Whole Foods Market: Business Strategy Analysis
Info: 7987 words (32 pages) Dissertation
Published: 23rd Aug 2021
Table of Contents
Company Profile, Mission & Values
Macro Enviroment – PESTLE Analysis
Introduction
This project’s purpose is to deeply analyze and assess the Whole Food Market’s business strategy and analyzes individually the company’s internal and external environment, mission, vision and recommending action plans for the strategy implementation.
Company Profile, Mission & Values
Founded by a 24-year-old young college dropout and his 21-year-old friend in Austin Texas back in 1978 SaferWay became what we know today as Whole Food Market inc. a leader in natural and health foods in the United States. The firm showed evidence that it will be pioneer in the sector after the 1980 merge with Clarksville Natural Grocery that lead to the introduction of a large health store at the time with the under the name Whole Food Market. The 19 staff grocery store ended up having revenues of $12.9bn in 2013 and 379 stores in the second quarter of 2014 in USA, Canada and UK. The same period the company ranked 8th in the top 10 of the largest food and drug retailers in the US with over 7 million customers while being the first to ever acquire certification for organic grocery.
One of the founders of WFM, John Mackey, vision was to make WFM the top natural food retail globally by offering high quality products that are organic, natural and as unprocessed as possible so as to transform costumer’s diets and eating habits and offer them a healthier and more prosperous way of living.
The WFM visions, moto in a sence, is “Whole Foods, Whole People, Whole Planet” leads and is in line with their creator’s view, for global reach and success through innovative practices, while being friendly and respective towards customers, shareholders and the planet (Whole Food Market, 2014). In addition, the fact that WFM has been around for more than 30 years does not limit its vision implication about its future business and direction since the natural and organic food sector it’s still growing around the world. In the mission statement, also presented as “Declaration of Independence”, the alignment with the vision statement, making reference to the quality of the products, core values, high standards in all business aspects and finally a “Quality state of Mind at Whole Foods Market”. The latter is in line with John Mackey’s statements about healthier lifestyle, enjoyable and entertaining shopping style in WFM (Johnston, Cairns 2013). Discussing in more key take-aways from the mission statement and the WFM vision we can observe that the firm is taking action to implement this values, for better communities offering privilege to each employees such as discounts, insurance premiums and gainsharing programs and privileged saving accounts. The core values of the firm are also present not only for actions regarding the employees but also for other members of the community with program such as “Whole Planet Foundation” creating partnerships with developing world economies “Local Producer Loan Program” committing a budget of $25m for low interest loans to local producers and “Whole City Foundation” aiming to deliver high quality products and services to underserved communities. Core values application has led to recognition for WFM’s strategy and leadership being included in the Fortunes “100 companies to work” for 19 consecutive years, first place in the Harris Interactive of Wall street journal receiving the best score of all companies for social responsibility.
External Analysis
Macro Enviroment – PESTLE Analysis
The PESTLE or PESTE analysis is one of the most common and widely used approaches for examining the external business environment. This includes analysis in Political, Economic, Social, Technological and Environmental factors and gives a description of the macro-ecoconimic factors that lead to threats and opportunities that could affect a company’s operations and strategies. (Gupta, 2013 and one more source). In this study this factors will be analyzed for WFM in the order mentioned above in order to give insights on the market conditions.
- Political
In 1990 the organic food and production act was introduced and since then many amendments and regulation have been surfaced to protect costumers. On the other hand, as commerce has evolved favorable agreements regarding free trade limitations and barriers have been introduced. Budget cuts to organic farmers
- Economic
Organic food in comparison to synthetic comes at a premium thus making the organic products more elastic and volatile. In cases like the 2008 economic crisis that could be repeated elastic products suffer severe hits. Higher economic stability in the US after the 2008 crisis and increased percussing power positively affects premium products. Labor costs in both developing and western countries together with economic stability returning in US and Europe after 2010 are macro-economic factors that need to be looked closely.
- Social
Healthy life style trend has increased significantly over the last years, with the contribution of social media. Increasing awareness about disadvantages of processed food both customers and to the environment has sifted demand towards more natural resources. Also after the 2008 crisis while awareness has increase so has wealth gap affected severely the middle class, while it should pay more attention to women audience since it is a major driver behind market trends (CCN, 2014, Harvard Business Review, 2009). Women controlled globally $20 trillion in consumer spending per annum (Forbes, 2013), while millennials another key driver while they have less purchasing power than previous generations, tend to eat healthier and are more attracted to specialty grocery stores than previous generations. (Business Insider 2014).
- Technological
Advanced technological systems and the evolution of social media are factors affecting every industry globally while logistics and computerized systems offer higher automation providing efficiency to businesses. Also mobile usage with smartphones has skyrocketed after 2010, offering the ability from advertising a product to making purchases and payments with your phone, significantly in 2014 more than 30% and 40% used mobile to do online purchases in UK and US respectively while more than 50% compere prices and reviews for both US and UK (ermarketer 2014). Furthermore, technological evolution has led to heavy panting especially in GMO’s and other similar areas.
- Legal
Strict law framework in US is affecting all business aspects, while this is also a phenomenon in European and other developed countries. Legal framework with regards to pollution could have a double effect leading to establishment and strengthen of a company’s position in the market or serve a severe hit by penalties and bad publication leading to low costumer preference as the firm would be stigmatized. Also strict antitrust legal framework in the US is a factor that should be closely watched.
- Environmental
Over the last years’ major concern has been the environmental effect of production in global warming and pollution. This surely includes concerns regarding animal and plant production that affects the eco-system in different ways such as poisoning pasture and cropland. Also this has led to regulation about complex and high end waste management systems and disposal regulations together with a trend for more sustainable operations. This factors affect operations supply and demand following a chain reaction and affecting prices, variety quality all leading to affecting costumers in different ways.
Industry Analysis
Industry Overview
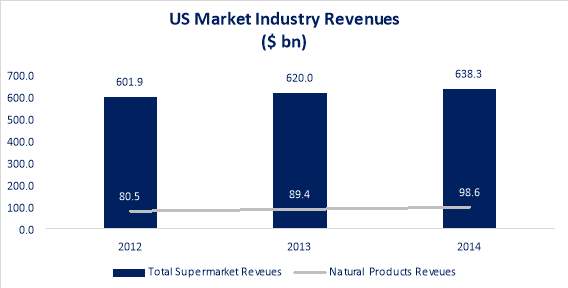
Supermarket Industry in the US is constantly growing and had US $638.338 billion revenues in 2014 an increase of 2.9% compared to 2015. Natural food products accounted for 15.44% of total revenue in 2014 with US $98.6 billion. dollar sales increased by 10.2% since 2013. The growth in natural food sales is driven by millennials and the preference towards a healthy life style as well as increased awareness hand in hand with the increase in educated population with higher environmental concerns.
Porter’s Five Forces
The model of Porters five forces is a significant analysis tool that leads to understanding key factors that affect business strategy, while the external analysis provided by this model evaluates important criteria of the macro economic environment regarding consumers, suppliers and competitors. (Grundy, 2006)
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Purchasing Power and bargaining power of buyers in retail and supermarket industry is strong. When it comes to organic food however this power is limited but that does not mean it is weak. Regulations regarding organic food narrow choices of costumers. Socio-cultural characteristics such as education and consumer awareness together with quality information drive consumer to do research and compere prices, products and accessibility giving them strength and limiting switching costs however something that is subject to narrow choices for organic foods compered to regular products. This also drives sector thus WFM and competitors to respond to the aforementioned matters.
Bargaining Power Suppliers
As demand for organic food grows as a natural consequence bargaining power of suppliers will grow as well. The limitation in pasture and cropland in US certified as organic, less than 1% in 2011, adds extra power to suppliers, however using producers in developing countries could counter balance that force. Also using local farmers which WFM is supporting through social responsibility programs instead of using large suppliers that have more bargaining power. Notably as demands grows it is possible that more organic retailers will surface creating an unequal portion of fewer suppliers to more retailers thus increasing the force they can impose to the company. This is considered a force of moderate strength.
Threat of new entrants
This force as all could have more than two sides and aspects. Small and medium grocery stores could easily convert their business to operate as organic groceries, however limitations in regards to legal framework, regulations and geographical impact could require a higher capital costs for transformation to be achieved this to be achieved thus making it more difficult, making this force moderate.
Threat of substitutes
This force is strong since the increasing demand for organic foods together with a premium in their price has led to the introduction of cheaper products of natural style and even sometimes labeled as non-GMO coming from groceries that sell natural rather than organic products in cheaper prices, responding to demand for healthier food to lower income population.
Intensity of rivalry
This force is strong in the industry as big players in the retail, grocery and supermarket business in the US have the means, both operational and financial to respond to the organic trend and introduce organic products in their catalogues increasing price and demand competition offering more quality choices to consumers. As an emphatic example, Walmart a giant in the industry provides grocery at ¾ from the prices of organic founds increasing competition. (Shelly, 2014). Low switching costs together with high demand for organic and natural groceries in addition with their higher profit margin has led big and small and medium players to a shift towards this products introducing them to their selves. (Thompson, 2014).
Driving Forces
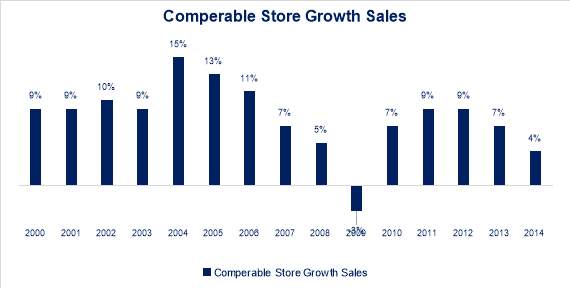
Driving forces are a combination of key internal and external forces such as competence management skills economy and competition that significantly influence the market and the organization (Thompson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland, 2015). One of the main if not the main force for WMF is the expansion of organic food industry over the last years for many reasons with the key reasons being shortly presented and discussed previously on this paper. Demand is constantly increasing for organic and natural founds and in hand with the increase in total revenues for groceries and supermarkets in the US and the UK. Of great importance is the increase in US reached almost US $35 billion in 2015 from a low figure of US $9 billion in 2002 implying an increase of 3.88x while for the period 2000 to 2014 the average annual increase for organic foods came at 15% for the period, and for the post crisis period (2009-2014) sales are growing with an average of 10% and a Cost of Average Growth Rate of 5%. The aforementioned numbers not only show the significance of natural and organic food sales but also prove that this trend has continues after the major financial crisis in 2008 which affected the industry and especially products with premiums that have elastic demand and are volatile to such events. The above together with the fact that according to Techsi Research the compounded growth until 2020 is projected at 16% a major increase that proves the importance of this sector. (CNBC, 2016)
Apart from the economic factors that are of significance force to the sector and to WFM there are other socio-cultural forces that drive influence to this industry such as health awareness and wellbeing of consumers together with the emotional impact the definition organic in labeling has to them. Furtjemore this trend has a close relation with sustainability and eco-friendly trends since organic and natural comes in a form that respect the environment and the animals implying ethical concerns and motives (Padel & Foster 2015). These factors all together with the act with significant force to the industry and have forced for the creation of stricter legal and regulatory frameworks in regards to these aspects. Adding to all these the impact technology, social media and internet have to advertising and information accessibility consumers especially the have become sophisticated and demanding and all these factors drives firms in the sector to respond to this demands by becoming more consumer friendly, use internet and technology to launch mobile apps and extensive use of e-payment methods while transforming their strategy towards eco-friendlier sustainable operations.
Key success Factors
Also known as KFS these are a combination of significant facts that are required from an organization so as to acquire competitive edge and succeed in achieving its business goals and surpass competitors and succeed in the industry. (source). One of the KSF in retail and supermarket industry is geographical allocation of stores to increase accessibility and convenience when shopping. Another KSF in also the brand/label positioning in store of well-known products that high sellers as well as brand positing of the firms label as well to increase awareness about company’s profile. In the organic and natural food industry promotion of wellbeing especially in the in-store-experience for the costumers is essential so products of high quality and an extended variety of products offered is critical, while hand in hand with staff adequately trained to support this experience with knowledge on the products and on healthy life style offering a supporting service to clients enchanting this way the quality of services. This adds values to the service and makes service more attractive value for money shopping experience.
Competition
Strategic Group Mapping
In order to compare and group rivals and firms with similar operations and strategy we use strategic group mapping which serves as a tool than can provide valid positioning and comparison for such purpose (Porter M, 1980 as cited in Feka, Xouris & Tsiotras, 1997, p.67). This tool could help a firm identify strategic opportunities by identifying close and more distant rivals as well as provide identification of attractive and unattractive positions in the market. The supermarket industry is a highly competitive industry with players from local level to international and worldwide supermarkets. Price of products and accessibility is some of the key drivers for this industry and is what I used for the strategic group mapping diagram with price ranging from high to low and geographical reach from narrow to wide taking into account not only the absolute number of stores but also presence in states and foreign countries.
Trader Joe’s
The firm was founded in 1967 and is a specialist in low cost and value for money shopping. The company offers a continually changing range of over 2,000 products including exotic and uncommon products offering to its customers an extensive variety. Notably more than 97% of its product line has to do with food of which there is a vast selection in organic, natural products including products without artificial ingredients. The firm has limited geographical aporach while it’s expansion strategy is not certain living us to believe that accessibility is a drawback. The company is the only private held company from the ones identified as competitors and they revenues in 2013 came at US $ 10.5 billion making it a very competitive player within the industry. (Thompson, 2014).
The Fresh Market
Introduced for the first time to the public in 1982, has now more than 150 stores in almost half of the states in US. The firms specialize in perishable goods has a strategy to open stores in high end areas with high traffic. The Fresh Market offers a different in-store-experience than most supermarkets with cozy design, relaxing music big displays and house oriented painting and lighting. The firm offers more than 9,000 products with some product catalogues being quite extensive such as cheese section with more than 200 different varieties. (Thompson, 2014). Apart from the costumer experience the firm engaged to provide quality employment experience by providing to its employee’s quality in-house training, generous discounts and beneficial health plans, an important benefit in the US, after only two months of employment showing commitment to invest to human capital and employee satisfaction. The emphasis in natural, fresh and quality products as a specialty retailer, together with employee satisfaction led them to achieve big consumer satisfaction which was translated to high revenues increases and the firms’ IPO in 2010. The company reported revenues and net income of US$1.32 billion and US$0.514 billion in 2012 US$0.641 billion and US$1.86 billion in 2013 and 1.51 billion in 2013 respectively (Yahoo, 2014).
Sprouts Farmers Market
The newest competitor in the map was found in 2002 growing rapidly with 170 stores after utilizing in the best way its IPO in the end of summer in 2013 and heavily deleveraging its operations giving room to finance new activities. As the aforementioned player, SFM is characterized as a specialist in natural and organic food industry while is has created an easy to remember quote “Healthy Living for Less” that could emotionally trigger costumer attention. (Thomson 2014). Its strategy includes private label brands making well-known products available at attractive prices while offering cheap high quality coffee and a vast majority of gluten free products and. In growth terms SFM is aiming to expand by a mix of strategies including new store launching but also through strategic merges and acquisitions. In 2013 SFM reported revenues of US$2.44 billion and net income of US$0.051 billion with a significant increase of 36.31% and 163.23% respectively while in 2014 revenues increased by 21.17% at US$2.97 billion but net income more than doubled at US$0.108 billion showing huge increase in profit margins of the firm.
Walmart
A well know brand, one of the major and bigger players in the US was introduced to the industry in in 1692, after 50 years in 2014 it was the biggest seller in food and grocery way ahead the second best. Walmart in 2014 had 4,203 in US and 10,942 worldwide making it a giant in the industry (Walmart Annual Report, 2014). Wallmart in 2006 informed the audience that it will enter the organic food market, indicating that the firm has planned and evaluate the upside of this sector way back. (NYTIMES, 2006). This plan reach peak in 2014 when the firm announced its collaboration with Wild Oats, in order to offer the latter’s products in its stores. This came with press reports indicating that Walmart’s higher management does not believe in premiums in the organic food sectors thus it will be offering the organic products at almost 75% of the price that they were offered from their competitors. The aforementioned highlights the high competition in the market while adding to this that Wild Outs was a subsidiary of WFM for 2 years in an acquisition deal taking place in 2007 but failing to comply with the US Federal trade commission in regards to unfair competition and price manipulation. (Grist 2014, Reuters 2009). All these sum up the severe competition together with the threats posed by strict legal framework.
Internal Analysis
Resources
The means by which a firm accumulates and utilizes its resources can sustain a competitive advantage (Dierickx and Karel, 1986). Although over the after the shift of manufacturing to service and technology measurement of resources and what is tangibility has been argued still resources are measured as tangible and intangible.
Tangible resources
In this category I will include WFM’s resources that are identifiable as tangible both in financial and in physical terms (tangible assets). The company’s inventory reach US$441 million in 2014 while in 2013 it was at US$414 million while another tangible measurement property and equipment shaped at US$2,923million for 2014 from US$2,428 million in 2013. This shows that WMF’s tangible value increased while in terms of physical resources WFM had 339 stores in 2014 of which 381 where located in 42 different states of the US a figure increased by 10.22% annually from 352 stores in 2012. The firm is a position that it can cover almost all its liabilities with its US$1.3 billion EBITDA will debt liabilities are only US$62million showing strong position and making the firm attractive for third party investment either through debt or equity to increase its operations and physical assets. Financials will be analyzed later in this paper.
Intangible resources
This category includes intangible assets and goodwill mainly, in other words identifiable assets referring to intellectual property of the company and the sum of excess of cost of acquired enterprises. This could include brand value of firms acquired as well as market reputation of WFM’s trademarks such as the company’s vision statement and logo. In 2014 Intangible assets increased by US$6 year-on-year million while Goodwill increased by US$29 million year-on-year reaching US$708 million. Increase in goodwill was increase after the purchase of 4 retail stores adding value and recognition to the company. Also WFM purchased US$20 million worth of intangible assets. (WFM Annual report, 2014). Furthermore, social responsibility initiatives such as “Local Producer Loan Program” and “Value Matters” and other are included in this category since they promote social well-being and raise awareness regarding eco-system. Least but not last the intense social media as part of the company’s strategy is consider an intangible resource with WFM having more that 1.7 million subscribers each week to newsletters and social media accounts while responded to approximately 1,200 messages daily through 830 social media channels.
Competences & Capabilities
The company’s ability to reach a competent outcome by deploying its resources through organizational processes in considered a capability (Amit & Schoemaker, 1993). Distractive competencies of the company come from the implementation of its core values to their operations. Commitment to engage and support local producers goes hand in hand with commitment from more sustainable environment from the initiative “World Trade Guarantee” giving ethical dimension to the brand, while both the aforementioned create costumer and supplier engagement and loyalty creating a major competitive advantage. The high quality products the quality checks and the dedication to find them such as the salmon coming from a local salmon buyer working with no commercial fishermen goes hand-in-hand with high quality in-store-service which is driven by WFM’s management initiatives for decentralized team operation, fair treatment and clear goal performance to be reach on a transparent base create a competitive advantage. (MIT Sloan Management, 2010). Also initiatives such as the “Healthy Stands Hear” which guides consumers to choose healthier food guiding consumers to build healthier meals and the “Unacceptable Ingredients for Food” list with ingredients inacceptable thus not contained in the products sold in stores made WFM the first national certified grocer by USDA creating a sharp competitive advantage.
Financial Analysis
Value Chain Analysis
As value chain is defined the series of processes that are characterized as value-activities from the start of operations in purchasing basic material from third party suppliers and all the activities leading to the products finalized version customers (Shank, 1989)
Primary Activities
- Supply chain management
WFM pursuits high quality products that are being produced and acquired with the respect to the environment and the costumer. This has been achieved with initiatives of the company to locate pure raw materials or provide own brand healthy products while supporting local producers so as to ensure quality and long lasting relationships bringing all of the above in line with the company’s mission.
- Operations
The company as mentioned has teams and stores working in decentralized showing trust and empowering local teams with strategies as to allow local managers to stock according to what they believe is essential to the local community. Staff is highly trained, provided with motivation through goal-achieving reward system and benefits ensuring that human capital will promote company’s vision for satisfied customers and unique in store experience.
- Distribution
Regular checks before acquiring products but also before putting them into selves with acts like “Seafood Quality Standards” characterize the importance to all this. WFM tries to shorten supply chain and decrease time needed for a product to reach it selves by 18 distribution centers, on site buyer’s and by using local producers for each area. This has led to fresh salmon from Alaska being in stores in less than 48 hours. (MIT Sloan Management, 2010) Supermarket Inc.
- Marketing
WFM relies on light marketing and social media. Using Word-of-mouth marketing and with intense presence in social media has achieved to engage costumer by peer-to-peer recommendations and proven record of customer satisfaction by reviews. WFM takes times and resources to respond daily to costumers, in line with their core values for customer satisfaction, while this strategy keeps marketing cost down. (WFM, Annual Report 2014)
- Service
WFM gives emphasis to high quality services, with staff trained and educated to help and provide advice according to customer needs and demands. Initiatives like in-store cooking lesson and seasonal product recipes to guide costumers into healthy life style.
Secondary Activities
- Human Resources Management
WFM believes that human capital is one of the key components what driving company’s success thus they invest on human capital by training, educating, and providing benefits it’s employees while giving the responsibilities and decision making power in key operating functions.
Product R&D, Technology and Systems Development
WFM’s management states focused on technology while making additional investment in the field. WFM makes research to respond to costumers’ demands and problems, while constantly introducing new rating and evaluation systems such as the “Good, Better, Best” system to help customers find healthiest promoting food in store (WFM, annual Report 2014).
- General Administration
WFM uses a decentralization strategy as one of the means to create a connection between mission and vision statements and administration. WFM promotes competition among stores while store managers promote the company’s culture and mentor employees to grow. WFM gives to employees for deciding what to stock or purchase when working as on-site buyers showing the trust higher management has to them.
Competitive strength assessment
| Key Success Factor | Importance Weight | WFM | Walmart | Spouts farmer market | Trader Joe’s | The Fresh Market | |||||
| Marketing | 0.15 | 8 | 1.2 | 8 | 1.2 | 8 | 1.2 | 8 | 1.2 | 9 | 1.35 |
| Branding | 0.15 | 8 | 1.2 | 10 | 1.5 | 8 | 1.2 | 8 | 1.2 | 9 | 1.35 |
| Skilled Employees | 0.2 | 10 | 1.5 | 8 | 1.2 | 8 | 1.2 | 6 | 0.9 | 8 | 1.2 |
| Effective Supply chain | 0.2 | 10 | 1.5 | 10 | 1.5 | 8 | 1.2 | 9 | 1.35 | 9 | 1.35 |
| Accessibility | 0.1 | 9 | 1.35 | 10 | 1.5 | 8 | 1.2 | 7 | 1.05 | 8 | 1.2 |
| Product Uniqueness | 0.2 | 10 | 1.5 | 7 | 1.05 | 9 | 1.35 | 9 | 1.35 | 9 | 1.35 |
| Sum of Importance Weight | 1 | ||||||||||
| Overall weighted competitive strength rating | 8.25 | 7.95 | 7.35 | 7.05 | 7.80 | ||||||
Following the analysis of WFM and its competitors we conducted the above Weighted competitive strength assessment taking into consideration the analysis for the external environment as well as KFS analyzed prior in this study. (Add Supply chain in KSF). Skilled employees that provide high quality services hand-in-hand with product uniqueness and effective supply chain that ensure fresh and high quality products are significant factors that lead to costumer engagement, loyalty and satisfaction factors crucial for business success.
Present Company Strategy
According to Porter there are two main strategies according to which a company can achieve competitive advantage namely cost leadership and differentiation strategy (Porter, 1980). WFM has adopted a differentiation strategy since its strategic focus in to provide unique high quality organic products to its customers. As part of its strategy WFM primarily plan to expand through new store opening and acquisition of smaller chains. This will not only allow them to penetrate into more geographical areas but also allow them to incorporate to their team experience team member adding quality to their human capital and increasing brand strength and recognition. Also promotion of wellbeing, sustainability and support of local societies creates valuable bonds with suppliers and communities in which them operate further improving company’s financial and market position.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis was introduced in the 60s and it is a tool that provided analysis for a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats based on its external and internal environment. (Al- Araki, 2013)
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|
|
| Opportunities | Threats |
|
|
Strengths
High quality products are a result of continuous controls on raw material and suppliers. This together with the initiatives for sustainability and wellbeing such as “Animal Welfare” and Whole Planet Foundation, are key strengths for WFM and is also what differentiates them in costumer’s and markets conscience from other competitors and positioning them as “America’s Healthiest Grocery Store”. Supporting and having long lasting relationships with suppliers is another strength of the company that add value to its operations. Employee satisfaction and motivation boosts productivity and increase service quality giving strength to WFM. One of the facts that the management has succeeded in implementing its strategy comes from the fact that in market terms WFM is a leader in organic food while also being in a strong financial position with strong returns on capital employed and assets, good free cash flow and a successful low cost marketing strategy satisfying its shareholders and investors as well. (WFM, Annual Report 2014)
Weaknesses
The firm has a premium cost on its products, thus making it difficult for low income or price caution costumers that would shift their attention towards cheaper products. Also WFM has to deal with its limited operations overseas. Low number of stores abroad increases costs since it gives limited bargaining power to WFM, while on the same time it increases reliability only in US operations creating a big exposure economic and political threats in the states. Furthermore, as mentioned before there as a very limited certification for organic land in US and with the increase of demand for organic food with could drive prices up limiting WFM’s profit margins while this could affect quality and product diversification.
Opportunities
The increasingly healthy life style trend through the internet and social media is an opportunity for WFM. The company already uses the same marketing strategy if I may say as the one deliberately used by the health and wellbeing “movement” while close monitoring of this trend together with the marketing practices could WFM a synonym to this healthy life style. Increasing demand for exclusive brand has an obvious positive impact in WFM generating from 365 Everyday Value brand US$1.8 billion of sales accounting for 13% of total sales and 18% of non-perishable sales up by 1% and 2% from 2013 respectively while on an industry level the average growth of store brands is 5% versus the 2% of national brands. Expansion of the brand could favor WFM profit margins while more intense production could reduce cost addressing the high price weakness. WFM has also the opportunity using favorable free trade agreements to expand its operation abroad in markets such as Europe and Australia when in several countries economic stability and prosperity will serve positively the introduction of organic products at a premium.
Threats
WFM faces and as demand for organic food increases will face severe competition by major players while it’s also possible that new player’s may enter the market responding to the trend challenging market share and competitive advantages. Also strict regulation in regards to organic food production, environmental changes could have negative impacts to WFM while antitrust and fair competition legislation could harm the company’s reputation and profitably and operations as it happened in 2009 when WFM had to sell Wild-Oats after a regulatory decision. WFM faces also the threat of poor economic conditions since products coming at a premium are subject to elastic demand making them volatile more economic changes.
Identified Front Burner Issues
WFM as all organizations needs to be ready to respond to existing or emerging problems.
- Premium (high) Prices
Premium in prices limit the costumer market to which WFM addresses, making the brand unattractive to lower income receivers.
- Limited overseas operations
WFM operates mainly in the US thus has a big risk exposure in micro and macro-economic events while missing opportunities in other markets.
- Rising labor and raw material costs
Rising labor and raw material increasing costs are driven by macro-economic events, high demand for organic together with limited supply affecting WFM by reducing profit margins, or driving sales prices up.
Identified Alternatives
In this part alternative courses of actions are presented for each Front-Burner Issue.
- Premium (high) Prices
- Higher volume orders from main suppliers together while entering commercial agreements in order to serve larger WFM stores so as to achieve better pricing while keeping local producers for smaller areas as well as adding clauses for quality to the contract so as to avoid quality drawbacks.
- Enter foreign exchange forward/option contracts in order to decrease the already existing cost allowing for price reduction without affecting margins. As a counter measure avoiding foreign exchange risk that could affect revenues and lead to prices increasing is also beneficial for the operations.
- Consider merges and acquisitions of producers in order to reduce cost and provide a safe decrease in prices without reducing margins while conducting this in an ethical manner in-hand with WFM’s core values as not to harm public image.
- Increase productivity of exclusive 365 Everyday Value brand driving costs down and providing them at lower prices without decreasing value since the company’s brand complies with its values.
- Limited overseas operation
- Enter oversea market such as Asia, Europe and Australia. Organic and healthy life style trend is global and need to be responded.
- Create stronger supply chain operations overseas that will enhance foreign relationships and add value to store operations similarly to the US strategy.
- Franchise in international Markets while keeping management and operations to ensure quality of products and services.
- Rising labor and raw material costs
- Avoid rising labor costs in production of food by exploiting opportunities in countries with lower labor cost and more beneficial legislation.
- Enter forward and option contracts for raw materials prices, avoiding risk of price increase due to environmental phenomena’s such as floods and storms that could destroy productions and drive prices up.
Decision Criteria
A company’s strategy in order to be a winning strategy has to pass the following three tests:
- The Fit Test: How well does the strategy fit the company’s situation?
- The Competitive Advantage Test: Is the strategy helping the company achieve a sustainable competitive advantage?
- The Performance Test: Is the strategy producing good company performance?
(Thompson et al., 2015)
Implementation & Recommendation Plan
WFM should pay attention to the need for value for money products and lower prices. Entering commercial agreements that will not affect quality will reduce costs and prices. This will have an impact and engage on consumers such as millennia’s, middle income class and women with the latest being a biggest opportunity than china and India together (Harvard Business Review, 2009). By acquiring small and middle producer facilities WFM will reduce cost and be able to offer products at lower prices while by applying the current acquisition strategy discussed before it will enhance human capital and contribute to social and local well-being since as a parent company it can provide to a small and middle enterprise a better protection to market risks than the one it had as a standalone business. WFM is traded publicly so solid financial position of the group is well-known. This can attract investors in order to provide funds for acquisitions, oversea expansion and create valuable synergies for the operations while reducing US exposure risk. Furthermore, franchise agreements could also serve this purpose with WFM keeping management and operations, this could lead to a smoother expansion with less risk while keeping quality and core values intact. A deal like this could also boost revenues since apart from the franchise fees WFM could record revenues from management fees, while expanding and enhancing its brand recognition and reputation globally. The later could serve as a first step for further expansion to unknown markets, and when the necessary market experience is gained WFM could launched wholly-owned or partnership stores.
Conclusion
WFM has managed over time to grow and create valuable bonds with suppliers and customers. Its strategic plan implementation is successful and in market and financial terms while keeping in line with its core values and mission. However, there are weakness to be addressed, threats to be proactively responded and opportunities to be exploited in order for the company to continue to prosper and improving.
References
Al-Araki, M. (2013). SWOT analysis revisited through PEAK-framework. Journal Of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 25(3), 615-625. doi:10.3233/IFS-120668 (Al- Araki, 2013)
Dobbs, M. (2014). Guidelines for applying Porter’s five forces framework: a set of industry analysis templates. Competitiveness Review, 24(1), 32-45. (Dobbs, 2014)
Grundy, T. (2006). Rethinking and reinventing Michael Porter’s five forces model. Strategic Change, 15(5), 213-229. (Grundy, 2006)
Thompson, A. Peteraf, M. Gamble, J. & Strickland, A.J. (2015). Crafting and Executing Strategy: The quest for competitive advantage: Concepts and Cases (20th ed). US. McGraw Hill
Wage and Hour Division (WHD). (2009). Retrieved from United States Department of Labor: https://www.dol.gov/whd/regs/compliance/whdfs2.htm
Whole Foods Market. (2012). 2014 Annual Report and Proxy Statement. Retrieved from: https://www.wholefoodsmarket.com/sites/default/files/media/Global/Company%20Info/PDFs/2012-WFM_Annual_Report.pdf
Whole Foods Market. (2013). 2013 Annual Report and Proxy Statement. Retrieved from: http://www.annualreports.com/HostedData/AnnualReportArchive/w/NASDAQ_WFM_2013.pdff
Whole Foods Market. (2014). 2014 Annual Report and Proxy Statement. Retrieved from: http://s21.q4cdn.com/118642233/files/doc_financials/2014/annual/2014-WFM-10K.pdf
Yuksel, I. (2012). Developing a multi-criteria decision making model for PESTEL analysis. International Journal of Business and Management, 7(24), 52.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Business Analysis"
Business Analysis is a research discipline that looks to identify business needs and recommend solutions to problems within a business. Providing solutions to identified problems enables change management and may include changes to things such as systems, process, organisational structure etc.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




