The Impact of Technological Advancement on Risk Management
Info: 10492 words (42 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
Tagged: TechnologyRisk Management
Abstract
In the last three decades, incorporation of information technology in our lives has made technological advancements indispensable in solving problems in social ventures. Every organization uses information technology in one way or another to make important decisions in its field of expertise. Risk management is a critical tool that plays a role in ensuring that the information assets of an organization are kept safe and free from exploitation. Using technology to assess risks that an organization may face from time to time and put preventive measures to prevent them is a critical role that management personnel must adopt. Managing risks in an organization demands that the most popular channels of exchange of information are made safer and reliable. Risk management is paramount in any organization because it helps them address the unknowns and position themselves to mitigate them. As a risk manager, the researcher was interested in applying the best methods in risk assessment that can be used efficiently to interpret data while being easy to understand. The aims and objectives of this assignment were to show that technology has claimed its place in society and risk management assessors need to incorporate it when doing their risk analysis. This paper was successful in establishing the impacts of technological advancement on risk management in many organizations. It established the level of impacts at several key fields in risk management. Additionally, it came up with ideal measures to deal with risk as it arises within any organization. The researcher recommends that there be more studies on the particular management practices of risk and how they control specific impacts of technology change within the departments of risk management in an organization.
Table of Contents
Challenges of Technology on Risk management
Moral and Ethical Consideration
Characteristics of the design and approach
Weaknesses of the design and approach
Introduction
Background
In the last three decades, incorporation of information technology in our lives has made technological advancements indispensable in solving problems in social ventures. Every organization uses information technology in one way or another to make important decisions in its field of expertise. Communication has shifted from using the letters and faxes to using emails and social media platforms to exchange ideas and directives within an organization. In such interactions, there may be obstacles that companies may face that may pose a risk to the entire business. Risk management is a critical tool that plays a role in ensuring that the information assets of an organization are kept safe and free from exploitation (Hellström, 2003). Using technology to assess risks that an organization may face from time to time and put preventive measures to prevent them is a critical role that management personnel must adopt. Managing risks in an organization demands that the most popular channels of exchange of information are made safer and reliable.
In numerous organizations today, innovation is viewed as the most key capital venture and data, imperative for the accomplishment of an element. It may be in data framework or data innovation foundation. Risk administration, particularly in-store administration, is vital procedures that limit the risk presentation to venture to help the profits. Any element that adjusts the risk synthesis of the venture condition will thusly influence the normal returns. The sole business of store chiefs is to boost returns for their customers. Consequently, need to comprehend if the constant change in innovation has any impact on risk administration (Williams, 2015).
Today different business groups are adjusting innovation to lead a business. Innovation is progressing at a high rate, which is influencing both decidedly and contrarily in different areas of the economy. The impact of mechanical improvements as of late tremendously affects how we lead a business. These improvements have changed how the speculators assemble data about their ventures, how support administrators spread their report and other money related exchanges (Williams, 2015). Advancement of new items and the idea of money related building have been presented. By and large, positive enhancements have been experienced. Be that as it may, then again risk has steadily expanded. To have the capacity to keep up the venture returns, risk administration needs to cook for these progressions viably. On the supply side, we have seen extraordinary development in new markets for the exchange and sharing of these risks. Innovation propels in the data handling and media communications have empowered money related administration firms to give productive fences and certifications to deal with these risks.
Resource administrators follow up on a trustee limit of the benefit proprietors, contributing the customer’s advantages inside particular venture rules of a given command. Resources contributed are held by outsiders alluded to as the overseer henceforth lives inside the earth of various players. Information is transmitted among gatherings, handled by resource supervisors and conveyed back to outsiders. This information move ought to be consistent, convenient and effective to separate customers. Risk administration includes all periods of speculation process and input between resource estimation and distribution. Risk administration can be characterized as the anticipating and assessment of monetary risks together with the recognizable proof of systems to keep away from or limit their effect. Risk administration is a practice that has been set up since time immemorial (Lytras, 2012). As innovation enhances the reserve chiefs are progressively embracing different procedures to improve rivalry and gainfulness. The inalienable risks and different data and innovation capacities can be overseen successfully to yield the ideal execution for the different reserve directors in the nation.
Individuals’ cooperation with innovation while outside work is a region not frequently considered on risk registers. For instance, the risk of staff sharing individual and possibly touchy organization data by means of person to person communication locales, for example, Facebook. This may incorporate data which can be utilized to trade off security on clients’ corporate system accounts (for instance, date of birth, life partner name, house number, and families’ dates of birth (Williams, 2015). What is being done to oversee security breaks which begin outside the working environment?
Colossal volumes of information extending from client buying propensities, to exchange following logs have been working up inside corporate frameworks for a considerable length of time, however throughout the following decade we will see a blast both the capacity and the open doors for undertakings to endeavour this information. What has already been a differentiator will turn into an essential for survival. Information quality may progress toward becoming as essential as item quality in figuring out which of today’s endeavours are still here in 2020 (D’Addario, 2013). Is the inability to sufficient misuse business information being dealt with genuinely enough as a risk?
The counterpoint of risk is the opportunity and IT capacities which can viably deal with their risks will empower their organizations to profoundly outflank those organizations which are put off by or just not up to the test. Organizations where IT feels engaged to impact business basic leadership by showing how business enablement can be driven by successful administration of innovation risks, will flourish enormously to the detriment of those organizations where obliviousness or dread of new or changing innovation risk zones either keeps them from moving into new territories, or results in disappointments when they endeavour to. This is the ideal opportunity for IT pioneers to venture up and put themselves and their capacity at the focal point of driving their business forward (Williams, 2015).
Justification
Risk management is paramount in any organization because it helps them address the unknowns and position themselves to mitigate them. As a risk manager, the researcher was interested in applying the best methods in risk assessment that can be used efficiently to interpret data while being easy to understand. The researcher’s organization of risk assessors would benefit if it turns out that technology would help to make the process simpler and lesser capital intensive.
The ultimate goal of any risk assessor is helped to put a strategy in place that ensures there is total avoidance or risk (Adler, Leonard, & Nordgren, 1999). Systems, however, are not always ideal, and the assessors have to settle for the other options at one time or another. The risk assessor has to understand the four strategies so that when risk is determined, the intervention mechanism is geared towards taking the right approach.
Risk management in organizations is very broad and its applications as diverse. Some risks arise from wrong systems while others are unavoidable. In assessing risk analysis, it is important to delimit the realms of the risk assessment to ensure that any intervention mechanisms derived from the evaluation report are specific to the sector that it is based on.
Towards this end, the researcher proposed to have a paper on a risk assessment that is specific to one industry so that the findings do not encompass solutions that are too general for practical applicability. The topic of risk assessment meets the criteria for me, and the researcher would gravitate towards the impact of technological advancement on risk management in the automotive industry as the researcher’s preferred sector.
Aims and objectives
The aims and objectives of this assignment was to show that technology has claimed its place in society and risk management assessors need to incorporate it when doing their risk analysis. Technology is important in making things easier to understand and helping in the end. Technology however also comes with added risks that are supposed to be assessed concurrently. While various technological aids are essential in creating efficiency, they usher in their risks as well (Hancock, 2012). An assessment of the risks would involve the determination of both the efficiency brought about by the new systems as well as the added risks involved by incorporating them. Its impact on risk assessment in any organization and the role it plays to make the process easier is the focus of this paper.
Research Questions
The paper seeks to answer the questions of;
- What has changed in technologically laden risk assessment approach?
- Does including technology in risk assessment make it more efficient?
Literature Review
The present day business world walks to the beat of innovation’s drum and has done as such for a long time. As the web and email developed in the 1990s, organizations started to adjust and take up the innovation. With the coming of fast broadband in the 2000s, organizations again additionally grasped the prospering tech, taking it to the heart of their operations. This has proceeded into the present decade where cell phones and tablet PCs are universal, and Big Data assumes a critical part in the everyday operations of many firms. Besides, for money related foundations the happening to online card instalments, headways in portable innovation and contactless instalments have expanded their business offerings and their client reach (IBM, 2011).
IT outsourcing has likewise turned into an alluring suggestion for organizations and money related establishments. With less expensive and more abundant work accessible in many developing markets, and with the vital mechanical capacities, foundations have discovered fewer barricades to outsourcing large portions of their administrations globally (Khatta, 2008).
Obviously, innovation has changed the way we work together. It has globalized the economy and affected unavoidably on regular daily existence at home. Monetary establishments have come to depend on innovation to help bolster their business procedures and handle enormous measures of basic information. Given the significance of innovation and the effect that it has on corporates, it is fundamental that associations put innovation risk administration at the highest point of the corporate motivation. Notwithstanding the positive ramifications of grasping innovative progression, the choice to mix organizations and our working existence with innovation is not without its risks (D’Addario, 2013).
Safety net providers depend on actuarial examination to help settle on educated choices in evaluating, and risk and capital administration. They have settled procedures for setting up the investigation utilizing demonstrated strategies. Before, the impediments of PC innovation constrained statisticians to utilize improved or surmised procedures in making their computations and planning examination. Infrequently this is impeccably proper, as brilliant demonstrating systems can give a reasonable level of exactness for some data prerequisites (Williams, 2015). However, some of the time the organization requires the most exact examination conceivable. Luckily, late mechanical headways have realized a stage change in the investigation that backup plans can use in evaluating their items and in overseeing risk and capital. Presently the organization can get the data the organization require speedier, leaving more opportunity for keen thought to settle on better business choices.
In today’s worldwide market, one has to make savvy, sound, and snappy choices. Having the get to and perceivability into the required data accomplishes that goal. From a specialized point of view, setting up or knowing the organization’s condition is pivotal as it sets the scene on what assets are accessible to fulfil the target. Like risk administration, one would need to recognize and comprehend what the organization are really going after or against. Knowing the organizational condition and what is accessible highlights the limitations that the organization may experience and what is expected to address the organization’s risks (D’Addario, 2013).
The setup gets down to the particular. This is the place the organization tweaks a granular necessity and ties it together with the organization’s financial impacts. Separating it much further, one would need to design if there is exclusion to revealing. In specific cases, the exception could be a normal for an exchange, for example, an intercompany exchange or credit. In truth, however innovation could be designed to decide if an exchange meets all requirements for an exception and also arranged to deal with those that must be accounted for; without a congressman or congressperson attempting to make sense of the meaning of a subsidiary and postponing the procedure (Lytras, 2012).
According to IBM (2011), once the association comprehends what they are managing and what it needs or is required to do, the following stage is to catch and store the obliged data to cling to the necessities. Each association needs to deliver a yield in view of the info. Appears to be basic, be that as it may, if the information caught does not bode well and is not applicable, by what methods can the report or the numbers bode well? Regularly, the nature of the info is specifically subject to knowing the earth factors and the arrangement that influences what one is attempting to catch. It doesn’t make a difference if the information to be caught is CRM, subsidiary, or social insurance. In the event that the information components are mistaken, the entire framework will not be right; in this manner, the yield will be pointless (Williams, 2015).
Not all information should be prepared and can be a straight go through, however sooner or later the information will be utilized to create a report, a chart, a bookkeeping passage, or even a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) (IBM, 2011). The subsequent yield is significant to all C-Level officials inside and remotely. The perpetually changing business sector combined with financial unpredictability requires the innovation stages and frameworks to be prepared for the progressions while additionally keeping up dependability inside a corporate association.
Since the organization have the data post handling, what do the organization do with it? There are a large group of specialized issues, yet that is taken care of by the organization’s IT division. The researcher jumps at the chance to consider revealing and re-dispersion as a direct procedure. One has to get the information from indicating A point B without losing the trustworthiness. The briefest separation between two focuses is a straight line and innovation has assumed a vital part by shortening the time and pushes to spread the immense measures of data. In the over a wide span of time, this was dealt with by Information transports. Today, the data interstate has advanced with Web Services and XML (IBM, 2011).
Risk Management
Understanding the risk involved in any venture done by organizations is important since it allows both the risk assessor and the clients manage their systems in ways where all the vulnerabilities are addressed. The risk is managed through mitigation, transference, acceptance or avoidance.
Mitigation
The strategy aims to reduce the vulnerability of the systems being exploited by preparing and planning for them. Elimination of risks is almost impossible, but a firm assesses what could go wrong and put preventive measures to ensure it does not happen or if it does, has minimal risk (Page, Dixon, & Choudhury, 2007). Different circumstances may not prevent the probability of there being a power failure, but a risk assessor imagines that it may happen and advice on putting measures like standby generators so that if it happens, the systems are not adversely affected. It is the same concept employed in vehicles accidents where automakers devise the supplementary restraint system to minimize the risk of fatality if an accident happened.
Transference
It is not very practical in technologically based risks, but it is important in reducing the impact that any risk has on an organization by deflecting it (Levy & Scala, 2012). While accidents brought about by faulty or malfunctioning equipment in the medical field may result in injuries or fatalities, managing such risk is a complicated issue. Healthcare facilities may not replace a life that has been lost but strategies can be put in place to ensure that in the event of such an occurrence happens, their pieces of equipment are not lost but are insured so that the financial consequence is manageable.
Acceptance
Understanding that a risk exists may not look to be a good way of managing it, but by accepting that there are risks, the eventualities would be better managed. Risk assessor evaluates the possibility of a particular risk occurring and help in putting measures in place to ensure that the effects are better addressed. The supplementary restraint system incorporated in vehicles may not prevent accidents or injuries, but understanding that it may happen and posting air rescue systems when it happens increases the rate of survival by the injured. Such systems cannot be put on standby in a system that is fully committed to avoiding them. In the enterprise systems, the technological information systems are designed in a way that they can be put back in place to perform the most critical duties while other problems are addressed (Nilsen & Olsen, 2007). It results in systems conceived in a way that they share different servers for different tasks such that if one breaks down another lifeline can be activated.
Avoidance
Risks can be managed by avoiding them altogether so that any vulnerability is prevented from exploitation. If a particular technology has had cases of having adverse effects when used, organizations completely avoid it until such issues are solved even when it affects their efficiency (King, 2016). If a certain brand of equipment has shown tendencies of resulting to unwanted consequences, other than sticking to it and suffering them, an organization avoids it altogether. In information technology, if a certain operating system shows signs of instability, it is shunned by users until the time that the experts give it a clean bill of health. If an operating system is used in operating a critical system in an organization but in the course of assessment it is realized that it increases the probability of wrong outputs, other than putting up with it and suffering, an alternative is sought (Drobny, 2013).
Different systems have different vulnerabilities that would be exploited and result in a spread of risk. Flaws in the designs, procedures or implementation may lead to an enhanced risk that would impact organizations differently. In researching on the risk avoidance, management, and its impacts, it is important to look at both the microenvironments and the macro environments to determine what kinds of risks are unique to an individual system and which ones are more generalized. By understanding what can be specific about a certain problem, addressing it would be easier and more localized (Sawczuk, 1996). Some risks are brought about by wrong use of systems and risk assessors should be able to determine what is brought about by either flawed equipment or misuse.
Challenges of Technology on Risk management
There is a lot of literature on how technology has impacted the lives of people but the real impact on any adverse effects it may have had are not so profound. The researcher anticipated a situation where he/she had have to work on very little data and more on deducing the information by incorporating the what if rhetorical questions. Studies done on the subject of risk emanating from technology have been largely hypothetical, but the same approach was necessary in determining what may go wrong and put intervention measures in place.
Many types of equipment and the technologies in use have changed the lives of very many individuals, but there is hardly any statistical study on their rates of failures that negatively affect individuals in a variety of ways. Most of the studies done have tended to show the success rates and how they have become effective in transforming the lives of individuals. There is very little information available to the public on how they fared before they were perfected before they became an indispensable component in the medical fraternity. Advanced technology helps to ease the ways of doing things while increasing efficiency (Titarenko, 1997). The information is available on the fatalities that have arisen out of automobile accidents and can access such data at the click of a button. The same cannot be said of the deaths resulting from the medical imaging machines that are in all the main hospitals. While the efficiency of systems in automobiles are tested using crash dummies before the products are released as safe for public use, there is little data to show that the effectiveness of the medical equipment is tested to such standards before use.
In risk assessment, it is important to determine at what point a failure by an advanced medical intervention device owing to power failure, wrong input or common malfunction is blamed on the system. Without a comprehensive audit of such advanced processes, the discourse may be more hypothetical other than factual in determining the impact of technology on a variety of issues. The determination of risk relies on the parameters of impact and likelihood of some things happening so that the risk ratings are calculated to show the most likely figures (D’Addario, 2013).
Every healthcare institution has to make an informed decision on whether the risks brought about by using technologies that are risky are worth investing in and how to approach litigation issues if they come to light. Additionally, healthcare institutions are also faced with the additional responsibility of managing risks associated with their clients’ data. They are custodians of patient information that is very critical and sensitive if unauthorized persons accessed it. Risk assessors have to show them the impact that such breaches may have on their brand and how to manage the data entrusted to them safely. The impact of an institution mismanaging private health data and public availability of such data may be an enormous blow to it concerning being trusted with such information in the future. Risk assessors have to craft a way of avoiding such data breaches, mitigating any leaks and ensuring that institutions are better prepared for such an eventuality (Lytras, 2012).
Theoretical Framework
The study on the impact of technology on risk assessment has been done before. The researcher plans to interrogate the academic and practitioner writings concerning the incorporation of technology in risk assessment. An article written by Charles Dahlquist, Kirton and others are among the writings that the researcher will explore to form the basis of the researcher’s assessment on the subject. The researcher also intend to study the legal cases arising from the adoption of technology in the workplace or the information technology solutions to understand their impact on the lives and how any risks that they may have brought are taken care of. the researcher intend to assess whether technological advancements have brought a substantial change in the way people interact and whether there are risks associated with more technology in the workplace (Rabechini Junior & Monteiro de Carvalho, 2013). Any suits arising from technological advancements that malfunctioned and brought distress will be investigated to explore whether sufficient care was in place and form the basis of which a thorough assessment is possible.
The internet is the source of most of the information that will be used in the determination of the risks involved in different technologies and their effects in the society. Scouring the internet for suits related to technological use that adversely affected operations is a rich source of information that can tell the better picture on the impacts of technology on risks in the workplace. Another additional risk brought about by advancements in technology that has spread the risks profoundly is data management (Anantatmula & Fan, 2013). Studying on how data breaches have contributed to financial losses across the globe would be another source of information that shows technology advancements and how it has affected weighting risks. Such information is not readily availed to the public but a comprehensive audit on the profits and losses a company makes and comparing it with major data breaches will give a general perspective on the economic value of the loss.
Theories
There have been numerous theories and findings on the impacts of technology advancement in risk management. Many conclusions have been drown form the subsequent theories as researchers tried to test them. This paper will look at three main theories on the impacts of technology advancement in risk management. The theories include situational theory, modern portfolio theory and the diffusion of innovation theory (D’Addario, 2013).
The situational hypothesis was broadly used to clarify measurements to recognize an issue, level of contribution, and imperative acknowledgement (Lytras, 2012). Advanced examination of the situational hypothesis has distinguished three autonomous factors that clarify the outer and inside measurements could be adjusted through correspondence. Publics can be grouped into the individuals who know about the issue and what they do about the issue. Correspondence is recognized as methods for making mindfulness and adequately tending to such difficulties. To elucidate encourage on the situational hypothesis is the development of the possibility hypothesis that expresses an ideal approach to arrange will rely on upon the way of nature in which a substance must relate. Development on the hypothesis distinguished variables that could modify condition instability of a substance could impact execution of an association. The primary regions recognized incorporate innovation, government, clients and contenders (Lytras, 2012).
The diffusion of innovation theory clarifies how a thought can be conveyed after some time and spreads through the populace or social framework (Rogers, 1995). Diffusion can be depicted as the procedure which development spreads and is acknowledged in the general public. Many variables connect to impact the spread or dissemination of innovation. It includes imparting the thought, the time it takes to spread and the way of the general public in which it’s presented. It goes more remote to clarify and research how the different components associate, encourage the new development and the impacts of the creation. This teaches a culture in individuals and embraces the thought or item after some time. Throughout the years, dispersion hypothesis has been utilized broadly both in innovation and financial aspects. More hypotheses have been inferred out of dispersion to clarify spread of different advancements in the general public (Rogers, 1995).
In Information innovation, the utilization of engineer based hypothesis and adopter based hypothesis. Authors clarify the appropriation utilizing the rate of reception hypothesis that characterizes how developments diffuse to frame an example that is S moulded bend. It distinguishes how the thought takes after a way from beginning at a moderate slow development before detonating into fast development. Diffusion hypothesis is additionally bolstered by the hypothesis of saw characteristics that clarifies the capability of advancement adopter’s judge in light of five properties of innovation. They include relatively preferred standpoint, similarity, recognisability, many-sided quality and ultimately triability (Surry, 1997). Surry bolsters this recognition which assumes a noteworthy part in the reception of innovations in the general public
The modern portfolio hypothesis discloses how to augment returns for a given level of portfolio risk or then again to limit risk for a given level of return. It elucidates the significance of immaculate resource choice concerning the risk introduction of a financial specialist. The hypothesis contends that for resources with comparable risk yet unique returns a financial specialist will choose a benefit with less risk. It is a hypothesis that has been utilized broadly by store administrators to amplify estimation of their customers’ portfolio. Also, there is the post present day portfolio hypothesis that additional the idea of understudy rate of coming back to gauge the connection amongst resources and liabilities. It varies with present day portfolio hypothesis in risk estimation by utilization of mean return. The utilization of this hypothesis was made conceivable by the utilization of programming created by Rom that profoundly empowered market advancement (Sharpe, 1963).
Methodology
This area gives a straightforward and expressive system of the study procedure grasped for this survey. This part starts with a consultation that is focused on the picked approach standards, and framework. Other than the convincing trade of the data aggregation frameworks and an assessment of their deficiencies and qualities, the plan and audit setting are similarly presented.
Research Design
For the most part, research, as coordinated by Saunders and Lewis (2012) has both seen and exhibited the philosophical perception kept up by an individual or researcher so to speak and assessing the key impact the general approach a researcher gets while finishing a research methodology. As demonstrated by the researchers, a research worldview can basically be described as the researcher’s view on the world. The research worldview includes impressions that provoke a thought and illustrations and exercises that a researcher investigations fundamentally.
Each research is interpretive in nature as demonstrated by Saunders and Lewis (2012). This is being that the views of the researcher fundamentally fill in as the unmistakable segment helping the whole research arranges. From the perspective of an interpretive researcher, the fact of the matter is seen as a socially manufactured wonder which must be discovered through attracting individuals inside the social setting being alluded to. Thusly, deriving a more balanced focus on the areas of individuals or people so to speak constitutes the social situation. This is fundamentally while going for having better, unique impressions held about the on-going development (Saunders and Lewis, 2016).
In the subsequent association with these, an interpretivism worldview was basically attracted for the audit as it makes, to an enormous degree, better opportunities to understanding human experience matters. According to prior expressed, this research highlighted whether client impression of convictions and believability can be affected by computer game gushing, and how the purchasing choice can be impacted by it as a showcasing device (Saunders and Lewis 2012). Nonetheless, essentially actuating the choice of this worldview is its momentous attribute of getting to know the themes, conditions or matters of the perspective of the individuals involved. This primarily will assist in the fulfilment of the objectives as the aggregate of the examination to be driven on the impacts of technology advancement in risk management.
Besides, it offers better open entryways for the change of more sensible proposal to be proffered as it depends for the most part on the primary data assembled from individuals (buyers). Interpretivism is identified with a dependence nature of relating with their research individuals. In like way, Saunders et al., (2016) propose interpretivism to be basically launched into the social field of the theme in context of understanding condition better from the untouchables’ perspective.
The approach
The natures of the audit and its objective have been shown to be primary contemplations in assisting the gathering or assurance of an approach in research (Saunders et al., 2016). In following association with these recommendations, a research approach that is inductive was used for the case study considering its exploratory and investigative nature. The close grouping of the approach was on observing better and correct research settings. Moreover, it focused on the versatile part of not being bound to theoretical improvements while giving satisfactory elucidation of relationship effects between elements that require its determination for the present survey (Saunders and Lewis, 2012). These components are basically basic since the confined revelations included inside the survey setting. Also, keeping an eye on the set-out research focuses, to an immense degree, requires both a fundamental examination and surveys on the theoretical perspective rising and developed from the data assembled and explored (Saunders et al., 2016). The approach (inductive) essentially gave room for the results to be created from consistent winning and recurring subjects inside the data assembled especially for the audit
A case study research is a research system that includes a genuine examination of a viably existing component with respect to a certifiable condition. This framework on a very basic level highlights gathering data particularly in association with an on-going activity inside any industry. At the point when all is said in done, thorough case studies have demonstrated the research’s ability to address the questions at hand (Saunders et al, 2007). Notwithstanding, it inside and out incites the assurance of this method that was its primary centralization of satisfactorily observing a study subject through the engagement of a present case.
The case study was focused at managers to view on the impacts of technology advancement in risk management. The review utilized questionnaire to get the perspective of the focused on respondents on the impacts of technology advancement in risk management.
In addition, the picked style and configuration was communicated too much of the time incorporate tyrannical business positions as a bit of the general business among the study populace. This in a way improves open chances for a more fruitful generalizable proposition to be made inside the research theme. Moreover the technique’s associated attribute of neglecting to consider confinements sensibly and often grasp various data gathering frameworks particularly underpins an interpretivism approach and the exploratory audits in this way affirming its decision.
Data Collection
Prior research, as proposed by Saunders and Lewis (2012), has in this way reported and associated basic limitations with interpretivism standards. This is the extent that it is having an ambiguous approach to manage finish overview and choose the acceptability, endurance and immovable nature of its revelations which are regularly subjective. With regards to these recommendations and furthermore, the study’s settled nature a mixed model research choice was secured for the study. Affecting the assurance of this technique was a result of its familiar component of offering a more solid and elegant investigation of both research request and goals and what’s more in like manner proffering sensible level of steadfast quality on the disclosures. This procedure basically includes the usage of both a subjective and quantitative data accumulation framework which could be separated and deciphered independently (Saunders et al., 2012). Also, a various technique helps in getting the applicable way of any segment of study being investigated.
Also, as opposed to the thorough comprehension of complex sensible issues gave by subjective procedures, quantitative revelations are proposed to highlight more exactness, strategy for thinking and generalizability in results (Saunders and Lewis 2012). Thusly, a blend of data sourcing medium to a huge degree mitigates the insufficiencies related with the grasped research worldview. More, especially questionnaires explored by controlled survey were the fundamental data amassing approach embraced for the study.
Questionnaires were utilized as a part of for this specific study. The sensible traits of the system go similar to its versatility. Moreover, they audit the ability to give better odds of getting an all-around detail and cognizance on the theme particularly from an outcast’s perspective and defended its application. All the more, a total of 20 respondents were brought together and worked as risk managers. Willing individuals were courted online via LinkedIn. A questionnaire was sent to them where they filled it and sent it back to the researcher. In reference to this, updates were sent especially to individuals who could not make to fill the questionnaires immediately.
Research has both seen and recognized studies as a specific strategy used as a piece of getting accurate data on a communicated point or theme (Saunders and Lewis, 2012). However a few researchers recommend that the path in which studies are overseen fills in as determinants of the authenticity of the study. This is being that it basically impacts the way of the data procured.
Emphatically, an almost completed survey including a total number of twenty questionnaires was regulated to individuals who were enlisted by the researcher. The respondents were in a general sense moved closer and addressed by the researcher on the impacts of technology advancement in risk management. Also, respondents were furthermore supported of characterization for any information accumulated, as all request issued and data gathered was finished in a split second and within the sight of the interviewee.
Secondary information was needed for the examination to be finished. Information on the impacts of technology advancement in risk management was gained from library and web sources. The optional information utilized was from and eBooks and books in the library, from the web and printed copies of diaries, journals, magazines and articles. An optional source was chosen for incorporation relying upon the significance on the point being researched. Sources that had pertinent information and eBooks were embraced for the study.
The study utilized both essential and auxiliary information in concocting conclusions. Because of the utilization of both sorts of information from various sources, a meta-examination was fundamental. The meta-examination thoroughly analysed related data gathered from various sources. In this way, triangulation was essential when attempting to think about information gathered from essential and auxiliary sources. Triangulation made it workable for a similar investigation of both essential and optional information (Saunders and Lewis, 2012).
Moral and Ethical Consideration
Because the review included individual interactions with people who filled in as the respondents, moral aspects were reviewed both before and in the research. Despite the way that the association with people was aimed at getting particular sentiments and viewpoints in association with the theme of the study, their personal data was secured. Such measure included getting the consent of the respondent. In addition respondents were also instructed of their privilege and liberty to abandon the questionnaire whenever they felt like.
Characteristics of the design and approach
Considering the exploratory strategies for the study and furthermore its developed enquiry, the interpretivism worldview to a generous degree allowed to the important issue enveloping the fundamental subject to be totally studied and audited start to finish. Moreover, the study’s legitimacy was out and reached by comparative segments of giving sufficient primary perspectives of a subject point. It was done in a perspective that it is a decision that defines the basic groupings. The guidelines rules were distinguished for studying and surveying the effect association between two variables being examined. The principles, subsequently, must be effectively reflected subjectively as it included essential parts of the research in deciding if client view of convictions and validity can be impacted by computer game gushing, and how the purchasing choice can be affected by it as an advertising device. Moreover, the gathering of interpretivism worldview, be that as it may, induced the usage of the subjective and quantitative data informational indexes. This is a result of its related deficiencies along these lines influenced earnestly in general study as it updated the steadfastness and nature of both the research revelations and proposition made from the inspected data.
Weaknesses of the design and approach
Interpretivism ideal models, as a result of their primary and organized design, have been prescribed to oftentimes come up with less correct, generalizable and undependable disclosures. Similarly, its accentuation on aptitudes that are interpretive fill in as a tremendous level of limitation in light of the obliged capacities focused within this perspective being the researcher initially attempt at it. Along these lines, this could be a showing of the possible comprehension of the questioned points of view or enunciations and furthermore segments of researchers’ biasness being reflected which may therefore influence the proposed disclosures.
Analysis, Results and Discussion
Analysis and results
Data collected from the study was subjected to different levels of analysis mostly being in the measures of central tendencies. The results were presented in form of charts and graphs. This presentation is often preferred because the results are easy to comprehend and are simple in nature.
A total of 20 questionnaires were sent online to risk and financial managers profiled through LinkedIn. A response rate of 100 percent was recorded. As such a descriptive summary chart was derived after thorough analysis of data. They were required to answer on the various factors that are thought to impact risk management due to the advancement of technology.
| N | Max | Min | Mean | |
| Technology | 20 | 2.90 | 1.10 | 3.9 |
| Data Management | 20 | 2.83 | 1.35 | 2.5 |
| Risk management practices | 20 | 3.11 | 0.99 | 3.1 |
| Compliance and Training | 20 | 2.0 | 2.90 | 2.7 |
Table 1 showing means of the sections of risk management compared to technological advancements
This research was divided in several section of risk management. The risk and financial managers were asked how technology advancement affected the different sections
From the results and answers of respondents, it was found that data management had a mean of 2.5. The compliance and training mean was 2.7. For the risk management practices the mean was 3.1 and for technology was a 3.9.
| N | No or little Impact | Medium Impact | Huge Impact | |
| Technology | 20 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.9 |
| Data Management | 20 | 2.4 | 1.4 | 6.5 |
| Risk management practices | 20 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 5.1 |
| Compliance and Training | 20 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 6.7 |
Table 2 showing impacts of technology advancement as per the respondents on several sections in risk management
From the research also, it was found that most respondents believe that there is no relationship between risk management and technology. However, a majority believe that there is a huge impact when the technology in use is continually changing. Training and compliance are seen to be positively affected by technology advancement and use. In similar manner, the respondents believe that risk management was impacted negatively by technology in terms of practices used to manage the risk. Finally, data management using technology was seen to be affected by advances in technology is a huge way.
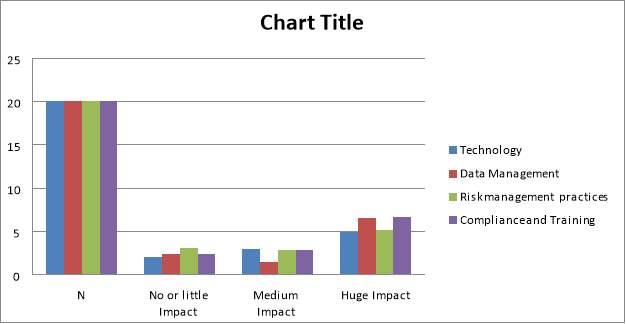
Figure 1 showing impacts of technology advancement as per the respondents on several sections in risk management
| Agree (in percentage) | Disagree (in percentage) | |
| Mitigation | 56 | 44 |
| Transference | 69 | 31 |
| Acceptance | 45 | 55 |
| Avoidance | 66 | 34 |
Table 3 showing various responses on the management of risk resulting to advancement of technology
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to show that technology has claimed its place in society and risk management assessors need to incorporate it when doing their risk analysis. Technology is important in making things easier to understand and helping in the end. Technology however also comes with added risks that are supposed to be assessed concurrently. According to Hancock (2012), various technological aids are essential in creating efficiency usher in their risks as well. An assessment of the risks would involve the determination of both the efficiency brought about by the new systems as well as the added risks involved by incorporating them. Its impact on risk assessment in any organization and the role it plays to make the process easier was the main agenda behind doing this research.
The study basically compared several fields of risk management with technological advancement and understood how each was impacted. Additionally, there were several ways of managing technological advancement impacts among the different fields of risk management as presented in the above section.
Comprehending the risk involved in any venture done by organizations is important since it allows both the risk assessor and the clients manage their systems in ways where all the vulnerabilities are addressed. The results established that risk is managed through transference, acceptance mitigation, or avoidance.
According to King (2016), risks can be managed by avoiding them altogether so that any vulnerability is prevented from exploitation. If a particular technology has had cases of having adverse effects when used, organizations completely avoid it until such issues are solved even when it affects their efficiency. If brands of equipment have shown tendencies of resulting to unwanted consequences, other than sticking to it and suffering them, an organization avoids it altogether. In information technology, if a certain operating system shows signs of instability, it is shunned by users until the time that the experts give it a clean bill of health. If an operating system is used in operating a critical system in an organization but in the course of assessment it is realized that it increases the probability of wrong outputs, other than putting up with it and suffering, an alternative is sought.
Similarly, Drobny (2013) postulates that different systems have different vulnerabilities that would be exploited and result in a spread of risk. Flaws in the designs, procedures or implementation may lead to an enhanced risk that would impact organizations differently. Some risks are brought about by wrong use of systems and risk assessors should be able to determine what is brought about by either flawed equipment or misuse (King, 2016). In researching on the risk avoidance, management, and its impacts, it is important to look at both the microenvironments and the macro environments to determine what kinds of risks are unique to an individual system and which ones are more generalized. By understanding what can be specific about a certain problem, addressing it would be easier and more localized.
Levy and Scala, (2012) believe that it is not very practical in technologically based risks, but it is important in reducing the impact that any risk has on an organization by deflecting it. While accidents brought about by faulty or malfunctioning equipment in the medical field may result in injuries or fatalities, managing such risk is a complicated issue. Healthcare facilities may not replace a life that has been lost but strategies can be put in place to ensure that in the event of such an occurrence happens, their pieces of equipment are not lost but are insured so that the financial consequence is manageable.
The strategy of transference aims to reduce the vulnerability of the systems being exploited by preparing and planning for them. Elimination of risks is almost impossible, but a firm assesses what could go wrong and put preventive measures to ensure it does not happen or if it does, has minimal risk according to Page et al. (2007). Different circumstances may not prevent the probability of there being a power failure, but a risk assessor imagines that it may happen and advice on putting measures like standby generators so that if it happens, the systems are not adversely affected. It is the same concept employed in vehicles accidents where automakers devise the supplementary restraint system to minimize the risk of fatality if an accident happened.
Finally, Drobny (2013) alludes that Understanding that a risk exists may not look to be a good way of managing it, but by accepting that there are risks, the eventualities would be better managed. Risk assessor evaluates the possibility of a particular risk occurring and help in putting measures in place to ensure that the effects are better addressed. The supplementary restraint system incorporated in vehicles may not prevent accidents or injuries, but understanding that it may happen and posting air rescue systems when it happens increases the rate of survival by the injured (King, 2016). Such systems cannot be put on standby in a system that is fully committed to avoiding them. In the enterprise systems, the technological information systems are designed in a way that they can be put back in place to perform the most critical duties while other problems are addressed (Nilsen & Olsen, 2007). It results in systems conceived in a way that they share different servers for different tasks such that if one breaks down another lifeline can be activated.
Conclusion
This paper was aimed at establishing the impacts of technological advancement on risk management. A study was done where several IT, risk and financial managers were assessed. Additionally, empirical data was used to come up with conclusion. This study established that several sections of risk management are affected in different ways by the advancement of technology.
It was established that that there is no relationship between risk management and technology. However, it was noted that there is a huge impact when the technology in use is continually changing. Training and compliance are seen to be positively affected by technology advancement and use. Similarly, risk management was impacted negatively by technology in terms of practices used to manage the risk. Finally, data management using technology was seen to be affected by advances in technology is a huge way.
This paper also established that risk can be managed from negative effects of technology advancement using measures like avoidance, transference, acceptance and mitigation. These measures can be used concurrently or individually according to the views of the insurer or risk manner. Additionally, the usability of these management practices can be based on the nature of the risk and where it affects the most within an organization.
In conclusion, this paper was successful in establishing the impacts of technological advancement on risk management in many organizations. It established the level of impacts at several key fields in risk management. Additionally, it came up with ideal measures to deal with risk as it arises within any organization.
In this manner, the researcher recommends that there be more studies on the particular management practices of risk and how they control specific impacts of technology change within the departments of risk management in an organization.
References
Adler, T., Leonard, J., & Nordgren, R. (1999). Improving risk management: moving from risk elimination to risk avoidance. Information And Software Technology, 41(1), 29-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0950-5849(98)00095-0
Anantatmula, V. & Fan, Y. (2013). Risk Management Instruments, Strategies and Their Impact on Project Success. International Journal Of Risk And Contingency Management, 2(2), 27-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.4018/ijrcm.2013040102
Ashoori M. & Teymouri M. (2010). The Impact of Information Technology on Risk Management. Tehran, Iran. Elsevier Ltd.
Beroggi, G. and Wallace, W. (2012). Operational Risk Management. The Integration of Decision, Communications, and Multimedia Technologies. Berlin. Springer Science &Business Media
Chorafas, D. N. (2011). Risk Management Technology in Financial Services: Risk Control, Stress Testing, Models, and IT Systems and Structures. Michigan. Ponemon Institute.
D’Addario, F. (2013). Influencing enterprise risk mitigation. Oxford: Elsevier.
Drobny, C. (2013). Stark Realities of Managing Cybersecurity Risk. Journal Of Petroleum Technology, 65(11), 122-123. http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/1113-0122-jpt
Hancock, S. (2012). Risk assessment and management of information assets. Engineering & Technology Reference, 1(1). http://dx.doi.org/10.1049/etr.2015.0126
Hellström, T. (2003). Systemic innovation and risk: technology assessment and the challenge of responsible innovation. Technology In Society, 25(3), 369-384. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0160-791x(03)00041-1
IBM. (2011). Supporting Information Technology Risk Management. New Jersey, Morgan Stanley Publication.
Khatta, R.S. (2008). Risk Management. New Dehli. Global India Publications
King, S. (2016). Risk Avoidance. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, 9(1), 110-111. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2015.11.025
Kouns, J. & Minoli, D. (2011). Information Technology Risk Management in Enterprise Environments: A Review of Industry Practices and a Practical Guide to Risk Management Teams. New York. John Wiley & Sons
Levy, K. & Scala, J. (2012). Transference, transference interpretations, and transference-focused psychotherapies. Psychotherapy, 49(3), 391-403. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0029371
Lytras, M. D. (2012). Trends and Effects of Technology Advancement in the Knowledge Society. Hershey. IGI Global Low, S.P, Lui. J. Y. & Hui, S.M. (2014) Enterprise Risk Management and the Performance of Local Contractors in Singapore. International Journal of Construction Management 13(2):27-41
Nilsen, A. & Olsen, O. (2007). Resistance or Acceptance? Mitigation Strategies in Risk Management. Risk Management, 9(4), 255-270. http://dx.doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250032
Nilsen, A. & Olsen, O. (2007). Resistance or Acceptance? Mitigation Strategies in Risk Management. Risk Management, 9(4), 255-270. http://dx.doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250032
Novick, B (2014). The Role of Technology within Asset Management. View Point BlackRock. Accessed online from http://www.blackrock.com/corporate/en-us/news-andinsights/public-policy
Page, V., Dixon, M., & Choudhury, I. (2007). Security risk mitigation for information systems. BT Technology Journal, 25(1), 118-127. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10550-007-0014-8
Rabechini Junior, R. & Monteiro de Carvalho, M. (2013). Understanding the Impact of Project Risk Management on Project Performance: An Empirical Study. Journal Of Technology Management & Innovation, 8, 11-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/s0718-27242013000300006
Rogers, E. M. (1995). Diffusion of innovations (4th ed.). New York: The Free Press.
Sawczuk, B. (1996). Risk avoidance for the building team. London: E & FN Spon.
Sharpe, W. F. (1963). A Simplified Model for Portfolio Analysis. Washington DC, USA
Surry, D. W. (1997). Diffusion Theory and Instructional Technology. http://intro.base.org/docs/diffusion/
Titarenko, B. (1997). ‘Robust technology’ in risk management. International Journal Of Project Management, 15(1), 11-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0263-7863(96)00018-x
Tuckett, D. and Taffler, R. J. (2012). Fund Management: An Emotional Finance Perspective. Charlottesville. Research Foundation of CFA Institute
Williams, C. (2015). Effective Management. Chicago.Cengage learning.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Risk Management"
Risk Management is a process for identifying, understanding and mitigating any risks that are associated with a particular task or event. Individuals and organisations implement Risk Management to provide a layer of protection, allowing them to minimise risk in their operations.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




