Structure and Organisation of the Retail Sector
Info: 10116 words (40 pages) Dissertation
Published: 21st Oct 2021
Introduction
In this task I have been asked to describe the structure and organisation of the Retail Sector. The changes in retail and how it has developed over time will be looked at. As well as different types of ownership and functions of the retailer.
The structure and organisation of the Retail Sector
The Retail involves the selling of goods to the public, typically in small quantities. Where the products sold are usually bought for use or consumption rather than reselling.
The quote: “Retail is the process which is the selling of consumer goods and/or services directly to the customers through multiple channels of distribution in order to earn a profit.” Which is referenced from (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retail)? Also, since it began in the years from the 1500-1700s, retail has become an enormous part of modern day evolution and as since the time keep constantly changes, so does the characteristics of retail. Some interesting dates in the history of retail include;
- 1568 – The Royal Exchange shopping gallery was opened
- 1883 – The first cash register is invented by James Ritty
- 1929 – The very first supermarkets in America were established
- 1950 – The start of shopping malls, where stores made their way into
- 1970 – Credit cards were invented
- 1974 – Barcodes were created
- 1994 – Online shopping is born
- 2000 – Online shipping is growing
- 2010 – Growth of E-Commerce means it starts to dominate.
In most retail scenarios, the products have usually came from the manufacturer, which is then passed to the wholesaler, then directly to the retailer and onto the consumer. However, it is common for some manufacturers to operate their own retailing outlets.

Retail in the UK
The UK’s retail sector involves a lot of spending by consumers both in shop and online. The retail sector
Is made up of the wholesale sector which this means it supplies the shops which the consumers go to for their desired goods and services. In March 2015, UK consumers spent around £34 billion. The most was spent in the retail sector, online and in shops. The remainder was spent in food stores, such as fuel and in market stores. The UK’s retail sector has come under significant pressure in recent years which has been in many ways including small shops which have been shut down due to the significant growth of supermarkets, online retailing and also including the most recent recession which started to have its first effects in the year 2008.
GBP generated as a result of retail
The Retail sector has generates billions of pounds ever year. In 2014, retail in the UK had an economic output of around £180 billon. This was approximately 11% of the total UK economic output. Looking back to 2007, the retail sector grew even more than the UK economy. However, due to the recession which had resulted in the late 2007/early 2008 financial year, the retail sector had declined significantly quicker than the whole UK economy. This was because people simply couldn’t afford to spend their money in shops as money was scarce. It can be seen that the economic output trend of the UK and the retail sector economic output in the UK is directly related. It tends to be that when one rises, the other also rises. This can be seen in the graph below.
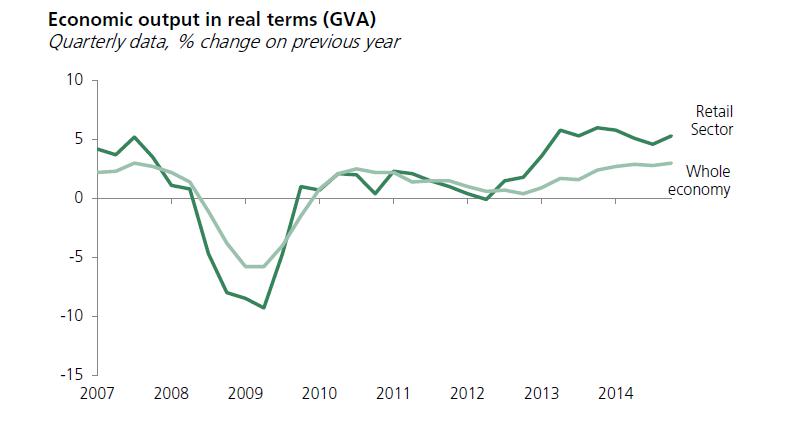
Employment figures of the retail sector in the UK
In 2013, the retail sector employed around £4.3 million people. This was nearly 16% of the total people in Great Britain, showing how massive the retail sector is in the UK, and how important it is due to the amount of people employed in it. It is the largest industry in the UK in terms of the number and proportion of employees.
 Between the years of 2013 and 2020, the retail sector workforce is predicted to grow by nearly 55,000 people, with the majority of growth expected to be in managerial positions. Retail is an increasingly competitive market where businesses have to compete in order to provide better quality of service to consumers in the store and online, and employees are expected to provide this high quality service.
Between the years of 2013 and 2020, the retail sector workforce is predicted to grow by nearly 55,000 people, with the majority of growth expected to be in managerial positions. Retail is an increasingly competitive market where businesses have to compete in order to provide better quality of service to consumers in the store and online, and employees are expected to provide this high quality service.
The Enterprises in the UK
In the UK, there are over half a million businesses operating in the retail sector. This is a massive figure when we take into consideration that it accounts for over 10% of UK businesses. In more recent times, people are trying to set up their own retail enterprises. However, with stiff competition it can be difficult to succeed in the retail sector.
Business online is growing significantly. Internet sales as a proportion of retail sales went from 2.7% in Jan 2007, to 12.8% in Jan 2014. In December 2014 alone, £1.1 billion was spent in online shops. This figure is huge and shows how much the internet is now being used for retail and business in general. This increase in internet sales is due internet only stores, where these stores only offer their product and services online to the consumer. In the space of seven years, internet sales grew by over five times the original figure. Internet sales are convenient for the consumer. However, this massive increase in online sales means stores start to struggle, such as HMW which went into administration in 2012.
Retailers and the types of products they sell
When we visit a shop to buy goods, we never think about the type of store we are actually in. The type of retailer will depend on the products and services they provide. Different types of retailers, also including different products they typically sell are highlighted below.
Food stores; Food stores are commonly known as grocery stores. A grocer sells food in bulk.Food stores usually sell non-perishable food that is in boxes, cans or bottles. However, some sell fresh produce such as milk, eggs and chicken. Examples of food stores include Tesco, ASDA and Safeway.
Non-specialist stores; Non specialist stores are the stores that don’t specialise in a specificretail market. These stores can sell a range of goods and do not generally specialise in a particular product or field. Examples of a non-specialist store would be Debenhams and Walmart.

Textiles, clothing and footwear stores; These stores sellclothing, shoes and other sorts of fabrics. They have become extremely popular as fashion is always changing. They also sell things like carpets and decorations, as well as bed clothes. Examples would be Nike, River Island and Fabric Warehouse.

Household goods stores; As the name suggests these stores sell all things household-related. However, they typically have a large range of goods. This may range from decorations, electronics, to cleaning products. Examples of household goods stores would be Home base, B&Q, Home Bargains.
Non-store retailing; Non-store retailing is theselling of an item or service that is not in-store (which does not occur in an everyday facility). It is retailing outside of shops and stores. Non-store retailing can be done in a number of ways.
Two of the biggest ways are the E-Commerce which directly involves the selling of goods and services online, and also the direct selling can be referred to a mobile service. Non-store retailing has become extremely popular now with the ever growing interest in the internet. It means people can decide to buy and sell items from the comfort of their own home. It also means no overhead costs for the seller, i.e. rent, rates and electricity costs which would have to be paid if the business had a store. Examples of non-store retailing include Amazon, EBay and a local business such as Paws and Claws (which is a mobile pet grooming business).
Types of ownership within retail
Retailing is more complex than just the word itself. There are so many different types of retail. Some are basic, others are extremely sophisticated. Some of the different types of ownership in retailing are now explained below.
Independent retailing
An independent retailer is a person who builds their business from nothing and grows their business by themselves. An independent retailer does everything; which is the planning their own business to the opening of their business, to the growth of their business. Also when they need help with their business, the independent retailer can decide to recruit staff. A huge advantage of being an independent retailer is that you are your own boss. You make all the decisions and have the businesses exactly how you like it. This has its advantages and disadvantages. If you are left alone with the entire decision making, it can be extremely stressful and time consuming.
Multiple retailing
Multiple retailing is also known as multi-channel retailing. It’s about operating a retail business where they can sell goods to the consumers through multiple retail channels. Stores, catalogues and the internet are three examples of channels. Also, if the company offers products and services through more retail channels, this will result in a higher likelihood of making sales which results in higher profits. This is because the good or service is available to people in more than one way. For example, the internet is a fantastic channel to use in the multiple retailing which is open to customers 24/7. Whereas, in-store have set opening times.
Voluntary retailing
Voluntary retailing is less common than the typical grocery retailer you see. Voluntary retailing involves people who work for nothing in return; the company doesn’t have to pay out wages to its staff as the main aim is to not to make a profit. Its main aim is more so to help out the local community. People who work in voluntary retailing may work for their own personal happiness or also their personal satisfaction. Quite often charity shops fall under this type of retailing. It is a retailer increasingly central to the health and well-being of society. People may feel good about working voluntarily and people feel good about buying things from voluntary organisations as they know their money is being used for something important in society.
Franchises

A franchise is where the company (the franchisor) sells another company (the franchisee) which is the rights to set up a company using their own name/brand. Examples of franchises are McDonalds and Burger King.
As the franchisee is purchasing the franchise and they will already be buying an-already established business, but they must pay a proportion of their profits to the franchisor. Moreover, the franchisor does however provide training, expertise and marketing campaigns which help out with all branches of the franchise. Buying a franchise is an excellent way for anyone wanting to set up a company because
- They are buying a business which is already established
- They will always have support and backup from their particular franchisor
There will always be less risk in the setting up as a franchisee than operating as sole trader as the customers already will know about your company and also the particular products you have to offer.
Functions of the retailer
For a business to be successful, to attract customers and to retain customers, the retailer must look at what is going to give them the competitive edge over their competitors. Some of the functions a retailer must take into consideration are explained below.
Convenient Location; The location of a business is extremely important. The businesslocation is the key to success and growth. When a business owner chooses the location of their business, they need to consider company requirements, customers, employees and the goods and services they provide. The location of the business should be easy for customers to get to and the customers should feel comfortable and safe when they arrive to the store. Many businesses are now moving locations: from the high street to online and to larger shopping centres where footfall is higher.

Range of goods; this is where a larger range of goods will then mean that the products and services that they offer will appeal to alarger audience by this. If a company extends their range of goods, they are also extending their customer base and target audience. Many companies will start off selling one product and then they will decide to branch out in order to sell more ranges of goods so that they can grow and increase the sales and profitability of the company.
Breaking Bulk; breaking bulk is where a supplier willbuy products in massive quantities. They will then break these products down into smaller groups and then sell these separately to different companies. Breaking bulk is a great way to maximise profits for a business as they are buying in large quantities at discounted prices. They can then sell these products to the companies at a higher price which will result in huge profit margins if it is done correctly.
Holding stock; for any business to manage theirstock successfully they need to find a balance between the benefits and costs of holding stock. The costs of holding stock will include both the money that they have to spend buying the stock and also include the costs of storage. Benefits of holding stock mean you will always have stock to meet the demands of customers. It will lead to increased sales, improved cash flow and new investors. However, if your holding of stock isn’t managed correctly, it could lead to an extra expense for you if items are held too long and go out of date. Having the wrong levels of stock will then lead to a loss of income from lost sales.
Information to customers; providing information to customers is an excellent way to build arapport with them. If they are updating their knowledge on the products and services they have to offer, then they must be more informed about their business and customers will be more inclined to buy from you. Companies involves getting to know your customers and your target audience so informing customers about new promotions, products and services can lead to massive increases in sales and overall profitability of the business.
Information to suppliers; the retailers have to have good relationships with their suppliers and theactivities of each company has to be fully understood by both parties. The retailer and the supplier need to work together and will have a set agreement laying out the payment dates, delivery dates and times as well as what products are going to be delivered. The suppliers must have regular contact with the retailer and when there are any changes made for example such as a change of delivery times then this has to be addressed immediately. The information they provide to each other is very important in the success/profitability and growth of both businesses.
After sales service; this is the activitieswhich is carried out which will then make sure that the customers will be fully satisfied and are happy with the products and services that they receive from the company. With good customer service, customers will recommend the business to other customers. Word of mouth will play such an important role in the promotion of brands and products. After sales service will then make the customer feel valued and appreciated. After sales service generates loyal customers. It brings more people and subsequently higher profits for a business. After sales service plays a significant role which is in the building of a better relationship between the business and its customers. An example of after sales service would be creating a support line for customers if they had any enquiries about their purchased product or service.

Dealing with complaints; the way in which a company will deal with its complaints will theninfluence the retention of its customers and this will be a very important in the building of a good reputation for the company. Retailers should remain calm in complaint situations; they should understand the customer, empathise with the customer and act accordingly. If a customer has a complaint, then this doesn’t mean that you have automatically lost this particular customer. If the complaint is handled well and the customer feels like they have been treated with respect, that customer could be back within the business the following day. The retailer must always deal with customer complaints effectively and professionally. Other complaints could come from suppliers. For example, if they are unhappy with the time it is taking for the retailer to pay them. The retailer needs to meet with its suppliers, address the issues and act accordingly to ensure the reputation of the business never falls which can be detrimental to any organisation.
Credit sales; this is where products or services which are sold on theagreement that they will be paid for a later period of time. It is sales made on an account. For example, if you go to a furniture store then you have the ability to buy the items on credit. You could be charged interest on credit sales as you are taking longer to pay for the product. A sofa could be £500. However, if you agree to pay for it over 6 months, you could actually end up paying £570 for it. Credit sales do not involve cash. Businesses like to receive cash.
However, in more recent times due to the economy not doing well there has been a massive increase in credit sales. It does mean the business does not receive the full amount of money straight away, but long-term they could be receiving more due to interest paid with credit sales.
Retail Outlets in the UK
When it is in retail, there are different types of retail outlets. Although they all have the same aim which is to make a profit, some have different characteristics to others, some are bigger than others, and some are more complex than others. Some of the different types of retail outlets are going to be explained below.
Independent Retailers
An independent retailer is a person who builds their business from nothing and grows their business by themselves. An independent retailer does everything; which is from planning their company to the opening of their company, to the growth of the company. For help with their business, the independent retailer can decide to recruit staff. A huge advantage of being an independent retailer is that you are your own boss. You make all the decisions and have the businesses exactly how you like it. This has its advantages and disadvantages. If you are left alone with the entire decision making, it can be extremely stressful and time consuming. An example of an independent retailer would be Atif superstore, which a small convenience and Halal meat shop in Woking.
Multiple Chains
Multiple retailing is also known as multi-channel retailing. It’s about the operating of a retail business where you have to sell goods to the customers through multiple retail channels. Moreover, the Stores, catalogues and the internet are three examples of channels. If a company offers the products and services through more retail channels, then this will mean a higher likelihood of making sales which will then result in higher profits. This is because the good or service is available to people in more than one way. The internet is a fantastic channel for the use in multiple retailing as this will be open to customers 24/7. Whereas, in-store have set opening times. An example of a multiple chain retailer would be Next clothing.
Variety Stores
Variety stores are retail stores that sell a huge range of household goods. The goods will be typically inexpensive, and this will make them extremely popular for customers who decide to shop in. Variety stores sell a variety of lines such as food and drink, home and gardening tools, electronics, toys and pet supplies to name a few. It is becoming more common for variety stores who will be selling a large range of goods which will be at the same price. An example of a variety store would be Pound land.
Department Stores
The Department stores are retail stores who offer a wide range of consumer goods. These are the goods which are separated into different categories known as “departments”. In the 19th and 20th century, department stores became extremely popular.
Department stores have many sections which include clothing, toys, furniture, paint, electronics, baby products and pet food. Some department stores will be owned by independent retailers and they will be a part of multiple chain stores. Department stores have also moved online where people can browse through the different departments using the internet. This can be seen on Amazon. Examples of department stores also include Argos and John Lewis.
Discount Stores
A discount store is defined as a retail store which sells products and services at prices which are lower priced than the typical market price. Discount stores may focus more on price rather than service or the display of the store. There can be general discount stores who decide to sell a variety of products which are at discounted prices. There are also “category killer” discount stores which specialise in selling a particular product at discounted prices such as jewellery.
“Next” have stores around the world. However, it also has discounted stores which sell clothing and items at discounted prices for reasons such as discontinued items and for items which are now last season. Another example of a discount store, which is one of the biggest discount stores worldwide, would be Aldi.
Convenience Stores
A convenience store is defined as a small store which stocks a range of everyday products which can include groceries, snacks, drinks, tobacco and newspapers. They are sometimes called “corner shops” or sometimes referred to as “CTNs”, which is a confectionary, tobacco and news retailer. Moreover, a convenient store could also be part of a fuel station. In some places, convenience stores will have long opening hours, where some are open for 24 hours. Typically, convenience stores usually charge higher prices than supermarket as they do not benefit from economies of scale due to them usually not ordering as many products from suppliers. However, they will make up this with long opening hours, when they are in more rural locations and then they will have shorter cashier lines. An example of a convenience store would be Mace.
Franchises
A franchise is when a company (the franchisor) sells another company (the franchisee) the rights to set up a company using their name/brand. Examples of franchises are McDonalds and Burger King.
As the franchisee will be purchasing the franchise and they will be buying an-already established company, then they will have to pay a proportion of their profits to the franchisor. The franchisor does however provide training, expertise and marketing campaigns which help out with all branches of the franchise. Buying a franchise will be a good way for anyone wanting to set up a company because
- They will be buying a business which is already established
- They will always have support and backup from the franchisor
Moreover, there will always be less risk in the setting up as a franchisee than a sole trader where the customers will already know about the company and the products that they have to offer.
Factory Outlets
A factory outlet is a brick and mortar or online retail store where manufactures sell their stock directly to the customers (public). At factory outlets, there will be products that are sold from one brand only. Also, the Manufacturers who sell only their own products which will be at a reduced price run factory outlets. Traditionally, a factory outlet will be a store which is attached to a factory, whereby sometimes allowing of the customers to actually watch the production process of their product. An example of a factory outlet would be Coach Accessories.

Cash & Carry
Cash and carry is a type of operation which is within the wholesale sector. However, it does involve retailers too. It involves goods which are sold from a wholesale warehouse, whereby that the customers (retailers) will come in and buy the products in bulk. The retailer benefits from this as they are getting each unit at a discounted price as they are buying it in a larger quantity. This means that when the retailer goes to sell their products directly to the consumers, then they will get a higher profit as they have bought the product at a cheap price. An example of Cash and Carry would be Hancock’s.
Not for Profit Organisations

Non-profit organisations are organisations that don’t operate with the aim to make a profit. Any surplus revenues are used to further achieve its purpose or mission. Non-profit organisations will be affiliated and have taxation implications which will include income tax exemption and charitable status. Non-profit organisations can be charity shops or animal shelters. An example of a Non-profit organisation would be The Dream Giver organisation.
Wholesalers
Wholesaling is the sale of goods to retailers, to business users, or to other wholesalers. Typically, it is the sale of goods to anyone other than the usual consumer. Wholesalers frequently physically assemble sort and grade goods, break bulk, repack and redistribute in smaller lots. Wholesaling can take place in warehouses and wholesaler markets. Wholesalers play a vital role in getting the products from manufacturers to consumers. An example of a wholesaler would be Heartlands Furniture.
Hypermarket
A hypermarket is a superstore combining a supermarket and a department store. A hypermarket will be a huge retail facility which will have a wife range or products under one roof, which will include massive grocery lines and general merchandise. Moreover, the Hypermarkets will also allow the customers to satisfy all of their routine shopping needs which will only be in one trip. A hypermarket is seen as having all grocery needs under one roof. Examples of hypermarkets would be ASDA and Tesco Extra.
Mobile shops
Mobile shops will be retails shops which aren’t confined to existing in one area. They can be portable shops who can visit different locations and sell their products. Mobile shops are particularly useful for visiting things like fairs and shows. Mobile shops can visit different destinations on demand so know that wherever they go, customers will be waiting for them. An example of a mobile shop would be The Fashion Truck, a mobile boutique.
Superstore/Supermarket

A superstore/supermarket is a large form of grocery store. It is a self-service shop offering a wide range of food and household products which are organised into different aisles. It is larger than a typical grocery store, but smaller and more limited in range than a hypermarket.
A supermarket or superstore will typically offers meat, fresh produce and dairy which will be along with shelves which will be containing packed and canned products. Some of these stores will also have household departments too. They will then occupy a large floor space and will be usually situated near a residential area so that they then will remain convenient to customers. They operate to make a profit. Examples of superstore/supermarkets include ASDA, Sainsbury’s and Tesco.
Indoor/Outdoor markets
As the first real form of retailing, this is not a great deal which has actually changed. Also, there are any people that have tried their hand at market trading and only some of them have made vast fortunes. For example, this includes Marks and Spencer, Tesco, and New Look which have all started from a barrow or a stall. The life also is very tough and the hours can be very long but there are certain families which have been involved with this particular industry, for many generations and they will usually be linked to the same trade or line. Other markets are seasonal. For example, the Christmas Market in London is a huge success and it then attracts thousands of people every year to the stalls that have thousands of items which are on sale.
E-Retailing

E-Retailing, also known as E-Commerce is trading in produces and services online, using the internet. It has become a sensation in the last number of years as it’s so convenient for customers. People can buy things from the comfort of their home. It saves them going to the shop and waiting in queues in-store. It also benefits the business as they may not have to pay for a store, which has expenses such as heating, electricity and lighting. E-Retailing is becoming a massive hit and is set to be the future of retail. Two excellent and successful examples of E-Retailing are EBay and Amazon.
Cooperatives
Cooperatives are associations of people who voluntarily cooperate for their mutual, social, economic and cultural benefit. These can include non-profit community organisations and businesses that are owned and managed by the people who work there or people who use their services. Cooperatives will frequently have social goals which they aim to accomplish which is by the investing of a proportion of trading profits back into their communities. Examples can include housing cooperatives and credit unions.
Compare the function of formats and locations which are used by one organisation in retailing for example Tesco. You need to identify why different retailers prefer different locations and explain the retail functions they perform. (M1)
Introduction

In this task, I have been asked to compare the function of formats and also the locations which are used by an organisation. I will be looking at Tesco as my chosen organisation.
I will be identifying why different retailers will prefer different locations and I will also look at the different retail functions they perform.
The importance of securing the correct location of a retail outlet for any product
Securing the correct location of a retail outlet for any product is extremely important in the success of the product. The product has to be placed in a location where it is going to be seen by a lot of people and will be in a place where the intended audience will also be present. If a retail outlet opens in a location where there is little footfall, the product may not sell well which could result in the future closure of that particular retail outlet.
Picking the right location can be the difference between success and failure. Many factors have to be considered when choosing the correct location for a product;
- Type of business; before looking for any location the type of business beingoperated must be carefully looked at. The amount of products you have will then influence the size of the location which the company will choose. The shopping experience for the customer must be considered before any location can be purchased. Tesco would need to consider the size of the aisles which are in their store, as well as car parking and also including other customer needs.
- Demographics; the target market of the product should be understood. This includesboth the target shopper and will include the geographic area which surrounds the location of the retail outlet. Things must be considered such as how far customers will travel to the retail outlet, the disposable income of the area and the employee demographics of the chosen area. Tesco would not build a store which is in an area where there is no money to sustain the company. It will then open its stores in areas where there is a gap in the market for a store like it to dominate.
- Competition; this includes an extremely important factor to consider when it is the securing ofcorrect location of a retail outlet. There may be good and bad competitors for the proposed business. Bad competitors are those who will ultimately have a negative effect on the product you sell. For example, a business may already be established selling the same product so moving into a location close by could be a risk. Good competitors are retail stores that compliment your business. For example, they could draw a similar target audience to your retail outlet. It would be highly rare to see Tesco next door to ASDA where there are huge competitors. So, Tesco would carefully consider where they choose the location of future stores.
- Traffic; when choosing the location for the retail outlet, then there will be traffic patterns of the areathatshould be considered. This includes the footfall of customers. Is there easy access to the store? Is there public transport nearby? The number of cars which are passing the location and will include the number of pedestrians who are passing will need to be looked at carefully before a location will be chosen. Communities are annoyed often with stores like Tesco opening in towns as it can cause traffic problems and congestion in the area. However, Tesco do try their best to prevent this – even though this can be difficult.

Viability; for any business tosucceed, it must be viable. The business owner must ensure that the location for the retail outlet attributes to the viability of the company. The location should help the business make a profit for many years. Tesco stores are extremely viable and in addition this can be seen with the growth of the business in recent years. It’s has now become one of the world’s largest retailers.
Moreover, the choosing of a location for a retail outlet is going to be one of the most important decisions a business owner can make. The location can affect many aspects of how the retail outlet operates and can ultimately affect the sales, profits and how costly the business is to run.
How has the location of retail outlets changed within the last 50 years?
Over the past 50 years, dramatic changes have happened which is in the location of retail outlets. In the 1960s, shops and retailers were situated on the high street. These retailers were situated in middle of towns which are usually on one street, which were known as the high street or more commonly known as the main street. This would have included sweet shops, bakeries, corner shops and trade stalls. The location of these stores stayed the same for many years. In the 1980s, retail outlets became ‘out of town’. Many shops opened in the one area. It would be convenient for people to go and do all of their shopping in one place. These outlets will be preferred over the stores which were on the high street as there would be more variety in one area. A typical outlet can have a range of goods such as grocery, clothing and electronics. An example of a local out of town outlet would be The Outlet Banbridge. Out of town outlets became common in the 1980s and through to the present day. However, in the past decade there has been a boom in online retail.
Although online shopping was invented in 1979, it wasn’t until the early 2000s where it became huge. With the increase use of technology and the internet, online shopping has never been easier. Consumers can purchase goods online and have them delivered the same day! The growth of e-commerce is one of the fastest growing ways in which business is now carried out. In 2013, online sales have now reached over £1trillion and this will show how fast this market is growing. As more and more shops close on the high street and out of town, e-commerce is set to become the most popular way of retailing in the future.

Tesco as a major retail operator
Tesco is a multinational grocery and is also a general merchandise retailer which was founded in 1919 by Jack Cohen, who was a market trader in London. Since then, it has grown to become the third largest retailer in the world in terms of profitability.
Tesco is the UKs largest retailer. It has around 7,000 stores and nearly 600,000 employees, nearly half of those staff are in the UK. Tesco has now gone global and they have stores in 12 countries and are growing more and more every day. Currently, there are more than 27 million Tesco Club card holders outside of the UK which goes to show how fast it is growing internationally. In 2014, Tesco had sales of around £1.02 billion every week!
The mission statement of Tesco identifies their approach to communities and the environment as the aim of their business and their purpose is ‘to create value for customers to earn their lifetime loyalty’.
Tesco have around 100 million customers per week and this will help them possess a market share of around 30%. This goes to show the scale on which Tesco operates. A 30% share in the retail market is huge especially when a company is in retail which is a massive industry.
Tesco doesn’t just sell groceries. As Tesco grew, they have now started to sell more and more goods and now offering more and more services. Some of these include;
- Groceries
- Eye testing
- Insurance
- Fuel
- Clothing
In order for any business to operate. It has to have a purpose. It has to have aims and something to work towards. Tesco’s main purpose is to make a profit and they will be able to use some of their profits, to grow and grow. Tesco aims to provide the best shopping experience for customers to help them in order to enjoy a better quality of life and have an easier way of living. As well as the main aim to make a profit, Tesco will now aim to provide an excellent service to all of its customers.
Tesco is always looking at ways to grow and expand. Apart from opening more stores across the globe, Tesco have now branched into E-Commerce. You can now purchase goods and services online from their website. This branch out to online sales proved to be extremely successful. In 2014, over a 6-week period at Christmas, Tesco brought in £450 million through online sales alone. In February 2006, Tesco announced that it planned to move its brand into America. By December of the same year, there were
200 stores in the United States. A contributing factor as to how Tesco grows so fast is because of their massive profits it makes. But how does it make so much profit where other businesses can’t seem to compete? It’s because the goods and services are so cheap and affordable. The general public loves the products due to that they will be getting their money’s worth and because Tesco has been getting bigger, they will be benefitting more from economies of scale. They can buy in bigger quantities so the price per unit decreases. These behind the scene methods of saving Tesco money which has ultimately lead to huge turnover.
With Tesco being a global organisation, it has many benefits for the company. These include;
- Increase in revenue. This is because there are more stores bringing in money. This iscalled greater revenue streams.
- Market share increases. Becoming larger and growing helps dominate a particularmarket. Diversification of a company helps to increase market share, which is exactly what Tesco did.
- Customer growth. Obviously opening more stores worldwide means morecustomers. But, looking into it more: If a company start to grow to the point where they can start benefitting from economies of scale (production costs going down), then they will be able to sell the products for less which means cheaper goods and will result in happier customers.
Tesco has a few sources of finance such as retained profits and sales of assets/products in-store and online. However, because Tesco have grown to be a large company, whereby there is a large source of their finance comes from the shareholders. This means members of the public can buy shares of Tesco. These shares are available on The Stock Market and as of September 30th 2015, one share in Tesco would cost 178.85p. Owning shares in Tesco will then enable you as a result to receive a share of profits in the form of a dividend. The more shares you own, the higher your dividend will be. Being a shareholder doesn’t mean that you have control over how the company will be run. Each shareholder has limited liability so they can only lose what they have invested in the business.
Tesco is a public limited company (PLC) operating in the private sector. The reason that Tesco operates in the private sector is to maximise profits. It is not in the public sector as it not owned or controlled by the government. Public sector businesses typically have the aim to provide a service more so than to make a profit. So, Tesco remains in the private sector as it aims to make profit. It also remains a public limited company so shareholders can buy into the business which is a way of raising capital. There is no limit to the amount of shares which are available to be owned by the public but there has to be at least two shareholders at one time. If there was only one shareholder, that person would have ultimate liability. However, there are many shareholders in Tesco, each having limited liability. With Tesco being a public limited company, the business can raise a large amount of capital as there is no limit to the amount of shareholders. Also, the business has separate legal entity. So, if any of the shareholders die, the business won’t dissolve.
However, with Tesco being a PLC, it has its disadvantages. The setting up and running of the business involves a lot of legal formalities. To any business, this is both costly and time consuming. Tesco would also have to public its accounts which can be seen by the public and other competitors. With being a PLC and shaving the shares being available to the public, the owner can actually lose control of their company if a majority of the shares will be purchased by an individual. This is a particular risk to public limited companies. With Tesco being so huge, then the making decisions can be a slow process which can involve a lot of meetings.
Moreover, with Tesco being in the private sector then they will have many advantages. Tesco also have private ownership and control so this means that only the owners dictate the way in which it operates. The government doesn’t have control over the company as it isn’t in the public sector. There are also more opportunities for the company to grow as their profits will be used according to what the owners have decided to do with them and not what the government want to do with them. Disadvantages to Tesco of being in the private sector are that there are many businesses with the aim to make a profit so there is a lot of competition. Companies will be competing with each other in order to become the most favourable, dominant and then have the highest profit margins.
Tesco can be found in the secondary and tertiary sectors. It is found in both because;
- Secondary sector; this is where Tesco create their own brand of food or products. They alsodesign and manufacture their own products.
- Tertiary sector; this is where Tesco also sell their products such as food, fuel and clothing. Theyalso provide services such personal loans, credit card services and opticians.
Tesco have many different types of stores to suit the different shopping patterns of its customers. These include;
- Tesco Express; This format combines a petrol forecourt and convenience storestocking a range of 1,400 products
- Tesco Metro; Located in prime high street sites, Metro offers a range of productsspecially selected to attract town centre shoppers.
- Tesco Compact; this is where the Compact stores are designed in order to offer the range of Tesco superstoreproducts and also the services which are on a smaller scale
- Tesco Superstore; this is where the superstore format is the most common, whereby the supplying of weeklyfood and grocery shopping. With the vast range of products on offer, most of the family’s needs can be met in one convenient time-saving trip.
Tesco has become such a profitable business today as it not only just fulfil its purpose in making high profits, but it also further meets and also exceeds customer expectations so where the customer service they receive will be better than anywhere else. With excellent strategic decisions and expansion plans, it is predicted that Tesco will dominate the retail market for the next number of years.
Factors that influence the owner/manager of Tesco
For any retail outlet – for example like Tesco – to operate efficiently, effectively and profitably, then the owner/manager of the store has to consider many factors which are going to affect the running of the company. The manager then will be responsible to make any adjustments or changes to operations within the store. Factors which may influence the owner/manager of a retail outlet for example Tesco will include;
Location; The location of a new company is one of the first things the company owner has to consider. The owner should choose a location which is convenient for customers. This will ensure that high amount of sales will be met which will help with the profitability of the company. Owners of Tesco must decide on a location where the store is surrounded by a large number of people to ensure it is convenient for its customers.
Footfall; Footfall has to be carefully thought of when an owner/manager of a store for example Tesco has to decide to open the store. When the owner thinks of opening the store in a particular location, the footfall of locations should be considered. This will include both the amount of pedestrians which are passing the store, as well including the traffic which is passed by the store. A store with a high footfall is more likely to viable.
Pricing; the manager of a Tesco store could be influenced and can change the price of some products of the store if they are cheaper with a rival store such as ASDA. Pricing is very important to the owner as if the price is too high it will mean no sales as customers will shop elsewhere. The owner must be very much aware of the price of products. Owners need to change their prices as trends in the industry change.
Accessibility; The owner of a store like Tesco would then have to design the store to be accessed easy by all of their staff and customers. The store should be accessible and easy to navigate around. There should be sufficient space for things like Lorries to come in for deliveries. The store should be accessible and fit for purpose.
Parking; Store owners will want a store which customers can come to and park without difficulty. The car park should be of appropriate size with plenty of room. A lack of space can cause trouble and congestion to the store whereby the owner will have to ensure that the parking space is appropriate to the size of the store.
Earning power; the earning power of the people in the area should be looked at before any business owner opens a store. Furthermore, a store for example Tesco whereby this will typically involves a high spending shopping trip would have to be built in an area which has a high affluence. People need to be able to afford to shop in Tesco so the earning power of the area is very important.
Employability; Owners and managers have to decide if the location of the store is an area of high or low employability. A store could not open in an area where there is nobody to work. A typical Tesco store has around 50-100 staff. That is a significant amount of people who need to be employed so that the store can run efficiently and effectively. So, owners and managers will then look at the rate of unemployment in the area and see if the store can bring jobs to the area.

Why do customers choose a particular retail outlet?
When a customer goes to a store there is a reason for it. Customers will be influenced by many things which a retail outlet does. For example, Tesco have built up millions of customers and they all return for many reasons. These include;
- Competitive price; From my research, Ihave now discovered that a main reason why a customer goes to a store for example Tesco is because of the competitive prices they have. Tesco is known for having affordable products at cheap prices. Tesco will usually compare its prices to other rival stores such as ASDA and Morrisons and if the customers think that Tesco is the cheapest, then they will be sure to shop with them.
- Brand/Reputation; Customers want to buy from a reputable store. They want to buyfrom a retailer which has a good reputation and also have a corporate image. A great example of this showing its effect was in 2012 when some of the meat in Tesco was found to be contaminated with horse meat. This almost had detrimental effects to Tesco as they lost thousands of customers. However, after publicly dropping that supplier, Tesco managed to get back some of its lost customers.
- Convenience; the retail outletmust be convenient. Customers don’t want to have totravel miles to get their groceries. They want a store which is close by and easy to get to. It must be convenient to get to and convenient when the customer arrives too.
- Quality of products; the quality of products is very important in the eyes of thecustomer. Customers don’t want to be paying for goods which are of bad quality or not fit for purpose. My research has taught me that high quality products can easily help with the brand/reputation of Tesco and this will then ensure the return and keeping of millions of customers.

Range of products; Customers want to shop in a store where everything is under oneroof. To facilitate those customers, then Tesco will have branched out into many different types of stores which will include Tesco Express, Superstore, Metro and Extra. Customers choose Tesco as covers more products than most other stores in the same market.
- Customer service; Customer service is very important to customers and tobusinesses. Customers want to walk into a store and feel valued. They want to be respected and feel valued. Tesco have a customer service team to facilitate those customers who have any queries – something customers really appreciate.
- Parking; some large stores will attract thousandsof people into their store every day. There must be reasonable and appropriate parking to facilitate these customers. Customers will then want to arrive to a store for example Tesco and will find it easy to park which then will keep the shopping experience quick and easy.
- Opening hours; Opening hours of stores haschanged in recent years. Stores which have opening longer hours to facilitate customers which are those who can’t shop at particular times throughout the day. For example, Tesco attracts customers as they now open 24 hours in some places. This suits their customers which work all day and who can only shop in the night. From my research I’ve found out that stores can become up to 25% more profitable from opening 24 hours a day.
- Quick checkout; Customers who don’t like to visit a store for example Tesco and will have to stand in queuesfor hours. They want to arrive in the store, get their groceries and checkout quickly. Tesco has several tills in each store and they haven’t introduced self-service checkouts to speed up the checkout time for its customers.
- Deals/Promotions; Many customers shop in stores which are carrying outdeals/promotions. Customers want value for their money and will get discount when they can. Tesco heavily market and advertise their deals and promotions which customers make full use of.
Customers will shop in a store which suits them. They want a store which supplies excellent quality products at affordable prices. Tesco has been extremely successful in keeping their customers shopping with them over the years and growing as satisfied customers will return again and again.
Functions of the retailer
For any retailer to operate, different people and different departments have different functions. They all work together for the smooth-running of the business. Some of the functions Tesco perform include;
Customer Service; Tesco carry out this function by providing information, giving advice, providing credit facilities, delivering goods and by providing after sales service. Finance; The financial department will then carry out this function by preparing accounts, paying wages and salaries, and also obtaining capital and resources and whereby the allocating budgets to other departments within Tesco.
Marketing; The marketing department within Tesco help carry out this function. It involves the marketing mix, and will involve the carrying out of market research and sales promotion. This function helps Tesco to maximise sales and overall profitability.
Distribution; There are many things for Tesco to decide with regards to distribution. Which method of distribution will be used, which channel of distribution will be used and how to get the products to the right place at the lowest cost all have to be carefully considered.
Sales; Different people within the company Tesco will be responsible for carrying out this function. For example, this can include the sales director will be responsible for the overall function. However, within that the sales manager is responsible for the sales staff and so on. This function must be carried out appropriately to ensure high sales.
Production; Tesco will have to obtain resources in order to produce goods or services and they then will organise these resources so that these particular goods and services will be delivered appropriately. Many things have to be considered in this function such as the aims of the business and the budgets of the related departments.
Human resources; Tesco is known for having a huge human resources team within the company. They carry out many functions such as recruitment, retention and dismissal of staff, training and development of staff, as well as good working conditions/health and safety.

Administration; The administration department of Tesco will make sure the operations are run smoothly. They carry out functions such as clerical work (record keeping, document production), maintenance, security, health and safety and the running of ICT within the company. As well as the functions highlighted above, Tesco will also then carry out the following functions which is then seen more clearly from the eye of its customers rather than from the staff running the business;

- Deals/Promotions
- Banking
- Online Shopping
- Free Delivery
- Alcohol
- Electrical
- Club cards
- Self-Service
- Clothes
- Insurance
Conclusion
The Retail sector has changed significantly over the years, when it was from the very first supermarket to online retailing. Moreover, there have been many different types of ownership in retail and there are also certain factors which decide on the ownership which can include the type of store, the brand and the product being sold. Also, the Retailers have many functions whereby will help them work more efficiently and effectively. These functions will encourage the return of customers which then will boost sales and subsequently overall profits.
It can be seen that Tesco has grown to become one of the largest retailers in the world. It has got everything right. It opens stores in the correct locations and then they will change its operations as trends across the market change. For example, introducing online shopping as the internet became more popular. As Tesco keeps up with modern day retail, they then will decide to extend its functions and gathers more and more customers, where it has now become one of the most successful and fastest growing businesses in the history of retail.
References
http://www.shopperdoodledoo.co.uk/research/retail-origins
http://researchbriefings.files.parliament.uk/documents/SN06186/SN06186.pdf
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Retail"
Retail can be described as the process of goods or services being sold directly to the end-user. The most common form of Retail is through selling products in brick-and-mortar stores.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




