Contemporary Issues in Marketing Management in Morrisons
Info: 8322 words (33 pages) Dissertation
Published: 13th Dec 2019
Tagged: BusinessManagementMarketing
Introduction
Customer knowledge has been known as a main source that can be used to support research and development, improvement and innovation, facilitate better understanding of market opportunities and support long-term relation with customers. Capturing this knowledge and analyzing it, the organization will achieve competitive advantage and can offer new products and services, improve customer service, respect customers, make customers satisfied, find customer needs and respond to those needs (Afrazeh, 2005).
- Explain the concept of knowledge management and its role in relationship marketing.
Knowledge Management : Today is the era of knowledge-based organizations. In order to access new resources, knowledge management has attended new theories such as knowledge management community with the goal of achieving immense resources of customer knowledge. Today, creating and maintaining relationships with customers, not just to sell products and services, but also to access their information and knowledge, is a new concept discussed in knowledge management systems (Retna and Tee, 2011).
Customer relationship management is a process to collect information about customers and its aim is to find and record customers’ important features to implement marketing activities base on customers demand and quality. Customer relationship management is the process of attracting, keeping, and growing profitable customers and by focusing on the traits and characteristics that demonstrate the added value to customers, trying to loyal customers (Handen, 2000).
CRM initiatives have two main purposes within the organization. The first is to collect high quality customer information and create customer profiles.
To evaluate the need of CRM within the corporate environment of Morrisons to explore the challenges in the implementation of CRM and determine the technologies to sort out the major issues. First is to collect high quality customer information and create customer profiles. With access to detailed, up-todate customer information, employees can handle customers’ queries more effectively. Priority treatment can be given to favoured customers. The analyse the prevailing CRM strategies and system. This examination is wanted to investigate the impact of CRM techniques on client maintenance in Morrisons. In any case, there was no satisfactory information about the CRM procedures and techniques that must be embraced in Morrisons.According to Henricks (2000), the tasks of CRM include:
- collecting customer data in one place;
- making it widely available;
- identifying the best customers;
- finding more like them;
- determining their needs; and eventually
- turning prospects and first-time buyers into long-term loyal customers.
CRM therefore allows an organization to generate better sales leads, enable faster response to changing customer needs and ensure that everyone in sales and marketing has the right information at the right time for every customer.
Customer knowledge management (CKM) is a process to help integration of customer relationship management and knowledge management (Gibbert, 2002). In fact, customer knowledge management transfer knowledge management processes from theoretical goals to applied goals. According to Dalkir (2005) presented an integrated CKM process model including three stages: customer knowledge, sharing, and customer knowledge acquisition and application. In the transition from customer knowledge capture stage to the stage of customer knowledge sharing, knowledge content is assessed. In order to understand and utilize this knowledge it has to be contextualized to move into knowledge acquisition and application stage. This stage then feeds back into the first one in order to update the knowledge content.
- Explain the ways that ICT can support the customer relationship management process in Morrisons.
The purpose of customer relation management (ICT) systems provide in the information on staff performance and thus enabling of the managers to monitoring of people. The introduction of Information Communication Technology has tended to lead to the organisational structures.
Informational and Communication Technologie (ICT) most of the organisation to use, keepand process data. M!orrison use ICT for fast to communication an data processing but also to improvebusiness processes to cost of efficiencies and maintain a competitive advantage in themarketplace.The business strategy is developed with IT components, that will help to organisation the business to increase productivity and serve customers more effectively ICT is about information, communication and technology. ICT means the components that areused in information technology. There are following ways which could be used to make ICT support in customer relation management of the Morrison’s
improve customer&s services and demand (Porter, 2001).

- Website: Morrison could use its separate web page portal or unique website to interact with clients so that an effective nexus could be established to interact with clients. Management department use this portal to resolve client’s grievance in context with the current offering in market.
- Email: Are delivered extremely fast when compared to traditional post and created as a way to improve customer service.
- Communication: Cloud technology has done away with the need for
planning could be very much helpful for Morrison in customer relation management. As this will result into automation in resolving all the problems and grievance of the Morrison customer relation management functioning.
- Software: CRM software can be used to automate lead and sales processes, and to collect all of this customer information in a centralised place. Therefore in order to establish effective customer relation management in Morrison there is need to use sophisticated technology in determined approach.
- Providing quicker services to customers: There is needs to establish a separate portal for the clients so that they their grievance could be handled by separate department in effective way in order to increase their experience with eth Morrison customer relation management.
In addition to this using of upgraded technology and newly developed mechanism will result into highly data management, insight driven marketing, automation in the business functioning and development of synergy in orderly manner.
- Loyalty cards:The Morrisons loyalty card offer information about the customers, about their purchase and this can be considerate a type of statistical survey. But also using loyalty card organisation can offer point rewards to retain the customers.Points can be converted into vouchers that provide discounts on products or services.Each customers’ loyalty card has a unique card number linked to a database which stores information about them and their purchases.
Information technology (IT): Information technology is a growing field that offers relatively secure positions for those with solid technical skills .The field of information technology (IT) covers the design, administration and support of computer and telecommunications systems. Information technology is a growing field that offers relatively secure positions for those with solid technical skills .The field of information technology (IT) covers the design, administration and support of computer and telecommunications systems. Some of the positions in this field include database and network administrators, computer support specialists, computer scientists, software programmers and system analysts. The majority of career tracks in IT entail design and operational tasks related to computer hardware components, networks and software applications. Morrisonsmost people, don’t normally think that way. So initially a lot of energy went into trying to “think like a computer” to get them to produce results of value, at the expense of focusing on user requirements
- Describe the benefits of customer relationship management in Morrisons.
Customer relation management involves the Morrison corporate function which are required to contact customers directly or indirectly: marketing, customer services, field sales and field services. Traditional marketing strategies focused on the four Ps (price, product, promotion, and place) to increase market share. The main concern was to increase the volume of transactions between seller and buyer. Their reciprocate behaviour throughout the time of Morrison business functioning.There are following benefits that could be drawn by Morrison form the customer relation management.(Wyner, 1999)
Customer: The customer is the only source of the company’s present profit and future growth. However, a good customer, who provides more profit with less resource, is always scarce because customers are knowledgeable and the competition is fierce.The information technologies can provide the abilities to distinguish and manage customers. CRM can be thought of as a marketing approach that is based on customer information (Wyner, 1999).
Relationship: The relationship between a company and its customers involves
continuous bi-directional communication and interaction. The relationship can
be short-term or long-term, continuous or discrete, and repeating or one-time.
Relationship can be attitudinal or behavioral. Even though customers have a
positive attitude towards the company and its products, their buying behavior
is highly situational management. CRM is not an activity only within a marketing department.Rather it involves continuous corporate change in culture and processes. The customer information collected is transformed into corporate knowledge that leads to activities that take advantage of the information and of market opportunities. CRM required a comprehensive change in the organization and its people.
- Make justified recommendations for the improvement in customer relationship management for Morrisons.
Analysis– There will be made complete analysis over the customers behaviour and their reciprocate acts toward the Morrison’s offering. This analysis will assist management department to evaluate its existing business decision making (Kerr, 2013).Customer relationship management (CRM) is a term that refers to practices, strategies and technologies that companies use to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle, with the goal of improving business relationships with customers, assisting in customer retention and driving sales growth. The purpose of customer relationship management is to maximize the customer informationand to use it to increase loyalty of the customer. It is an integrated approach of focusing oncustomerces retention and relationship development. CRM is a customer focused business strategy that dynamically integrates sales, marketing and customer care services. The purpose of CRM strategy is to create and add value both to the company and its customers.Morrison has already achieved so much in the customer satisfaction but due to the changingcompetitive environment they need to continues improvement and research to retain their bestcustomers, to convert good customers into loyal customers and to get rid of the unprofitablecustomers. (Chalmeta,2006).
TASK 2: BE ABLE TO UNDERSTAND THE ROLE OF MARKETING IN NON- TRADITIONAL CONTEXTS
2.1 Carry out a stakeholder analysis for a voluntary sector and a public sector organisation.
Stakeholder analysis aims to identify the key stakeholders an map them out to grow better understanding of the environment, in which the organization is operating in. The analysis also aims as well to describe the dynamics between the identified stakeholders (Carroll & 2006).
According to (Freeman , 2010) the stakeholder the identification of stakeholders, which builds a basis for stakeholder management, is an essential part of organizational understanding of how to run a successful business. The goals and purposes of an organization affect and are affected by the parties that participate in the operations of an organization.
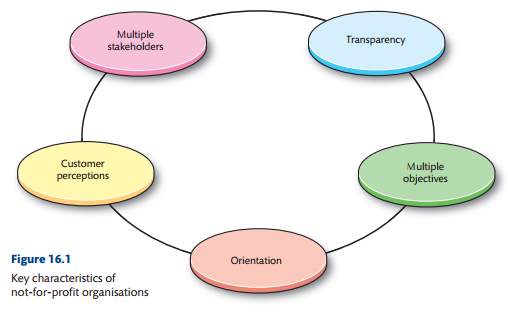
The voluntary sector is made up of organisations whose main objective is to enrich andbenefit the society, without any profit as a motive and without government intervention. It is differentfrom the private sector where the return and generation of profit to the owners are emphasized, themoney earned by an organisation in this sector is normally invested back to the organisation or the community.(Saigonin1951) NCVO Volunteer Centre is the one of the largest voluntary sectors which is running their business with a view to provide high quality of series throughout the world without any intention to earn any money. Volunteer’s week is an annual event which is organized yearly by the NCVO which takes place and accomplishing the needs to people national wide, NCVO Volunteer Centre is local partners providing assistance to individual.
Role of marketing- Marketing of this NCVO Volunteer Centre is to collect the money form the people all over the world. Ideally customers who availed the services and donors who make grants to the company are the most valuable clients for the proper running of the business. Marketing department of NCVO Volunteer Centre needs to prepare a sophisticated plan which could be presented before donors and other voluntary sector organizations.
Marketing plays an important role in establishing relationships between customers and the organizations offering to the market. It gives us the confidence to want to try a new product in the market as opposed to situations where the products enter the market without publicity. This makes the marketing function critical in every organization irrespective of whether the organization is a profit or non-profit centred. Marketing shapes the image of the organization, how people associate the organizations products or services and indeed give people the confidence about their products or services.
For example, customers may believe a company is dynamic and creative based on its advertising message these benefits include:
- Developing products that satisfy needs, including products that enhance society’s quality of life
- Creating a competitive environment that helps lower product prices
- Developing product distribution systems that offer access to products to a large number of customers and many geographic regions
- Building demand for products that require organizations to expand their labor force
- Offering techniques that have the ability to convey messages that change societal behavior in a positive.
2.2 Describe the nature of the relationships with customer within two selected not-for-profit organisations.
According to Mbller and Halinen (2000) define the Relationship marketing is based on two arguments. Firstly, that it is more expensive to win a new customer than it is to retain an existing one and secondly, the longer the association, the more profitable the relationship for the firm. Whilst it would depend on the individual, it is claimed that getting a new customer is 5-10 times more expensive than retaining one. This is not only because of the direct costs that are incurred but also the costs of unsuccessful prospecting that can be saved. Reichheld and Sasser (1990) further claim that as customers become more satisfied with the service they receive, the more they buy. As purchases increase, operating costs fall due to the advantages of the experience curve and this in turn leads to increased efficiency. Relationship marketing’s stress on loyalty, customer retention and long-term relationships is a key to profitability (Gummesson, 1998). However, on the other hand, thenon-profit organisation related with spreading of a social message have least or no interaction or relationship with the end customers as the main aim is to disseminate information rather thanbuilding supportive contacts.
2.3 Compare methods used in marketing within the public, private and voluntary sectors.
According to Boone and Kurtz (1998) defined marketing as the process of planning and executing the conception and pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, services, organizations, and events to create and maintain relationships that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives’. Thus marketing its a multi-directional strategy that is being employed the public private and voluntary organizations in publicizing and executing their business processes. However, the exact marketing methods in each to a reasonable for others. As the public sector is essentially a non-profit-making sector. The marketing services are mainly concerned with the satisfaction of the customers (Judith, 1998). The information that are normally communicated include the ideas, benefits and values. Thus, communication is the central strategy that is normally used by public sectors organization in its marketing operations (van Riel, 1995). This category of organization may also used a customized blend of the four – product ,price, place and promotion.
This competition has made it very necessary for them to have proper marketing techniques. The most suitable techniques are those specific strategic marketing techniques that require comparatively less budgets as compare to the traditional marketing techniques used worldwide (Kotler, 1996).
2.4 Explain the key issues involved in marketing in a selected virtual organisation.
The virtual organization is a unique type of institution, whose members are located in different geographic locations. The members usually work together with the help of electronic tools like computer e-mail and groupware, which make it to appear as a single, unified organization with a real physical location. The term can also be used to represent a network of firms, that team up together, often temporarily, to produce a service or product.It is a very good example of a virtual organization. Its operational processes are very complex and unavoidably problematic.The virtual firms are faced with the problem of strategic planning, as they strive to determine the right combinations that will be very effective in achieving core competencies. The cooperating individuals and firms of Ensemble have common vision and goals. Each firms of the institution developed close interdependencies, which make it difficult to determine where one firms begins and the other ends. Therefore, it become very mandatory for the institution to have the expertise required to manage this boundary-blurring effectively. Coordinating mechanisms are critical elements for supporting these loose collections of firms. The virtuality of Ensemble means that the managers at the head office of the organization have limited control over many of the company’s operations. The implication of this loss of communication is that; new set of managerial skill, great deal of trust, communication and coordination are required among all cooperating individuals and firms.The virtual organization, Ensemble’s employees are faced with lots of uncertainty. These uncertainties focused mainly on job roles, organizational an the membership, superior-subordinate relationships, career paths, profit-sharing formula etc. The benefits, staffing, employee development and other employee-related issues (Vakola and Wilson, 2004).
TASK 3: BE ABLE TO UNDERSTAND THE IMPORTANCE OF APPLYING THE EXTENDED MARKETING MIX IN THE SERVICE SECTOR
3.1 Describe the use of the extended marketing mix in selected service sector businesses.
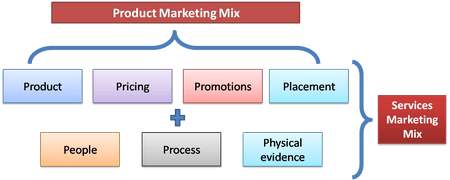
Business:The marketing mix is a combination of several elements used by a business to enable it toaccomplish its needs and customers& expectations. It is referred to as market mix since all elementsare closely related top each other. The major problem is to ensure that all elements work together toobtain the marketing goals.The long time, the market mix is considered to have four elementswhich include product, promotion, price and place.This has changed, and three more elementshave been added to the mix.
People:In the marketing mix the first p is concerned people who work for the organisation. A team needs to hire and train the right human resources since they are the people who will deal with the customers. These people include, sales representatives, customers service representatives, among other workers who deals with their clients
Physical evidence:This includes how a company presents a product to the customers, and it includessurrounding. The company should be welcoming. The customers should be given easily navigationto access the products they are to buy.Zeithaml et al (2008)
Process:This is the final it deals with the ability of a company to offer services, handle complaints, customer services, predict issues that are likely to happen before they happen. This increases the trust of the client and confidence since the company can handle any issue that comes on the way.
Marketing as management:The view of marketing as a management began in the 1950s which have supported the sales functions in a company. Two major developments marked the transition which includes the view of marketing concepts as a management philosophy that focuses on customers. The other view is the integration of behavioural science and quantitative methods into the marketing sectors. These have seen marketing become a separate discipline in a business sector. Thus, marketing highly focuses on the customers wants and needs (Dabholkar,2015). Service cannot be touched and has no physical presence.The services include haircuts, banking, photography, repairs and transportation. The market mix has seven Ps where three Ps deals with services and include people, physical evidence, and process. People are the organisations employees who interact with customers. The process is the way in which a business uses to satisfy its customers.For instance, in the bank where out of date cards can be replaced.
3.2 Explain how the product/service mix can be used to enhance value for the customer and organisation.
A company can enhance its value by constantly assessing and developing on how it is taking care of the needs and wants of the customer. The product service mix is a very important element in this effort. the blend is outlined by integrating the 7C and the 7P’s Kotler and Armstrong (2010).
Price is the amount the consumer must exchange to receive the offering .The company’s goal in terms of price is really to reduce costs through improving manufacturing and efficiency, and most importantly the marketer needs to increase the perceived value of the benefits of its products and services to the buyer or consumer. Solomon et al (2009).
Product:Place includes company activities that make the product available to target consumers. Place is also known as channel, distribution, or intermediary. It is the mechanism through which goods and/or services are moved from the manufacturer/ service provider to the user or consumer.Kotler and Armstrong (2010).
Promotion includes all of the activities marketers undertake to inform consumers about their products and to encourage potential customers to buy these products Whilst there is no absolute agreement on the specific content of a marketing communications mix, there are many promotions elements that are often included such as sales, advertising, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, online communications and personal selling Solomon et al (2009).
Physical Evidence: Physical evidence is the environment in which the service is delivered, and where the firm and customer interact, and any tangible components that facilitate performance or communication of the service. There are many examples of physical evidence, including some of the following buildings, equipment, signs and logos, annual accounts and business reports, brochures, website, and even the business cards.Zeithaml et al (2008)
3.3 Explain how difficulties peculiar to the marketing of services can be overcome in one of the above service business mentioned.
There are lots of challenges or difficulties are faced by the Tesco and they need to overcome from these situations such issues.Cost savings for the marketing strategies should be achievedwith the help of effective operational strategies to aim at doling right things in a right way to containthe cost within the present techniques.
- Intangible:One of the most obvious challenges in marketing services is that you are selling somethingintangible. People can touch and see a product and are exchanging money for something theyneed and can take home to use. Conversely, people only see the results of a service, which maynot always be immediate. It requires faith on the customers‘ part that they will get the desiredresults for their money. For example, if you own a cleaning service, you have to convince yourcustomers to trust you that their homes will be cleaned to their satisfaction.
- Demonstrating Empathy:Convince your customers in your marketing efforts that you understand their problems and areoffering a solution. Do this using people, processes and physical evidence. For example, if youand your employees have families and work full time, this identifies with working families whohave no time for housecleaning. Before-and-after pictures in your marketing materials, such asyour website, brochures and advertising, are all physical evidence.
- Competitive Pricing:How you price your services is an important marketing element. You need to be competitive, soresearch several competitors‘ prices to gauge what your prospective customers expect to pay.Then assess your costs — your overhead such as rent, insurance, salaries and supplies — todetermine if you can meet your costs and make a profit with that pricing.
- People:As a services company, marketing your people, including you, is paramount. A service isconsumed when it‘s purchased or produced — just the results or effects linger, and sometimestemporarily. For example, your customer‘s home will get dirty again, so the result of yourcleaning delivery is temporary. The client may or may not call you again based on the overallexperience.
- Customer Perceptions of quality: Gap model discusses the gap between customer’s expectation of services and service marketers perception of the customer. This result in incorrect designing and standard of service. Further this is in inappropriate service delivery and finally communication gap due to incorrect service product design and delivery. This make service make Tescoovervalue or undervalue customer expectations.
The difficulties can be easily overcome by making a proper paining and strategy about marketing. Intangibility, Inseparability, heterogeneity, and perish ability; these all have long-lasting solutions (Bilbao-Osorio, et.al, 2013).
3.4 Explain the role of ICT in services marketing management in one of the above service business mentioned.
IT plays a pivotal role in processing, storage and accessing of information to improve the servicesector and its marketing management by providing innovative solutions of products and for their marketing.Let us start our construction of a holistic enterprise ICT quality approach with a small illustration characterising an enterprise in its market. In our systemic view, an enterprise can be regarded as a black box, located within markets and getting requirements from their markets, customers, and potential customers and being able to satisfy their customers’ needs. Looking into this black box, it is usually driven by experienced and intelligent people using powerful ICT products to efficiently conduct the corresponding processes for building and offering the enterprise’s products, i.e. goods and/or services ( Barrett 1998).
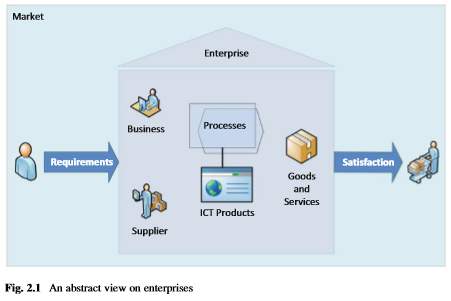
The question thatremains is what are the stakeholders’ views and expectations on quality of the ICTsystems in use?
- Market: Customers require and accept the quality of the corresponding products and the quality of the buying channels; Competitors may gain an advantage on the market if the product or channel quality is poor.
- Enterprise:Shareholders missing quality of the ICT systems or channels may lead todecreasing revenue and subsequently to falling stock price and loss of money.Board members have overall responsibility for the quality and reputation ofthe business and decide on investment in quality. Administrative departments support the business and ICT, such as financialadministration and human resources.Enterprise academies provide and organise internal and external seminars.
- Business domains:Managers have responsibility for the requirements for the ICT systems, including the detailed quality characteristics, and must accept ICT quality afterwards.They need quality for their daily work and therefore define requirements,including the detailed quality characteristics, and verify the quality during acceptance.
- Product-related:Product Owner is responsible for a product and its quality. End users are affected in their daily work by missing quality andare interested in achieving stable and reliable systems with good performanceand security. Quality engineer refines high-level quality characteristics down to design and code level and validates and verifies them to find out where the errors and causes lie before the system.
TASK 4: BE ABLE TO UNDERSTAND THE REASONS FOR THE INCREASING EMPHASIS ON ETHICS AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY IN MARKETING
4.1 Explain some of the current issues of ethical and social concern to marketers in the industry.
The marketing ethics is the area of applied ethics which deals with the moral
principles behind the operation and regulation of marketing.Practising ethics in marketing means deliberately applying standards of fairness, or moral rights and wrongs, to marketing decision making, behaviour, and practice in the organization.Some marketing ethics of advertising and promotion overlap with media ethics. The marketing is ethical marketing is about satisfying and developing a long-term relationship with the customers (Kotler & Armstrong, 2009).
In the area of marketing ethics we can identify following framework attributes:
- Value-orientated framework: analysing ethical problems on the basis of the values which they infringe: e.g. honesty, autonomy, privacy, and transparency.
- Stakeholder-orientated framework : analysing ethical problems on the basis of whom they affect: e.g. consumers, competitors, society as a whole.
- Process-orientated framework :analysing ethical problems in terms of the categories used by marketing specialists: (e.g. research, price, promotion, placement).
- None of these frameworks allows, by itself, a convenient and complete categorisation of the great variety of issues in marketing ethics.
- Power-based analysis: Contrary to popular impressions not all marketing is adversarial, and not all marketing is stacked in favour of the marketer. In marketing, the relationship between producer/consumer or buyer/seller can be adversarial or cooperative. If the marketing situation is adversarial, another dimension of difference emerges, describing the power balance between producer/consumer or buyer/seller. Power may be concentrated with the producer, but factors such as over-supply or legislation can shift the power towards the consumer. Identifying where the power in the relationship lies and whether the power balance is relevant at all are important to understanding the background to an ethical dilemma in marketing ethics.
4.2 Explain the concept of CSR with reference to Morrisons.
The Corporate social responsibility is good not just for the society and the environment but also the company’s reputation. Company’s such as Morrison stands a chance of having a good reputation and gaining public trust due to their good social responsibility.Also, when a company has a good reputation, consumers tend to use their products.
Morrison has been making effective efforts in its corporate social responsibilities around all over the world in context with building up of corporate reputation, economic, legal and other factors. In simple word CSR is related with giving back to society at least it has been taken for running the business operation in society. It is concerned with accomplishment of social responsibities and completing its moral and social responisbitles in determined approach. However, CSR activities have high amount of impact on company’s brand image as completing its social activities along with business operation it results into high amount of credibility in the mind of stakes holders at large.
- Economic:The corporate social Responsibility is good phenomena for economic which as broad implications for the organizations, customers, employees, government, investors among others. The presence of social stakeholder preferences, organizations may use CSR strategies to maximize their profits while satisfying the stakeholders.
- Legal responsibility: This is the requirements placed on a company by law. According to the theory of corporate social responsibility, a company must ensure it abides by all rules and regulation so that it can become profitable. Legal responsibilities can range from labour law and securities regulations, criminal law and environmental law.
- Ethical responsibilities: Legal and economic responsibilities are the major obligations of an organization. After the organization meets these major obligations, it can then focus its attention ethical responsibilities. Ethical responsibilities are the obligations undertaken by a business not because it’s an obligation but the right thing to do. Auch responsibilities include paying fair salaries, being environmentally friendly and boycotting to doing business with oppressive countries (Chell, 2006)
- Philanthropic responsibilities: These responsibilities are met after a company has met all other responsibilities. These requirements go beyond what is expected from a company and what is believes its right. Auchresponsibilities include donating services to the society, initiating projects that benefit the environment and donating money for charitable works.
Published or broadcast media affecting supermarkets in the UK
There are several cases published by media concerning supermarkets. Use of food scares isa good example on how media can sway the public on the risk perception.The instance, in 1996 there was a case of mad cow in the UK where media claimed that meat produced could causebovine spongiform encephalopathy. This story made many people stop eating burger leading tolosses on the businesses. Marketing evolution is commonly believed to have fivedistinct phases of evolution. These phases include simple trade era, production era, the marketingdepartment, sale, and marketing department era.
4.3 Evaluate the role played by a selected pressure group in influencing ethical and social marketing policies for Morrisons.
Role Played by a selected pressure group in influencing ethical and social marketing. A pressure group is an organized group that seeks to influence government (public) policy or protect or advance a particular cause or interest. Groups may promote a specific issue and raise it up the political for Morrisons or they may have more general political and ideological objectives in mind when they campaign. Marketing practices must be targeted towards social cause as it is the main essence of this pressure group. (Rose 1999)
Pressure Groups and Political Parties: Pressure groups have to be differentiated from political parties. Political parties, in the strict sense of the term, are associations of individuals sharing common values and preferences. They are organised on ideological lines and present a vision for the future. They have well trained cadres who are engaged in continuous political mobilisation of the masses! They use all the political means available to capture the power and consolidate their position to attain or realise their ideological goals. In a broader sense they are also interest groups. They have a social base whose interests it must protect and promote.
Pressure Groups and Lobbying: Pressure groups and lobbying is not one and the same thing. Lobbying takes place when a few members of pressure groups loiter in the lobbies of the legislatures with a view to securing an opportunity to interact with legislators and to influence the decisio ls of the legislators. Parity cannot be drawn between lobbying and pressure groups even though the lobbyists are the representatives of particular interest groups. Lobbying is a communication process used for persuasion; it cannot be treated as an organisation. Lobbying is used in governmental decisionmaking and it aims at influencing the policy process. It acts as an instrument that links citizens and clecision-makers. Lobbying is different from pressure groups in the sense that pressure groups are organised groups and they perform various functions including lobbying. (Goyal,1977)
There are following types of actions are taken by selected groups to change government policy and ethical program.
Example– In one of advertisement issued by Morrison’s it was observed that company was not portraying a positive sign and developed negative sign for customer and make lucrative offers to only name majority of people. With this marketing practice it was observed that company was following wrong marketing practice that results into pressure group gathered and rose March against the Morison’s. This protestation results into lock up of all the supermarket of the Morrison’s in UK.
4.4 Evaluate the role played by published or broadcast media in influencing ethical and social marketing policies for Morrisons.
The media industry is an important stakeholder in published or broadcast specialization to deliver content and information either in a direct way or an indirect form.It has been indicated earlier on that, marketing ethics involves the application of morally justifiable principles in the operation and regulation of the marketing processes. These include such marketing properties like advertisement, promotion etc. It’s important to note that some aspects of marketing ethics overlapped with those of media ethics. Solomon (2013)
The ethical and social marketing policies of product industries are increasingly being influenced by both published and broadcast media. The media houses basically fulfilled this obligation by enlightening members of the public, on the ethical and social marketing principles expected from the product industries.The instance, the media can expose the industries, whose marketers aren’t being truthful about the products. The media can also alert members of the public, whenever a potentially dangerous chemical is used in the manufacturing of the products.
Media is the catalyst to shapethe opinion of the company and its consumers towards adoption of ethicalpractices concerned with marketing scenario. Broadcast media acts as an asset in marketing mix as it is an integral part of advertisement for the software companies to reach a broader mass in remoteregions and ensure the consumers that the company do follow ethical standards as set by thegovernment (Rowe, 1993).
In this context the technology is used to create an environment which facilitates different forms of online activity For example:
- social community media, like Facebook, and LinkedIn, which enable sharing of ideas, interests, socializing and having conversations.
- social publishing media like YouTube, pintrest, Flickr which enable signed-up members to publish and distribute editorial content, movies, audio, photos.
- social commerce media like TripAdvisor, Groupon and Facebook, which enable buying and selling, trading, building relationships.
- social entertainment media like come2play, Zynga12 which enable game playing andentertainment across communities.
Bibliography
Gebert, H., Geib, M., Kolbe, L. M. and Riempp, G.,(2002), Towards Customer Knowledge Management – Integrating Customer Relationship Management and Knowledge Management concepts, The Second International Conference on Electronic Business, Taipei, Taiwan, pp.296- 298.
Handen,L.(2000).Putting CRM to Work : the rise of the relationship. In Stanley A. Brown(Ed.),Customer Relationship Management: A Strategic Imperative in the World of eBusiness.New York : john Wiley&sons .p.8.
Retna, S Kala & Tee NG Pak, (2011), ” Communities of practice: dynamics and success factors”. Leadership & Organization .,Development Journal 32 (1):41-59
Dalkir, K. (2005), Knowledge Management in Theory and Practice, Boston: Elsevier, Butterworth–Heinemann.
Freeman, R. E., Harrison, J.S., Wicks, A. C., Parmar, B. L. & de Colle, S. (2010). Stakeholder Theory: The State of the Art. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Carroll, A. & Buchholtz, A. (2006). Business and Society: Ethics and Stakeholder Management. 6th edition. Mason: Thomson/South-Western.
Gummesson, E.,. Relationship marketing as a paradigm shift: some conclusions from the 30R
approach. Management Decision 35(4), 1997.
Boone, L. E. and Kurtz, D. L (1998), Contemporary Marketing, Cincinnati:
Southwestern/Thomson Learning.
Reicheld, F. (1996). The loyalty effect, Harvard Business School Press: Cambridge MA
van Riel, C. B. M. (1995), Principles of Corporate Communication, Harlow: Prentice Hall
Vakola, M., and I.E. Wilson. “The Challenge of Virtual Organization: Critical Success Factors in Dealing with Constant Change.” Team Performance Management 10, no. 5-6 (2004): 112–120
Easton, P., T. Harris, and J. Ohlson. 1992. Accounting earnings can explain most of security returns: The case of long-event windows. Journal of Accounting and Economics 15: 119-142.
Barrett R (1998) Liberating the corporate soul: building a visionary organization. ButterworthHeinemann, Woburn
P. Kotler & G. Armstrong, “Principles of Marketing” (Prentice Hall, 2009, 13th Edition) P.20
Fuller, D. A.: Sustainable Marketing: Managerial – Ecological Issues: ManagerialEcological
Issues. Sage Publications, Inc. 1999. ISBN-13: 978-0761912194
[3]iGrančičová, K.: Základné etické princípy v marketingovej komunikácii. In: Podnikateľské prostredie a etika podnikania. Zborník z vedeckej konferencie KPH FPM EU v Bratislave, Bratislava 2006, ISBN 80-225-2199-X.
Goyal, O.P., 1977, India: Government and Politics, Light and Life Publishers,
New Delhi.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Marketing"
Marketing can be described as promoting and selling certain products or services to meet the needs of the customer. Tasks involved with Marketing include market research, content creation, advertising, and more.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




