Dissertation on Sustainable Energy Sources
Info: 12898 words (52 pages) Dissertation
Published: 12th Nov 2021
Tagged: EnergySustainability
Abstract
The objective of this research is to investigate the possibilities of sustainable sources of energy in African nations and how to strengthen, advance and value the development of sustainable sources of energy in African nations to close the gap of half the population of these nations. It had no entrance to an ecologically pleasant energy.
Alternative sources of energy are great and magnificent choices as they are unlimited. We will not keep up with them, as we could briefly discuss the fossil powers that are the main sources of energy in African nations. In addition, it is not only the decline in the levels of unsustainable sources of energy that are the main major concern that will cause these nations to adjust and change to the use of sustainable sources of energy. Environmental change, which is a consequence of carbon sequestration and natural pollution, is attracting global consideration and forcing national governments to plan strategies that will enable their countries to adjust the use of sustainable sources of energy to reduce ecological pollution At least dangerous atmospheric devotion has become a topic and a worthy question of the world today and later.
Two distinctive research techniques were used as part of the research observation piece. At first, the organized review of the survey was completed. In addition, meetings were held. The use of both research strategies proved useful to investigate the energy situation in African nations and to accept sound results. In light of the experimental results, the problems of energy are clear.
The primary end of the review is the potential of resources for sustainable energy in African nations are put in abundance of 1.5 times that of fossil energy resources in terms of energy. Solar energy would be the best response to the emergency taken by biomass and hydroelectric, which also have notable potential to improve and have some effect on the low level of power in Africa, with emphasis on provincial regions, through the selection and use of this sustainable energy is based on the reasonable improvement.
Click to expand Table of Contents
Contents
Literature review
- Fossil fuels – Coal:
- Fossil Fuels – Natural Gas:
- Solar power:
- Nuclear energy:
- Wind energy:
- Biofuels and Biomass:
- Fuel cells:
- Geothermal energy:
- Oceanic energy:
- Energy of the Antimateria:
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
- Background
- Objectives of the research
- Research problems and research questions
- Disposition of the thesis
CHAPTER 2: sustainable DYNAMISM SOURCES
- Energy Process
- Solar dynamics
- Wind energy
- Water energy
- Energy of biomass
CHAPTER:3 DYNAMISM SITUATION IN AFRICA
- Energy Demand projection
- Energy Supply Projection
- Potential of sustainable energy sources in Africa
- Energy of hydroelectric power Renewals in Africa
- Solar Dynamics Resources in Africa
- Wind dynamics Resources in Africa
- Biomass energy Re-sources in Africa
CHAPTER 4: METHODOLOGY
- Research strategy
- Research Methods
- Qualitative research method
- Method of quantitative research
CHAPTER:6 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS OF THE THESIS
- Results of research
CHAPTER: 7 CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
- Conclusion
- Suggestions
- Summary
References
Literature review
Nuclear vitality, sun-oriented vitality and the vitality of wind and bio energy are just a couple of promising options for a cleaner and greener future. Other moderately new vital wells are being investigated, for example, energy devices, geothermal vitality and sea vitality. In the areas that go with it, we will investigate the current sources of vitality and examine potential sources of vitality in the future.
Fossil fuels – Coal
Non-renewable energy sources are the remaining parts of dead plants and creatures on land and on the seabed. These are formed from the fossilized stays of dead creatures and plants that are presented to the warmth and weight outside the world for a great number of years.
Non-renewable energy sources are mainly composed of hydrocarbons. They contain carbon and hydrogen in changing proportions, for example, methane, which has a low carbon to hydrogen ratio, or anthracite coal, which is practically unadulterated carbon. Hydrocarbons are formed when the fossilized stays of dead forms of life are artificially adjusted over a large number of years because of the extraordinary weight and warmth found on the world deck. The compound vitality “set aside” in these energies is discharged in the middle of the burning to create electrical energy.
As indicated by the energy Information Administration’s assessments, non-renewable energy sources account for 86 percent of the added vitality delivered on the planet. Oil represented 36.8 percent, coal 26.6 percent and petroleum gas 22.9 percent. In any case, petroleum products are inexhaustible sources of vitality. It takes countless years to shape and drain substantially faster than new saves can be made. It is estimated that 23.5 tons of fossilized natural material is required on the seabed to deliver 1 liter of gas. In 1997, the aggregate amount of petroleum derivatives used was proportional to the plant matter that developed over the entire land and sea surface of the Earth over a period of 422 years.
Another drawback of our overwhelming reliance on petroleum products is the measure of carbon dioxide delivered in the midst of burning, which is estimated at 21.3 billion tonnes per year. In any case, common procedures are equipped to retain almost the portion of the aggregate sum of discharged carbon dioxide discharges into the climate, implying each year the measure of carbon dioxide in the environment is expanding by 10,650 Million of tons, which is conjectured to be the main supporter of a dangerous atmospheric devastation that could conceivably have exceptionally unfavorable consequences for the biological system.
Fossil Fuels – Natural Gas
Gasoline is usually found along with non-renewable energy sources, in the informal accommodation coal in different types of smoothie. It is made by living methanogenic beings that are displayed in landfills, marshes and wetlands. Normally it is made up of methane and small measurements of different gases, for example, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hydrocarbons of higher subatomic weight, sulfur, helium and nitrogen. Components of flammable gas other than methane must be expelled before gasoline can be used as a fuel source. Perused Natural Gas Generators: An alternative to Diesel, for a case that demonstrates the existing innovation that uses a characteristic asset, one that is better for the land, as fuel.
Although it is believed that flammable gas is cleaner than other petroleum products, it has still been found to add to the pollution and a dangerous atmospheric deviation. While it can be used to complement the world’s eternally exhausting stores of traditional non-renewable energy sources, it is not a 100 percent clean, no dirt choice. In 2004, carbon dioxide emissions from the use of petroleum gas remained at 5.3 billion tones, while coal and oil added up to 10.6 billion tons of carbon dioxide discharges and 10.2 billion tons of carbon dioxide. In any case, this pattern is required to invest in 2030 when oil gas is likely to produce 11 billion tons of carbon dioxide instead of 8.4 billion tons of coal and 17,200 tons of oil around then. In addition, when it is discharged directly into the air, flammable gas is a much more intense substance that damages ozone than carbon dioxide, since this occurs in small amounts, is not currently a reason worth worrying.
Solar power
Virtually everything in this world eventually gets its vitality from the sun. Instead of getting the vitality of the sun from aberrant sources such as petroleum derivatives, scientists and associations around the world are specifically seeking to draw from this infinite source of vitality.
The earth gets about 174 billion megawatts of energy in the upper air, therefore, from solar radiation. About 30 percent of the occurrence of solar radiation is reflected again, while the rest, which adds up to 3.85 x 1024 Joules consistently, is consumed by the climate, seas and land masses. The measure of the solar vitality that is accessible to us in the middle of an hour is more than the aggregate sum of vitality spent around the world in a whole year. In any case, it is a type of diffused vitality, rather than concentrated, and the best proof lies in saddling it.
The heat and light radiation of the sun can be braked using semiconductors oriented towards the sun. Radiance based on the sun of vitality energizes the electrons in these tables and encourages the creation of electrical vitality. One of the biggest obstacles to saving the vitality of the sun is in building solar panels with financial know-how. The cost of solar energy is around US 8-15 cents per kilowatt-hour when compared to the cost of coal-based electric power at US $ 6 pence per kilowatt-hour.
The capacity for proper vitality is another real obstacle. The vitality based on the sun is not accessible around the time of the night, but rather the current frames of vitality more often than not expect a constant accessibility of vitality. Hot-mass frames, warm-up frames, scenario change materials, off-grid photovoltaic frames and pumped-up hydropower frames are a part of routes where light-based vitality Solar can be set for later use. In fact, even with most of the mechanical advancements, vitality innovation with solar power is still in its early stages. Until we have consummated innovation and can curb and store sun-based vitality in an appropriate and practical way, petroleum products will remain the most regularly used resource of vitality.
Nuclear energy
As the general interest for power continues to increase, atomic vitality is increasing in importance as a spotless source of energy required to address the global issue of environmental change. The unpredictability in the costs of oil derivatives and the growing concern of countries to ensure supplies of vitality are different drivers of atomic vitality.
There are currently 439 nuclear power reactors operating in 30 nations around the world. This accounts for 14 percent of the world’s aggregate power age. The International Atomic energy Agency expects the capacity of the world’s atomic energy era to shift from the current 372 gigawatts (GW) to 437-542 GW by 2020 and 473-748 GW by 2030. However, for atomic energy Increase as a solid and clean source of vitality, they would have to face some difficulties. Some of them incorporate changes in monetary intensity, highlighting protected and solid atomic plants, the management of spent fuel and the transfer of radioactive waste, creating sufficient skilled manpower, ensuring open confidence in atomic energy and ensuring the Atomic expansion and security.
Atomic vitality is the team by the part (division) or mixture (combining) the nuclei of at least two iotas. The atomic division most often uses uranium during the time devoted to equipping vitality. At our current utilization rates, uranium found in the Earth’s outer layer can last for about a century. However, scientists predict that the use of vitality will triple in the next century, implying that accessible uranium assets will only last us for about 30 years. One option is the reprocessing of spent fuel. This spent fuel is rich in plutonium and when bonded with the rest of uranium, it can be reprocessed in a mixture known as MOX, which can be used as fuel. This can extend uranium assets accessible for a couple of decades. The major disadvantage of this source of vitality is the transfer of radioactive waste and the high cost of building atomic power plants.
The atomic division, then again, could be the solution to our vitality issues. The division uses hydrogen, lithium and boron isotopes. The earth’s lithium reserves, coupled with those of the ocean, can last more than 60 million years. Deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen, can last another 250 million years. Be that as it may, the way to curb the vitality of this isotope is genuinely confusing is still in its early stages. In the possibility that we can effectively figure out how to use the atomic combination for the era of vitality in a practical way, it could be the world’s new lord of vitality. The atomic combination is a perfect process, with emanations of low carbon dioxide, and the radioactive waste also has a generally short half-life.
Wind energy
The wind ranches are developed to saddle the mechanical vitality of the wind and change it in electrical vitality. These wind farms are then associated with electric power transmission systems for energy transport. In general, only 20 to 40 percent of the added vitality limit of a wind farm can be used.
The restrictive element in the equipment of the wind vitality is that the wind speed is variable and to a large extent the wind vitality must be successfully saddled with wind speed and strong constant winds. These generally occur at higher elevations. The vitality of the wind also requires extensive open fields of land taking into account the ultimate goal of building wind ranches.
In 2008, the overall limit of the wind-control era was maintained at 121.2 GW. Normally, wind control now accounts for only 1.5 percent of the global limit of the power era. In any case, this part has grown two layers in the three-year period 2005-2008. Wind control accounts for 19 percent of the aggregate power era in Denmark, 10 percent in Portugal and Spain and 7 percent in the Republic of Ireland and Germany.
Biofuels and Biomass
These incorporate fuel from the plant and creature sources. Oil or ethanol obtained from plants, for example sugar cane, switchgrass, green growth, poplar and maize can be used specifically or mixed with different energies, eg, business diesel and fuel to give control. In fact, even plant matter, for example, dead wood, leaves, wood shavings, and branches can be sung to create vitality. Normally it is a delegated biomass. Biomass also incorporates any biodegradable plant residue and creature sources that can be sung for fuel.
The limiting element in the use of bio energizes is that a substantial number of products must be developed to collect the vitality trapped in the plants. This requires unlimited territories of mature land. In addition, not all plant sources offer high performance. The trials are in progress to hybridize and inherently adjust these products to make them more potent and increase their performance. Biofuels are very encouraging for small-scale use because they are low in depletion of ozone-depleting substances, they are a successful framework for waste management and create small air pollution.
With the advance of new innovation and the improvement of new bits of knowledge in our environment, researchers have had the ability to think about energy alternatives that are much bolder. These incorporate modules of energy, geothermal vitality and vitality of tides and waves, to give some examples.
Fuel cells
Power devices are like batteries but use reactants from an external source, rather than batteries that are independent. On the off occasion that fuel and oxidant levels in energy units are maintained properly, the energy can be produced persistently. The efficiency of the energy components is relative to the power that is extracted from it. They are equally lightweight and surprisingly solid.
Geothermal energy
The interior of the Earth contains a ton of heat. Shallow areas contain hot water, agitation and steam. Deeper inside, the magma is very hot. This heat can be approached to create electrical vitality and drive different applications. Giving geothermal vitality requires no fuel or insignificant earth. Generally, it is a source of modest vitality and extremely bearable, since the measure of warmth contained in the bed of earth is enormous to the point that, irrespective of the possibility that it assembles more vitality than we need, in any case will be sufficient for a large number of the next years.
Oceanic energy
The seas are unfathomable and contain enormous measures of vitality in the currents of water, and the warm and salty inclinations. The vitality of tides and waves can be saddled to create electrical vitality. Distinctions in temperature occurring at different depths can be used to drive hot engines, which thus generate electrical energy. The distinction of osmotic weight between salt water and new water can also be used to create energy. Although most of these strategies are still in the exploratory stages, if properly asked, they can be an achievement for humanity. The seas may have the ability to extinguish our hunger for vitality and plunder the crown as the lord of the energies.
Energy of the Antimateria
A highlight among the most confusing speculations of vitality delivery is the use of matter and hostile to matter to create electrical energy. Antimatter is the inverse of matter. In the possibility that matter is about particles, hostile to matter is contained against particles. The researchers suggest that if matter and matter were to impact, they would erase each other and unleash unfathomable measures of vitality. However, this is still a hypothetical source of vitality. Regardless of whether anti matter exists somewhere in the universe and can be slowed in some way is still a puzzle for humanity.
There are different methods to extract the vitality of the earth that humanity has found and used to further strengthen their good fortune. As humanity develops, we will persistently seek more up-to-date and more proficient types of vitality that have a minimal measure of effect on the earth. At present, the most monetarily effective fuel has turned out to be oil. Later, when the oil reserves of the world are exhausted, we will use another source of vitality; Potentially one that has been specified previously. Be that as it may, the truth is that we should be proactive in researching new types of vitality to advance the progress of human progress and ensure a high standard of living that, as a whole, has become habitual.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
The primary passages of the postulation state the basis of the theory, driven by the research objectives, to examine questions and research questions. From this point, the restriction, the meaning of the sentences and the meaning of the proposition are introduced.
Background
Africa is the most populous dark country on the planet, and regardless of its immense normal sources, it is still one of the poorest nations in the world with an expected GDP for each capital of USD 2,162. For a long time the nation has faced a crisis of energy that is hampering its financial development. Energy is one of the key foundations for monetary improvement and, in addition, it is essential for all human exercises in this period. There is a lack of extraordinary power in Africa and the reasons for this lack are identified with issues related to money, socio-political and auxiliary that drives the division of influence in Africa to record losses of high energy of the era of influence and burden (Maczulak, 2010).
An expected 60-70 percent of the African population has no access to electricity. The demand for energy in Africa is governed by firewood and the ladies and young people are most influenced by the crisis of energy. At present only 10 percent of rustic family units and 30-40 percent of the nation’s total population have access to power. The energy sector in Africa depends absolutely on the government finance fuel and the subsidy of the main energy plants and the energy capital extends by the national government, states and government offices (Johansson and Burnham 2013).
Africa is invested with endless reserves of oil and gas and, in addition, a great amount of potentials of sustainable energy. However, the nation is experiencing a crisis of energy, which mainly affects its ability to reduce the need and achieve the Millennium Development Goals (Maczulak 2010).
Perhaps it is only the people who do not live and work together in Africa who do not realize that the absence of adequate energy provides particularly power is the greatest challenge the nation is facing to fully use its monetary possibilities in others to achieve progress financial. This is also the most massive element that is influencing the race of the nation to be one of the largest and largest twenty economies in the world by 2020. It is also obviously the question of how to find lasting and perpetual answers to problems has followed Being a necessity of each Progressive in the last ten years (Johansson and Burnham, 2013).
The African government has not had the ability to discover perpetual arrangements that solve the problems due to the adjustment here and now, hasty approaches and, in addition, projects of energy that are a disadvantage of the policies of energy in the long term that will help the country to achieve sustainable development. Energy and energy. For example, what the nation has done is still the use of the different options that are still within the confinement points of petroleum products, which are the main source that now controls the country’s economy (Choppin 2014).
Objectives of the research
Reaching energy is important for financial improvement and alleviation of destitution. A challenge of colossal progress in Africa is to connect with 60-70 percent of the African population that has no entry to power and services of modern energy. The technology of sustainable energy is a promising response to the crisis of energy in Africa. Sustainable energy, apart from being feasible and unlimited, can be established in small units and is thus appropriate for the administration and possession of the group. Adopting the use of sustainable sources of energy will lead Africa to achieve a supply of stable energy and, in addition, achieve the efficiency of energy (Bocarnea, Reynolds and Baker 2013).
Alternative sources of energy are great and magnificent choices as they are unlimited. We will not keep up with them, as we can summarize the fossil fillings that are the main sources of energy in Africa. In addition, not only the declining levels of unsustainable sources of energy are the main real concern that will make Africa fit and shift to the use of sustainable sources of energy. Environmental change, which is a consequence of carbon discharges and natural pollution, is attracting world attention and forcing national governments to devise arrangements that will enable their countries to adjust the use of sustainable sources of energy to reduce ecological pollution at Less An alteration of temperature around the world has become a notable theme and issue of the world today and later.
The objective of this research is to investigate the possibilities of sustainable sources of energy in Africa and how to strengthen, advance and dare the development of sustainable sources of energy in Africa to close the hole of 60-70 percent of Africans who have no entry. Which is naturally benevolent.
Research problems and research questions
The subject of the review of this research is the potential of sustainable energy in Africa. What is the purpose of discovering answers to the exploration questions?
- What are the monetary and social variables that influence the use and development of sustainable sources of energy in Africa?
- What are the problems related to the organizations that are faced in the construction of a source of energy in Africa?
Disposition of the thesis
The first part gives the data of the foundation of the investigation and a question of exchange of the territory of the examination, which requests two directions of inquiry that have been specified before. The second section deals with the process of energy and presents the four sources of sustainable energy and how to generate energy from these sources. The third part will analyze the energy situation in Africa, the demand and supply of projected energy, which are influencing the development of sustainable energy in Africa and the projected growth of sustainable energy. Section four covers and clarifies the philosophies that were used as part of the course of exploration and gives data of individuals in general organizations and the two case organizations. Section 5 contains the results and investigations of the theory from the information collected. Part six is the conclusion, proposals and summary that will help further investigate, open African, establishments and organizations that are intriguing in the development of sustainable energy in Africa.
CHAPTER 2: Sustainable DYNAMISM SOURCES
This part clarifies the process of energy and the four sources of sustainable energy that are sought in the research, that are the solar energy, the wind energy, the hydroelectric energy and the biomass. It also represents how to generate energy from the four sustainable sources of energy.
Energy Process
There are four components required in the process of energy. Just the opposite, the source of energy, which clarifies where we get our energy. Second, the production of energy clarifies the energy. Third, the transfer of energy reveals how the energy will be exchanged. Finally, the consumption of energy represents how to save as much energy as imaginable. Figure 2 is the process of energy.
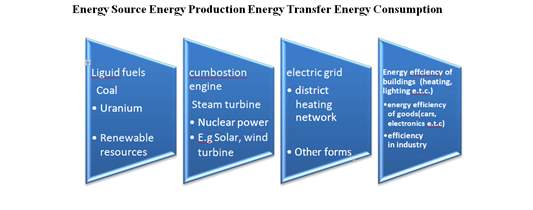
Figure 2. Energy Process
It is also essential to clarify some key terms of electric power that will help the reading to see more about the exploration work and the field of energy when everything is said in fact. Powers are measured in watts and energy is the amount of power supplied or used per unit time and is measured in watt-hours.
W = Watt; Indicates power capacity
Wh = watt-hour; Indicates the amount of energy produced or consumed
KW – kilowatt = 1000 MW
MW – Megawatt = 1000 KW
GW – Gigawatt = 1000 MW
TW – Terawatt = 1000 GW
Solar dynamics
The energy or solar power is the use of daylight for the era of power. The energy generated by the sun should be possible through an immediate strategy using photovoltaics, or using the receding technique, where daylight or energy focuses on bubbles and heat water that is used later to give control. Mainly the energy driven by the sun alludes to the use of solar radiation for the era of power. Be that as it may, adjacent to geothermal and tides, all other sources of sustainable energy get their energy from the sun. Figure 3 shows how to produce energy from the sun:
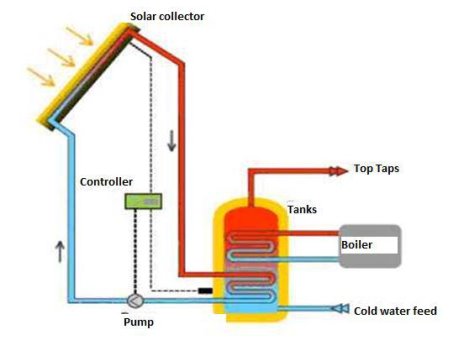
Figure 3. Generation of energy from the solar thermal method.
The dynamic energy of solar radiation is the declaration of energy thickness that is used to demonstrate the number of watts per square meter. Basically, the radiation of the sun that the Earth has begins in the photosphere, which is a thin layer that covers the convective mantle of high turbidity. Photospheres comprise several levels of ionization, including free electrons.
Wind energy
Wind power is the use and preservation of the twist to provide the energy for the era of control for valuable purposes, cases of wind power are using wind turbines for energy eras, wind factories are Used for the mechanical era was, or candles used to transport energy by moving it. Wind control should be incorporated for financial reasons, implying that most of the accessible yield must be taken into account as hydroelectricity and standard load management strategies for supply to meet demand. The photo below describes the wind turbine:

Figure 4. Wind turbine.
The measure of monetarily extractable energy that is accessible from the wind is said to be more than the actual use of human energy from all sources. As indicated by an estimate of about 72 terawatts of torsional power on Earth that is monetarily feasible. The quality of the wind changes in several areas, a normal incentive for a particular area does not show the added amount of energy that the wind turbine could create there. To ascertain the recurrence of rotational velocities in a given area, a flowability capability is used and is often adjusted to observe the information accurately, in light of the fact that it is obvious that the winds accelerate the changes of Appropriation of area to area.
Water energy
Hydraulic energy is the use of the gravitational limitation of the fall or the flow of water to create energy. Hydropower is the largest and most comprehensive framework of sustainable sources of energy that can be discovered in virtually every aspect of the world. Basically, hydroelectric power plants are built and are located in huge dams that have high gravitational forces, the hydroelectric does not deliver any waste specifically or in an indirect way that they are considered as the sources of energy that have lowered the carbon level yield of the Nursery dioxide. Hydropower was approached to represent 20 percent of world power, and in addition 88 percent of the aggregate power produced from a sustainable energy.
The photo below shows how to generate energy from the hydroelectric:
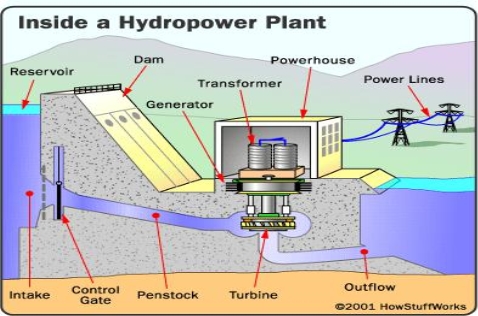
Figure 5. Generation of energy from hydro.
Essentially, a dominant part of hydropower and energy comes from the dammed water that is driving a water turbine and a generator. The energy of water is based on the volume in the distinction in height and weight between the water that flows and the spring of the water. The distinction of carving as a term is known as the head. The added sum of the potential energy of water is based on the head.
The accumulation of hydroelectric power produces power to supply high demand higher therefore to move the water between the supplies in several levels. In case of high power request, the additional age limit is used. If there is a higher power request, the water is discharged back into the lower tank by the turbine. Capacity offers the most essential business methods for large-scale storage of network energy and is improving the daily limit of the hydroelectric creation framework. Power-generating hydroelectric plants that had no supply limit are plant maintenance, as it is impractical for water storage. Tide energy era plant that uses variations of day by day of water according to the tides; The sources of tidal power are more surprising, and a few conditions allow the development and establishment of repositories and more often than not can be dispatched with the ultimate goal of the era of energy amid time of power appeal.
The basic recipe to use while determining the approximate generation of electric power in a hydroelectric plant is: P = phrgk, P speak of control in watts, p is the water thickness, h is the height in meters, r is the flow Water In cubic meters per second, g is the acceleration to gravity of 9.8 m / s2, and k is the coefficient of efficiency extension of 0 to 1. Productivity is greater with the larger and current turbines. The annual power that is created from the production of energy of hydroelectricity is based on the accessible supply of water. Some establishments, the rate of flow of water change by a figure of 10: 1 a year.
Energy of biomass
The energy of biomass is a source of sustainable energy that is obtained organically from living materials or life forms, similar to waste, wood and liquor filling. Biomass sources are rarely desired to create power or to deliver hot from them. The most commonly used biomass are dead trees, wood chips and tree triumphs. It also incorporates plants or creatures that are used for the generation of chemicals and filaments. It could also incorporate waste that is biodegradable, meaning waste that is generally burned as a fuel. Biomass sources of energy exclude natural material such as the petroleum product. The photo below shows how to generate energy from biomass:
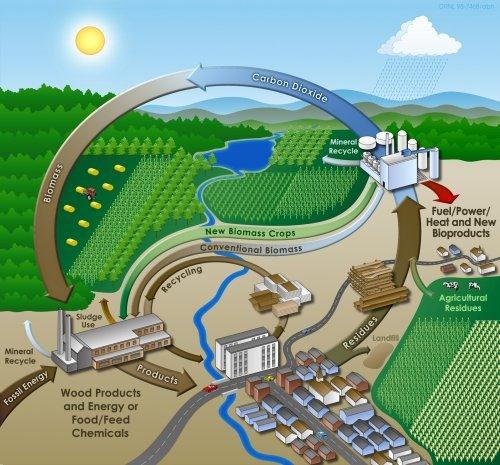
Figure 6. Generation of energy from biomass
The process of energy based on biomass as a rule begins with the capture of daylight by the plants and the generation of the compound of the substance. This is called photosynthesis, which causes glucose. This makes biochemical changes a lot with incredible business esteem. Ordinarily, photosynthesis continues with efficiencies of less than 8 percent. A plant is supposedly a structure that supports large organs comprising wood and specific leaves that perform photosynthesis and some particular roots that collect supplements and water. In biomass generation, the preparation materials are typically transported starting with one site and then with the next so it is known as sap and the organic products included in the process perform sexual multiplication. Roots and tubers store the energy in a plant and also the energy is stored in the soil sap products.
CHAPTER:3 DYNAMISM SITUATION IN AFRICA
This part clarifies the dynamics of the situation in Africa, the projected demand for energy using the Dynamic Demand Analysis Model that was created by the International Atomic Dynamics Agency and also the projected energy supply in Africa using the Model for the energy. Environmental Impact, which was produced by the International Atomic Dynamics Agency, which clarifies the possibilities of the four sources of sustainable energy, its limit of use and also its normal future development in Africa.
The African economy is heavily dependent on oil, which accounts for more than 95 percent of the tariff paid and, moreover, accounts for almost 85 percent of the country’s income. Africa has an estimated 36.2 billion barrels of oil saved as in 2009, it is the tenth largest nation on the planet producing oil. Despite oil, Africa had demonstrated gas stores of more than 5 billion cubic meters; It is the seventh largest gas savings nation on the planet.
Oil and gas reserves are mostly found along the Niger Delta, Gulf of Guinea and Bonny Bight. Most of the research exercises are devoted to deep and ultra-deep to the sea with exercises arranged in the bowl of Chad, in the upper east. Light and coal reserves are valued at 2.7 billion tons, and tar sands around 31 billion barrels of oil counterparts, and hydropower destinations have distinguished an expected 14.250MW. At present, the introduced threshold of matrix power in Africa is about 6,000 MW, 67 percent is warm and the rest is hydroelectric. For 2005, the transmission includes 6,000km of 132KV lines and 5,000km of 330KV lines. The transmission channels are overloaded with a lower limit of less than 4,000 MW. The transmission channels have a poor voltage profile which are organized particularly in the northern part of Africa, a poor control and dispatch frame, a delicate and extended array, extremely high transmission destruction and a continuous wrinkling of the frame.
Energy Demand projection
The demand for energy projections in Africa were registered using the Dynamic Demand Analysis Model created by the International Atomic Dynamics Agency, the model incorporates the main drivers of demand for energy, namely innovation, demographics, The socioeconomy. The MAED application needs a developing point-to-point on the economy, demographics, dynamics and efficiency. MAED breaks down the conclusive use of the country’s energy consumption in several areas and individual levels of reliable end use. The MAED processed projections of demand for African energy from 2005 to 2030.
The contributions of the MAED breakdown to the recognizable test of the monetary, social and specialized variables that affect the different classifications of energy demand. The energy of Africa demands case that demonstrates, four financial situations used like takes later:
Reference scenario: 7 percent of GDP development
High growth scenario: 10 percent GDP growth
Optimistic scenario I: 11.5 percent of GDP development; Y
Scenario II optimistic: GDP growth of 13 percent.
Table 2. Four economic scenarios for energy demand.
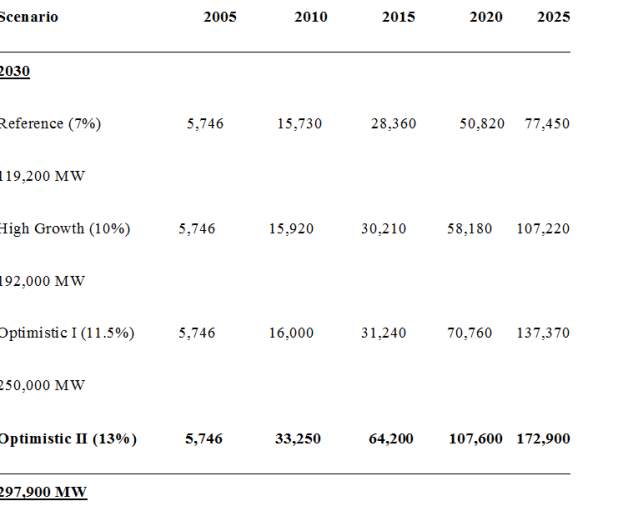
Figure 7 below illustrates electricity demand projections per scenario, MW.
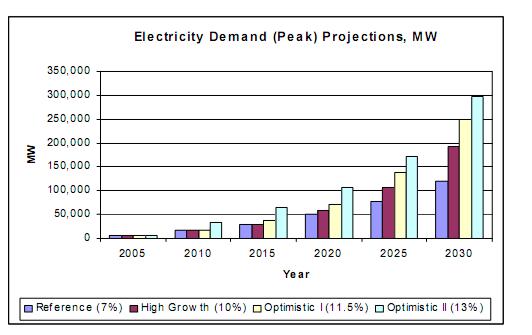
Figure 7. Electricity demand production capacity MW.
Energy Supply Projection
Dynamic supply projections in Africa were processed using the Model for Energy Supply Strategy Alternatives and their General Environmental Impact and it is also filled as an apparatus that will use projection of demand for energy as information that will provide a procurement process. The MESSAGE is energy supplies, which speak of the dynamic conversation and use of the energy system procedures and their natural effects conceivable for a specific request for ultimate energy. The model is used for medium-improvement procedures, of 30 years even fixing. Instability related to innovative advancement means that time is limited. Elements of the energy system are shown by a multi-period approach. The mode is an improvement that sets the new current and conceivable advances and chooses the most remarkable point in choosing the rule mix of advances that will cover Africa’s application of various types of energy throughout the period of research. Similar situations that are used as part of MEAD are used here to calculate the supply of African energy.
Table 3. Computation of African energy supply.
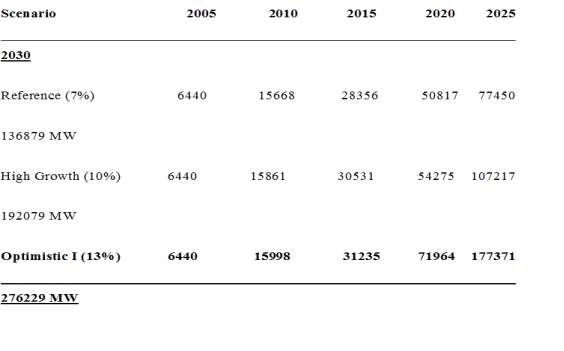
Figure 8 below illustrates electricity supply projections per scenario, MW.
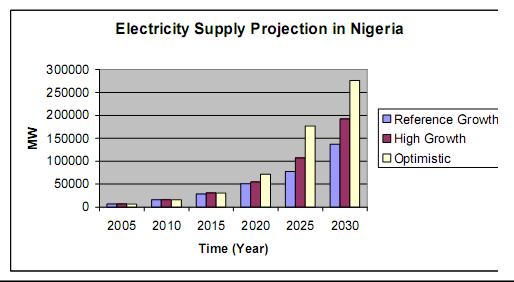
Figure 8. Electricity supply projections per scenario.
Potential of sustainable energy sources in Africa
Africa is enriched with abundant sources of sustainable energy, the most essential being sunlight, wind, biomass, small hydro and enormous hydroelectric power and also has the potential for hydrogen fuel, sea and geothermal energy. The motivation behind this research is to consider the possibilities of the four main sources of sustainable energy that are sunlight, wind, biomass and small and wide sources of hydraulic energy.
Energy of hydroelectric power Renewals in Africa
Africa’s hydroelectric potential is high and so far, accounts for about 29 percent of Africa’s total power control supply. The first and extensive hydroelectric power station in Africa is located in Kainji on the Niger road in the state of Niger, where it has an introduced limit of 836 MW and also has agreements for a further development up to 1,156 MW. The second largest hydroelectric station is in Jebba, Niger state, with an introduced limit of 540 MW. Shiroro in the state of Kaduna, Ikom in the state of Cross River and Makurdi in the state of Benue was expected to assess its aggregate capacity at around 4,650 MW. The indicator of currents of the Mambila plateau was put at 2.330MW. Below table 4, which gives the general sources of hydroelectric power it contains, the level of generation and use in Africa.
Table 4. Hydropower re-sources.
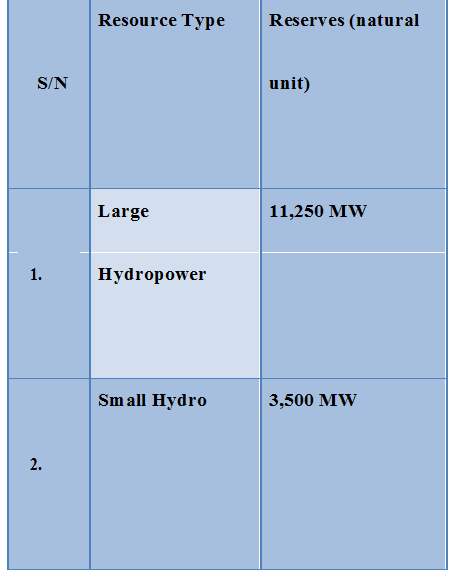
As can be seen in the table above, the general hydroelectric potential possibly exploitable in Africa stands at 14,750 MW. It should be noted that the slightly smaller hydroelectric power plants that provide electrical energy are in the range of 15 KW to 15 MW whereas those providing less than 15 are considered to be scarcely miniaturized. To ensure that both the small scale and the small hydroelectric frames have impressive favorable position, more substantial of the large hydroelectric frames, since they are not related to the issues of geography. The small hydroelectric framework can be established in most of Africa so that the potential energy that can occur in the extensive system of streams can be changed in the electric energy that will quickly improve and trace provincial enterprises of shaking.
Solar Dynamics Resources in Africa
Africa is enriched with an annual daily light that is average of 6.25 hours, which goes between about 3.5 hours in the beach front territories of the northern limit of the nations. In addition, it has an annual sun-day daylight radiation of around 3.5 KWm2 / day in the territory opposite the beach which is in the southern part and 7.0 KWm2 / day in the northern boundary. Africa also gets about 4909,212 kWh of sun energy which is identical to about 1,082 million tons of oil; This is about 4000 times the current generation of crude oil every day, and in addition put in about 13 thousand times day-to-day creation of flammable gas based on the unit of energy.
This enormous energy re-sources the sun’s potential is accessible for around 26 percent of the day. Africa also has an icy and dusty climate which is experienced in the middle of the harmattan, in the northern part, which more often than not happens for four months every year. Harmattan clean has a decrease in radiation energy from the sun based.
In light of the African terrestrial region of 924 km2 and a normal of 5,535 kWh / m2 /, the nation has a normal of 1831.06 kWh of solar energy episode annually. The annual insolation of the solar energy is estimated around 27 times the national conventional energy reaffirms in units of energy and in addition more than 117,000 times the measure of electrical energy that was created in 1998. About 3.7 percent only of the property region of the country should be used with a specific final goal to measure up to the country’s conventional energy reserve. The generation abundance of 240 kWh of solar PV or 0.01 million MWh / day and the level of use is situated in the overabundance of 0.01 million MWh / day of solar PV.
Wind dynamics Resources in Africa
Africa, internationally, is situated within the low zone of the direct energy of the wind. An exploration of the energy of the wind for several African urban areas was carried out, which shows that the annual wind speed varies between 3.89 m / s for Sokoto in the far north and 2.32 m / s for Port Harcourt in the south. The most notable removable control per control unit for similar premises is found at about 4.51 and 21.97 watts per square meter of leading edge area, individually and the highest estimated energy achievable is a 25m wide wind turbine Which has a proficiency of 30 percent to 25m tallness At about 97 MWh each year in Sokoto, which is located in high wind speeds in Africa, Kano has 50 MWh each year, 25.7 MWh each year for Lagos and 24, 5 MWh each year to Port Hacourt.
Biomass energy Re-sources in Africa
Sources of biomass energy in Africa can be distinguished as wood biomass, accumulations and residues, scavenge grasses and shrubs as well as oceanic biomass. Wood, besides being a notable source of energy in the type of firewood, is also used for commercial purposes in various structures such as lumber, plywood, electric poles and paper articles. For energy purposes, the area is using 80 million cubic meters of wood consistently for cooking and other residential purposes. The energy content that is being used of firewood is 6.0x109MJ which barely between 5-12 percent is the part that is used to benefit cooking and residential purposes.
Biomass sources in Africa have been evaluated at about 816 M.J. The biomass plant can be used as fuel for small-scale organizations and businesses. It could also be matured by microscopic anaerobic organisms to create a flexible and shabby biogas, ie, combustible gas. Assessment of biogas in Africa, recognized raw material substrate that has been considered as an economically attainable biogas program incorporating compost, water lettuce, water hyacinth, cassava license, strong residues, urban cannot, agricultural and wild deposits. Table 5 below presents the current level of biomass savings, generation and use in Africa.
Table 5. Biomass re-sources in Africa.
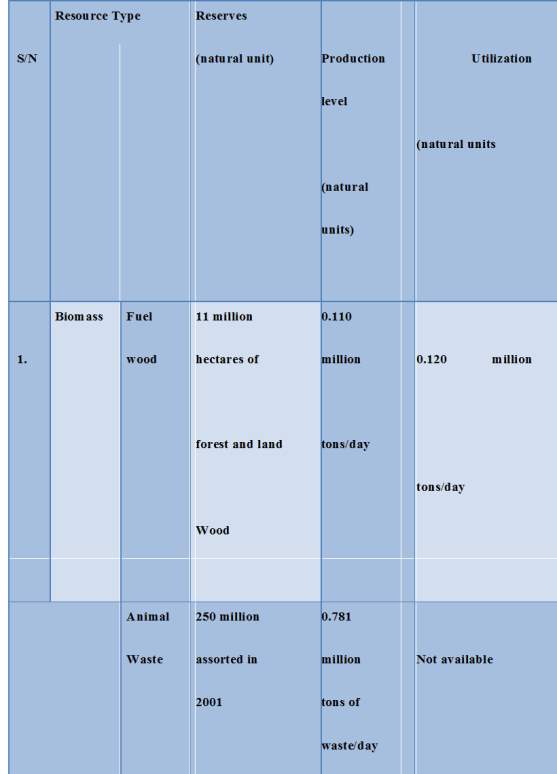
Africa distributes around 227,500 tons of new waste of creatures day by day and 1 kilogram (kg) of raw wasted creature to create gases of 0.03 m3, then the region can deliver about 6.8 million m3 of biogas day to day. With the expansion of urbanization and industrialization, the generation of biogas will help to reduce or in spite of the dispensation of irritation and the threat of urban waste in many urban areas of the nation by reusing them.
CHAPTER 4: METHODOLOGY
This section discusses the methodological decisions made by the scientist. In particular, research procedure dialogue, inquire about strategies, information accumulation strategy, research system, population organizations in general and case organizations.
Research strategy
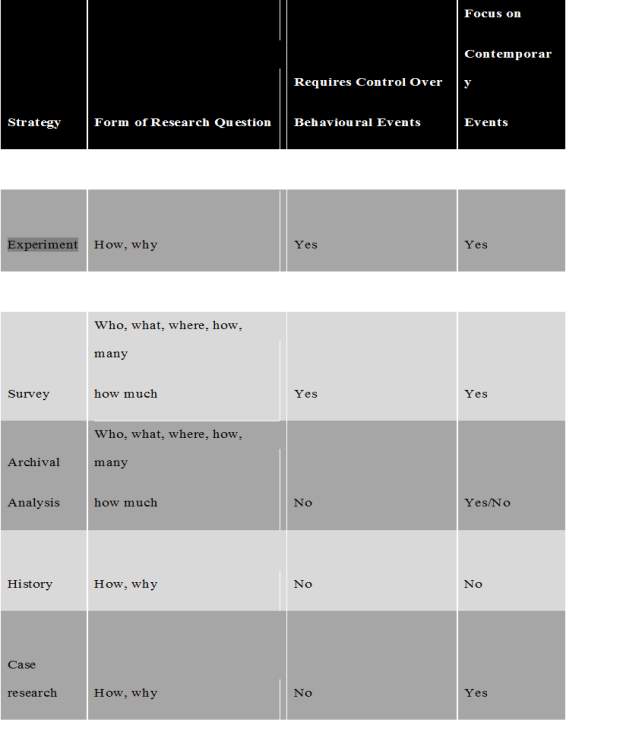
The examination technique is characterized as a general arrangement, clarifying how the specialist expects to discover answers to the examination questions. According to Yin the accompanying primary research methodologies are; Studies, exams, histories, documented research and contextual analysis. Notwithstanding all this, the creator specified that the decision of an examination procedure is controlled by some criteria of determination; The type of direction of the exploration, the level of control that the scientist has on the actual occasions of conduct and the level of concentration and consideration that are set on contemporary occasions versus the chronicles. Table 7 shows the connection between the three methodologies and the condition by Yin.
Table 7. Relevant situation for different research strategies.
Research Methods
Here the subjective and quantitative research techniques are presented and analyzed. The technique of subjective and quantitative research varies in the way they are addressed. The most ideal approach to conduct an exploration is to consolidate examination strategies in order to complement each other in light of the fact that one strategy cannot be specified as superior to the next.
Qualitative research method
The subjective research technique is generally a method to apply in sociology and advertising research, but has now been adequate in a wide range of scholastic controls. The goal of subjective scientists is to accumulate a top-down learning and understanding of human behavior and the reasons that represent such behavior. The strategy of examining what, where, when, as well as why and how of basic leadership.
The distinctions of the subjective research strategy and the technique of quantitative research are obstructing the investigation, detail and examination of the discoveries. The consequences of subjective research are not numerically detailed as in quantitative research. The objective of the subjective research technique is not to test models and some other theory of fact, but it depends on more sources. The evaluation and characterization of the results should be according to the examination and the case. In research, subjective investigations are vital here are some rules on the most competent method to delineate a subjective inquiry questions:
- The main vital is the meaning of the direction of exploration.
- Making the direction of the test clear for all is also imperative.
- It is also critical to say a ton in respect to almost nothing, rather than saying little in regard to a considerable measure.
In the course of the transmission of the scan sometimes the examination organizes the changes as some new thoughts of discoveries can happen and in this way change the exploration organize. Subjective research is more adaptive contrasted and quantitative research strategy. Moreover, as a rule, quantitative research is more affordable than the subjective research technique. The measurement of the data obtained from each respondent is considerable due to the scarce estimation of the specimen and, in addition, requires that the analyst has extraordinary abilities to meet the objective of leading a fruitful meeting. The type of research in the subjective strategy is exploratory and the research is subjective and interpretive. The strategy for collecting information in subjective research strategies is in two ways: meetings and perception.
In spite of this, official reports, articles, and tables that are referred to as optional information may also be brought together to reinforce essential information gathered in notable cases. The subjective research technique, as specified above, is used for the most part as part of social and behavioral science, making it appropriate for the investigation of people, meetings and associations. The issue related to subjective information is a pair of perceptions and, in addition, another question concerns the accumulation of information and the examination, since it often ends frequently in the meantime, which gives some concerns about the legitimacy and unshakable quality of an investigation.
Method of quantitative research
The quantitative research strategy is said to be the deliberate observational discoveries of quantitative properties, wonders, and their connections. The goal is to create and use scientific models, speculations and theories that influence wonders. The estimation procedure is indispensable for the technique of quantitative research, since it gives the essential association between the exact perception and the scientific articulation of the connections.
The quantitative research strategy is more objective, although subjective research is more subjective. The information collected is more objective and the subject of the examination is accurately characterized and the collected materials are measured numerically. The objective of the quantitative research strategy is not to obtain more information and understanding of the wonders as it is in the subjective research technique. The outcome and conclusion in the quantitative research strategy depend on the measurable examination.
In conclusion, the information must be reliable and substantial and also coordinate the motivation behind the research. Essentially, the methods for collecting information in the quantitative research strategy are usually found in secondary sources of information and from time to time self-accumulating. The side effect of the quantitative research strategy is the number and, in addition, the result is shown in tables, graphs and rates and different types of measures examination with the help of the Statistical Program of Social Sciences Programming. Here are the most widely recognized courses used for social occasion materials for the quantitative research strategy:
- Interviews
- Surveys
- Observation
- Experimental cases
The regular technique used as part of the social occasion information is organized survey. The survey is composed in such a way that it will make it easier for respondents to answer questions. Survey surveys are planned in a pre-established manner that makes the procedure coordinate and in addition, investigations more often than not have elective answers that the respondent can without much of a stretch control. One of the benefits of using an organized survey around is that it is anything but difficult to monitor and the information gathered is reliable as a rule, and it is also easy to investigate and decipher the information.
The measurement of the data obtained from each respondent differs due to the expansion of the estimation example and, in addition, it requires that the analyst has little capacity of meeting in opposition to the technique of subjective investigation. The type of research in quantitative technique is enlightening or causal and the examination is measurable and adds up. Several types of overview strategies are close to home-based meetings, telephone interviews, video chat, and mail-in interviews, depending on the topic of exploration. The decision of the review strategy is influenced by the schedules, the spending plan, the mental states of the respondents and the data required for an investigation.
Exploratory research in the generally used quantitative research strategies are; Who, what, when, where and how much. The drawback of the quantitative research strategy is that the subject’s deeper learning and understanding cannot be obtained using structure surveys. In addition, another question of the use of the survey is the delicate or individual questions about the salary or religion of the respondents. On some occasions, the respondent cannot uncover any question reasonable answers in the organized surveys. The specialist assumes an alternative part in the quantitative research technique contrasted with the subjective research strategy since he carefully considers the structure of the general view and also examines the consequences of the review.
CHAPTER: 6 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS OF THE THESIS
The information was collected using the research strategy both subjective and quantitative. The combination of the two research strategies is known prominently as triangulation, implying that an issue of exposure can be driven and considered using an assortment of methodologies. It is argued that the consolidation of the two research techniques is the most ideal on the basis that it is exceptional to obtain the best result of the exploration.
A survey was carried out with 11 consultations (see addendum 1) and sent to Africa by email and three contact persons were used in March 2010. A pilot test was carried out, 5 surveys were sent to check if the surveys met with the aim of research.
Table 9. Percentage rate of answers.
| Questionnaire | Numbers |
| Sent | 160 |
| Received | 84 |
| Percentage | 52,5 |
160 surveys were sent to the target population by e-mail and were presented to three contact persons who helped the scientist distribute the surveys to the respondents. Contact persons have an understanding of the research work. The main individual is Senior Bookkeeper with State House, Abuja. The second individual is an Oil Station Manager at one of the Mega Stations of the African National Petroleum Corporation in Sokoto State. The last guy is a job with Finbank in Abuja. In addition, the update messages were sent after two weeks of the primary email. We obtained 84 responses from the 160 surveys, which set the reaction rate at 52.5 percent.
The survey was received from previous examinations that were conducted by the European school in Gladenbach whose aim is to investigate the mentality of individuals from different nations towards sustainable dynamic sources. It is all planned and organized in a way that is simple for those surveyed. When looking at the full survey tables, it appears that surveys were certainly known by respondents. In order to foster a powerful measurable investigation of appropriate responses, questions and answers were transported to the Statistical Social Sciences Program. SPSS is a program that allows imported information to be dissected and inspected through various tables and graphs.
7 inquiries were produced and used for telephone meetings and email interviews. E-mail queries were sent to 4 people out of 7 who were the target population and the rest of the 3 people were served by telephone.
Results of research
The survey was transmitted to 160 Africans. 84 respondents rounded the survey and sent it back, giving a reaction rate of 52.5 per cent. The strategy used was the accommodation examination technique, since the objective of the research is to investigate, as opposed to predicting the variables that influence the use and development of sustainable sources of energy in Africa. The accommodation examination technique implies that respondents have been chosen on the basis of their accessibility. The use of the comfort examination strategy to direct an investigation can provoke a high reaction rate that occurred in this research. A dominant part of the 84 respondents were among those aged 19-25.
The two initial investigations in the survey were objective in collecting some data from the foundation. The main question was about the age of respondents, and the second questioned whether respondents know much about different sources of sustainable energy. A bar graph of each of the investigations is done with the rates exposed and clarified. In addition, some observations that have occurred of the results are included, the whole survey is broken down.
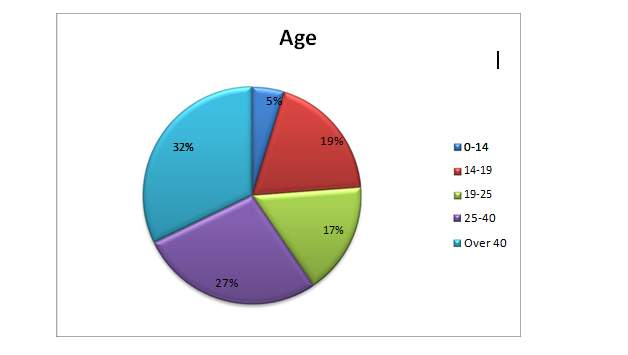
Figure 9. Age of the respondents.
Figure 9 shows the age of respondents who help us to see how respondents’ attitudes and information differ with age. The most astonishing number of respondents is between the age of 19-25 years, which adds 27 percent of the 84 respondents. Taken afterwards by knees of the age of 25-40, the minimum number of responders is 0-14 which filled 4 of the targeted surveys and constitutes just 4.76 percent of the aggregate responders. The age of the respondents shows that more young people in the nation are giving careful consideration to issues that are related to the use of sustainable energy in the nation, because of global efforts worldwide to advance the use of sustainable energy for Supplant the regulars, and meanwhile more consideration is paying the creators.
The second research question “would be able to list three sources of sustainable energy” helps us to understand that the respondent’s mental states depend on learning rather than on preference. 58 responded “yes” to 69.05 percent, this shows that respondents ‘moods depend on information not preference when primary questions are related to second consultations that complements the respondents’ provisions based on their Vision and age. This shows the attention to the different sources of alternative energy that is developing when looking at the side effects of this research with previous exams. Moreover, more work needs to be done to advise the general population on sustainable energy and its various sources if one considers the number of respondents who cannot list 3 sources of sustainable energy at 30, 95 percent, adding up to number 26. A greater part of the respondents can have fundamental competence since the vast majority of them live in urban territories.
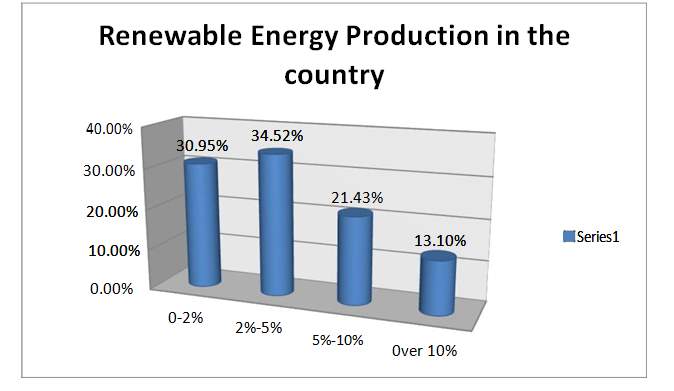
Figure 10. Opinions of sustainable electricity production percentage.
Respondents could explore distinctive options for the rate of power that is delivered by sustainable energy resources in Africa. There is a ton of assortment in the appropriate answers regarding this question. The majority of respondents, that is, 34.52 percent addressed that 2 to 5 percent is the rate and a portion of those surveyed imagine that it is between 0-2 percent, and the 21.43 percent found Between 5-10 percent, were as a part of respondents believed to be more than 10 percent. Why the appropriate responses are so unique in relation to respondents and there is a wide gap and a clear lion share between rates is on the basis that most of them are confident that given that Africa is a country that Has an inexhaustible conventional energy. And lately the administration continues to contribute in sectors of conventional energy aimed at enhancing the situation of strenuous power in the nation.
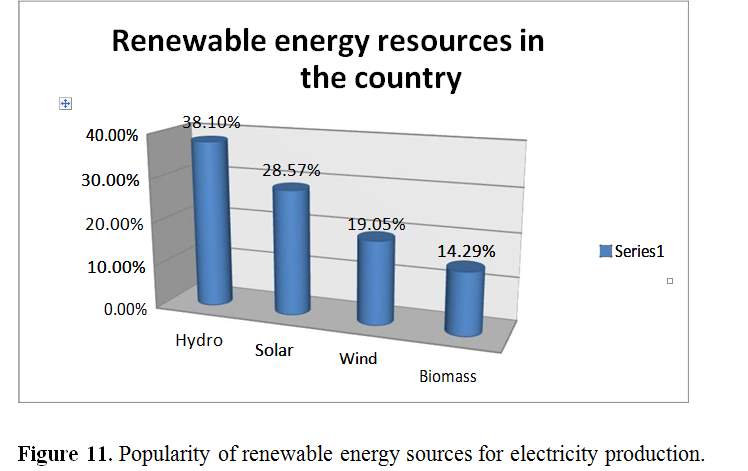
The figure shows the four sources of sustainable energy in Africa and the prevalence of them in respondents. This question helps us understand if respondents could know the most common source of sustainable energy in Africa and also recognize the sources. The majority of the respondents, that is to say, 38.10 percent chose the hydroelectric as the best known among the four; 28.57 percent directed the sun-driven sun in the nation; 19.05 percent chose the most recognized source and 14.29 percent chose biomass as their answer. Hydro is the most widely recognized source of sustainable energy in Africa, which is the majority of the good alternatives of each respondent.
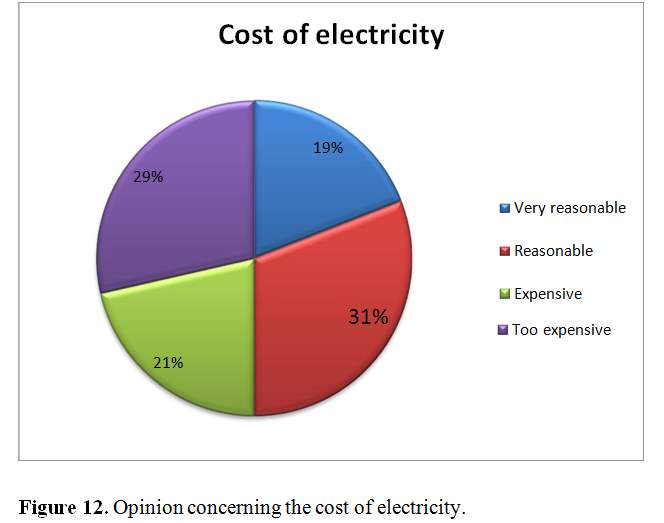
This question refers to the need to recognize how respondents rate the cost of the current electric load, which will help to understand if the population will have the capacity to recognize any expansion of the electric load in others to advance the use of sustainable sources of electric energy in the nation. 30.95 percent of the respondents believe that the current energy load framework in Africa is sensitive in contrast to other countries in sub-Saharan Africa. 28.57 percent was directed that it is excessively costly in connection, making impossible the despicable state of the power supply that is flimsy, 21.43 percent of respondents tackled costly and 19.05 percent of the respondents addressed that cost Of power is very sensible. Africa is one of the nations in the world in which the administration pays the appropriation in all sectors of the energy of the nation. In this way, the energy and tariff costs framework is a critical element in the advancement and use of sustainable sources of energy in Africa.
” Do you pay for your power? “This question was incorporated as a reflection on the conduct of respondents towards the use and use of people in general public services. Most respondents answered “Yes” “which represents 60.71 percent who pay their electricity bills and 39.29 percent answered” No “. The rate of respondents who do not pay their bills is very high when you consider the cost of energy from the age to appropriation. Respondents who are not paying for their energy bills may not have a stable power supply. Competition and security appear to be central to Africans before a larger part of the population pays their electricity bills.
In this question, it was vital to know whether respondents will pay any additions that may arise in others to promote sustainable sources of power in the nation. A dominant part of the respondents, 41.67 percent, considered that 2-5 percent of additions is very reasonable, which is reasonable for a large part of the respondents, 29.76 percent argue that nothing should expand, while That 27.38 percent 10 percent is impressive and 1.19 percent directed that more than 10 percent increase. The biggest thing here is that a majority of respondents agreed that and the increase should be made however that which will be reasonable for the African population, with respect to the country’s current financial substances.
This is an open question that asked the need for recognition if the interviewee knows much about the effectiveness of the use of sources of sustainable energy. 41.67 percent of the respondents said that it will improve the conditions of power of the nation “marginally”, followed by a 28.57 percent who believes that the miserable energy situation in Africa will increase “and a lot” 25.00 percent 4.76 percent of the respondents are very enthusiastic about the expansion in the use of sustainable sources of energy because they are confident that it will enormously build the circumstances of power in Africa. It seems that the vast majority of respondents realize that the expansion in the use of the sustainable energy of electricity in the nation will improve the power situation in the nation, which will clear the way to achieve the efficiency of energy within the majority Limited time.
This question helps us understand the willingness and willingness of respondents to recognize the use of sustainable energy by specifically underestimating them, not by actually sitting tight for the legislative or open framework. Respondents have different options 57.14 percent, which are the lion’s share answered ” Yes ”, 22.62 percent are undecided, while 20.24 percent are not buying home that have sustainable energy facilities. It is an intriguing revelation to realize that most respondents are likely to buy the house that have sustainable energy facilities, this will help organizations that provide sustainable sources of energy in speculation options. ” Is it fair to say that you are attentive to any accessible prize to help you install sustainable energy or efficient dynamic technologies? On the off chance, please give points of interest. “This question includes whether the respondent knows that any administration gives or reinforces that it will urge the general population to introduce different dynamic alternative sources.” 100 percent of the respondents replied ” No. “This is a fascinating revelation to realize that the administration did not give any support to the family to introduce alternative sources of energy.
This is an open question included for recognition of the need if respondents know much about the ecological effect of sustainable energy resources. Most respondents responded ” Very ”, it will improve the land. 32.14 percent imagine that it will improve the states of the earth. “A considerable amount,” 27.38 percent said they would marginally improve the land, and 7.14 percent believed it had no constructive results for Earth. It seems to be very fascinating to realize that a lion’s share of respondents are aware of the land that discovers that there is a brighter future to improve the use of environmentally friendly sources of energy in the not so distant future in the nation.
CHAPTER: 7 CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
The objective of this proposal is to discover how to strengthen, boost and promote the development of sustainable sources of energy in Africa to close the gap of almost 60-70 percent of Africans who do not have access to energy, not just energy, but rather to the energy that is well-disposed land that will also help the nation to achieve energy efficiency that will strengthen its financial improvement. Both the subjective and quantitative research strategies had been investigated. A solid conclusion can be achieved through the union of these two research techniques.
Conclusion
Africa is a nation that is honored with generous regular and unconventional sources of energy (fossil fillings and sustainable sources of energy). There is a need to foster the evolution of a mix of energy that places greater emphasis on the need to preserve non-sustainable sources of energy in such a way as to boost its export performance that will continue to generate revenue for the legislature for many years. Was to be expected under the circumstances. The appropriation of sustainable solutions of energy by the nation with accentuation for the provincial advance will drive the internal decrease in the use of petroleum-based products and gas.
Significant preferences for non-conventional energy solutions (sustainable energy solutions) incorporate simplicity of support, ease of innovation and also their natural disposition over conventional energy systems (petroleum products).
In the course of this research, the specialist discovers that the interest for power in Africa is high; Be that as it may, the supply is not sufficient and constant to meet the demand that left many African residents with no alternatives that use frames of exclusive power creation of conventional energy. The use of traditional energy creation frameworks is costly and, moreover, not environmentally friendly.
The potential of sustainable energy resources in Africa lies in an overabundance of 1.5 times that of fossil energy in terms of energy. Sunlight, wind, hydroelectricity and biomass have enormous potential for enhancing and having any effect on the low level of access to electricity in Africa, with an emphasis on provincial chains, through the reception and use of These resources of sustainable energy. Manageable improvement.
Suggestions
In the light of the implications of the review, the attached recommendations were made. It is evident that the use of sustainable solutions of energy in the nation at the present time is evident. In any case, there is a requirement for the advancement and use of sources of sustainable energy, especially in provincial improvement. In the perspective of this there is an extreme need for the monstrous support of the legislature and private division for innovative new approaches to work, and in addition the requirement for a foundation of energy expansion teams. The current innovative work approach needs to be strengthened and updated bearing in mind the ultimate goal of completing the quality of innovative work drills while the dynamic outreach focuses must be accused of broadcast duties and display exercises of the system Sustainable energy.
Due to the hesitation of neighborhood creators and business visionaries to receive large-scale manufacturing and marketing of sustainable energy systems it is necessary to put more effort into the preparation of specialists in the development, planning, operation and Maintenance of various Dynamic technologies in-use gadgets. In view of this, after such preparation programs there is a requirement for the creation of sustainable energy which will be filled as instruments for the settlement of the forces of budgeting to suppliers, neighborhood producers and end customers of sustainable energy Electricity putting more accentuation to the ranks of the country. On the other hand, it is necessary for the arrangement of good financial motivations that will help the nearby producers and suppliers of the sustainable electricity advance segments
There is a need to outline a complete national energy Master-organize to advance the policy of energy for the ability to support, and in addition gigantic battle of edification to the people in general on the effectiveness and ecological disposition of sources of electricity of energy sustainable.
Most of the aforementioned proposals, measures and implementation procedures, which are objectives to advance the development and use of systems and practices of sustainable energy, must be achieved and recognized through the reinforcement of establishments that are responsible for promoting energy sustainable. In this way, the Federal Government must support and fulfill a national policy of in-depth energy for the nation and also distinguish the associations in the states and the levels of neighborhood government that are mandated to guarantee the execution of companies and projects of sustainable energy the electricity.
Summary
The objective of this postulation is to discover how to strengthen, advance and strengthen the development of sustainable sources of energy in Africa to close the gap of approximately 60-70 percent of Africans who do not have entrance to the energy not only the energy, but rather The Energy that is benevolent land that will also help the nation to achieve energy efficiency that will strengthen its financial improvement. More importantly, this research tells us about sustainable energy, in particular the sun, wind, hydroelectricity and biomass. The crisis of energy facing Africa despite its immense amount of traditional and unconventional sources of energy.
The research identifies the different components that influence the development of sustainable electricity in Africa both from the point of view of organizations and from the client side and the different advances that must be made by the administration and the foundations that are in charge of advancing the development and use of sustainable electricity in Africa. It also makes us understand the productivity of the technologies of sustainable energy and its natural disposition and also the financial importance and the progress it transmits to a country.
In the exact section, two quantitative and subjective research strategies were used as part of the request to better understand the situations of sustainable energy in Africa in relation to the monetary and social elements that influence the use and development of sustainable sources of energy in Africa And, in addition, the specialized organizations that are faced in the construction of a source of option of energy in Africa to obtain more reliable results. The strategies used were structured questionnaire and meetings. By joining the organized survey and the meetings one could say that new and profitable data on the issues of sustainable energy in Africa were obtained. The legitimacy and unshakable quality of this research is high due to the mixture of these two research techniques and gives an incentive to this research.
References
Bocarnea, M, Reynolds, R, & Baker, J 2013, Online instruments, data collection, and electronic measurements, Hershey, Pa, IGI Global, USA.
Choppin, B 2014, ‘Interpreting Research: Sampling’, Educational Research, Vol.16, No.3, pp.218-221.
Farret, F.A 2006, Integration of Alternative Sources of Energy , Hoboke, John Wiley & Sons.
Fthenakis, V & Kim, H 2009, ‘Land use and electricity generation: A life-cycle analysis’renewableand Sustainable energy Reviews, Vol.13, No.6, pp1465.
Hazen, M. E 2013, Alternative energy : An introduction to alternative &renewable energy sources, Indianapolis, IN, Prompt Publications.
Johansson, T.B, & Burnham, L 2013,renewable energy : Sources for fuels and electricity. Washington, DC, Island Press.
Kruger, P, 2006, Alternative energy resources: The quest for sustainable energy , Hoboken (NJ: J. Wiley.
Maczulak, A. E 2010,renewable energy : Sources and methods, New York, Facts on File.
Tiwari, G. N & Mishra, R. K 2012, Advancedrenewable energy sources, Cambridge, RSC Publishing.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Sustainability"
Sustainability generally relates to humanity living in a way that is not damaging to the environment, ensuring harmony between civilisation and the Earth's biosphere.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




