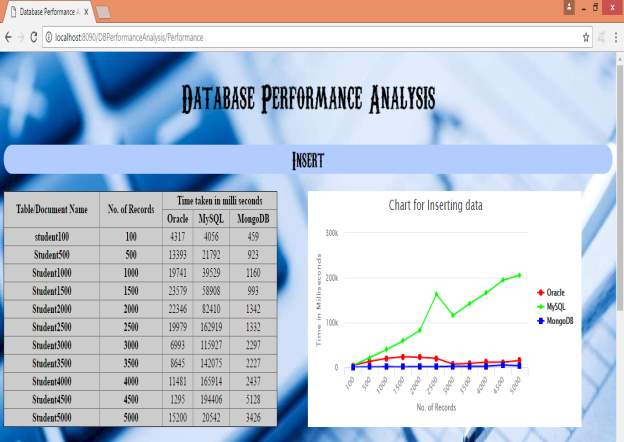 5.2.4 Graph generated by the above results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases
Transaction type: Read
5.2.4 Graph generated by the above results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases
Transaction type: Read
| Table/Document Name | No of records | Time taken in milli seconds | ||
| Oracle | MySQL | MondoDB | ||
| Student100 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Student500 | 500 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| Student1000 | 1000 | 1 | 7 | 0 |
| Student1500 | 1500 | 1 | 29 | 0 |
| Student2000 | 2000 | 1 | 14 | 0 |
| Student2500 | 2500 | 1 | 17 | 0 |
| Student3000 | 3000 | 1 | 18 | 0 |
| Student3500 | 3500 | 1 | 30 | 0 |
| Student4000 | 4000 | 1 | 24 | 0 |
| Student4500 | 4500 | 1 | 62 | 0 |
| Student5000 | 5000 | 1 | 36 | 0 |
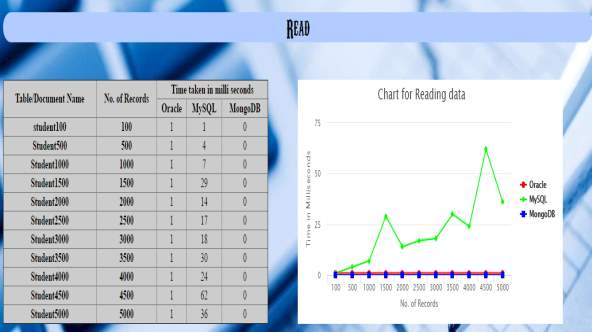 5.2.5 Graph generated by the above results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases
Transaction type: Delete
5.2.5 Graph generated by the above results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases
Transaction type: Delete
| Table/Document Name | No of records | Time taken in milli seconds | ||
| Oracle | MySQL | MondoDB | ||
| Student100 | 100 | 215 | 303 | 163 |
| Student500 | 500 | 319 | 364 | 52 |
| Student1000 | 1000 | 511 | 158 | 44 |
| Student1500 | 1500 | 600 | 322 | 70 |
| Student2000 | 2000 | 646 | 201 | 45 |
| Student2500 | 2500 | 649 | 120 | 49 |
| Student3000 | 3000 | 1972 | 492 | 48 |
| Student3500 | 3500 | 1613 | 1926 | 48 |
| Student4000 | 4000 | 1386 | 982 | 2 |
| Student4500 | 4500 | 1453 | 1261 | 40 |
| Student5000 | 5000 | 2030 | 320 | 61 |
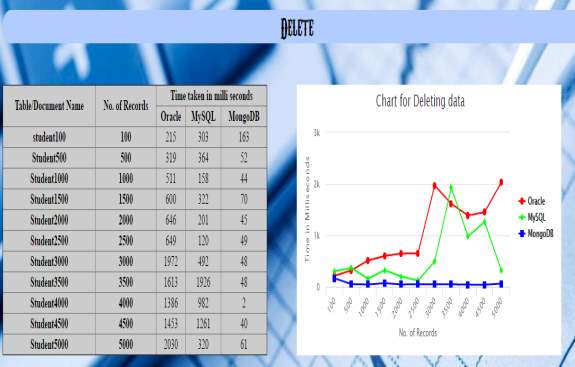 5.2.6 Graph generated by the above results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases
5.2.6 Graph generated by the above results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases
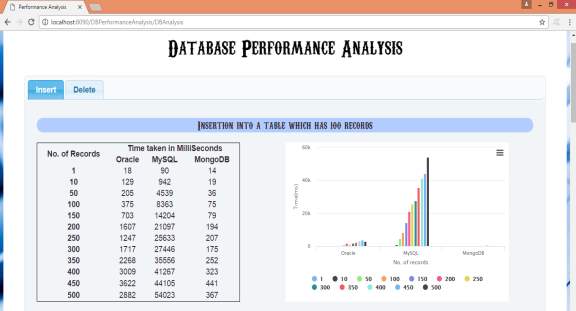 5.2.7 Graph generated by the below results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases for insertion into a table which has 100 records:
5.2.7 Graph generated by the below results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases for insertion into a table which has 100 records:
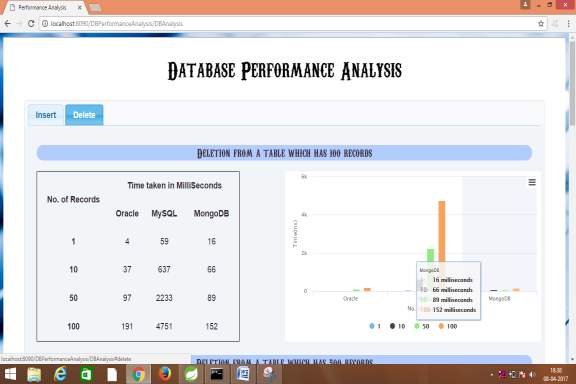 5.2.8 Graph generated by the below results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases for deletion from a table which has 100 records
5.2.8 Graph generated by the below results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases for deletion from a table which has 100 records
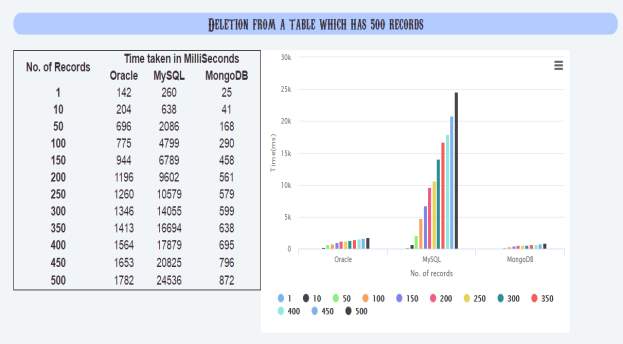 5.2.9 Graph generated by the below results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases for insertion into a table which has 500 records
5.2.9 Graph generated by the below results for performance analysis of oracle, mysql and mongodb databases for insertion into a table which has 500 records
6. TESTING
.
Software testing is a basic component of programming quality affirmation and speaks to a definitive surveys of detail, outline and coding. Testing presents a fascinating irregularity of the product. Amid prior definition and advancement stages, it was endeavored to manufacture programming from dynamic idea to a substantial usage
The testing stage includes the testing of the created framework utilizing different set information. Introduction of test information assumes a fundamental part in framework testing. In the wake of setting up the test information the framework under review was tried utilizing test information. While testing the framework by utilizing test information blunders were found and revised. A progression of tests were performed for the proposed framework before the framework was prepared for execution.
6.1 Purpose of testing
Programming testing is performed to check that the finished programming bundle capacities as indicated by the desires characterized by the necessities/determinations. The general target is not to discover each product bug that exists, but rather to reveal circumstances that could contrarily affect the client, ease of use or potentially practicality.6.2Testing Objectives
The principle goal of testing is to reveal a large group of blunders, efficiently and with least exertion and time. Expressing formally, we can state,
Testing is a procedure of executing a program with the goal of finding a mistake.
A effective test is one that reveals a so far unfamiliar mistake.
A great experiment is one that has a high likelihood of discovering mistake, on the off chance that it exists.
The tests are deficient to identify perhaps display blunders.
The programming pretty much affirms to the quality and dependable guidelines.
Levels of Testing:
With a specific end goal to reveal the blunders show in various stages we have the idea of levels of testing. The essential levels of testing are as demonstrated as follows…
Framework Testing
The logic behind testing is to discover blunders. Test cases are formulated in light of this. A technique utilized for framework testing is code trying.
Code Testing:
This procedure analyzes the rationale of the program. To take after this technique we built up some test information that brought about executing each guideline in the program and module i.e. each way is tried. Frameworks are not outlined as whole nor are they tried as single frameworks. To guarantee that the coding is flawless two sorts of testing is performed on all frameworks.
Sorts of Testing
• Unit Testing
• Link Testing
Unit Testing
Unit testing centers confirmation exertion around the littlest unit of programming i.e. the module. Utilizing the nitty gritty outline and the procedure details testing is done to reveal blunders inside the limit of the module. All modules must be fruitful in the unit test before the begin of the combination testing starts.
In this venture each administration can be thought about a module. Client giving diverse arrangements of questions and table names has tried for every module. When building up the module and in addition completing the improvement so that every module works with no mistake. The information sources are approved when tolerating from the client.
In this application engineer tests the projects up as framework. Programming units in a framework are the modules and schedules that are gathered and coordinated to shape a particular capacity. Unit testing is first done on modules, autonomous of each other to find blunders. This empowers to recognize mistakes. By this the mistakes coming about because of communication between modules at first evaded.
Interface Testing
Interface testing does not test programming yet rather the joining of every module in framework. The essential concern is the similarity of every module. The Programmer tests where modules are composed with various parameters, length, sort and so on.
Combination Testing
After the unit testing we need to perform combination testing. The objective here is to check whether modules can be incorporated appropriately, the accentuation being on trying interfaces between modules. This testing action can be considered as testing the plan and thus the accentuation on testing module collaborations.
In this venture coordinating every one of the modules shapes the principle framework. When incorporating every one of the modules I have checked whether the coordination impacts working of any of the administrations by giving distinctive mixes of contributions with which the two administrations run flawlessly before Integration.
Framework Testing
Here the whole programming framework is tried. The reference report for this procedure is the necessities archive, and the objective is to check whether programming meets its prerequisites.
Acknowledgment Testing
Acknowledgment Test is performed with reasonable information of the customer to show that the product is working tastefully. Testing here is centered around outer conduct of the framework; the interior rationale of program is not stressed.
In this venture I have gathered a few information and tried whether venture is working accurately or not.
Test cases ought to be chosen so that the biggest number of qualities of a proportionality class is practiced without a moment's delay. The testing stage is an imperative piece of programming advancement. It is the way toward discovering mistakes and missing operations and furthermore an entire check to decide if the targets are met and the client necessities are fulfilled.
White Box Testing
This is a unit testing technique where a unit will be taken at once and tried completely at an announcement level to locate the most extreme conceivable blunders. I tried stride savvy each bit of code, taking consideration that each announcement in the code is executed at any rate once. The white box testing is additionally called Glass Box Testing.
I have created a rundown of experiments, test information, which is utilized to check every single conceivable mix of execution ways through the code at each module level.
Discovery Testing
This testing strategy considers a module as a solitary unit and checks the unit at interface and correspondence with different modules rather diving into subtle elements at articulation level. Here the module will be dealt with as a square box that will take some info and produce yield. Yield for a given arrangement of information mixes are sent to different modules.
Criteria Satisfied by Test Cases
Test cases that decreased by a check that is more noteworthy than one, the quantity of extra experiments that much be intended to accomplish sensible testing.
Test cases that disclose to us something about the nearness or nonappearance of classes of blunders, instead of a mistake connected just with the particular test within reach.
6.2 Sample Test Cases
Test Case 01: successful connection establishment Test Case 02: connection establish failure Test case 03 : Failed to locate assosciate port number6.3 Testing Screen shots with description
Test Case 01: Test Case Name: successful connection establishment Description: In This Test Case we will Test whether the connection is established or not. If the connection is successful the below page will be displayed.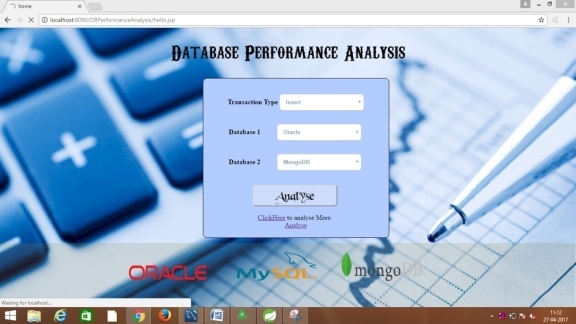 Test Case 02:
Test Case Name: connection establish failed
Description: In This Test Case we will Test whether the connection is established or not. If any error occurs the following page is be displayed.
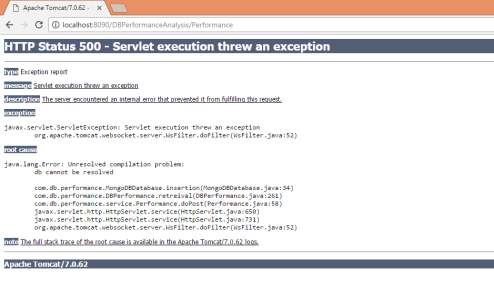
Test Case 02:
Test Case Name: connection establish failed
Description: In This Test Case we will Test whether the connection is established or not. If any error occurs the following page is be displayed.
 Test case 03
Test Case Name : Failed to locate assosciate port number
Description: In This Test Case we will Test whether the database is loaded with correct port or not. If any error occurs the following page is be displayed.
Test case 03
Test Case Name : Failed to locate assosciate port number
Description: In This Test Case we will Test whether the database is loaded with correct port or not. If any error occurs the following page is be displayed.
 7. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE ENHANCEMENT
7. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE ENHANCEMENT
7.1 Conclusion
With the project we are concluding that, the performance of MongoDB is more than the performance of Oracle and MySQL, when the number of records in the table is large in number. For the tables with small number of records performance of MySQL is Good. Because MongoDB is document based whereas Oracle and MySQL are row based. To perform reterival operation in MySQL it will give a maximum performance than Oracle. 7.2 Future Enhancement At present the graph is generated for only three databases based on time , later we can analyze for multiple databases based on time as well as cost. 8. REFERENCES- OracleJDBC-Developer’sGuide http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/java.112/e16548/toc.html
- MySQL Tutorial - http://www.mysqltutorial.org/
- MongoDB Tutorial - https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/
4. Java - The Complete Reference 8th Edition Author: Herb Schildt
- Software Engineering: A Practitioner's Approach, 7/e by Roger S Pressman, R. S. Pressman & Associates, Inc.
- http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/overview-summary.html
- Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 by Diana Lorentz
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Research Methodology"
Research methodology describes the specific methods and techniques used in a study in order to justify the approach used in ensuring reliable, valid results.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




