Is There Truly an Employee Engagement and Patient Satisfaction Link?
Info: 7785 words (31 pages) Dissertation
Published: 23rd Feb 2022
Table of Contents
Click to expand Table of Contents
Project Description
Introduction
Purpose
Main Problem:
Examined and Covered Objectives
Out of scope
Significance of the Study
Significance to Author
Significance to the Healthcare Organization
Broader Implications
Organizational Overview
Identification and Discussion of Issues
What is employee engagement and why is it important?
What strategies can healthcare leaders employ to improve employee engagement and what are the benefits?
Is Engagement and Patient Satisfaction Closely Linked?
Steps Taken to Obtain Data
PROJECT SOLUTION
Information and Literature Review
Reasons for Disengagement
Responsibility of Leadership
Is There Truly an Employee Engagement and Patient Satisfaction Link?
Analysis of Key Issues
Strategies
Link
Recommendations and Conclusion
References
Appendices
Project Description
Introduction
Employee engagement is important in all industries. Motivated employees perform their best to contribute to an organization’s profitability. When the organization such as those within the healthcare field directly service customers or patients, the employee’s level of engagement can potentially have an impact on the patient’s level of satisfaction and their overall experience within the organization. Based on studies conducted by sources such as Press Ganey and other analyses, this paper will review employee satisfaction and why engagement is important, what healthcare leadership can and should do to improve employee engagement, and whether there is a direct link between employee engagement and patient satisfaction.
When conducting the research, it was not only important to obtain information from studies conducted across various health systems like Crittenton Hospital Medical Center, as a method for understanding what trends are occurring across the healthcare industry, personal experiences of the author and other healthcare leaders within Cleveland Clinic were included to show whether there is a consistent viewpoint between these studies performed by outside sources and an internal perspective. The analysis reveals that employees drive the experience of the patients, and if employees are disengaged, their lack of engagement is reflected in their behaviors and interactions. As a result, healthcare leaders must understand the causes of disengagement and employ the best practices for creating a positive work environment and higher standards of care. Lastly, the author will provide recommendations for what healthcare leaders should do to address disengagement within the hospital system and how to improve the patient experience when low employee engagement is identified.
Purpose
The purpose of this paper will be to explore whether employee engagement in the healthcare industry has an impact on patient experience. Everyday caregivers in the healthcare industry come to work not realizing their work plays a critical role in the way patients perceive their experience with that hospital or clinic. Whether a receptionist, nurse, or physician each caregiver must put forth effort and have a personal interest in the work they do. When there is disengagement between caregivers and their work, this is portrayed in various ways and can potentially cause patients and visitors to feel unwelcome or this disconnect can possibly result in poor patient care. Through research, this study will discuss the impact disengaged employees can have on the overall performance of a hospital system such as Cleveland Clinic, specifically the experience these employees create for those entering its facilities each minute or hour of the day.
Main Problem
For many hospital systems such as Cleveland Clinic, measuring and understanding its staff’s level of engagement is vital to understanding the “why” behind the patient’s perception of their visit. When its employees, also known as “caregivers”, are disengaged and not performing to the best of their ability, this is often shown in the way patients and visitors are treated. Reasons for disengagement stem from being overwhelmed with their workloads is caused by inefficient workflows, or there are people in positions who are not the best fit for providing the level of service that is required to take care of the sick (Rohario et. al, (2016). Lastly, when caregivers feel unappreciated by leadership, employees lack the drive to perform well.
It is common for healthcare leaders to focus on things such as aesthetics or offering additional services as a potential means for improving the patient’s experience. However, to help healthcare leaders truly understand the drivers for improving patient satisfaction, the focus will be on the most visible factor, the caregiver and patient interactions that result from engaged or disengaged employees.
Examined and Covered Objectives
While there are many factors which can influence a patient’s experience. The objectives this case study will specifically examine are ways healthcare leadership can stay in tune with employee engagement levels. The study will review whether there is a specific group of employees whose level of engagement matter most for patients, what steps healthcare leaders can take to improve employee engagement and lastly, the overall impact of employee engagement on patient satisfaction.
Out of scope
While it is proven that employee engagement also has an impact on clinical outcomes, this study will not include patient care impacts because of low physician or registered nurse (RN) engagement.
Significance of the Study
Significance to Author
As a healthcare leader within Cleveland Clinic, I have observed the differences between those caregivers who are engaged employees versus those are disengaged. Employees who fail to demonstrate care and compassion in their work negatively impact the work environment. This disconnect and lack of interest typically spreads or causes resentment and conflict amongst those coworkers who are engaged and want to do their jobs well. When there is conflict in a work environment this is not only observed internally, patients are also witness to the behaviors and lack of teamwork, and potentially lose confidence in the care they receive.
Additionally, disengaged employees cause negative experiences for patients. High-quality patient experience depends on the compassion, dedication, and skills of hospital employees. When healthcare employees lack care and concern about their performance level, they typically do not provide friendly, empathetic, and compassionate interactions that are necessary for this field. In most situations, patients are visiting healthcare organizations, not because they choose to, but because there is a need for them to receive care or treatment for a disease or illness. When patient interactions with healthcare employees are negative they either decide to leave the hospital system and transfer their care elsewhere, disregard the need for care, or rate their experiences poorly.
Significance to the Healthcare Organization
When patients come to the Cleveland Clinic they expect to receive “World Class” care as well as “World Class” service. During a patient’s healthcare experience, they expect to feel respected, valued and heard, when the level of care and service fail to meet their standards, these negative interactions are shared with others. According to Kruse, patients will tell nine to fifteen people about their negative experience with a healthcare system but will report their positive experience only 20 percent of the time (www.forbes.com). This negative ‘word-of-mouth” publicity can deter other patients from choosing a healthcare system unless there is an absolute need.
Moreover, when patients observe or experience negative interactions with disengaged employees, they are more susceptible to rating the healthcare system poorly on the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey. The HCAHPS survey is a standardized data collection methodology for measuring patient’s perspectives on hospital care (www.hcahpsonline.org). Many hospitals including Cleveland Clinic use this survey to obtain feedback from patients on their entire experience from the time they call in to make an appointment through the care experience they receive from the healthcare provider. This information is used by healthcare executives and leaders within Cleveland Clinic to identify the organization’s areas of opportunity according to the patient’s experience during their most recent visit.
With the enactment of the healthcare reform law in 2010, this law brought a focus to patient satisfaction, provider-preventable conditions, and re-admission rates (www.cms.gov, 2018). Healthcare systems were now obligated to focus on delivering high-quality service and receiving high patient satisfaction ratings on their organization’s HCAHPS scores. If those patients surveyed on their experience score the system poorly, hospitals are liable to lose or receive lower amounts of service reimbursements, ultimately impacting the organization’s bottom line. Therefore, hospital leaders must dig deeply to identify the root cause of its employees’ engagement.
Broader Implications
Having employees who are disengaged is a grave concern for management. Disengaged employees are one of the most important concerns because of its impact on various hospital metrics. For health systems such as the Cleveland Clinic the main metrics besides safety and access that healthcare leaders and management focus on are employee engagement and patient satisfaction. Since 2009, when the health system began using the HCAPHS assessment to survey patients, leadership has closely analyzed its patient satisfaction scores as well as verbatim comments provided within the survey to determine main reasons for their dissatisfaction. When looking at various segments of the patient’s experience throughout their visit, often higher percentages of dissatisfaction were related to their interactions with front office staff or medical assistants or their observations of a lack of teamwork.
According to data obtained by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) through the implementation of the HCAHPS survey, this isn’t just a local issue. Healthcare organizations nationally are performing below expectations and providing sub-par levels of customer service. Because of this many organizations, hospitals and medical associations, consumer groups, and government all share an interest in improving hospital quality and have created incentives to not only participate in HCAHPS, but also to provide high-quality customer service (www.cms.gov, 2018). For example, hospitals subject to the Inpatient Prospective Payment System (IPPS) annual payment provisions who fail to collect and submit HCAPHS data risk receiving a reduced annual payment update, and the Affordable Care Act includes this survey data to calculate value-based incentive payments (www.cms.gov, 2018). Knowing what the stakes are and what is at risk, healthcare organizations are taking a deeper dive into the data to determine what is needed to “move the needle”, and the telling story points to improving the engagement of the healthcare staff.
Organizational Overview
Healthcare is a thriving industry. At some point in time every person has a need to seek preventive, remedial, or diagnostic services from medical providers. Cleveland Clinic, a non-profit organization founded in 1921, has always worked to carry out its mission of “Better care of the sick, investigation into their problems, and further education of those who serve” (www.clevelandclinic.org, 2018). Located in the heart of Cleveland, the health system has seventeen community hospitals, 145 health centers, and 45 Express Care and emergency departments. Over the years, the health system has grown seeing over seven million visits per year (www.clevelandclinic.org, 2018). Cleveland Clinic is not only become the top employer in the Cleveland area, but has become a globally renowned, academic health system, nationally ranking amongst the top 3 hospitals according to U.S. News & World Reports, for various services which it provides.
As a result of Cleveland Clinic’s forward-thinking, innovations, integration of healthcare with research and education, and highly qualified medical staff many are familiar with the health system’s commitment to providing “World Class Care”. The hospital system has initiated open-heart surgery, face-transplants, and other breakthrough discoveries. However, although many patients are willing to travel hundreds of miles to receive what many perceive to be the best care in the world, there are many more who have not shared such positive sentiments for its level of customer service. As patients visit Cleveland Clinic’s various facilities to seek care or to accompany a friend or loved one, the last thing one expects to encounter is a rude or unfriendly healthcare employee who lacks compassion and is inattentive to their needs.
When Cleveland Clinic began using the HCAPHS survey to gather feedback on their patient’s experience, there was a large disparity between how patients rated their interactions with the hospital’s caregivers versus their rating on the care they received. Because of the organization’s commitment to its guiding principles of Quality, Innovation, Teamwork, Service, Integrity, and Compassion, executive leadership understood the importance of identifying and understanding the reasons why patient experience ratings were not in line with the level of customer service the organization thought caregivers were providing. Additionally, executive leaders were aware of the resulting impact that would affect the organization’s profitability.
Simultaneously, through use of the Press Ganey survey, Cleveland Clinic was also measuring the level of engagement of its caregivers; looking at engagement levels of those holding a physician or provider-level position down to the organization’s front-line staff. With the charge to do more with less, the focus was on improving productivity because of the Healthcare Reform Act, which would give many more individuals access to healthcare. However, such pressure in addition to new initiatives, and constantly changing priorities can create added stressors to an already highly- stressful and overworked employee population causing high levels of disengagement (Costello, 2002). This misalignment between the company’s mission to provide great service and the caregiver’s willingness or want to perform at this level were reflected in both the HCAPHs and Caregiver Engagement survey results.
There are many factors which can influence a patient’s level of satisfaction, however, research conducted by Crittenton Hospital Medical Center shows there is a strong correlation between highly engaged employees and high levels of patient satisfaction. (“Nurturing Employee Partnerships”, 2012, p. 9) For executive leadership and management, understanding the key drivers of disengagement is critical. It is the organization’s employees who ultimately have an influence on the attitudes and behaviors of its patients. If managers are ignorant or fail to learn the root cause of their employees’ disengagement, this can result in various negative outcomes. Analyzing and discovering the reasons for disengagement can help healthcare leaders develop methodologies for improving employee satisfaction.
Identification and Discussion of Issues
Employee engagement is not simply about making an organization’s workforce satisfied or happy with the work they do. Satisfaction and engagement cannot be used synonymously, because an employee can be satisfied with coming to work each day but doing the bare minimum level of work. When healthcare leadership fail to acknowledge the reasons for disengagement it is a disservice for both the organization’s patients and its employees. As a leader, it is one’s responsibility to help foster a loyal, engaged, and productive team because the needs of the employees are of primary importance. According to Bateman and Snell (2015), the servant- leader’s relationship with employees is more like that of servicing customers…it is a way of relating to others to serve their needs and enhance their personal growth while strengthening the organization” (p.455). But what causes employee disengagement and why are there individuals who are more engaged than others? This isn’t an easy question, and organizations are spending significant amounts of money and resources to better understand this using employee feedback surveys. Failure to learn the reasons for employees’ disengagement causes missed opportunities to improve their quality of work which can impact the level of service provided to an organization’s customers or in this case their patients.
What is employee engagement and why is it important?
Employee engagement is measured by the level of motivation and effort one puts forth in their work. According to the author, an engaged employee cares not only about personally doing a good job but is committed to their organization’s success. There is a sense of empowerment and enthusiasm to do what is right and achieve the best possible results. These employees propel innovation that help the organization move forward. After understanding employee engagement, it is also important to recognize the linkage between an engaged employee and patient satisfaction, among other organizational metrics. For healthcare organizations like Cleveland Clinic who are committed to continuous improvement, employee engagement and patient satisfaction is a top priority, and many studies conducted by Press Ganey have shown that employee engagement and their commitment influence patient satisfaction and ultimately organizational growth.
Strategies to Improve Engagement and the Benefits
Many organizations have taken a strong interest in gauging and tracking their employees’ level of engagement. With the assistance of such companies such as Gallup, Cleveland Clinic uses its services to survey its caregivers and measures the engagement data on a manager, department, and organizational levels. Leadership then conducts engagement planning sessions which help employees understand the purpose of an engagement survey and survey questions. After discussing what the results mean, leadership then uses this information to determine two to three areas where engagement levels are low and develop actions plans for making improvements within those identified areas. The action plans, however, are not created solely by leadership, it is important for the leaders to involve their staff in the creation of these plans. There are no “cookie cutter” solutions to include within these plans, it is important to obtain employee input so that the solutions are meaningful for all of those involved. Additionally, when the employees are engaged in these discussions, there is a greater chance for buy-in as processes and practices are implemented.
While it is best for leaders to obtain employee input, according to healthcare leaders from Southwest Medical Center, there are some practical measures which aid in improving employee engagement (Petaschnick, 2006). For example, employees should feel they have an opportunity to do what they do best and have a connection between their work and the company’s mission. They also want their opinions heard and want to feel like their ideas or suggestions are important and they are a part an organization. The benefits to ensuring these employee needs are met will aid in a company’s growth; when employees are happy they are more productive, generally highly motivated, and committed which aids in a customer satisfaction and a better financial performance.
Is Employee Engagement and Patient Satisfaction Closely Linked?
Within the healthcare industry, many studies show there is a direct link between employee engagement and patient satisfaction. (Trustee Health Forum, 2007). There are many characteristics for explaining employee engagement. Communication, respect and support, as well as the organizational culture, are all drivers of engagement. When employees feel there is open communication, where they can communicate with their leaders and transparency with their leaders, employees feel informed and feel their expertise is valued. Leaders must also show respect and support for their employees, this in turn, builds trust between them and their teams. This is a motivating factor because employees expect to be treated in the same manner that would be expected by leadership. An organization’s culture is key to engagement because a negative or positive culture is not only visible to those within it but can be obvious to the patients as well. Such behaviors as cooperation and teamwork (or lack thereof) are observed, and when a patient sees and is within a healthy culture with engaged employees they are more likely to return and utilize an organization’s services leading and have higher levels of satisfaction.
Steps Taken to Obtain Data
To obtain information related to this case study research was conducted via the internet to identify research studies analyzing the impact of employee engagement on patient satisfaction within the healthcare industry. A search was also conducted to identify what other healthcare organizations have done to improve their employees’ level of engagement and why improving employee engagement is important for this industry. In an effort to include leadership perspectives within the Cleveland Clinic, Donna Citizen, a Nurse Manager within the hospital was interviewed for her personal insight, and lastly, the personal experiences of the author were also included in this analysis. As a leader within Cleveland Clinic, the author has worked with both engaged and disengaged employees and have been responsible for identifying root causes for both low engagement amongst healthcare staff as well as reasons for stifled patient satisfaction scores while developing improvement methods.
PROJECT SOLUTION
Information and Literature Review
The intent of this research is to explore whether employee engagement in the healthcare industry has an impact on patient experience. Everyday caregivers in the healthcare industry come to work not realizing the work they do plays a critical role in the way patients perceive their experience with that hospital or clinic. Whether a receptionist, nurse, or physician each caregiver must put forth effort and have a personal interest in the work they do. When there is disengagement between caregivers and their work, this is portrayed in various ways and causes patients and visitors to feel unwelcome or this disconnect can result in poor patient care.
According to 2013 research performed by Aon Hewitt a human capital and management consulting service, 40 percent of healthcare employees are “passive or actively disengaged” compared to 30 percent in the overall workforce as noted by Gallup’s “State of The American Workplace” (beckershospitalreview.com, 2014). These statistics are astounding as it is the healthcare employees who drive a patient’s experience when visiting a healthcare organization. If employees are disengaged and unhappy, these attitudes and behaviors are reflected in their interactions and quality of work. In a case study using 29,000 healthcare employees, surveys revealed only thirty-eight percent of disengaged employees displayed a genuinely caring attitude toward patients (educationhealthcaresource.com, 2014). Positive and compassionate behaviors are necessary when dealing with a population who in many instances would prefer to be elsewhere and have no other choice than being hospitalized.
Reasons for Disengagement
Having employees who are disengaged is a grave concern for management. Disengaged employees are one of the most important concerns because of its impact on business outcomes. If managers are ignorant or fail to learn the root cause of their employees’ disengagement, one factor present would be a negative effect on the overall work environment. This disconnect and lack of interest in one’s work typically spreads or causes resentment and animosity in those around them who want to do their jobs well. Additionally, when healthcare employees lack concern about their performance level, they typically do not provide friendly, empathetic, and compassionate interactions that are necessary for this field, which in turn affects patient satisfaction.
The research suggests a few reasons for this disengagement: lack of organizational commitment, and exclusion or lack of participation. When there is a lack of commitment, there is an impact on outcomes such as patient satisfaction. The results from a study published by the Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology noted organizational commitment had a more persistent influence at the business level, which suggests that job attitudes precede outcomes and that leaders should aim to improve job attitudes in order to boost performance (Kruse, 2014). But there is a foundation that must be built to have a highly engaged staff. To name a few, an organization must have the right people in the role, there should be opportunities for development, recognition for great work, and most importantly employees want to have a voice and participate in improvement opportunities. Recent research completed by Press Ganey shows that employees are most dissatisfied when they cannot provide input and are excluded from organizational plans as shown in Figure 1. (Kimberlain & Lindberg, 2018). Employees will gain satisfaction from processes they helped improve, and patients will ultimately benefit from a better experience.
Responsibility of Leadership
Some would question is it truly the leader’s responsibility to improve employee engagement. Patient experience is increasingly becoming a top priority for many healthcare organizations and in order to make improvements healthcare leaders must drill down to what is necessary to improve it. This is why many healthcare leaders are becoming just as committed to the engagement of their employees, those who are responsible for driving the experience of the patient. In 2017, 82 percent of hospitals identified patient experience as a top priority with 46 percent citing employee engagement as the next priority for their organization (Merisola, 2018). The increased focus in these two areas shows that healthcare leaders have an understanding and commitment to achieving positive patient experiences by having a highly engaged staff. The literature notes highly engaged staff/employees factor shows an increase of 24 percent in just a period of two years (Figure 2); healthcare leaders are seeing the correlation between employee satisfaction and a successful organization.
As a leader, it is not only one’s responsibility to focus on task performance behaviors, a leader must also take necessary actions to ensure their employees are satisfied. Bateman and Snell note, focusing on people’s feelings and comfort, showing appreciation, and stress reduction, in turn, has a strong impact on employee satisfaction, motivation, and leader effectiveness (2015). Healthcare leaders must provide the needed infrastructure if they want to improve patient satisfaction. People have different needs motivating and pushing them toward varying goals. Leaders must have an understanding of the employees’ needs and employ the necessary actions to satisfy them. This research suggests that leaders must strive to create a work environment where employees are engaged and take pride in the organization they work for. It is also critical to create a culture where employees feel empowered to do their best.
Is There Truly an Employee Engagement and Patient Satisfaction Link?
Throughout numerous studies noted by Harvard Business Review, its research shows there is evidence that employee engagement directly impacts patient satisfaction, because staff attentiveness has a significant impact on perceptions of service quality and behavioral intentions (Amabile & Kramer, 2007). The results of this study also showed the relationship between employee engagement scores and patient satisfaction scores within various hospital. As shown in Figure 3., there is a linear relationship between the two. As employee engagement increased, the hospital’s patient satisfaction scores did as well. As discussed in Trustee Health Forum, organizational growth and profit are highly stimulated by patient loyalty and satisfaction, and healthcare employees who are satisfied with their work provide higher levels of customer service (2007). However, both are largely dependent on the work conditions. As a result, healthcare leaders must determine what workplace conditions are most critical for improving patient satisfaction. Once those conditions are identified, leaders must work to improve both processes as well as their ability to motivate its employees. Successful healthcare organizations find ways to develop and recognize their best patient caregivers without promoting them out of the roles in which they excel (Blizzard, 2003).
Cleveland Clinic is an example of a hospital system which understands there is an existent relationship between employee engagement and patient satisfaction and therefore regularly measures the two. When opportunities are identified from caregiver engagement and patient satisfaction surveys, leadership involves multidisciplinary employee teams to help with identifying solutions to low employee and patient satisfaction. According to Donna, a Nurse Manager within the health system, “participating on these teams not only allows employees to be a part of the solution, they are also encouraged to take ownership in improving their work environment; empowering employees to make these types of decisions holds them accountable to actions that not only are beneficial to them and their teams but also our patients” (personal communication, September 22, 2018). This involvement also helps employees maintain a high level of job satisfaction. When healthcare employees are happy and care about they work they do, this leaves a good impression with their patients which is key to whether patients decide to return.
Analysis of Key Issues
For many healthcare organizations, the key focus is on how to make its patients happy and how to ensure their return, but they must also keep in mind how employee happiness and engagement shape its overall performance. Employee engagement is not simply making an organization’s staff satisfied or happy, it is about helping employees feel a connection to the work they do and the mission of the organization as well as feeling supported and recognized for their work. (“Study confirms strong link”, 2004). Throughout the research various studies such as that conducted by Press Ganey and Associates show that healthcare employees drive the experience patients have through every encounter: from the patient’s interaction when scheduling their appointment through their interactions with frontline clerical work, and to medical care experience with the healthcare provider. Employees who are not connected to the work they do and who fail to put forth the effort to interact positively with patients, result in close to seven trillion dollars in lost productivity (www.forbes.com, 2018), and statistically have an impact on patient satisfaction because everyone contributes to the success of the organization.
However, for many healthcare organizations it is not optional for hospital employees to provide high-quality service. In fact, with the mandate to improve patient experience, there is now a direct link to the reimbursements and financial results and according to McHugh, Lee-Kutney, et. al, the HCAHPS survey has become mandatory for hospitals to receive their full annual payment update under CMS’s inpatient prospective payment system (2011). Through use of the HCAHPS survey, hospitals use this method to survey patients on their experience with the hospital system including staff. Using this data, leaders can drill down to department level to determine where patients are receiving the most instances of negative experience and understand where this is a systemic issue or if there are specific employees who are disengaged and causing these poor experiences.
Lastly many healthcare systems such as are also measuring employee engagement, along with other metrics, via a balanced scorecard when evaluating the overall performance of the organization. When evaluating metrics such as patient experience, safety, and financial performance many organizations are finding these metrics rely on employee engagement. (“Study confirms strong link”, 2004) When engagement levels are high, there is a higher likelihood that employees’ level of performance will be above average for many key hospital metrics (see Appendix 4).
Strategies
Everyone has experienced that situation where an employee has failed to acknowledge our concerns or barely wants to provide a patient with assistance, and when this occurs patients do not want to interact with these individuals. However, the reality is, any healthcare employee can demonstrate these behaviors and provide negative interactions if they are not treated properly or feel supported. Leaders set the tone for their environment and the culture of the organization. Employees want to know their leaders value their work, and it is the healthcare leader’s responsibility to keep their employees happy and productive. This can be achieved by creating an open environment to share concerns, provide activities that help build the team, and foster teamwork (Dukes, 2011).
Healthcare organizations also need to take the time to examine and understand the reasons for low engagement. A method used within the Cleveland Clinic which aids in this process is the use of a system-wide employee engagement survey that helps leadership understand how its employee’s viewpoint around patient experience and their role in shaping that experience for their patients. With this data, leaders create department specific goals to ensure everyone is working towards common results and are accountable for the same behaviors. Based on the data found, this approach is shown to be effective because everyone then shares the same understanding of what is important to the organization. It is fundamentally important to ensure there is no confusion about the goals and direction of the organization. When leaders show this level of respect towards their employees, these feelings are reciprocated. And as they feel they are respected and valued they will make an effort to work according to the set standards. Additionally, engaged employees translate to more positive and pleasant interactions with patients.
Link
When employees aren’t happy or engaged, there is a high likelihood that a hospital’s patients aren’t either. How employees treat and interact with patients has a direct impact on the experience of the patient when visiting a healthcare organization. As healthcare leaders work to improve their employees’ engagement, it represents a start towards addressing patient satisfaction. Providing excellent care doesn’t just refer to the clinical component, from a patient’s perspective, this includes all aspects of one’s behavior which is typically determined by the individual’s level of engagement. The work environment and culture must be conducive for creating happier and more productive employees. When this shift occurs there is improved morale, a sense of community, and the importance of patient satisfaction becomes central for all.
Recommendations and Conclusion
It is not only an organization’s employees who have a direct impact on the company’s success but also the organization’s leadership, because leaders affect employee engagement which ultimately determines the level of customer service which is delivered. To drive employee engagement and patient satisfaction, the healthcare leader must employ strategic and operational actions that drive success and profitability. First, this must be done by identifying what is imperative and setting the tone and direction for its employees. This includes identifying and clarifying metrics, values, vision, and culture of the organization (Brooks, 2000). Strategy must be supported and delivered by leaders for employees to understand the vision and make a connection to the work they do.
Employee engagement is more than just job satisfaction. Employees want to be treated fairly and have a sense of justice within their organization. If there is perceived inequality or unfair treatment there will be a direct impact on the employee’s motivation level and ultimately affect the patient. Those who feel organizational leadership and resources are present to support them and when there is an emphasis on quality of work, customer service, and employee development, employees are more likely to be engaged. The leader must provide this as they have the biggest impact with employee engagement. “When companies put employees and customers first, their employees are satisfied, their customers are loyal, their profits increase, and their continued success is sustained” (Kotter & Heskett, 2011). It is the leader’s responsibility to create a work environment where the employees are engaged, demonstrate passion in their work, and have an understanding of their roles and responsibilities when this occurs employees, in turn, will have a desire to provide quality care and service.
After creating a positive work environment, by demonstrating trust and respect and having open and transparent communication, the leader must also involve and engage its employees in the decision-making process. Employees want to feel heard, know they have a voice, and their opinions are valued. It’s critical for healthcare leaders to help their employees feel included in organizational plans by creating forums to promote idea exchanges. This can be accomplished by creating special project teams, having an open-door policy, inviting employee suggestions, or creating cross-functional teams or committees.
To improve engagement and ultimately patient satisfaction, leaders must also reward and recognize their employees as well as develop their skills and abilities. Employees want to know they are appreciated for their work and the effort they put forth. As a result, healthcare leaders must provide written or verbal praise that is sincere and timely. Recognizing employees for their hard work builds morale and motivates the employee to maintain efforts towards doing a good job. Lastly, leaders must continuously evaluate the skills of its employees and in collaboration with their staff develop goals and development plans that will help them not only learn and grow in their current role but prepare them promotional or other opportunities where the employee can best utilize their skills and abilities. Following these practices will not only make the environment a better place to work through reduced turnover and increased employee engagement, it will also create a better experience for patients visiting the healthcare system to receive care.
The goal of this paper was to understand the link between employee engagement and patient satisfaction and the key drivers for employee engagement. The author used research conducted via the internet, studies and surveys completed by Press Ganey and Gallup, and personal experiences of leaders within healthcare organizations as the foundation for measuring the link between the two. In addition, the author proposes methods for identifying key drivers of employee engagement and improvement opportunities. From a managerial perspective, this paper contributes to understanding these drivers and how to eliminate the gap between employee performance and ultimately hospital performance through the patient’s experience.
References
Amabile, T. M., & Kramer, S. J. (2007). Inner work life. Harvard Business Review, 85(5), 72–83.
Bateman, T. & Snell, S. (2015). Management Leading & Collaborating in a Competitive World (11th edition). United States of America: McGraw-Hill Education
Bateman, T. & Snell, S. (2015). Management Leading & Collaborating in a Competitive World (11th edition). United States of America: McGraw-Hill Education
Best Practices: Linking Employee and Patient Satisfaction. (2007). Trustee Health Forum, 60(6), 3.
Blizzard, R. (2003). Engagement key to improving balanced scorecards. Gallup. Retrieved September 4, 2018 from, https://news.gallup.com/poll/9634/Engagement-Key-Improving-Balanced corecards.aspx
Blizzard, R. (2003). Engagement unlocks patient satisfaction potential. Gallup. Retrieved, September 4, 2018 from https://news.gallup.com/poll/8650/Engagement-Unlocks-Patient-Satisfaction-Potential.aspx
Brooks, R. (Mar/Apr 2000). Why loyal employees and customers improve the bottom line. Journal for Quality & Participation, 40. Retrieved September 4, 2018 from https://www.forbes.com/sites/groupthink/2017/10/09/why-loyal-employees-and-customers-improve-the-bottom-line/#748832264780
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Retrieved September 18, 2018 from https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/HospitalQualityInits/HospitalHCAHPS
Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved September 18, 2018 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/about/overview/who-we-are/mission-vision-values
Costello, M. A. (2002). Employees drive culture of quality at Baptist. AHA News, 38(19), 6.
Dukes, J. (2011). Employee Satisfaction — Unlocking the Potential Within Your Staff. 20/20, 38(10), 155-158.
Engaged, empowered, enthused: the link between employee engagement and patient experience. Retrieved, September 10, 2018, from https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/hospital-management-administration/engaged-empowered-and-enthused-the-link-between-employee-engagement-and-the-patient-experience.html
Fulmer, R. M., & Goldsmith, M. (2000). The Leadership Investment. New York: AMACOM Books.
Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems. Retrieved September 4, 2018, from http://www.hcahpsonline.org.
How to achieve sustainable employee engagement in healthcare. Retrieved September 4, 2018 from https://www.forbes.com/sites/workday/2018/05/08/how-to-achieve-sustainable-employee-engagement-in-healthcare/#1c54f1b84c28
Kaldenberg, D. O., & Regrut, B. A. (1999). Do satisfied patients depend on satisfied employees, or vice versa? Health Care Registration: The Newsletter for Health Care Registration Professionals, 9(1), 10.
Kimberlain, J. & Lindberg, L. (2018). Engage employees to improve staff and patient satisfaction. H&HN: Hospitals & Health Networks, 80(3), 67.
Keeping happy. (2004). Marketing Health Services, 24(1), 6.
Kruse, K. (2015). The roi of employee engagement in hospitals. Retrieved September 10, 2018, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/kevinkruse/2015/02/26/the-roi-of-employee-engagement-in-hospitals/#18aac36e54ce
McHugh, M. D., Kutney-Lee, A., Cimiotti, J. P., Sloane, D. M., & Aiken, L. H. (2011). Nurses’ widespread job dissatisfaction, burnout, and frustration with health benefits signal problems for patient care. Health Affairs, 30(2), 202-210. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2010.0100
MERISALO, L. J. (2018). Patient Experience: A Commitment on the Rise: Engaged employees, internal motivators key drivers of success. Health Care Registration: The Newsletter For Health Care Registration Professionals, 27(6), 1-12.
Nurturing Employee Partnerships: A Key Success Factor. (2012). Health Care Registration: The Newsletter for Health Care Registration Professionals, 21(4), 8-10
Petaschnick, J. (2006). EDITOR’S PERSPECTIVE: Employee Satisfaction Leads to Patient Satisfaction. Health Care Collector: The Monthly Newsletter For Health Care Collectors, 19(9), 2.
Raharjo, H., Guglielmetti Mugion, R., Di Pietro, L., & Toni, M. (2016). Do satisfied employees lead to satisfied patients? An empirical study in an Italian hospital. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 27(7/8), 853-874. doi:10.1080/14783363.2016.1190641
Study confirms strong link between patient and employee satisfaction. (2004). H&HN: Hospitals & Health Networks, 78(1), 67.
When workers are happy …. (2009). Modern Healthcare, 39(50), 31.
Appendices
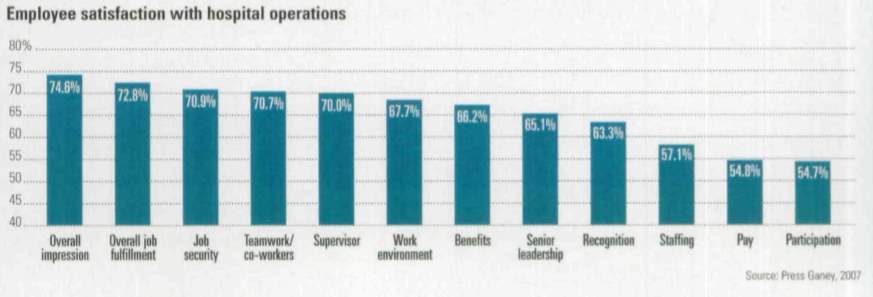
Appendix 1. Employee Satisfaction with Hospital Operations

Appendix 2. Important Factors in Achieving Positive Patient Experience
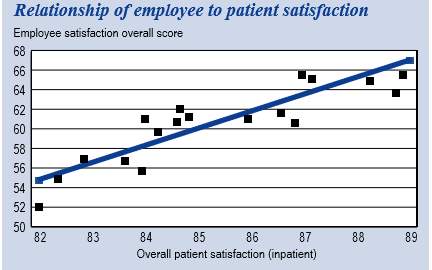
Appendix 3. Relationship of Employee Engagement to Patient Satisfaction

Appendix 4. 2003 Meta-Analysis – Findings (Improvement in Probability of Success)
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Patient Experience"
Patient experience encompasses the overall feeling a patient has about the care they receive including how they feel about health care facilities and systems, and all interactions with care staff whether they be doctors, nurses, hospital staff etc.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




