Effect of Organization Culture, Training and Technology on Firm Performance
Info: 7632 words (31 pages) Dissertation
Published: 9th Dec 2019
Tagged: BusinessTechnology
2.0 INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides and discusses the definition of both dependent variable which is organizational performance and independent variables which are organizational culture, training, technology and incentive. The review of relevant theoretical models is used as the foundation to develop the conceptual framework. We will formulate conceptual framework through identifying relevant variables and discuss directions of the relationships among the variables in the research. Hypothesis development is formed and discussed in this chapter.
2.1 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1.1 DEPENDENT VARIABLES – FIRM PERFORMANCE
Performance is one type of effectiveness indicator with both advantage and disadvantage. (Richard, Divinney, Yip and Johnson, 2009) Therefore, we need to differentiate the organization performance and organization performance effectiveness.(Venkatraman and Ramanujam, 1986) According to Campbell’s (1999) say, organization performance can be defined as the activity and behavior that can be measures in proportion to the organization’s goal. Besides that, firm performance also can be defined as behavior and results. (Brumbach, 1988) Behavior refers to the conversion of the issuer’s behavior from abstract performance to action. (Cania, 2014) Besides that, the behavior itself is the result and not just the tool for the results, they are the work of the mental and physical when task appliance and can be judged from the results.(Cania, 2014)
Firm performance can be identified from three perspectives. (Ford and Schellenberg, 1982) One is goal approach which is assumes that the firm will pursue their identifiable and ultimate goal. (Etzioni, 1964) Second is the system resource approach which is emphasize that how the organization ability to ensure scarcity and precious resources. (Yuchtman and Seashore, 1967) Third one is the process approach which is defined the behavior of firm actor. (Steers, 1977)
Firm performance is important. This is because firm performance is a critical measurement for an effective organization management. (Demirbag, Tatoglu, Tekinus and Zaim, 2006) Since the process improvement cannot without the outcome measurement, therefore, organization performance need a measurement to identify how the business performance affected by organization resources. (Gadenne and Sharma, 2002). Firm performance included three specific areas of organization outcome which are financial performance like profit, product market performance like sales and shareholder return like total shareholder returns. (Richard, Divinney, Yip and Johnson, 2009)
For firm effectiveness, it is more widely held to organize performance and external measures. (Richard, Devinney, Yip and Johnson, 2017) Furthermore, these measures are generally considered to be more effective in operations relating to internal performance results and other economic value considerations like reputation corporate social responsibility (Richard, Divinney, Yip and Johnson, 2009). Besides that, firm effectiveness had includes other organization functioning like lack of internal strain, resource accessing, defect for legal activity and achieving the goal. (Cameron 1986)
An effectiveness firm performance can be measures by four performance dimension. According to Cameron (1980) say, an effectiveness firm performance can be measure by whether the organization achieve its objective and goals, whether the company can obtain the important resources, whether the organization has an effective system and internal trust and the last is are the organization can contentment the stakeholder? In others hand, Ford and Schellenberg (1982) also have proposed three model to measure the effectiveness of firm performance which are goal- based model, system models and multiple constituency models. For goal- based model, it is measure a firm performance when the firm achieves its unique goal. (Etzioni, 1960)For the multiple constituency models, it evaluates effectiveness firm performance in whether the firm can meet the stakeholder goal who was provided the relevant resources to the company. (Connolly, conlon et al, 1980, Pfeffer and Slancik 1978) For the system model of performance, it had suggested that performance is a multi-dimensional and should use a set of measures that can suitable for the population’s interest and can comparison between the organizations. (Carton, 2004)
Improve the performance and effectiveness of organization is a topic that has been formed since the 1980 s, academia and the business is widely discussed. ( Bass and Avolio,1994) For retailing companies, they had evaluated their performance in various measurements like gross margin, net profit margin and contribution margin. (Mekraz and Gundala, 2016) Stand in the retailing industry sides, a good performance of firm like high profit margin means a company has a better control in their operating expenses compare with their competitor. (Kotsiopulos and Jikyeong, 1998)
2.1.2 ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE (INDEPENDENT VARIABLE)
Defining the concept of “organizational culture” is a daunting task. The definition epends on the concept of its reflection, the author’s approach and focus, depending on the shape. The feeling of each member organization to all aspects of the enterprise the life of the statistics is the organization culture. Therefore, the organizational culture covers all core values, beliefs and common assumptions help to make employees serious and motivated (Mobley 2005, 12). According to Mobley (2005) organizational culture, is a source of less definite factors competitive external quality, cost, technology, consumer service brands and so on? Group Culture once introduced to all employees recruitment, which helps them to be familiar with organization and events in the system (Fakhar et al, 2012).
Organizational culture means to a system of common meaning an organization that distinguishes them from others (Robbins, 2001). Organizational culture is a lasting force the natural evolution of the life system into order this is especially true of any organization’s stability think of people’s organization network interaction and activity (Richard Weeks (2010:44). For Imran et al. (2010), organizational culture is decisive staff performance and organization success because it brings personal staff of the spirit of innovation, organizational culture is the value system of employees different background and different levels similar organizations have (Robbin and Sanghi, 2007). Organizational culture is “This is a basic hypothetical model by a group of inventions, discoveries or developments because they learn to deal with external problems adaptation and internal integration work very well, they think it is valuable can teach new members.”
The literature proves the effectiveness of the organization as a way to promote cultural values and to exploit the value of their resources (Schein 2010). Stewart (2007) also added that the normative form of each organization’s lifestyle affect all participants in the organization. These norms become important for the organization that is intended to be achieved to achieve competitive advantage. Gallag and Brown (2007) pointed out that culture organization affects the company’s work, operation, focus, and how to treat customers, staff and shareholders expect. The culture of each organization always includes customs, beliefs, norms, morality, ethics and values, often through their language, stories, signs (symbols), rituals and ceremonies (Daft, 2000). Webster’s Dictionary regards culture as a norm, tradition, regulate the skills, art and values of directing and protecting someone’s attitudes and behavior. This definition is not sure what kind of culture the most effective society will not survive the fact everyone can accept it. Detert, Schroeder and Mauriel (2000) point out that culture is a way of life the success of each organization is also indispensable to the value of human resources.
Frambach & Schiilewaert (2002) argues that while the right culture is the essence of the success of everyone organization, but not always the means of end. Stewart (2007) added that in interpreting organizational culture, inevitably taking into account people’s beliefs and ideas, because it is the same person hold up the culture. For example, if the organization’s belief is to reward high-performance, this will in turn reflect and influence the organization’s performance and effectiveness. It must be noted that as the level of confrontation and struggle increases rapidly, changes often occur in the organization culture (Cameron, 2003).
All of these definitions in order to ensure the development of the company, managers need to innovate and innovate innovative activities, from groundbreaking and groundbreaking innovations to small modernizations that deliver measurable results (Flaszewska, Szymanska, 2013: 261). Many researchers like Tierney (1988), whose ideology is focused on emerging cultural tasks, Schein (2010) defines the coercion of culture to organizational success; Daniels et al., 2004 and Piercy recognizing that culture is the main source of difference in performance management practice, (2003) examined the relationship between organizational culture and change management; Agnew and VanBalkom (2009) understands how organizational culture is internalized.
2.1.3 TRAINING (INDEPENDENT VARIABLE)
According to Tharenou, Saks and Moore (2007), training is a systematic acquisition and development of the skills, knowledge, and attitudes needed by employees to perform a job or to improve performance in the work environment. Beardwell and Holden (2001) stated that training is a planned process to amend skills, knowledge, and attitudes through learning experience to achieve effective performance in any company activity.
On-the-job training (OJT) is the most of the common form of training that conducted in the workplace during the working day. Off-the-job training (OFJT) is conducted off-site and off-line (Milhem, Abushamsieh, & Aróstegui, 2014, p. 19). Planned OFJT is designed to utilize the time spent away from the work to a maximum and is suitable when a large number of workers have a similar training requirement and when there are sufficient skills and resources for the provision of training and design (Rothwell, 2005). Group discussions, one-to-one tutorials, lectures, reading, training courses and workshops can involve in off-the-job training (Kempton, 1995). Off-the-job training allows trainees to learn and then apply new skills and knowledge in a safe working context (Kempton, 1995). Off-the-job training is normally designed to meet the shared learning needs of a group and the usual forms of off-the-job training methods are lectures, computer-based training, games and simulations (Alipour, Salehi, & Shahnavaz, 2009).
On-the-job training is planned, structured, and mostly conducted at the trainee’s workplace and it conducted in a special on-site training area (Milhem, Abushamsieh, & Aróstegui, 2014, p. 19). On-the-job training has a major impact on employee commitment, employee motivation and job satisfaction (Petrescu and Simmons, 2004). Managers, supervisors, trainers and colleagues spend a lot of time with trainees to teach previously determined skill sets in on-the-job training (Milhem, Abushamsieh, & Aróstegui, 2014, p. 19).
Planned on-the-job training is possible to minimize work distractions and this type of training is suitable when training at work will not represent a threat to health, safety, or productivity and when there are benefits to be gained from training in real time (Milhem, Abushamsieh, & Aróstegui, 2014, p. 20). Job instruction training uses behavioral strategy with a focus on skill development and is good for task oriented duties (Alipour, Salehi, & Shahnavaz, 2009). Job rotation program can reduce the training costs while enhance the impact of training because job rotation is a hand on experience (Alipour, Salehi, & Shahnavaz, 2009). Coaching is motivational tool for workers performing well and is directed at workers with performance deficiencies.
As mentioned by Jones, George and Hill (2000), training helps organizational members acquire the skills and knowledge they need to become an effective performers and teaching them on how to perform their current works. Holden (2001) found that employees should align their needs with the organization’s requirements and their own long term development because skills required by employees and information and technology are constantly changing as well as Human Resources Department planning for employee training should think over the current and future needs of the company.
Smith (2010) believe that training motivates worker and make them more productive and innovative and he opines that well trained workers are more capable and willing to assume more control over their works; they are more capable to answer customer’s questions which increase customer loyalty. Effectiveness with which company manage, develop, motivate, involve the contribution of those who are willing to work is a key determinant of how well these company perform (Hamid, 2011). According to Ospina and Watad (1999), the effectiveness of company lies on the employees who form and works within the company, therefore employees need to obtain relevant skills and knowledge to be able to perform their duties and make meaningful contributions to the success of the company goals.
2.1.4 TECHNOLOGY (INDEPENDENT VARIABLE)
Technology is one of the central and most important elements related to effective operations management in an organization (May-Chiun Lo, 2009). It can be defined as a body of knowledge used to create tools, develop skills, and extract or collect materials (Abang Azlan Mohamad, 2009). It is also the application of science (the combination of the scientific method and material) to meet an objective or solve a problem (Molinero, 2012). Technology is the knowledge used in practical ways in an industry (Oxford, 2005). It is also seen as the outcome of human learned an acquired knowledge or technical skills on how to do things well then just doing things correctly (Khalil, 2000). Moreover, it is the knowledge, process, tools, methods and systems used in order to create and deliver goods and services (Khalil, 2000).
Technology is a technique and use of tools, machines, materials and processes which help man to solve complex problems. Technology is a kind of human activity and hence it is more ancient than science and engineering (Mehrad Mokhtarband, 2015). Technological Innovation Capability (T.I.C) is an important section of the core competitiveness of the retail industry, and core competitiveness play a role in promoting or influencing technological innovation (Nye, 2006). Technology is adapted into the organization to be able to match the marketing capability of the organization and be seen as reflecting in the strategic plan of the firm and its overall success. It helps the organization to be effective (Shoeb Ahmad, 2014). Technology increases the prospect for conducting business in more efficient and effective ways that are methodically different from the past (Dasgupta, Gupta & Sahay, 2011). Every organization uses different form of technology for their business which has a critical effect on the nature, design, structure and work of an organization (Liao ,2001).
Technological advances bring huge opportunities as well as challenges for managers from all professional fields (Sheridan, 2002). Most organizations do not attach high or optimal priority to sophisticated technology that slows down an organization’s growth (Kazmi, 2008). In present competitive global economic scenario, organizations who fail to advance technologically are at potential risk of lagging behind competitively as well as in terms of productivity (Orlikowski, 2007).
Change is natural and the term “Change or perish” has become a new corporate mantra making rounds in every business circle (Shoeb Ahmad, 2014). The present study examines the introduction of technologies and their influence on organizations due to their extensive use (Abrahamson, 2000).
The use of technology within human resource management has grown considerably over the last decade with the majority of organizations now using some form of HR information system (HRIS). For instance, in Europe, found that 70% of the organizations surveyed used the Internet or Intranet to deliver HR services to employees with most respondents planning to enhance substantially their e-HR capabilities over the two years after the survey (Watson-Wyatt, 2002). An HRIS can perform a number of functions from the simple storage and communication of information, to more complex transactions (Parry, Tyson, Selbie, & Leighton, 2006). The use of technology has been shown to lead to faster, more accurate and more efficient processes, and reduced HR costs (Emma Parry, 2009)
Technology can also be used to provide HR information and to enable managers and employees to perform simple HR tasks themselves (Emma Parry, 2009). Other than that, the use of HRIS to reduce the administrative and transactional load on the HR function can lead to a change in the structure of HR and allow the function to play a more strategic role in the organization (Enshur, Nielson, & Grant-Vallone, 2002). The reasons behind an organization’s introduction of an HRIS may vary considerably from the need to facilitate efficient processes or cut costs, to improve communication and customer service, or the desire to create a shift in the role of the HR function from one that is mainly administrative to one that is more strategic (Ngai and Wat, 2006). This chapter will discuss the potential impacts of technology on HRM in terms of the possible rationale behind the introduction of an HRIS (Parry, Tyson, Selbie, & Leighton, 2006).
Based on this study, technology that has been adopted by company to be effective through the human resource practices of a company. Human resource practices can be staffing, recruitment, and also salary payment. The adoption of technology in the human resource management of an organization can be in any aspect as stated above. This implementation of technology helps the organization to improve its performance (to be more effective) as human resource management affects the organizations performance in retail industry.
2.1.5 REWARD SYSTEM (INDEPENDENT VARIABLE)
Rewards are some of the human resource management strategies used by employers to motivate, attract and retain the high skill workers as well as to increase their work performance and encourage them to put their best effort in work. Human resource manager will tend to design reward which will ease the organisation mission and individual employee goal. According to Maund (2001) incentive and reward are very important to an organisation which include program and practices which will motivate the employees in the organisation. Incentive and reward system purpose is to give positive consequences for contributions to desired organisation performance (Wilson, 2003).
Reward has been distanced in a few ways by different researchers. Reward can be defined as an external source of motivation when performing a task or a job. Incentive and reward practice can be adopted in either both public and private sector. According to Rys (2007) Organisational rewards can be more effective if it were implemented in organisation which the identification of reward system is strong. Identification is strong as the interest of the workers were similar to the interest of the organisation goal which they worked so that they can strongly identified themselves in the organisation. (Kankanhalli, Tan & Wei, 2005). Rewards can be either intrinsic or extrinsic. Intrinsic reward is referring to the psychological rewards or intangible reward such as appreciation and recognition, positive and caring attitude from employer, having new or challenging task and job rotation after completing the previous goal (Hafiza, 2011). Extrinsic rewards is referring to tangible rewards which the job or task performed by the employee. Example of extrinsic rewards are job security, salary or pay, bonuses, incentives, promotions, etc.
Every organization’s reward system should consist of on some major elements such as appreciation and recognition, compensation, and benefits (Sarvadi, 2010). Benefits such as medical covers, car loans, club membership, parking slots, ample office space and giving company cars for employees to drive are ways to reward employee and they will appreciate the benefit that the organization they work in. Recognition is to recognise someone before their peers for desired behaviour or even for accomplishments achieved, actions taken or having a positive attitude. Such rewards help employees to gauge their performance and know whether they are doing good or bad (Sarvadi, 2010).
Expectancy theory stressed on the perceived between pay and performance at work. It is consider that great employee performance is followed by incentive and reward system which will make upcoming performance to be better. According to Delaney and Huselid (1996), compensation system results the increase in the employees performance. Other than that, trust can be built in the organisation over time whereby higher trust of employees create better organisation performance. Managers with high trust of their employees tend to be more willing to rise their risk with various incentive and compensation.
A successful reward system always have positive reinforcement which encourage the employees to meet organisation performance. Reward must be well design in an organization to reinforce the positive behaviour which will lead to the firm performance (Hall & Torrington, 2006). A multinational manufacturer of brand-name product for customer required to develop level of employee motivation rapidly to improve firm performance. Human resource manager should focus on recognition which to raise the employee morale. When the employees receive certificates from organisation, the will feel appreciated which make them even more motivated to work in the organisation (Gyurcik & Brawley, 2000).
2.2 REVIEW OF RELEVANT THEORETICAL MODEL
Model 1
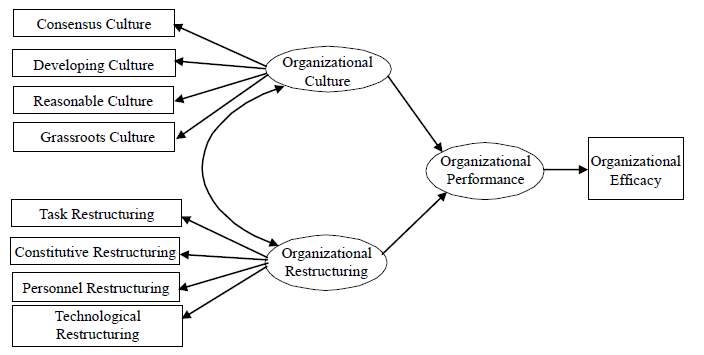
Independent Variable Dependent Variable
Figure 2.1
Source: Keng-Sheng Ting (2011), Research on the Influence of Organizational Culture and Organizational Restructuring on Organizational Performance: Taking Old Folks Nursing Organization in Taiwan. The Journal of Human Resource and Adult Learning Vol. 7, Num. 2, 96-109.
According to Keng-Sheng Ting (2011) organizational performance is concerned by organizational culture and organizational restructuring. The main purpose of this research is to examine and prove the influence of organizational culture and organizational restructuring on organizational performance. Studies have shown that organizational culture and organizational restructuring have a significant positive impact on organizational performance. This finding reveal that the independent variable consists of organizational culture and organizational restructuring. Organizational culture are included consensus culture, developing culture, reasonable culture and grassroots culture while organizational restructuring consists of task restructuring, constitutive restructuring, personnel restructuring and technological restructuring independent variable directly affect the dependent variable organizational performance that included organizational efficacy. (Keng-Sheng Ting, 2011)
Model 3

Figure 2.3
Source: Tim Jacks (2011), Impact of technology on organizational performance. Business Process Management Journal. Vol. 17 No. 5, 2011.
This theoretical framework explains impact of technology on organizational performance. An early example is (Porter and Millar’s, 1985) seminal work on the value chain, where information has the ability to provide value in each link of a firm’s value chain. An especially pervasive theoretical framework is the resource-based view (RBV) of the firm, which holds that a resource must meet four criteria in order to create value. Organizations are amalgams of physical, human and knowledge resources that confer competitive advantage to the firm that can control and leverage the unique characteristics of the resource (Melville et al., 2004). In contrast, Carr (2003) critically questions the value IT is able to confer to the firm, precisely because IT resources have become commoditized and are therefore no longer rare or hard to imitate. Certainly, some IT assets are not difficult to duplicate, such as infrastructure and networking components; however, resources alone do not explain the difference of firm’s competitiveness. Teece’s (1997) dynamic capabilities theory effectively addresses this issue
Model 3
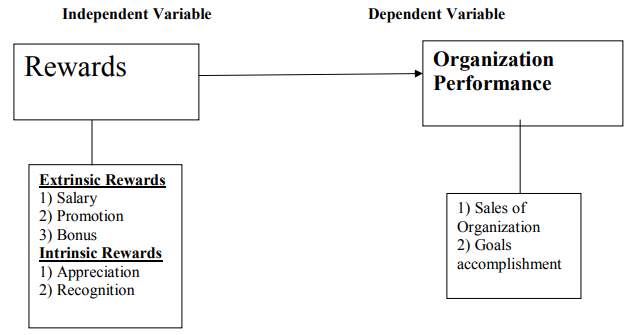
The theoretical model shows relationship between dependent variable and independent variable. According to (Yasmeen, Farooq and Asghar, 2013) rewards can be divided into 2 types which are intrinsic and extrinsic reward. He added that organization performance can be enhanced by giving incentives and reward in term of non-monetary or monetary rewards and intrinsic extrinsic rewards Intrinsic rewards is referring to appreciation and recognition while extrinsic rewards is referring to promotion, bonuses, and salary. It is proven that the previous study also indicates that there positive relationship between rewards and organization performance.
2.3 PROPOSED THEORETICAL/ CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
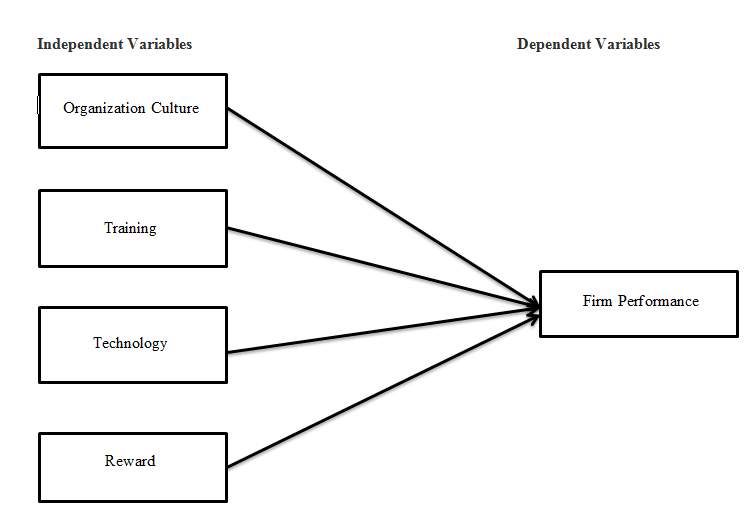
Source: Developed based on independent variables and dependent variables
The model of conceptual framework is formulated based on the previous literature review. This propose conceptual framework have develop by covering all of the independents variables which is organization culture, training, reward and technology which the dependents variable which is the firm performance. According to the study, all of these independents variables are the main factor that will affect the firm performance.
According to Kotter (2012) say, Organization culture can help to increase the employee job satisfaction and create awareness about the problem. Besides that, it also can increase the firm performance. The research conducted by Khan (2011) also shows that a good organization performance is reliable to the employee performance. This is because human resources capitals have play an important role to an organization. Therefore, training is important to enhance an employee performance and improve the organization performance. According to Sadiq (2012), technology can help the organization achieve their goal by help them making more and more strategic decision. Therefore, organizations nowadays have considered that technology in an integral part of the organization function. Besides that, rewards also have been proved that there has a linking between reward and firm performance. According to Armstrong (2006) say, reward practices can help to improving the firm performance by helping the organization maintain a positive motivational environment to employees.
2.4 HYPOTHESIS DEVELOPMENT
This study explores the relationship between organizational culture and firm performance. Theoretical and empirical studies seem to support this view and are explained below. Theoretical argumentation supports the relationship between organizational culture and organizational performance long term effective (Cameron, Quinn, 2006 and Zheng et al., 2010). Zheng et al, (2010) argues that organizational culture is one of the key organizational assets of extensive research based on the resource-based perspective, combined with organizational effectiveness. Oparanma (2010) argues that organizational culture stimulates or triggers many other activities bring business success.
Ogbonna and Haris (2000) suggests that despite issues related to cultural-performance linkages, sufficient evidence of the hypothetical relationship between organizational culture and organizational performance. Organizational culture can also bring competitive advantage to the organization (Martins and Martins, 2002). Empirical studies also provide evidence of organizational culture and organization Performance results. Kim et al. (2004) reported that culture was found to affect various organizations Processes and performance. The strength of cultural values is related to the organization several companies perform. Oparanma (2010) found that organizational culture is an important variable Consider organizational performance considerations. According to Duke II & Edet (2012) results, there is a positive relationship between organizational culture and performance. Zheng et al. (2010) reported the Positive Influence of Organizational Culture on Organizational.
There are some studies that reveal evidence of what type of organizational culture influence Performance results. Ogbonna and Haris (2000) reported that the highly competitive culture of innovation is positive Related to organizational performance. They also found that there was no relationship between organizational performance Bureaucratic and community culture. Some studies have compared the performance of various organizational cultures. The result comes from Studies of Tseng (2010) show that dictatorships are better than clan and class culture. Eccles et al (2012) found that high-sustainability enterprises have long performed better than rivals, whether it is the stock market or accounting performance. Elaborate theoretical and empirical research, Kim et al. (2004) concluded that if culture is strong (broad consensus), culture may affect organizational performance deep internalization and socialization), suitable for its environment (related to its industry and business condition). According to Magee (2002), organizational culture and performance management are interdependence. That’s why managers should understand the impact of the organization culture to get the highest return from performance management, a change directly affects the other.
The success of the company’s research and observation have shown a direct correlation strong corporate culture and performance. Moreover, the organization culture have an important and measurable impact on the company’s ability to implement the strategy (Ye et al., 2008). When dealing with the concept of risk, the organization’s culture cannot be ignored management, customer relationship management, change management or leadership (Tseng, 2010). More and more companies are encouraging employees to be more accountable give more freedom of action. In addition, they also encourage teamwork set up a team. A strong culture is a culture of employee co-operation effectively share the same core values and make decisions to meet the organization’s requirements main objectives and objectives (Cameron and Quinn, 2006).
H0: There is no significant relationship between organizational culture and firm performance.
H1: There is significant relationship between organizational culture and firm performance.
2.4.2 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TRAINING AND FIRM PERFORMANCE
Training has positive relationship with organizational performance as it influence the business performance outcome and quality performance outcome (Barrett and O’Connell, 2001; Ahmad and Schroeder, 2003; Aragon-Sanchez et al., 2003). Organizations tend to gradually know that human resource is definitely the most important one which contributes to organizational performance (Bowra et al., 2011). Thang et al. (2004) mentioned that training can generate a positive significant effect on organizational performance and they also explained that company can be shown the clear way to enhance performance with training.
Training directly affects the employee performance and puts indirect effect on the performance of the organization that is mediated with employee performance (Okanya, 2008). Choi et al. (2013) focused on the relationship between HRM practices and organization performance and indicated that training is one of the important attributes of organization performance. Increase the profit of the organization, safeguarding the organization stability, enhance the quality and quantity of the output of the organization, reduce the risk, decrease the organization expenses, establish the organization as national and international entities as well as enhance the organization’s management are the most significant impact of training on employees and organization performance (Barzegar and Shahroz, 2011).
Training improves the capacity of employees to contribute to the optimal organization performance (Olaniyan and Lucas, 2008). Provide training to employees to get overall goals of the organization in a better way and improve the overall performance of the organization is very necessary (Flynn et al., 1995; Kaynak, 2003; Heras, 2006) (Shepard, Jon et al., 2003). Training design plays a very important role in the organizational performance (Tsaur and Lin, 2004). Organization able to get good results when develop a good and suitable training design according to the need of the workers (Partlow, 1996; Tihanyi et al., 2000; Boudreau et al., 2001). Besides, training helps improve profitability and organizational performance, business development, management succession, employee’s morale, customer satisfaction, quality and productivity (Ndibe, 2014).
H0: There is no significant relationship between training and firm performance.
H1: There is significant relationship between training and firm performance.
2.4.3 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TECHNOLOGY AND FIRM PERFORMANCE
The independent variable technology and the dependent variable organizational performance have seemed to have positive relationship. Based on the previous studies that have been conducted the one of the most influencing factor of organizational performance is technology. Performance means the form or quality of function. Therefore, organizational performance is an overall structure that indicates the form of organizational operation. So the adaptation of technology brings improvement in the company performance (Mehrad Mokhtarband, 2015).
Technology has now become a buzzword. It has become a wide spread tool throughout the world since last couple of years. The incorporation of technology has enabled various sectors and areas to perform better (Truss et al., 2002). The advent and development of technology enabled services that has facilitate the retail sectors in numbers ways. The retail industry is able to collect and store the data about the customers and also to keep it updated. HRIS because helps the retail company in getting right information and in managing merchandise management, inventory management, procurement, billing, customer loyalty schemes, stock replacement, shelf-space and even effective shop floor management . Large and successful retailers of international levels like Wart-Mart, Sansbury, Metro AG etc. give a good chunk of their turnover towards making retail operations more technology oriented (Kovach et al., 2002).
HRM generally uses technology as Human Resource Information System (HRIS) which is an integrated system acquiring and storing data used to make analysis, make decisions in the field of HR (Hendrickson, 2003: 381-394; Luck, 2010). A HRIS is a dynamic data base about employees’ performance and demographic information. HRIS provides information about employees’ data, employment, application requirement, job characteristics, selection and staffing, procedures of employment, corporate structure, professional and individual improvement, education costs, performance appraisal, personnel planning, organizing ect. And these data are used for many purposes simple or complex (Lippert and Swiercz, 2005, 340–353; Bernik et al. 2007:130-133).
Furthermore, HRIS a technology application for supporting or connecting at least two people when participating in HR activities (Strohmeier, 2007, 19–37). In other word, HRIS is in which HR personnel, managers and other employees access via internet or intranet. Technology affects organizations and work relations in organizations by enabling to access information and to join people electronically (Ulrich, 1997, 175-179). With new processes and providing some benefits HRIS changes traditional HR processes and it is expected that HRIS will provide functionality for realization of units’ objectives and goals (Hendrickson, 2003: 381-394).
Cost that a retail company spends of HR department can be reduced. Effects of implementation of technology in HR reduce cost in several ways. First, it reduces costs of processes and works. For example, transforming from traditional HR to HRIS reduces costs of some HR applications, such as, postal cost, announcement cost and data processing cost (Lin, 2011, 235–257; Hendrickson, 2003: 381-394). Using self-service technology reduces the processing costs of HR up to 75%. E-selections and e-recruiting decrease costs of staffing and selections due to reduced employee turnover, reduced staffing costs, and increased hiring efficiency (Strohmeier, 2007, 19–37). Second, using self-service HR allows employees to perform their own work themselves directly. Thus, HR professionals spend less time on routine tasks (Baloh and Trkman, 2003: 498-505).
Other than that, technology also helps the retail company to save time. Technology allows HR professionals to spent less time on routine tasks (Gardner et al. 2003: 159–179) and make easier to acquire and analyze information (Bell et al. 2003). For example, researches show that recruiting process shortens twelve days. It also helps to increase efficiency; the intense use of technology aromatizes and standardizes routines. HR professionals may focus less on administrative activities and more on interpreting information (Baloh and Trkman, 2003: 498-505). HR professionals may spend more time on other aspects of their jobs. Thus, HR professional can access more information, respond the problems in a timely major from managers and employees and evaluate the complex information more effectively (Gardner et al. 2003: 159-179). Comparing with manual processes, reducing data errors, simplifying and fastening processes of HR practices make HRIS more advantageous (Ulrich et al. 2008: 829-850; Hendrickson, 2003: 381-394). Organizational efficiency begins to increase when the right information reaches the right place at the right time (Plunkett, 2001: 7).
Next the recruitment process, which is one of the most important function of HRM. One way in which human resources has been significantly impacted by technology is in the area of recruiting (Ömer Faruk Ünal1, Mehmet Mete2). Before the Internet, HR recruiters had to rely on print publications, such as newspapers, to post jobs and get prospects for open positions. Other methods such as networking also were used, but HR recruiters did not have the ability to post a job in one or more locations and have millions of people see it all at once (Hendrickson,2003: 381-394). Technology has made recruiting more efficient and, in the hands of the right recruiter, more effective as well. Attracting, retaining, and motivating employees, meeting the demands for a more strategic HR function, and managing the “human element” of technological change in the future has been enabled by advancements in IT to meet the challenges of HRM (Ashbaugh and Miranda, 2002). HRMSs can meet the challenge of simultaneously becoming more strategic, flexible, cost-efficient, and customer-oriented by leveraging information technology (Snell, Stueber, and Lepak, 2002).
Technological innovation was found to have strong impact and influence on firm performance (Nohria & Gulati, 1996). Proved that the technology capabilities of the firms have vital influence on long-term performance of the firms (Hitt, Hoskisson, and Kim ,1997). In addition, (Dave and Wayne, 2005) concluded that human resources regularly find new application of technology to improve their efficiency and their effectiveness in an effort to influence firm performance. The implementation of HRIS in human resource practices has helped the organization to be efficient and the outcome is good performance (May-Chiun Lo, 2009). (Khera and Gulati, 2012) argued that several authors stated in their studies that HRIS is increasingly used in strategic decision-making process of the HR (Khera and Gulati, 2012: 7-8). HRIS helps organization to perform better, so the relationship between technology and organizational performance is positive.
H0: There is no significant relationship between technology and firm performance.
H1: There is significant relationship between technology and firm performance.
2.4.4 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN REWARDS AND FIRM PERFORMANCE
The effects on rewards should be stronger in organization where stronger relationship between rewards and performance in organization will bring improvement to the organisation. If the employees are rewarded for what they have done, they will strive harder in order to achieve organisation mission. Hence, employees who maximize their ability and standard should be rewarded straightaway to motivate them to perform better. This will directly connect the reward with the employees so they can have a higher performance and better working behaviour in organisation (Njanja, Maina, Kibet, & Njagi, 2013).
The common hypothesis about the effects of monetary rewards on effort and performance is that incentives and rewards will lead to greater performance in the organisation. Increase in effort of employee is affected by increasing of reward system in performing a task. As the benefits provided in term of rewards greater than the cost of doing a task or activity, incentives will tied to performance which theoretically lead to effort in doing a task and activities.
Monetary rewards also motivate employees to put more effort in acquire the skills require to perform a new task so the future performance of the performance will be higher as they willing to learn new knowledge (Bonner, 1999). The influence of rewards on the effort can be measure by absenteeism and the task choice that they do (Kanfer, 1990). According to Thomas (2009), intrinsic rewards reinforce the self-management the employee efforts and motivate employees to be involve. Intrinsic rewards are based on feelings among employees in the workplace. The existence of reward and incentives builds positive feelings among employee in the organization and they will be more engage in the organization.
In conclusion, the hypothesis that shows positive relationship between the existence of rewards and task performance. The more the rewards and incentives, the more effort of employees which leading to increasing in performance of the organization in both short run and the long run of the business.
H0: There is no significant relationship between reward and firm performance.
H1: There is significant relationship between reward or incentives and firm performance.
2.5 CONCLUSION
In this chapter we have use literature review to on dependent variable which is firm performance with independent which are organization culture, training, technology and rewards. We developed the theoretical framework and hypothesis testing in this chapter. Next chapter we will discuss further discuss about the research methodology in our research.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Technology"
Technology can be described as the use of scientific and advanced knowledge to meet the requirements of humans. Technology is continuously developing, and is used in almost all aspects of life.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




