Survey of Data Breaches
Info: 7667 words (31 pages) Dissertation
Published: 23rd Feb 2022
Tagged: Cyber Security
Abstract
Data breaches are a significant part of our everyday lives and understanding their legal and financial impact is important. Data breaches have significant negative impacts on both the organizations that are breached, and the users that have affected data. Reputation of the organization is also something that can take a hit when large data breaches are publicized. There are a variety of methods which attackers can use to breach systems, including ransomware attacks, SQL injection attacks, Cross-Site scripting attacks, and good old fashioned social engineering manipulation among others. There are a variety of defense mechanisms which can be used to combat these attacks, but the technological arms race that is ever present ensures that when one defense is perfected, a new attack is developed. Technological growth impacts data breaches in a variety of fields such as the blockchain, cloud computing, the Internet of Things, and big data.
Keywords: IoT (Internet of Things), PII (Personally Identifiable Information), Litigation, Blockchain, Cloud Computing, Data Breach, Data Loss/Leak Prevention and Detection (DLPD)
1. Introduction
Data breaches are a relatively new phenomenon in the business world, with wide-reaching and impactful consequences. When data breaches happen, a variety of impacts are felt by the company: the reputation of the company can suffer, financial stress in terms of legal fees, lost revenue, and post-breach repair costs is inevitable, and confidence in the company’s ability to secure data in the future is damaged. A number of companies, such as Target, Uber, and Equifax, and a variety of industries, such as healthcare, education, and financial services, have been affected by data breaches in the past, and many more will be in the future.
There are a variety of negative implications for the average consumer as well. Losing sensitive information, especially financial and healthcare information, can be damaging to one’s personal safety. Identity theft can stem directly from these types of data breaches.
Defending against these types of data breaches is becoming increasingly important as more and more transactions and services take place digitally. The direction technology is growing points to heavier reliance on big data systems, meaning simply that there is more potential for data breaches to occur.
2. Implications For Corporations and Businesses
2.1 Reputational Damage
Reputational damage is a huge risk for corporations which fall victim to data breaches, especially data breaches which are publicized by the media. Research has demonstrated that up to a third of customers in healthcare, finance, and finance will fail to continue to carry on with business with companies that have been affected by data breaches [1]. Customers put lots of stake into the perceived security of a company, as they are handing over their financial and personal information [2].
2.2 Financial Issues
Any business can be threatened by cyber security vulnerabilities which could lead to possible litigation issues, which would be very expensive for the company. With new technology and the majority of businesses using the internet to collect data or sell products, cyberattacks are happening more often than ever. According to an article by SGR Law, a 2016 survey indicated a 38% increase in cyberattacks in 2014 and the average global cost of a data breach was $3.79 million, with U.S. companies was an average of $6.53 million. This specific breach took 206 days to identify and 69 days to contain it. SGR Law also states that a 2015 study found the average cost of cybercrime was $7.1 million, with U.S. companies reporting the greatest average cost at $15 million. This study found the average time to resolve the cyberattack was 46 days, with an average cost of $21,155 per day or roughly $973,130 total [3].
As technology rapidly advances, businesses and corporations must adapt and keep up with the new online era. Many organizations struggle to survive in this technologically advanced age of the internet; not only do they struggle to keep up with this technology, but they must also face compliance issues while maintaining various federal and state laws, rules and regulations dictating the compilation of private/personal data [4]
There many ways in which data breaches can victimize people around the world and depending on the breach, the victims could end up losing a big sum of money and in some cases, their identities. In May of 2000, the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) was created under the FBI in the United States to help with crime surrounding the internet. IC3 was established to organize, standardize, and categorize the types of crime that occur on the internet. This data helps navigate certain solutions towards the trending crimes for the following years. IC3 has been presented with an average of 284,000 yearly victimized complaints in the last five years. This collection of data is analyzed and is used for public awareness, to mitigate specific attacks. Table 2 describes the various types of internet crime and the average monetary loss by the victim [5].
2.3 Legal
Many people think that data breaches as a technological issue, however, these breaches must be viewed as a litigation. Every state in the U.S. has enacted a data breach notification law. This law requires a company to follow a certain protocol in response to a breach that affects that state’s residents and sometimes, other states’ involvements. All states have a certain amount of time to follow the protocol upon a data breach, for example, Vermont requires notice within 14 business days [3].
At the moment, there is no federal law which requires businesses to notify the government upon a cyber breach. Congress is considering the “Data Security and Breach Notification Act of 2015” [3]. Companies and businesses need to be aware of the possibility of these types of attacks and must secure/insure their data or data servers in order to maintain their business properly. A good idea would be to conduct cyber risk assessments under legal counsel in order to maintain attorney-client privilege. Figure 1 shows the amount of data breaches related to specific industries.
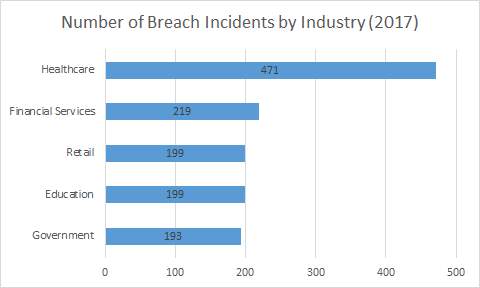
Figure 1: Breach Reports by Industry [6]
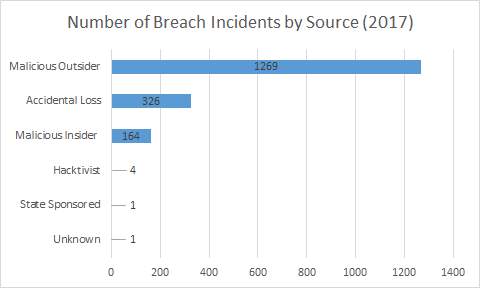
Fig. 2. Number of Breach Incidents by Source [6]
One of the biggest vulnerabilities for data breach attacks to occur would be to the medical industry, especially in the United States. Hospitals have been increasing their security ever since the malicious attack on the healthcare industry, specifically, Anthem Inc. in 2015 [7]. This breach contained 80 million individuals not only losing their protected healthcare information, but with a chance of fraud or identity theft. This attack along with the breach of Community Health Systems in 2014 prove that the medical field has the potential vulnerability of malicious hackers stealing important and private data. According to many experts, the hospital security surrounding their private healthcare information is poorly maintained [5]. If these security systems are not updated and addressed, the data breaches will only continuously increase. These attacks will threaten the financial aspect of these hospitals. Many plaintiffs may seek litigation to account for the loss of private medical information. Not only will the hospital lose financially due to the lawsuits, but they also have a federal fine attached dictated by HIPAA [7].
Hospitals store a plethora of medical and financial data, and they are bound by law to have enhanced protection of this data. The HIPAA Act (Health Information Portability and Accounting Act) requires patients to consent before giving up their medical information among different hospitals or other health agencies [8]. Both the GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act) and FCRA (Fair Credit Reporting Act) involve much more security protocols in securing individual’s credit information; many state and federal laws require correct disposal of social security numbers. “The probability of a lawsuit is positively correlated with the compromise of personal information requiring a heightened level of protection, such as Social Security numbers and financial, credit card, and medical data” [8].
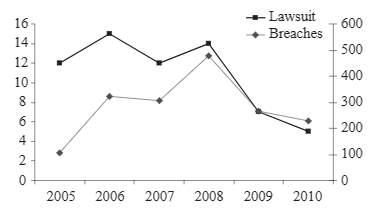
Fig. 3. Compares total data breaches with litigations [7]
The big concern is what constitutes a data breach for actual litigation. Figure 3 shows the number of data breaches versus federally-litigated breaches during 2005 to 2010. The left axis describes the number of actual lawsuits, while the right axis describes the number of reported data breaches. The biggest factor regarding the legitimacy of a data breach litigation would be the amount of harm done during the breach whether it be a financial or other malicious attack. A larger corporation has a better chance to go to a litigation because they usually have in-house attorneys that have the capability of relieving the breach or attack [8].
In 2005, the United States reported a consumer loss of around $56 billion due to identity theft resulting from corporate data breaches [8]. The current disclosure laws in the U.S. vary from state to state, however, they all have the same basic template, which require that the companies must let the public know when their private data has been lost or corrupted. Personal data usually is attributed to a person’s name as well as other identifying characteristic data such as a social security number, credit card number, passport, or driver’s license. Most notably, the law states that the notification from the corporation must be done in a timely fashion and if personal data has been breached by an unauthorized individual. A breach is defined as the “unauthorized acquisition of computerized data that compromises the security, confidentiality, or integrity of personal information maintained by the person or business” [9].
2.4 Real Life Examples
The very popular ride-hailing company, Uber signed a consent agreement with the FTC about their security system regarding customer financial information as well as driver information. Uber thought that their system was encrypted using the best technology at this time, however, their data was not secured properly. In May 2014, Uber experienced a data breach that allowed hackers to access drivers’ information including their financial and driver’s license information, and even their social security numbers [10]. Because of this breach, Uber had agreed to stop embellishing their security quality of their private data. Three years later, Uber was attacked again and failed to report it. They paid a ransom of $100,000 to keep this data from the public. The FTC became more irate as the attackers basically used the same attack method in both breaches.
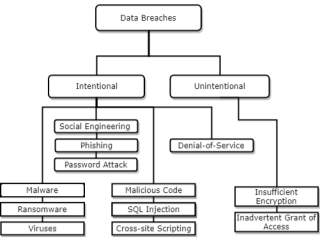
Fig. 4. Types of Data Breaches
3. Types of Data Breaches
3.1 Malware
Spam, phishing, denial of service attacks, botnets, and worms depending relies on malicious code referred to as malware. It is often used to infect computer of victims by exploiting software vulnerabilities or tricking users into running malicious code. Modern malware is becoming increasingly more complex and have been used to perform denial of service attacks and steal sensitive information [11].
3.2 Ransomware
Ransomware is a common method of attack from the evolution of malware. This kind of attack encrypts data has different levels of severity, however the most aggressive version encrypts data – making it inaccessible. The inaccessibility is permanent until a “ransom” is paid, and even then it is not guaranteed that the malicious agents will decrypt the files. Ransomware was one of the most important development in the attack landscape in 2017. Network-based ransomware worms removed the human factor when issuing an attack. Cisco expects to see many more attacks of this kind in 2018 [12].
WannaCry, a ransomware cryptoworm, spread very rapidly throughout May of 2017. It took advantage of a Microsoft Windows security vulnerability called EternalBlue that was leaked by a hacker group in April of the same year. WannaCry earned more than $143,000 US dollars through a series of bitcoin payments which is much lower than the exploit kit Angler, which earned around $100 million per year. Cisco estimates that 312 ransom payments were made. The US government and many security researcher believe the ransom component is used to hide WannaCry’s real purpose is to wipe data [36].
Before self-propagating ransomware, malware was traditionally distributed in three ways: drive-by download, email, or by physical means such as USB memory devices. All of these require human interaction to infect a device or system with ransomware [12].
3.3 SQL Injection
SQL injection attacks (SQLIA) are a common attack technique which exploits vulnerabilities in the database layer of web applications and services, most commonly against sites with dynamic content. They are listed in the Top Ten application security risks affecting organizations in 2017, and have been significant risks for the past few years [13]. Structured Query Language (SQL) is a programming language used to manage data in large databases and has been implemented in both open source and commercial databases. SQLIA utilize SQL statements designed specifically to subvert security measures in place. The attacker may wish to accomplish any of the following: bypassing authentication, co-opting, deleting, editing, or corrupting data, running arbitrary code, or gaining access to the main system [14].
Areas vulnerable to SQLIAs are called SQL injection vulnerabilities (SQLIV), and they fall into a few categories. Generally, SQLIVs exist where SQL statements do not keep statement structure and input separate [14].
- Bypassing web application authentication requirements
- Obtaining knowledge of database fingerprinting
- Injection with UNION query
- Damaging with additional injected query
- Remote execution of stored procedures
3.4 Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
In a similar vein to SQL injection attacks, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) involves injecting malicious code into a website. This time around however, the website and its data are not the target, but rather the users accessing the website. An attacker using XSS exploits vulnerable websites to interact with the users and co-opt their sensitive data [15].
There are a variety of methods for injecting malicious code into the path of a user. The most common method, however, is injecting the malicious script into the pages of a website, causing the user to inadvertently download the script from the website. While malicious scripts need not always run, the probability of them being run increases when sensitive data of the user is easily accessible. Three main types of XSS attacks steal cookies, undertake phishing attacks, and log keystroke information [15].
3.5 Social Engineering
Information security is a fast growing discipline. Security measures are becoming more and more secure as technology advances; however, people are susceptible to manipulation. The human element in security is a weak link. Social engineering targets this human element to obtain sensitive information [16].
Kevin Mitnick describes the social engineering attack cycle in his book, The art of deception: controlling the human element of security. Research is the information gathering process where information about the target is retrieved. The attacker should know as much information about the target before starting the attack[16].
Development of the rapport and trust is the next part of the process. Someone is more likely to divulge requested information to an attacker if he/she trusts the attacker. This can be accomplished by using insider information, misrepresenting an individual, referencing familiar names, asking for help, or impersonating authority [16].
The next step is exploiting trust of the target. Once the attacker obtains the trust of the victim, the attacker can ask for information or manipulate the victim into asking the victim for help [16].
The outcome of the previous phase is used/utilized to obtain the final goal of the attack or continue on with the attack [16].
Social engineering is one of the most common methods of breaching sensitive data because it focuses on the human aspect regarding data security. Phishing is one of the most common methods of social engineering occurs in emails and spam [16].
3.6 Phishing
Malicious email and spam are important aspects of malware distribution no matter how threats advance. Social engineering techniques such as phishing and malicious links and attachments are used to steal users’ credentials and sensitive data. Phishing and spear phishing emails caused some of the more notable breaching in recent times such as an attack that targeted Gmail users in 2017 and a hack of Irish energy systems [12].
Cisco threat researchers examined data from sources that investigate “phishy” emails submitted by users. Cisco found a peak of 101,934 phishing URLs in March of 2017. 59,651 of the URLS contained subdomains under aaaainformation[dot]org and also had subdomains of random strings between 50-62 letters in length. Another large spike in phishing occurred in June of 2017. The attackers used the name of a real tax agency of the United Kingdom to hide their attacks [12].
There are many types of common tactics that are used in phishing campaigns. Domain squatting is a method where domains are used to look like valid domain such as cisc0[dot]com. Domain shadowing, maliciously registered domains, URL shorteners, and subdomain services are other common methods used. Users need to be aware of the potential methods that these attackers use [12].
3.7 Password Attacks/Credential Reuse
These types of attacks prey on human nature, in a similar way that social engineering does. People know that it’s better to have robust, and varied passwords for their plethora of online accounts, but in practice this isn’t employed all that often. Once attackers have access to a list of usernames and passwords, by any of the previously mentioned cyberattack methods, they know there is a reasonable chance those passwords will be reused for other large accounts [13].
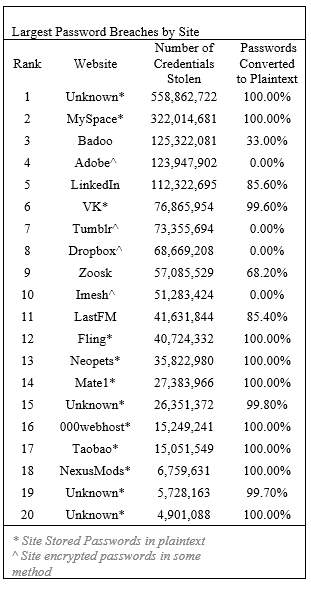
Table 1. 20 Largest Password Breaches [15]
In Figure 5, a list of large password breaches by site is shown, outlining the fact that passwords are not entirely safe. Once attackers have access to the stolen credentials, they can apply them in other locations easily.
3.8 Public Wi-Fi
Free to use public Wi-Fi is very popular in our day to day lives. Mostly every place we go has a public Wi-Fi network that anyone is allowed to use. Being able to join a Wi-Fi network can be convenient but it can also put your information at risk. Most public Wi-Fi networks do not offer much security in which the user’s activity is not encrypted so anything they do online can be tracked [18]. Public Wi-Fi uses two types of defense mechanisms to protect user’s information they are called Wireless Encryption Protocol (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). WEP was one of the first security resources used to protect wireless networking devices. This system that was and is still commonly used is weak and allows hackers to easily break into the system [18]. WPA was initially created to succeed WEP but was also found to be easily hackable and not reliable enough for the intended users. Without knowing it user’s information can be taken just by logging onto something using a public Wi-Fi network.
Rogue Wi-Fi networks also trap users into tapping into sensitive information while online using any Wi-Fi network. This type of Wi-Fi is where an attacker creates a hotspot that is open to the public where the attacker can see the conversation between the network and the unaware user [18]. Attackers can create these hotspots almost anywhere and can impersonate public or even home Wi-Fi networks. The best way for users to protect themselves is to not access personal information while on a public network and always make sure your computer’s security is up to date.
3.9 Denial-of-Service
Denial-of-Service attacks (DOS attacks) flood servers of a system with traffic, making it impossible for legitimate users to access websites, applications, or other resources. Often times, these types of attacks are used as a form or ransom, preventing use of the system until a price is paid. They can also serve as a distraction; something for the IT department to deal with as the actual data collection is done unhindered [19].
The term DOS attack often refers to an attack done by a single computer. The term DDOS attack, standing for Distributed Denial-of-Service attack, refers to a large scale attack done by many computers, organized in a botnet, oftentimes placed around the world. These are even harder to defend against simply due to overall volume of interference [19].
4. Personal Implications
4.1 Financial and legal
Financial issues are some of the most pervasive and destructive problems that can occur due to a data breach. In the world today, finances are a major part of people’s lives, and have yearlong implications. Most everything circles back to an individual’s credit score (in the US.) Credit scores affect a person’s ability to receive credit for a loan, or their interest rates – clearly a large factor into whether or not a person is able to keep their finances in order. A stolen identity will cause major issues. An identity thief can use PII to open lines of credit in the victim’s name. While this won’t directly come out of the victim’s bank or immediate finances, this will affect their credit score. If this isn’t noticed right away, long term damages can be done. If a credit score tanks, victims can no longer open up new lines of credit, or receive a favorable interest rate. There are other consequences however. Breached data can give people direct access to banks, investments and other financial resources used by a victim. While getting a credit score fixed is a long process and a major hassle, it can be done. But when bank access is used and money is stolen, that is much harder to get back. All of these can cause major headaches for a victim for years [20].
When thinking about a major financial leak, the Equifax and Target breaches are probably first and foremost in the mind. In the Equifax breach in September of 2017, roughly 147.9 million Americans data was released. This included peoples credit scores, birth dates, addresses and driver’s license numbers, as well as other PII were breached [21]. This information alone can be incredibly damaging to a person’s finances. However, it all being released at once is a major issue as access to resources can be achieved with what was released or just missing some information that would be easily accessible from other sites like social media targets breach was another issue. In 2013 about 110 million peoples credit card information as well as other PII was taken [20]. This was problematic, as hackers could use this information to make purchase using victims’ payment information.
When a consumer’s data is breached and their identity is stolen, there are a few legal concerns and avenues that they need to know about. If the information came from a large data breach, there is a good chance that there will be some sort of class action lawsuit or other legal action against the offending company. However, victims do have to watch out for legal issues such as bankruptcy and potential creditors coming after them for collections.
4.2 Security
Personal safety is an area of major concern with data breaches. Password protection is one of the most important cornerstones of cyber security. Improperly hashed passwords can lead to large numbers of credentials being stolen.
With stolen credentials, passwords to a number of sites are in jeopardy, as according to a survey conducted by in 2017 revealed, that 81% of Americans reused passwords across multiple accounts [22]. With this in mind, a lot of data is at risk for exposure. It may be benign information, but the fact of the matter is that there is other data at risk to be taken. When companies or organizations store passwords in plaintext, or fail to encrypt it securely, it can lead to these sort of breaches.
Another concern is the idea of personal safety. PII can be used to locate an individual for whatever, including malicious, reasons. In 2014, a group linked to the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS) released information retrieved from Facebook and other social media sites to create a “hit list” on military members [23]. While this information wasn’t from a data breach – it does signify the type of data that is of concern for breaches and other uses.
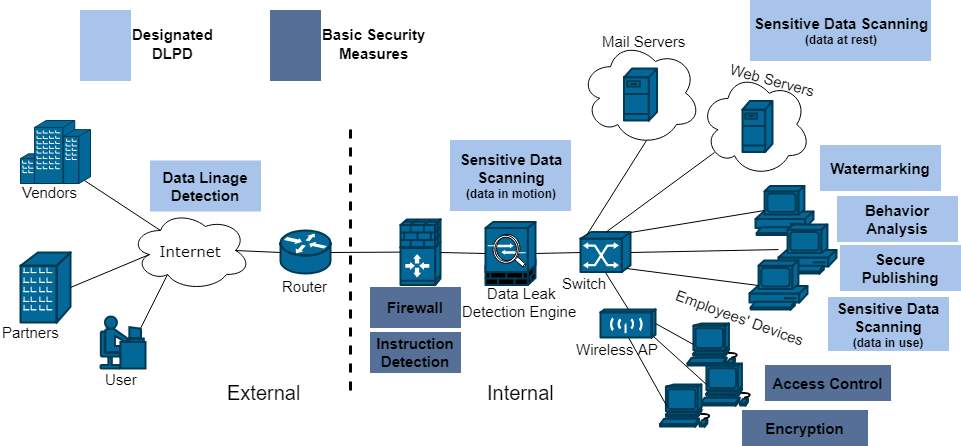
Fig. 5. DLPD Techniques [24]
5. Defense Mechanisms
Defense mechanisms are becoming increasingly important; no longer are they simply a luxury, they are a necessity in the current technological climate. Anonymous threats pop up every single day. Defending from cyberattacks will become more difficult as technology advances as well [24].
Companies have a vested interest in finding solutions to defense issues. For example, Google offers $10,000 rewards for penetration testers who identify vulnerabilities to SQL Injection and Cross-Site Scripting attacks. By paying attackers to find weaknesses, problems can be fixed and potential data breaches, disastrous for a data giant like Google, can be avoided [25].
The most basic defenses against data breaches are firewalls, intrusion detection, and anti-virus software. Firewalls limit access from external networks, but doesn’t monitor the status of internal networks. That is the job of intrusion detection, which detects inbound and outbound network activity in order to monitor for hacking. Anti-virus software is necessary for detecting and repairing virus-infected files. Also, at the minimum, data must be encrypted. It is a relatively simple technology, but one of the most effective for protecting mass amounts of data. Using an algorithm, data is transformed into unintelligible gibberish which can’t be decoded without the key [26].
Data Leak Prevention and Detection (DLPD) systems are workplace surveillance systems specifically designed to deal with data leakage threats. They are designed to detect, monitor, and prevent both accidental and deliberate exposure of data. They can be divided into two subgroups: content-based analysis, and context-based analysis. Content based analysis is based on the contents of the data, to prevent the unwanted exposure of information. Data fingerprinting, looking for keywords, is a common method of accomplishing this task. Context based analysis performs contextual analysis on metadata associated with monitored data. They look for look for users’ access patterns and tendencies and alert the system of intruders when the patterns don’t match [27].
Both content based and context based algorithms increasingly use machine learning to assist with their tasks. Neural networks can learn which information is sensitive and requires protection. Machine learning is able to increase the speed and accuracy with which this sensitive data is located and protected. This will become increasingly important in the coming years as big data becomes more of a force in our lives [27].
Having good data handling measures is also necessary for defense against data breaches. Social engineering, which involves tricking or otherwise coercing authorized people into revealing sensitive data, is a major factor data security but is often overlooked or forgotten. This works because it’s easy to appeal to people’s emotions. It may sound laughable, but these emotional vulnerabilities can open up the potential for data breaches. Companies need to have coherent methods for handling secure data in place. [26].
Dealing with data security as it is allocated to third parties is also risky and comes with its own set of challenges. When more people are involved, there is more chance that the date will be leaked. Ideally, handing over data to people who might leak it wouldn’t be necessary, but usually there will be a risky element. Using models, the likelihood of a leak appearing and the ability to trace it can be determined. Data allocation can be used to help identify the probability of these leaks [28].
6. Impacts on Technological Growth
As technology continues to grow the impact of data breaches remains a problem that requires continual monitoring. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a source that many people use on a day to day bases. It connects physical devices together into one network. Security plays a big role when looking into the IoT. This network holds personal data about items such as household appliances, cell phones and any other electronic device that connects to a network in order to exchange data [29]. The IoT is a continually changing network and can be complicated to understand. In order to protect the information within it, this complicated network needs to be understood.
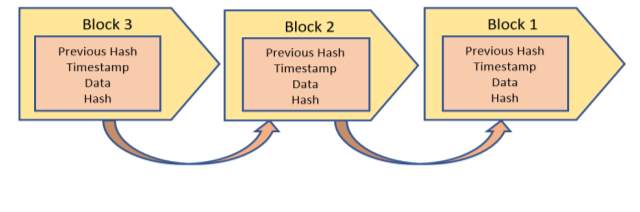
Fig. 6. Blockchain Flowchart
The main developments within the IoT include big data and Blockchain. Blockchain is the source of cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency miners use mining software to solve complex cryptographic problems/puzzles and are rewarded a certain number of “coins”. When a transaction occurs it is recorded and grouped with other similar, recent transactions called a block. The block is protected and sent to the network allowing miners to validate the transactions and receive cryptocurrency.
The blocks are time stamped and added to the existing chain of transaction blocks. These concepts are the main concern within the growing interest of the Internet of Things. The IoT is not the only growing technology to be of concern in the world today [29].
Cloud computing is another ever growing source that people use on a regular bases to store information. The users information is stored completely on the web and is send to a server farm and held by companies such as Google, Microsoft and other similar suppliers [30]. The cloud can be used by organizations or personal user to access information from any computer or server that is connected to the internet. The cloud can be split into three separate categories; Private Cloud, Public Cloud, and Hybrid Cloud [30]. The Private Cloud is for personal use, or organizational use and does not allow the public to access the information within it. The Public Cloud can be accessed by anyone and used at any location. The Hybrid Cloud is a mix between the Public and Private cloud. When the Private Cloud needs access to information it obtains it from the Public Cloud. Organizations can pick which cloud best suits their needs and use it to store information used within that company. Many people use cloud computing because it allows easy access and it can be used almost anywhere internet is available [31].
Cloud computing has many advantages but is still susceptible to data breaches. This occurs when a user’s information is access, used, or even viewed by users who were not allowed use by the intended users [32]. Personal information and vital information from companies can be taken without knowledge. This can create huge problems for the users whose information was taken. Credit card numbers, social security numbers, and other vital information about companies can be released and obtained by malicious users. Security in cloud computing can cause huge issues but it continues to be used and is a growing technology that we all know of today.
7. Recommended Solutions
As data breaches will always be a part of the technological world, there aren’t any real long-term solutions to end all problems. Instead, there will be a variety of preventative defences mechanisms, as previously discussed earlier in the paper, changing as technology changes. Ensuring that simple measures such as making sure to keep up firewalls and virus detection software to prevent hackers form obtaining passwords or account numbers are in place is the baseline, but much more than that needs to be done.
Quantum computing will influence data breaches in the future. Most websites have some sort of common encryptions that appear on forms. These encryptions are known as SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates. Currently, they contain a 4096-bit RSA algorithm, which is used for two-way decryption. Decrypting this key would be difficult with a regular computer, however, a quantum computer could do it in a timely manner. This could pose a threat for all current available websites which use this type of encryption. The solution to this problem would be to use quantum computing as a form of encryption to strengthen security. I think that as the quantum computers develop and become available for consumers, the quantum processing will be integrated into the cryptography.
8. Conclusion
Data breaches can impact businesses around the world and can damage their reputations forever. With these new types of attacks data and important information can be taken with little to no awareness. Once a data breach occurs a company takes on many types of impacts. These include personal financial burdens with legal fees, a loss in revenue and it can even cause the company to go under. Several big name companies have experienced this kind of new security breach and know the devastating loss it can cause.
Companies are not the only ones who lose valuable information when a data breach occurs. Consumers also can be impacted, when a company’s data gets breached consumers credit card information, social security number, and other personal information can be taken. Identities being stolen is a huge implication of data being breached.
Phishing attempts are a common type of data breach that many people are susceptible to everyday. Hackers use emails that entice users to click on a link or give out passwords. These types of data breaches can trick many people into giving out information without thinking twice about it. Password attacks and credential reuse can also cause users information to be vulnerable. By not creating unique passwords for every source an attacker can easily find and use these passwords to get into the sources and obtain sensitive information.
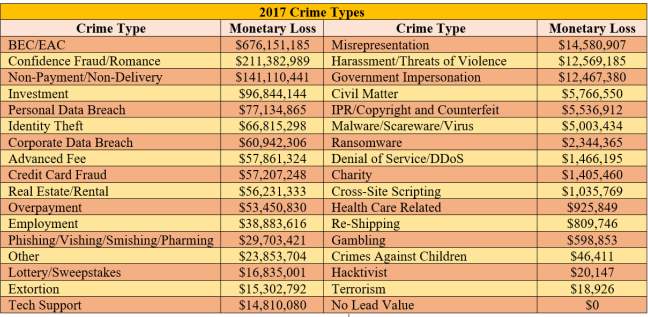
Table 2. Monetary Value of Cybercrimes [5] [33]
Malware, ransomware, SQL injections, cross-site scripting are all types of data breaches that can occur. Malware can directly affect a user’s computer and exploit software vulnerabilities. Ransomware is an evolution of malware and just goes to show that attackers use other approaches to evolve in order to get around security methods. SQL injections exploit vulnerable areas within database layers of web applications. Cross-site scripting is similar to SQL injections and is used to inject malicious code within a website. With this the website is not the user at risk it is the person that is clicking into things while using the website that has the malicious code within it. Data breaches can also happen by just logging onto a Wi-Fi network.
Free public Wi-Fi can be unsecure and allows hacker access to activity that is non-encrypted. Social engineering is also becoming more popular and allows hackers information based on the manipulation of human beings. In this case attackers use as much information about a person or company as possible in order to trick them into clicking or giving out sensitive information. Hacker live off of these methods of obtaining personal data and with technology growing data breaches will continue to cause financial heartbreak within companies and even personal users.
All of these things make it risky to store information usng technology and as easy as it is to use technology the safet of a consumer’s information should be kept the number on goal. Defense mechanisms are in place in order to protec personal information that a companies have obtained from purchases and medical data stored in their systems. Technology is continually changing and defending against data breaches is becoming more important than ever. The cost of data breaches can cause companies and people to be in debt for long periods of time. With the ever changing technology we have today data breaches are becoming a major problem and if security is not put at the forefront in securing consumers information many people will continue to lose personal information without even knowing it.
9. References
[1] H. Baginska, “What Happens After a Business Data Breach? | Pivotal Payments”, Pivotalpayments.com, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.pivotalpayments.com/blog/credit-card-processing/what-happens-after-a-business-data-breach. [Accessed: 05- May- 2018].
[2] N. Ismail, “The financial impact of data breaches is just the beginning”, Information Age, 2018. [Online]. Available: http://www.information-age.com/data-breaches-financial-impact-123470254/. [Accessed: 05- May- 2018].
[3] M. Ernst, “Data Breaches – SGR Law”, Sgrlaw.com, 2018. [Online]. Available: http://www.sgrlaw.com/ttl-articles/data-breaches/. [Accessed: 04- May- 2018].
[4] S. Talesh, “Data Breach, Privacy, and Cyber Insurance: How Insurance Companies Act as “Compliance Managers” for Businesses”, Law & Social Inquiry, 2017.
[5] Federal Bureau of Investigation. (2017). Internet Crime Report. Available at https://pdf.ic3.gov/2017_IC3Report.pdf
[6] The Year of Internal Threats and Accidental Data Breaches. (2018). [ebook] Gemalto. Available at: https://breachlevelindex.com/assets/Breach-Level-Index-Report-2017-Gemalto.pdf [Accessed 9 May 2018].
[7] T. Floyd, M. Grieco and E. F. Reid, “Mining hospital data breach records: Cyber threats to U.S. hospitals,” 2016 IEEE Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics (ISI), Tucson, AZ, 2016, pp. 43-48.
[8] S. Romanosky, D. Hoffman, and A. Acquisti,“Empirical Analysis of Data Breach Litigation,” Journal of Empirical Legal Studies, 11(1), pp.74-104. 2014.
[9] S. Romanosky, R. Telang and A. Acquisti, “Do data breach disclosure laws reduce identity theft?”, Journal of Policy Analysis and Management, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 256-286, 2011.
[10] R. Charette, “FTC Puts Uber on a Short Leash for Security Breaches”, IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://spectrum.ieee.org/riskfactor/computing/software/ftc-puts-uber-on-a-privacy-and-security-choke-chain. [Accessed: 04- May- 2018].
[11] M. Bailey, J. Oberheide, J. Andersen , Z.M. Mao , F. Jahanian, J. Nazario (2007) Automated Classification and Analysis of Internet Malware. In: Kruegel C., Lippmann R., Clark A. (eds) Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection. RAID 2007.
[12] Cisco. (2018). 2018 Cisco Annual Cybersecurity Report. Available at: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/m/digital/elq-cmcglobal/witb/acr2018/acr2018final.pdf
[13] Rapid7. (2018). The Most Common Types of Cyber Security Attacks | Rapid7. [online] Available at: https://www.rapid7.com/fundamentals/types-of-attacks/ [Accessed 9 May 2018].
[14] S. Sajjadi, and B. Tajalli Pour. (2013). Study of SQL Injection Attacks and Countermeasures. International Journal of Computer and Communication Engineering, pp.539-542.
[15] S. Gupta and B. Gupta. (2015). Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks and defense mechanisms: classification and state-of-the-art. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 8(S1), pp.512-530.
[16] F. Mouton, M. M. Malan, L. Leenen and H. S. Venter, “Social engineering attack framework,” 2014 Information Security for South Africa, Johannesburg, 2014, pp. 1-9.
[17] K. Thomas, et al. “Data Breaches, Phishing, or Malware? Understanding the Risks of Stolen Credentials”, Static.googleusercontent.com, 2017. [Online]. Available: https://static.googleusercontent.com/media/research.google.com/en//pubs/archive/46437.pdf. [Accessed: 04- May- 2018].
[18] “Public Wi-Fi Security 101: What Makes Public Wi-Fi Vulnerable To Attack And How To Stay Safe”, Us.norton.com, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://us.norton.com/internetsecurity-wifi-public-wi-fi-security-101-what-makes-public-wi-fi-vulnerable-to-attack-and-how-to-stay-safe.html. [Accessed: 08- May- 2018].
[19] Desai, S., Hadule, P. and Dudhgaonkar, P. (2018). Denial of Service Attack Defense Techniques. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(10).
[20] R. Abrams, “Target to Pay $18.5 Million to 47 States in Security Breach Settlement”, Nytimes.com, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.nytimes.com/2017/05/23/business/target-security-breach-settlement.html. [Accessed: 04- May- 2018].
[21] J. Dickler, “In the Wake of the Equifax Data Breach, Consumers more at Risk”, CNBC, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.cnbc.com/2018/03/10/in-the-wake-of-the-equifax-data-breach-consumers-more-at-risk.html. [Accessed: 04- May- 2018].
[22] Secureauth.com, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.secureauth.com/sites/default/files/secureauth_ciam_infographic_170714.pdf. [Accessed: 05- May- 2018].
[23] “ISIS Targeting Military Members Via Social Media”, Identity.utexas.edu, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://identity.utexas.edu/id-perspectives/isis-targeting-military-members-via-social-media. [Accessed: 05- May- 2018].
[24] K. Thakur, M. Ali, N. Jiang and M. Qiu, “Impact of Cyber-Attacks on Critical Infrastructure – IEEE Conference Publication”, Ieeexplore.ieee.org, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7502286. [Accessed: 04- May- 2018].
[25] Abela, R. (2018). An XSS Vulnerability is Worth up to $10,000 According to Google. [online] Netsparker.com. Available at: https://www.netsparker.com/blog/web-security/google-increase-reward-vulnerability-program-xss/ [Accessed 9 May 2018].
[26] C. Phua, “Protecting organisations from personal data breaches”, Computer Fraud & Security, vol. 2009, no. 1, pp. 13-18, 2009.
[27] L. Cheng, F. Liu and D. Yao, “Enterprise data breach: causes, challenges, prevention, and future directions”, Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, vol. 7, no. 5, p. e1211, 2017.
[28] P. Papadimitriou and H. Garcia-Molina, “Data Leakage Detection,” in IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 51-63, Jan. 2011.
[29] N. Fabiano, “Internet of Things and Blockchain: Legal Issues and Privacy. The Challenge for a Privacy Standard,” IEEE Conference Publication. 2018. [online] Ieeexplore.ieee.org. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8276831 [Accessed 4 May 2018].
[30] Barona, R. and Anita, E. (2018). “A survey on data breach challenges in cloud computing security: Issues and threats” – IEEE Conference Publication. [online] Ieeexplore.ieee.org. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8074287 [Accessed 4 May 2018].
[31] S. Subashini and V. Kavitha, “A survey on security issues in service delivery models of cloud computing”, Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 1-11, 2011.
[32] Y. Rahulamathavan, M. Rajarajan, O. F. Rana, M. S. Awan, P. Burnap and S. K. Das, “Assessing Data Breach Risk in Cloud Systems,” 2015 IEEE 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing Technology and Science (CloudCom), Vancouver, BC, 2015, pp. 363-370.
[33] Acunetix. (2018). The ROI of Protecting Against Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) – Acunetix. [online] Available at: https://www.acunetix.com/blog/articles/return-on-investment-protecting-cross-site-scripting/ [Accessed 9 May 2018].
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Cyber Security"
Cyber security refers to technologies and practices undertaken to protect electronics systems and devices including computers, networks, smartphones, and the data they hold, from malicious damage, theft or exploitation.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




