Risk Management in Construction Case Study
Info: 9174 words (37 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
Tagged: ConstructionRisk Management
Table of Content
Information about the organization
Relationship and perception of the stakeholders
Pestle analysis for Bouygues Construction Australia
Swot analysis for Bouygues Construction Australia
Risk management plan for the employees
Measurement of the risk management
Obvious risks that need to be handled
Figure 3: Formulate and select the treatment options
(Source: Fumasoli, Pinheiro & Stensaker, 2015, p.1038)
Overall judgment regarding the identified risks
Illustration of their likelihood and the possible impacts
Evaluation for setting the organizational Priorities
Figure 2: Evaluation for setting the organizational Priorities
(Source: Raghupathi & Raghupathi, 2014, p.3)
Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework
Risk Management Framework Massey University
RMF on ISO31000 for Bouygues Construction
Figure 4: RMF on ISO31000 for Bouygues Construction
(Source: bouygues-construction, 2017)
A GENERIC R M FRAMEWORK and PROCESS TEMPLATE
Table 1: A GENERIC R M FRAMEWORK and PROCESS TEMPLATE
Risk in workplace for poor management system
Variety of risk that is required to emphasize
New skill or knowledge that can develop to avoid these risks
Introduction
Effective risk management strategies generally allow an organization to verify their strength, weakness, threat, and opportunities. Here in the current assignment, the organizational risk factor of Bouygues Construction Australia is described along with their economic background. Moreover, some basic requirements, as well as sufficient treatment options, are illustrated to overcome the challenges as much as possible. Nonetheless, the Risk Management and Decision Theory, Organization Behaviour Theory and captivating field of decision theory are discussed to review and monitoring the implemented treatment to control the arising risks within the construction company. Apart from that Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework, J and J FRAMEWORK FOR ENT R M Risk Management Framework Massey University, W REGION RM F are also described to develop the poor management system in the Bouygues Construction organization.
Task 1
Background of Bouygues Construction
Bouygues Construction Australia is one of the most popular construction companies in Australia. As mentioned by Ghobadi (2015), from 2017 it is reported that the net debt of the organization was €2 billion at December 2016 and their net gearing was 20% and over the year their improvement point is 8 on 10. It is also evaluated that the sales of this construction company have increased up to 6 % in the year 2014. This reflects the organizational profitability and their sales outside economic condition rose sharply up to 13% on €5.77 million.
Bouygues Construction Australia recently is developing their operating strategies within their formulated framework. As commented by Beck (2014), their statement of purpose includes reducing the organizational risk by implementing promotional strategies by providing proper safety to their employees. Moreover, they also emphasize on their quality service by increase their market share in Australia (bouygues-construction, 2017).
Bouygues Construction has their official website where they declare their missions, services, executive team and their corporate ambition. They also announced that they provide service in design and construction, partnerships and alliances, property and asset management, PPP and concessions, and procurement in Australia. As opined by Jacquet (2014), they also allow the consumers to provide their review regarding their service and customer can contact with the organization whenever they needed.
As per the report on 2015,Bouygues Construction Australia will build NorthConnex new motorway in Sydney. Nevertheless, it is also announced in this year that Bouygues Construction recently delivered the Melbourne Metro with the Cross Yarra Partnership. As commented by Pemsel & Wiewiora (2013), it is also reported that the company is facing issues in managing and monitoring their risks within their business unit. Henceforth the supervising team fails to control the security of the worker and fail to ensure their service to their consumers.
Mission and vision A mission Statement defines the company’s business, its objectives and its approach to reach those objectives. A vision Statement describes the desired future position of the company. Elements of mission and vision Statements are often combined to provide a statement of the company’s purposes, goals and values
Goals Goal setting is the process of deciding what you want to accomplish and devising a plan to achieve the result you desire. For entrepreneurs, goal setting is an important part of business planning. This goal setting definition emphasizes that goal setting is a three part process.
PART A
Relationship and perception of the stakeholders
The organisation maintains health relationship with their internal and external stakeholders. As mentioned by Jacquet (2014), the internal stakeholders involve managers and the employees whereas the external stakeholders include creditors, consumers, suppliers and shareholders. The organisation shares the viewpoint of the stakeholders and prioritises their opinion in executing their performances. Nonetheless, they build the strong relationship with the supplier and consumers and meet them frequently to consult them regarding their demands and expectations. Nonetheless as per the perception of the stakeholder, the organization has recently implemented RMF on ISO31000 in order to minimise the possible risks as much as possible. They hire experiences staff and provide on the job training to make the labour more responsible towards their duties.
Pestle analysis for Bouygues Construction Australia
| Factors | Analysis
|
| Political
|
The company has incorporated specific government regulations such as RMF on ISO31000 and its section 2.13, 5.6 and 5.4 of to avoid the political interruption in their business sector. |
| Economical
|
The interest rate of Australia is 4.67%, Tax rate is 2%, employee turnover rate is 18.5% and GDP rate is 3.47%.therefore stimulating the GDP growth will reflect on the growth of the activities of this construction organisation |
| Social
|
The rate of increased population is 1.4% a rate of population demography is 36.6% in Australia. Along with that the brand name of this construction, as well as the positive impact of the involved stakeholders, plays a vital role in convincing the consumers. |
| Technological
|
Bouygues Construction uses modern technologies such as self-healing concrete and photovoltaic glazing. The company provides security by promoting the uses of MOOCs in their online services. |
| Legal
|
They also implement The Work Health and Safety Act 2011 (the WHS Act) and Construction Contracts Act 2004 to enhance collaborative performance and followed the guidelines of health and safety in construction industries and minimum wages allegation (Legislation.gov.au, 2011). |
| Environmental
|
Green construction management is being promoted.
They also emphasize on Waste management by implementing Hazardous Waste (Regulation of Exports and Imports) Act 1989 in their domain. |
Table 1: PESTLE analysis
(Source: Pemsel & Wiewiora, 2013, p.42)
From the illustration, it can be observed that the organisation implementing section 2.13, 5.6 and 5.4 of ISO31000 regulation to minimise the political interruption and formulated risks in their business sector. As asserted by Pemsel & Wiewiora (2013), the company has followed Information and Communications Technology (ICT) and uses Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) to enhance effective communication while executing their operational plans. Nonetheless, the perception of the stakeholders as well the brand image of the organisation acts as the positive influence in promoting their profitability in the business unit. However, the increasing GDP rate enhances customer purchasing power and reflects on ultimately increase profit percentage of the company.
The organisation has incorporated (the WHS Act) to increase their responsiveness towards emergency services. Again, they have followed Construction Contracts Act 2004 to modify their construction strategies by identifying the arising risk factors in the operation sites (Environment.gov.au, 1989). Apart from that, they also incorporate the Hazardous Waste (Regulation of Exports and Imports) Act 1989 (‘the Act’) to focus on the recreation and protection of the environment as well as the public life. This law also controlled the financial value by recycling their waste products (slp.wa.gov.au, 2004).
Competitive Environment
Buyers for Bouygues Construction Australia
Hawkins bay original councils and state government pr other original councils are their main clients. Big industries , companies and factories will be their other major clients as they mainly focused on technical development in their project.
Suppliers Bouygues Construction Australia
When the company buy the material from the suppliers for co many like wood, concrete, steel bars and technical knowledge. Company always adhere to our high quality, safety and environmental standards when selecting products and services.
Competitors for Bouygues Construction Australia
Jhonson controls international, china communications construction are the main competitors of the Bouygues construction Australia. Jhonson controls international is the biggest competitor of this company because this company is finically strong.
New Entrant for Bouygues Construction Australia
Small players they are all ready big and established companies and industry. New entrants like Hawkins construction, Covekinloch Nz ltd are new entrants. It is not possible for enterprises to enter into construction business because of cost, health and safety and other legal requirements. So the new entrant will be different.
Substitute for Bouygues Construction Australia
Automated construction by machines might be the substitute for the construction company like bougyues but this does not seem to be possibility in future.
PART B
Drivers and trends which impact on the organisations objective
Because of immigration policies labour is hard to find due to less migration of people from Asia and rest of the world. These things are going to effect on the organisation objectives. Recently labour Government announced construction of 100,000 houses in next ten years. So prospect seems to be positive for Bouygues and the economics of the Australia and New Zealand is stable so this is the stability of Bouygues.
Swot analysis for Bouygues Construction Australia
Strength
|
Opportunities
|
Weakness
|
Threats
|
Table 2: SWOT analysis
(Source: Taylan et al. 2014, p.107)
From the table, it can be analysed that, Bouygues Construction has followed the HRM regulation while hiring their staff and provide the training. AS mentioned by Gunduz & Laitinen (2017), they have authentic allocated resources that provide them support to maintain the huge financial requirement and help develop their infrastructure. Apart from that, they enhance private-public partnership business strategies to reduce the percentage of occurring risk in the construction sites. Moreover, the organisation also hires experienced labour in order to identify the possible risk factors in their operation spot as well as to manage them accordingly. The company also provides medical support to the labour and to avoid the major accidents the management team examine their construction plot before executing their operation.
PART C
Stakeholder map
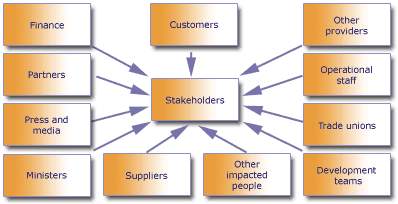
(Stakeholdermap.com, 2017)
Clients, consumers, management, employees, share holders, suppliers, creditors, society, public are the main stake holders for Bouygues construction Australia.
Most influence stakeholder are director and share holder. They need to make plan and descions about risk management. Employees work according health and safety regulation at work according to health and safety act 2016. This act is established by government of NZ. Regarding finical risk minister of business and invitation control this aspect. The projects by Bouygue are presented to society considering their current requirements and future expectations.
Organisational Clients and Markets
As Bouygue is a French company having subsidiary in Australia this subsidiary cater to clients. There is no risk of concretions activities are distributes in large geographical area.
External Industry Links
Bouygue constructions Australia rely on recruitment agency to hire labour and Project Managers. They need to maintain coordination Relationship with supplier of material for construction. They need to deal with some insurance companies as well because some time because of some external hazard like earthquake and some others if company have insurance so company easily claimed their insurance.
Organisational Critical Success Factors
Health and safety is of prime importance at Bouygue Construction Australia labour can accidently heart them self and others because of use of equipment and material. Labour has to be hired to minimise the accidents. So recruitment agency also makes an important role. Huge fancies are at stake so they have to develop strategy plan and manage appropriately.
Governance, organisation structure, role and accountabilities
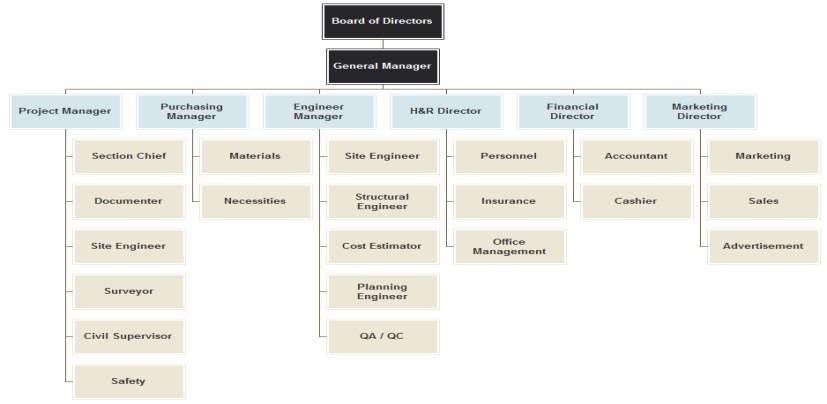
Source : ORG CHART, 2017
Project management is responsible for all the risk finical as well as health and safety of Bouygues construction Australia.
Top management and directors are responsible for providing strategic direction to Bouygues construction Australia. They need to have technical knowledge and innovation so has to reduce the risk of Bouygues construction Australia getting obsolete or lacking competence as compare to competitors.
Policies documents foe managing risk
B C A company has clearly prescribe health and safety documents which is strictly followed by all the staff during a construction project. Fire equipment and safety gear like gloves, safety shoes, jacket and helmet in sufficient quantity are provided on construction sites. They have high standards of developing and working their projects. The specification of the developed project is documented during the planning stage. This guides in managing the standards during the project.
Capability- resource and knowledge
In order to review and monitoring the treatment, the organization can follow the WHS regulation to provide proper safety to their employees. As opined by Castillo et al. (2015), Bouygues Construction can conduct feedback to identify their flaws regarding their service. Nonetheless, they can conduct the meeting to reshape their strategies to develop the communication among the construction team while operating their service. Along with that, as commented by Pournader, Tabassi & Baloh (2015), they can recruit experienced labour to avoid accidents. The management can arrange training to make the employees more efficient to gauge their technical risk in their workplace (Park & Kim, 2013).
As per the risk management and decision theory, Bouygues Construction can follow the risk management process to avoid the accidents. According to the process, Bouygues Construction can identify the risk of their workers to examine the perspectives towards their activities. Along with that, they must respond to the formulated risk by monitoring the performances of their workers (as influenced by Martek & Chen, 2013).
Capital– They has very large investments involved in every project so insurance is required to be finically by able.
People- In order to review and monitoring the treatment, the organization can follow the WHS regulation to provide proper safety to their employees. As opined by Castillo et al. (2015), Bouygues Construction can conduct feedback to identify their flaws regarding their service. Nonetheless, they can conduct the meeting to reshape their strategies to develop the communication among the construction team while operating their service. Along with that, as commented by Pournader, Tabassi & Baloh (2015), they can recruit experienced labour to avoid accidents. The management can arrange training to make the employees more efficient to gauge their technical risk in their workplace
Process– As per the risk management and decision theory, Bouygues Construction can follow the risk management process to avoid the accidents. According to the process, Bouygues Construction can identify the risk of their workers to examine the perspectives towards their activities. Along with that, they must respond to the formulated risk by monitoring the performances of their workers
Systems- During executing their operation, a construction industry needs to focus on the quantitative risk analysis of the organisation. Therefore, the project participants need to share their understanding to avoid various arising risk in the construction sites. As commented by Gunduz & Laitinen (2017), identified risks should be measured to reduce the probability of accidents in the operational sites. Again as per the ISO31000, the proper communication will mitigate to manage their long-term project within their schedule period. Therefore drawing on the mainstream organization performances is required to manage and monitor their risk factors within the organizational firm.
Technology- Bouygues Company need to have state of the art technology as they work on projects like dam, construction, stadiums or other big projects. For this they need to have qualified and competent staff which have knowledge about latest technology. This can reduce the risk with technological obsolescence.
Information system- Because of their wide spread business in big geographical areas communication of information is important in each level. Feedback by clients, suppliers and other stakeholders need to be carefully manage and they should be informed about the relevant context.
Information flows- Flow information at Bouygues Company is both top and bottom up. Finically reports are developed and managed by top level management where as risk easement and management documents are developed by project managers. Client’s feedback is regularly taken to make changes in the project according to latest specification information flow helps in appropriate monitoring of the project.
Relation with, perceptions and values of internal stakeholders
Directory managers and employees are the main internal stakeholders. Directors developed the strategic considering the capability and skills of employees and managers, Employees are loyal to the company as the company takes good care of their health and safety and the compensation. Project manager need to have coordinate relationship with staff, suppliers, clients so internal and external relationship has to develop and made staff take pride in working with Bouygues Company.
Organisational Culture
BCA Company believes in developing and maintaining health and safety standards to their employees they provide appropriate equipments and safety care of the site of construction. Relevant training is providing to employees. The construction industries can implement an effective training procedure in order to overcome the challenges as well as developed the skill of the employees regarding their activities. As commented by Pemsel & Wiewiora (2013), they need to implement effective training in order to provide the employees proper security in the construction site. Moreover, effective training will help the worker to verify the technical faults in the construction sites that reduce the chances of falling if the labours from 2 meter height and safe them from electrocution. Onsite workers need to be trained to tackle the lifting equipments to reduce the possibilities of their accidents it eh operational area.
Contractual relationships from and extent
Bouygue construction company have contractual relationship with suppliers of the construction materials companies. They have also source the labour, staff, project manager from external recruit agents and agencies as well. Sometimes they develop partnership with technical experts or regional players to bid for a project. BCA Company respect the commercial relationship with the parties but there is always risk of other part not honouring the commitments of the constructional relationship.
Relevant Act
Health and safety in employment Act 1992
This act is made for the safety of people at work. Health and safety committees more support to effective worker participation. This includes information on who can be a health and safety representative or on a health and safety committee, and health and safety representative training.
Privacy Act
The privacy act applies to all of the personal information the federal government collects, uses and discloses—be it about individuals or federal employees. This act mainly deals with the collection and discloser of personal information.
Standards Act
According to this act Bouygues Construction Company have to follow the standard which are set by the standard New Zealand like enhance their products and services, improve safety and quality, meet industry best practices and support trade in to existing and new markets.
Task 2
| Column 1 | Column 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Risk area | Specific risk | |||
| Information system | Software or hardware failure | |||
| Occupational Safety and health | Poorly equipped infrastructure | |||
| H R Risks | Ineffective monitoring of training sessions | |||
| Financial | interest rates rise |
Table 2 – Risk Consequence/Impact Rating
| Level | Risk Descriptor | Consequence |
| 1 | Insignificant | No interruption to operation |
| 2 | Minor | Disruptive operations |
| 3 | Moderate | Ineffective communication |
| 4 | Major | Reputation damage or Loss of more than $1billion |
N Table 3- Risk likelihood/Probability Rating
| Level | Descriptor | Likelihood/Probability |
| A | Almost certain | Is likely to Occurs frequently in a year |
| B | Likely | Is Likely to occur in a year |
| C | Possible | Possible to occur sometimes |
| D | Unlikely | Unlikely to Occurs |
Table 1
| Column 1 | Column 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Risk Area | Specific Risk | Likelihood rating | Impact | Risk mitigation and priority rating |
| Information system | Software or hardware failure | C | 3 | |
| Occupational Safety and health | Poorly equipped infrastructure | A | 2 | |
| H R Risks | Ineffective monitoring of training sessions | A | 1 | |
| Financial | interest rates rise | B | 4 |
C Evaluation
Table 4- Risk Mitigation Priority Rating
| Likelihood | ||||
| Insignificant
1 |
Minor
2 |
Moderate
3 |
Major | |
| A ( certain) | M | M | H | H |
| B (likely) | M or L | M | H | H |
| C ( possible) | L | L | M | H |
| D (unlikely) | L | L | M | M |
H = High risk, M = Moderate risk, L = Low risk
| Risk area | Specific risk | Likelihood rating of the risks | Impact | Risk mitigation priority |
| Damage of lifting equipment | Software or hardware failure | Injuries and financial loss | 2 | High |
| Electrocution of the engaged labour | Financial risk for the treatment of the labour | Major injury causes death | 1 | High |
| Risk of falling from 2-meter height | Financial risk for providing support to the affected labours | injuries | 3 | High |
| Injuries of these parties and labour | Interruption in operation reduces the profitability of their services (as influenced by Martek & Chen, 2013). | Major injury and causes damage to the construction equipment | 4 | Moderate |
| Lack of financial support for the affected labour | The organisation needs to provide support to the affected labours and that’s why they can face financial risk while executing their operation | Financial loss and reduction of profitability | 5 | Moderate |
Table 3: Measurement of the risk management
Source: Fumasoli, Pinheiro & Stensaker, 2015)
Task 3
Risk management framework
Part A
Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework
The Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework emphasize on training as well as the public-private partnership and this is related with the 4.5 guideline of ISO31000. The Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework also highlight on managing framework and financial status that is similarities with the 5.6 and 5.2 of the ISO 31000 guidelines (treasury.act.gov.au, 2017). This section preliminary provides support to develop the construction plan by maintaining the partnership performances within their business territory. Nonetheless as per the PPP model of Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework proper infrastructure must be maintained that is also mentioned in the 5.7 guideline of ISO 31000. Hence the Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework is principally emphasized on the training and education so all the factors are not exactly explicitly refer to the guideline of ISO 31000 (iso.org, 2017).
J and J FRAMEWORK FOR ENT R M
According to the enterprising risk management section of J and J FRAMEWORK FOR ENT, R M assessment framework will provide support for the sustainable and affordable construction, which also highlights on the 4.1 guidelines of ISO 31000. Again in this section “J and J FRAMEWORK”, proper trust, as well as healthy relationship, are also highlighted which is aligned with 5.2 guideline of ISO 31000. Moreover, the risk responses and control activities are discussed in the subsection of Components of Enterprise risk management framework of the J and J FRAMEWORK guidelines and that is described in 4.5 and 4.6 regulation of ISO 31000. Nonetheless in the internal environment and objective setting section of J and J FRAMEWORK different strategic principles are focused and complied with the 2.8 and 2.6 regulation of ISO 31000 (jnj.com, 2017). Apart from that, J and J FRAMEWORK also help to monitor the effective mitigation effort under the subsection monitoring of event identification and risk assessment that is explicitly referred to 5.6 guideline of ISO 31000. Henceforth it is seen that all guidelines are aligned with the regulation of ISO 31000(iso.org, 2017).
Risk Management Framework Massey University
In the principle, 1 Risk Management Framework Massey University proper commitment must be maintained that is also aligned with the 5.2 guideline of SO 31000 (Massey.ac.nz, 2017). Moreover, in the principle, 2 implementations of rules and regulation are necessary to enhance the activities along with training must be incorporated that is also highlight on the 5.6, 5.4 and 4.4 guideline of ISO 31000. However, according to the principle 3, monitoring and measure will help to maintain proper formulated risk management framework that is also aligned with the 4.3, 2.28 and 2.26 regulation of ISO 31000. Along with that as per the principle, 4 continuous improvements is essential to come across the objectives which are also aligned with the 4.6 section in the guideline of ISO 31000(iso.org, 2017).
W REGION R M F
According to the principle number II, an of W REGION R M F risk management generally integrated to E and IG decision by divisional strategic planning program through clear escalation channel that is aligned with the 2.21 and 2.27 section of the guideline of ISO 31000 (defence.gov.au, 2017). Again as per the principle, II b E and IG risk management are principally related to the business context to the stakeholders on the update service that is also highlighted in the 2.13 and 4.2 regulation of the ISO 31000 guidelines. Nonetheless, according to the principle IIc E and IG manager’s activity will depend on the perspectives of the risks within their unit did responsibility which is also focussed on the 2.6 guidelines of ISO 31000(iso.org, 2017).. Apart from that according to the principle IId E and IG generally use timely, structures as well as systematic approaches regarding the risk management to achieve their objectives that are all focussed on 4.3, 2.6 and 2.5 guidelines of ISO 31000. Furthermore, as per the principle, IIe training, as well as proper guidance, is required for the workers to take the responsibilities on their duties that are approximately explicit with the 5.6 section of the guideline ISO 31000. Therefore, it can be observed that the regulations of W REGION R M F are approximately aligned with the guidelines of ISO 31000(iso.org, 2017).
RMF on ISO31000 for Bouygues Construction
It is reported that the Bouygues Construction is recently formulated their risk factors to enhance excellence performances as well as the commitment with their stakeholders that is the highlight of the section 2.13 and 5.4 of the guidelines of ISO 31000 (bouygues-construction, 2017). Along with that, they also ensure their consumers about their innovative strategies to avoid the technical risks that are not exactly aligned with the guidelines of ISO 31000. Nonetheless, this construction organization also recruits experienced labour and conduct training to reduce the occurrence of accidents of their employees that is also explicit in the 5.6 section of the guidelines of ISO 31000(iso.org, 2017)

Figure 4: RMF on ISO31000 for Bouygues Construction
(Source: bouygues-construction, 2017)
Part B
A GENERIC R M FRAMEWORK and PROCESS TEMPLATE
Prospective risks……………………………………………………………………… 28
Affected person……………………………………………………………………….. 28
Head on control measure………………………………………………………….. 28
Risk rating……………………………………………………………………………….. 28
Defensive measure……………………………………………………………………. 28
Responsibilities…………………………………………………………………………. 28
Task 4
Personal statement
Risk in workplace for poor management system
As an employee of the Bouygues Construction employees faced the communication issues while working on the business unit, as I cannot communicate with my supervisor while they faced technical issues in the lifting equipment. Henceforth as per the 5.2 section of the guideline of ISO 31000 Bouygues Construction can develop their communication strategies to enhance immediate service to their labours. Along with that, they must improve the quality of the lifting machines before executing their activities. Hence the organization can develop their management system to provide support to their employees whenever they needed while working. Therefore as per the 4.5 regulation of the ISO 31000 guidelines, the company can supervise their service to avoid this organizational risk in the operational unit.
Variety of risk that is required to emphasize
Staff of theBouygues Construction they suggest to supervisor that the organization can emphasize on their management strategies to provide support to their labour to reduce the arising risks in their sector. Nevertheless, before executing their service, they can examine the plot to avoid electrocution or precaution must be taken while movement of a powered mobile plant energized electrical service, shipping lane, and traffic corridor. Along with that, the organization ought to emphasize the continuous improvement to maintain the safety of their labour to gauge their accidents in the service unit.
Chances to overcome the risks
Form the discussion is can be seen that Bouygues Construction Australia need to implement the guideline of ISO 31000 to improve their management strategies to avoid the accidents of the workers in their operating unit. Nevertheless, they can extend their schedule time to formulate their proposed plan, as it is time constraint to execute their activities. Again this construction company can emphasize on their technical risk to fulfil the demand of the statutory requirements within their business domain. Nevertheless, as per the Organization Behaviour Theory Bouygues Construction Australia can set up effective communication among their employees to increase their interaction with their operational domain.

Figure 5: Chances to overcome the risks
(Source: Gunduz & Laitinen, 2017, p.357)
New skill or knowledge that can develop to avoid these risks
As per the Captivating field of decision theory, the Bouygues Construction can identify they’re their technical risk to gauge their accidents in the operational domain. Moreover this organization suggest the management team that they must reshape their infrastructure to enhance their reputation by recoding the organizational issues within their service unit. Apart from that, feedback must conduct by the management to come across their flows towards their service. Along with that, they can implement training to make the labour more efficient towards their duties. Moreover, before executing an operation, they can discuss their formulated plan to identify the arising risk. Proper communication must maintain to provide emergency service to the employees whenever they needed.
Conclusion
From the above illustration, it can be seen that Bouygues Construction is facing a different organizational risk that reflects on their performances and reduce reputation in Australia. However, Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework, J and J FRAMEWORK FOR ENT R M, Risk Management Framework Massey University, W REGION R M regulation provide support to the company to compare their actives for developing their management system. The Organization Behaviour Theory and captivating field of decision theory will mitigate the management to reduce their technical risk by fulfilling the demand of the statutory requirements.
Reference list
Slp.wa.gov.au (2004),Construction Contracts Act 2004, Retrieved on 24th Oct, 2017 from : https://www.slp.wa.gov.au/legislation/statutes.nsf/main_mrtitle_188_homepage.html
Aminbakhsh, S., Gunduz, M., & Sonmez, R. (2013). Safety risk assessment using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) during planning and budgeting of construction projects. Journal of safety research, 46, 99-105. Retrieved from https://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/45376264/A16.pdf?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAIWOWYYGZ2Y53UL3A&Expires=1507181900&Signature=ZHbc%2Btdo%2BdBYvRY1Lp69yQ2xU94%3D&response-content-disposition=inline%3B%20filename%3DSafety_risk_assessment_using_analytic_hi.pdf
Araújo, N. A. M., Grassberger, P., Kahng, B., Schrenk, K. J., & Ziff, R. M. (2014). Recent advances and open challenges in percolation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1404.5325. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1404.5325.pdf
Beck, U. (2014). The brave new world of work. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons. Retrieved from https://static.cambridge.org/resource/id/urn:cambridge.org:id:binary:20161215103758111-0946:S0038038501269910:S0038038501009919a.pdf
bouygues-construction (2017), BOUYGUES CONSTRUCTION , Available at: www.bouygues-construction.com.au/ on 3rd Oct 2017
Castillo, T., Alarcón, L. F., Salvatierra, J., & Alarcón, D. (2015). Analyzing the Interrelation Between Management Practices, Organizational Characteristics and Performance Indicators for Construction Companies. In Proceedings for the 23th Annual Conference of the International Group for Lean Construction(pp. 691-700). Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jose_Luis_Salvatierra_Garrido/publication/286084200_ANALYZING_THE_INTERRELATION_BETWEEN_MANAGEMENT_PRACTICES_ORGANIZATIONAL_CHARACTERISTICS_AND_PERFORMANCE_INDICATORS_FOR_CONSTRUCTION_COMPANIES/links/5665ed9a08ae15e74634c202/ANALYZING-THE-INTERRELATION-BETWEEN-MANAGEMENT-PRACTICES-ORGANIZATIONAL-CHARACTERISTICS-AND-PERFORMANCE-INDICATORS-FOR-CONSTRUCTION-COMPANIES.pdf
defence.gov.au (2017), ESTATE AND INFRASTRUCTURE GROUP , Available at: http://www.defence.gov.au/estatemanagement/governance/Risk/docs/RMF.pdf on 3rd Oct
Environment.gov.au (1989), Hazardous Waste (Regulation of Exports and Imports) Act 1989 Retrieved from http://www.environment.gov.au/protection/hazardous-waste/about on 25th October 2017
Fumasoli, T., Pinheiro, R., & Stensaker, B. (2015). Handling uncertainty of strategic ambitions—The use of organizational identity as a risk-reducing device. International Journal of Public Administration, 38(13-14), 1030-1040. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tatiana_Fumasoli/publication/280575172_Handling_Uncertainty_of_Strategic_Ambitions-The_Use_of_Organizational_Identity_as_a_Risk-Reducing_Device/links/5770bd3a08ae0b3a3b7b9709.pdf
Ghobadi, S. (2015). What drives knowledge sharing in software development teams: A literature review and classification framework. Information & Management, 52(1), 82-97. Retrieved from http://ai2-s2-pdfs.s3.amazonaws.com/8834/96137996df940dde374edf7fe6347292f2d2.pdf
Glendon, A. I., Clarke, S., & McKenna, E. (2016). Human safety and risk management. Florida: Crc Press. Retrieved from https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=u9O1bblQHFEC&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Risk+in+workplace+for+poor+management+system+in+australia&ots=q7AqtVapiz&sig=zN02tWS7jRGQENve9425M5EO2s8&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
Gunduz, M., & Laitinen, H. (2017). A 10-step safety management framework for construction small and medium-sized enterprises. International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, 23(3), 353-359. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Murat_Gunduz2/publication/304031772_A_10-step_safety_management_framework_for_construction_SMEs/links/59648140aca2728c112755c6/A-10-step-safety-management-framework-for-construction-SMEs.pdf
Haimes, Y. Y. (2015). Risk modeling, assessment, and management. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons. Retrieved from https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=JvowBgAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP11&dq=knowledge+to+manage+the+organisational+risk+book&ots=DZZl-SNolH&sig=zMA5fu3WIq_cEQ7RCAaYg3zvBmI&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
Hwang, B. G., & Ng, W. J. (2013). Project management knowledge and skills for green construction: Overcoming challenges. International Journal of Project Management, 31(2), 272-284. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Bon-Gang_Hwang/publication/257094667_Project_management_knowledge_and_skills_for_green_construction_Overcoming_challenges/links/0c96052f3321e1fa02000000.pdf
iso.org (2017), ISO 31000:2009, Available at: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:31000:ed-1:v1:en on 2nd Oct
Jacquet, J. B. (2014). Review of risks to communities from shale energy development. Environmental science & technology, 48(15), 8321-8333. Retrieved from http://www.programmeofficers.co.uk/Cuadrilla/CoreDocuments/CD41/CD41.44.pdf
Jato-Espino, D., Castillo-Lopez, E., Rodriguez-Hernandez, J., & Canteras-Jordana, J. C. (2014). A review of application of multi-criteria decision making methods in construction. Automation in Construction, 45, 151-162. Retrieved from https://repositorio.unican.es/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10902/6160/A%20review%20of%20application%20of%20multi-criteria%20decision%20making%20methods%20in%20construction.pdf?sequence=1
jnj.com (2017), Framework for Enterprise Risk Management , Available at: https://www.jnj.com/_document?id=0000015a-678b-d85b-a1da-779f4cfe0000 on 5th 2017
Legislation.gov.au (2011), Work Health and Safety Act 2011, Retrieved on 24th Oct, 2017 from https://www.legislation.gov.au/Details/C2016C00887
Martek, I., & Chen, C. (2013). Localization typologies evident among foreign enterprises active in the Chinese construction market. Journal of construction engineering and management, 139(10), 04013001. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Igor_Martek/publication/273750063_Localization_Typologies_Evident_among_Foreign_Enterprises_Active_in_the_Chinese_Construction_Market/links/5511467c0cf2a8dd79c012fd.pdf
massey.ac.nz (2017), Massey University Policy Guide , Available at : https://www.massey.ac.nz/massey/fms/PolicyGuide/Documents/Risk%20Management/Compliance%20Framework.pdf on 4th Oct 2017
Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B., Zareipour, H., Amjady, N., & Ehsan, M. (2013). Application of information-gap decision theory to risk-constrained self-scheduling of GenCos. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 28(2), 1093-1102. Retrieved from https://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/30079880/behnam_igdt-ieee_2012.pdf?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAIWOWYYGZ2Y53UL3A&Expires=1507184904&Signature=EPD5A0ZxaxrUUmDrnypX0Xc3Hok%3D&response-content-disposition=inline%3B%20filename%3DApplication_of_Information-Gap_Decision.pdf
Park, C. S., & Kim, H. J. (2013). A framework for construction safety management and visualization system. Automation in Construction, 33, 95-103. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chansik_Park3/publication/257371496_A_framework_for_construction_safety_management_and_visualization_system/links/54d06abc0cf24601c09689b3.pdf
Pemsel, S., & Wiewiora, A. (2013). Project management office a knowledge broker in project-based organisations. International Journal of Project Management, 31(1), 31-42. Retrieved from https://www.cbs.dk/files/cbs.dk/pemsel_and_wiewiora_2013_0.pdf
Pournader, M., Tabassi, A. A., & Baloh, P. (2015). A three-step design science approach to develop a novel human resource-planning framework in projects: the cases of construction projects in USA, Europe, and Iran. International journal of project management, 33(2), 419-434. Retrieved from https://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/39654330/A_three-step_design_science_approach_to_20151103-13201-lncps8.pdf?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAIWOWYYGZ2Y53UL3A&Expires=1507184776&Signature=ATmaWxIwNB95j0ImZ7RG1ydOISY%3D&response-content-disposition=inline%3B%20filename%3DA_three-step_design_science_approach_to.pdf
Raghupathi, W., & Raghupathi, V. (2014). Big data analytics in healthcare: promise and potential. Health information science and systems, 2(1), 3.. Retrieved from https://www.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/2047-2501-2-3?site=hissjournal.biomedcentral.com
Stakeholdermap.com. (2017). Stakeholder | Definition – What is a stakeholder?. [online] Available at: https://www.stakeholdermap.com/stakeholder-definition.html [Accessed 11 Nov. 2017].
Taylan, O., Bafail, A. O., Abdulaal, R. M., & Kabli, M. R. (2014). Construction projects selection and risk assessment by fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methodologies. Applied Soft Computing, 17, 105-116. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Osman_Taylan2/publication/260014430_Construction_projects_Selection_and_risk_assessment_by_Fuzzy_AHP_and_Fuzzy_TOPSIS_methodologies/links/55dd948808aeb41644aefe1f.pdf
treasury.act.gov.au (2017), Australian Capital Territory Education and training RM Framework, Available at: https://apps.treasury.act.gov.au/infrastructure-finance-and-advisory/the-capital-framework on 5th Oct 2017
van der Vegt, G. S., Essens, P., Wahlström, M., & George, G. (2015). Managing risk and resilience. Academy of Management Journal, 58(4), 971-980. Retrieved from http://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=5743&context=lkcsb_research
Voo, Y. L., Foster, S. J., & Voo, C. C. (2014). Ultrahigh-performance concrete segmental bridge technology: Toward sustainable bridge construction. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 20(8), B5014001. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yen_Voo/publication/270576639_Ultrahigh-Performance_Concrete_Segmental_Bridge_Technology_Toward_Sustainable_Bridge_Construction/links/54ae69b20cf2213c5fe46945/Ultrahigh-Performance-Concrete-Segmental-Bridge-Technology-Toward-Sustainable-Bridge-Construction.pdf
ORG CHART, 2017. Construction company organizational chart – introduction and example. Retrieved from http://www.orgcharting.com/construction-company-org-chart/
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Risk Management"
Risk Management is a process for identifying, understanding and mitigating any risks that are associated with a particular task or event. Individuals and organisations implement Risk Management to provide a layer of protection, allowing them to minimise risk in their operations.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




