Cloud Computing Security
Info: 7825 words (31 pages) Dissertation
Published: 21st Feb 2022
Tagged: Cyber SecurityComputing
Abstract
Cloud computing has shaped the infrastructural and computing concept for future advanced computing technology. It is also one of the most trending technologies which have helped business for reduced cost for IT infrastructure building and providing the company with increased scalability and flexibility for computer processing. Cloud Computing in the past few years has become as a promising fastest growing idea for different IT and business industry. At the mean time, some of the most of the IT organisation have analysed the concerned on increased cloud security that has existed with the deployment of the services. Security can be a critical issue for any cloud service provider for its implementation of cloud computing services. In most of Cloud computing environment, the risk of security and privacy of data compromised. These risks associated with the remotely store data for the user and its access to them. Thus, security is one of the most asked and argued issues with cloud service provider. Data in the cloud environment stored in any geographical location and user has no control over the data stored in cloud storage. However, cloud computing has also a comparison that the user benefits with its deployment. So, even with the risk associated with security and privacy most of clients/users consequently adopt moving to cloud infrastructure for their business. With this literature and research review, we have summarised the security issue in cloud computing and also figured outs is reliability, availability and adaptation of the cloud computing services for various business or uses.
Keywords: Cloud Computing, Security, Privacy, Policies, Cloud Service Provider, Data and Information
Contents
1. Introduction
2. Importance of Security in Cloud Computing
2.1 Security Issues in Cloud Computing
3. Cloud Security Guidance
4. Cloud Computing Requirement
5. Open Security in Cloud Computing
6. Security Measures in Cloud
7. The Notorious Nine Cloud Computing Threats
7.1 Outstanding Issues
9. Conclusion
1. Introduction
In the 1960s, a terminology called ‘Internet’ came into existence in the world of computers, but until 1990s it wasn’t able to give any penetration to the businesses. In 1991, to make internet usable the World Wide Web (WWW) was born. As the Internet got matured with faster and reliable connections, new businesses called Application Service Provider (ASP) had emerged. ASPs took the legacy systems and built the business application for the customers. In order to use the services of ASPs, the customers have to sign a contract with them. In return, ASPs would build and maintain the applications and their infrastructures to keep applications executing (Salesforce Australia 2017).
In the late 1990s a technology came into existence which is Cloud Computing. In 2013, the cloud computing began to disrupt the other information technology services and penetrated market through its services. In the same year, Cloud computing estimated spending soared to $47 billion, and it went more than double to $108 billion by 2017. Cloud computing revolutionised the entire information technology sector, resultant, and many companies have been adopting the cloud services as a primary IT tool to solve their business problems (Salesforce Australia 2017).
Providing computing services like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, etc. over the internet is called cloud computing. The organisation providing cloud services are cloud providers, and the consumers who consume the cloud services have to pay for the cloud services as per their requirement.
Some of the important factors why cloud has been adopting globally by various companies are (Microsoft Azure 2017):
Quick implementation – Cloud shrinks the implementation and capital expenditure on buying the IT infrastructure (Software and Hardware) and resources. Businesses and individuals only have to sign up to start the services of any level instantly in few days or weeks rather than in months or years.
Scalability – The consumer can quickly scale up and scale down the cloud services as per their requirement. The main advantage is that consumers don’t have to pay for unused resources as they paid for ASPs.
Security – Customers can securely consume the services from any device. On a hidden layer, Cloud makes data backups, disaster recovery to make data more secure and gives continuous services faster, easier and less expensive. Data replicated to multiple servers on the Cloud.
No Maintenance – As the Cloud system is highly elastic in nature. Cloud providers are responsible for the maintaining and upgrading the system as per customer requirement. All up-gradation happens at the back whether it would be on application or database level without interrupting the client’s service.
Accessibility – Cloud system has round the clock availability with support from the cloud providers. Customers can access the services securely from any device.
2. Importance of Security in Cloud Computing
Today’s global IT infrastructure, services and applications are all running on the Cloud platform. Cloud acts as an intrinsic functional component of most of the daily applications whether users are using Dropbox, Google Drive, Facebook, Twitter, etc.
Cloud has revamped the business processes entirely. Today millions of organisations are consuming the services of the Cloud platform globally such as document creation, software (SaaS), platform (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). With over twenty-five thousand company employees use an average of 545 cloud services. Over half of the internet users using cloud-based email services like Gmail and Yahoo. Here are few more things you can do with the cloud (Salesforce Australia 2017):
- Create new apps and services
- Store, back up and recover data
- Host websites and blogs
- Stream audio and video
- Deliver software on demand
- Analyse data for patterns and make predictions
From both, the perspectives of Cloud consumers and providers, a wide variety of security constraints encompasses by Cloud security. The consumers will be apprehensive with the security policy of the cloud providers that how their data stored and where and who have the authentication to access that data.
On the other hand, Cloud providers’ deals with the issues like infrastructure’s physical security, access control of cloud assets, execution of cloud services and maintenance of security policies. Cloud security is a crucial aspect and significant reason for the organisation in an agitation of using cloud services. A non-profit organisation of IT industry specialist named Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), has led the frameworks of guidelines for enforcing and implementing security within cloud operating environment (Techopedia 2017).
Security is a highly-prioritised aspect of any computing services, in that context, safety and privacy issues are critical for handling the client’s sensitive data on Cloud servers. Before signing in to Cloud space, users have to get the information regarding authentication and management of cloud providers. From the Cloud providers end, it is important to verify the authenticity of the user’s credentials and maintaining the high-security standards otherwise security breach could happen (Boitnott 2017).
Cloud computing is the most valuable innovation given by the information technology domain to businesses possessed various characteristics like inexpensive virtual services. Consumers can store almost everything on the Cloud, but after storing data, the next big thing which matters a lot for customers is Security. For instance, Dropbox, a cloud storage platform hacked. The intruders hacked the system through unauthorised access to the personal information of users also sent the spam emails to user’s personal folders (Boitnott 2017).
According to Baker & Mckenzie survey, Security and privacy are the primary objectives of consumers before consuming the cloud services. The main disinclination in deciding whether to use cloud services are Security (88%) and Privacy (73.3%). The majority of consumers concerned regarding control and regulatory policies. Besides, 69% of buyers recognise that reputation of the cloud providers is the key criteria for choosing Cloud services. Overall, Security is the biggest concern among consumers or buyers to adopt the Cloud services (BakerINFORM 2017).
Two-thirds of the buyers identified that their providers should agree upon the customer specific security terms. ISO 27001 standards chosen by the majority of consumers on which they want providers to adopt. Many providers suggested providing users with control reporting environment through SSAE 16 SOC Type II reports. It gives the evidence that how much the Cloud security is critically significant for buyers especially for those providing financial or health services in a highly regulated environment (BakerINFORM 2017).
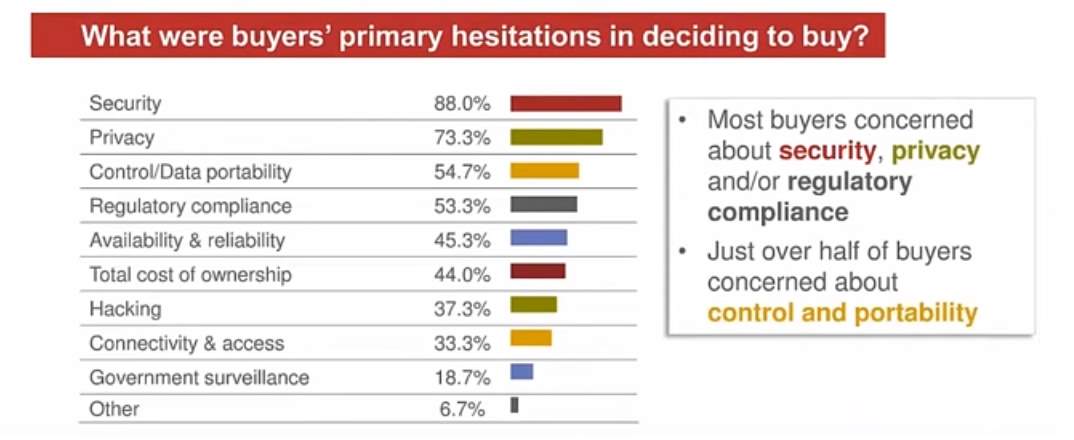
As mentioned above, security is the biggest hurdle for Cloud service providers and its users. The crucial factor is the location of data in Cloud security. The location is the main advantage of the Cloud flexibility and a security threat as well. Determining the location of the data storage will help in providing the security in some region and could act as a threat to other areas. For Cloud users personal and business data security compel the Cloud service providers to think about strategic policies. Technical security is not the only medium to solve the Cloud security issue.
Trust is another factor plays a vital role in this scenario because it is a mutual interest for all stakeholders of Cloud environment. Almost all types of intruders attacked on computer networks and data transmission are equally a threat for cloud services. Some of the threats are eavesdropping, phishing, man-in-the-middle, sniffing, etc. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) is one the major and common attack on Cloud computing environment and a potential problem with no option to assuage this. The data encryption and its authentication are the primary security concern fall under the practice of safer computing. There is a thin line difference between risk and security of Cloud. Vendor lock-in considered to be the potential risk in Cloud services which is unrelated to security term.
Provider business discontinuity, licensing issues and service unavailability are some of the examples which do not lie within the security domain from a technical perspective. Distribution of security services among different vendors would lead to inconsistencies which might transform into security vulnerabilities. Using the various kinds of security software tools in Cloud environment might have the execution loopholes which can cause a security risk to Cloud infrastructure (Ahmed & Hossain 2014).
Normally, Cloud computing using the public networks to transmit the data and make it available to the world, so cyber threats are standard for the Cloud computing. The existing Cloud services have been suffering security loopholes from which an attacker can take advantage. Due to the nature of Cloud computing approach made it prone to information security, privacy and network security issues would be the concern for the Cloud infrastructure. Different Cloud infrastructure factors such as human errors, software bugs and social engineering are dynamically challenging for Cloud. To reduce the security risks Intrusion detection plays a significant role in network monitoring (Ahmed & Hossain 2014).
There are varied angles from which various security threats might enter from into Cloud infrastructures such as virtual servers, database, concurrency control, load balancing and memory management. The two inevitable security threats for cloud users are session hijacking and data segregation. Scalability dynamism and level of abstraction are one of the challenges to building boundaries around the Cloud infrastructure (Ahmed & Hossain 2014).
2.1 Security Issues in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers three different segments to consumers – Infrastructure, Platform and Application /Service as a service. Each of them provides different operations and services corresponding to business and individual. There are various concerns regarding the security in a Cloud computing environment – Servers & Applications accessibility, Data Transmission, VM Security, Network Security, Data Security, Data Privacy, Data Integrity, Data Location, Data Availability, Data Segregation (Padhy, Patra & Satapathy 2011).
- Servers & Applications accessibility – In Conventional data centres, admin used to access the servers in a restricted or controlled way through directly or on premise connections. In Cloud architecture, the admin can access the system only through the internet which increases the risk and exposure of connection. While accessing the data by user, data access issues are primarily associate with security policies provided to users. To avoid the unauthorised data access, in that case, security policies should adhere to the cloud.
- Data Transmission – The data always transmits from one end to another end in encrypted formatted. SSL/TLS data transmission protocol use here. By providing different access controls to Cloud provider for data transmission like authentication authorization, auditing for using resources, and by ensuring the availability of the Internet-facing resources at the cloud provider. To interrupt and change the communication, an intruder can place themselves in between the communication to the user, this types of cryptographic attacks are called ‘Man-in-the-middle’.
- Virtual Machine Security – Virtual machines are dynamic in nature seamlessly moved between physical servers. Virtualization is one of the components of Cloud which runs various isolated instances on the same physical machine is one of the allocated tasks of Virtualisation. Virtual servers like Microsoft vulnerable to allow a guest operating system to execute code on the host OS and other guest OS. The main loophole found in the VMware’s share folder terminology which permits the guest systems to read and write in system files. Appropriate isolation methodology not implemented in current Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM). VMM should provide a secure environment so that none of the virtualized guests can access host system.
- Network Security – The networks categorised into different types like public, private, shared, non-shared and large or small area. The network level is consist of these security problems like Sniffer attack, DNS attacks, etc. In DNS attacks, a user can easily route to another Cloud server instead of what user requested. Domain Name Security Extension (DNSSEC) lessen the number of DNS threats but it not adequate to stop the re-routing the connection to other servers.
- Data Security – Whenever users want to store their data on the Cloud, the Cloud providers use the most common communication protocol which is Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). For ensuring data security and integrity, usage of Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) and Secure Shell (SSH) is common. In Cloud systems, the organisation data saved out of premises. Cloud providers can use the encryption techniques to avoid breaches. For instance, The Administrators of Amazon Elastic Cloud Computing (EC2) can’t access the user’s instances and do not have access to Guest OS. Administrators require their Cryptographically Strong Secure (SSH) keys to access the host instance. All accesses should log and audited timely.
- Data Privacy – With Data Security, Data Privacy is one the primary concern for Cloud service providers. Cloud providers should ensure the customer’s data privacy demand. Data on the cloud is almost distributed globally, which increases the concerns regarding data exposure and jurisdiction. Cloud providers might be at risk to not complying with the policies of the government.
- Data Integrity – It helps to reduce the level of data corruption occurs at storage. For data centres, integrity monitoring is crucial for Cloud storage. Database constraints and transactions contribute to maintaining the Data integrity. For Data integrity, transactions should follow the properties of ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation and Durability).
- Data Location – In Cloud data storage, users are not aware of the fact on which location the data stored or accessed. To serve this purpose, Many well-renowned Cloud providers have the data centres globally. Due to various countries data privacy laws and compliance this could be an issue. In many enterprises, the location of data highly prioritised. For example, Countries like South America has the local laws and jurisdiction on a particular amount of sensitive information.
- Data Availability – The enterprises should ensure the availability of data round the clock without any hindrances. Due to the unpredictability of system failure, data providers unable to attain that standard sometimes. To achieve the high scalability and availability of the system, service providers can make some changes at the application and infrastructure level. A multi-tier architecture is the best option to achieve the data availability seamlessly through load balancing and running the instance on separate servers. For any emergencies, cloud providers should design an action plan to cope up with disaster recovery and to achieve business continuity.
- Data Segregation – In cloud architecture, data typically shared among other customer data. To solve the data segregation issue, encryption is not the only solution to look. In some cases, consumers don’t want to encrypt their data because it might destroy the data. Cloud providers should ensure that encryption provides at all levels and encryption should implement under the supervision of experienced professional.
3. Cloud Security Guidance
As the companies inclining towards cloud computing, they should at least maintain or possibly surpass the level of security which they possessed in the traditional environment. The cloud security guidance includes steps that can be used to evaluate cloud provider security. However, every company should perform an analysis to choose the cloud services that can fulfil their needs. The following steps are about the security guidance (Cloud Standard Customer Council 2015):
- Ensure effective governance, risk and compliance processes exist – While adopting cloud computing, it is crucial to understand the risks associated with using the cloud services and own organisational policies. A master service agreement between the cloud provider and customer should be made to ensure the security of data and application of the consumers are following customer’s security policies. The cloud service vendors and customers should understand the specific laws that apply and obligations imposed on them. In a case of security vulnerability or breach, the cloud service provider must inform the customers about the situation and regulate the breach, restore secure access, start investigations and take corrective measures to stop the similar issues from occurring in the future.
- Audits–The cloud service providers should timely audit compliance of IT systems through independent auditors following established standards and give access to these audit reports to its customers. The auditors should provide access to the policies and procedures of the service provider related to security of their system. Auditors also require records to check the policies have implemented or not. Since there is a high risk of abuse of the information by the customer making changes to their application and authorization depending upon the type of cloud service, the audit must extend to these facilities as well.
- Manage roles and identities–Both the provider and the customer will have employees who will have access to different type of data at various service levels. Hence, the customer must ensure that the cloud provider has appropriate policies to access their sensitive data and application by the Cloud provider employees. Also, the providers must allow the customers to manage the authorization of their users as per their security policies. The cloud provider must have a system to maintain the unique identities of the users, and these should be monitored and logged for auditing and reference.
- Ensure protection of data – It is important to consider the security of data that stored somewhere and the data transferred over some media in cloud services. Data in cloud computing may refer to application programs or machine images, data files and databases.
Depending upon the type of cloud service, the data protection responsibility lies on the customer or the provider. For IaaS, the customer is responsible for the data. For PaaS, the client and provider both share responsibilities depending upon their security policies. And, for SaaS, the provider is in charge of the data.
- Enforce privacy policies – Security and privacy are interrelated, but privacy refers to the data that held by any organisation which may be exposed to others by a software bug or a hostile person. Data privacy requires implementation of limitations on the use and accessibility of personally identifiable information (PII).
When the data is being transferred or being stored in the cloud, the responsibility of the data may lie on the customer, the provider or a third-party data controller. So, it is important the involved parties enter into a written agreement that defines the roles of responsibility of the data. It is the responsibility if the customer to check if their cloud provider adheres to the established privacy policies and practices.
- Assess the security provisions – A compromised application can bring economic as well as reputational damage to the provider and the customer. It is important to identify the needed application security policy based on the type of cloud service. For IaaS, the customer has full responsibility for deployment of the system and the security policy. The client should focus on auditing, authentication, data encryption aspect of the IaaS system to enforce security.
For PaaS, the provider has responsibility for securing the infrastructure, operating system and middleware and the customer is responsible for application and obtaining access to the application. For SaaS, the provider is responsible for the data and security policy integrity. However, the customer should make sure that the provider’s policy come in line with their interests and the modified parameters in the application should not interfere with the provider’s security model.
- Ensure cloud networks and connections are secure – It is the responsibility of the service provider to allow or block network traffic depending upon its legitimacy. The responsibilities are traffic screening, denial-of-service protection, intrusion detection and prevention, logging and notifications. The customer should also be concerned about the internal network attacks such as confidentiality, integrity, availability breaches and hence evaluate service provider’s internal network security controls.
- Evaluate security controls on physical infrastructures – The security of the physical infrastructure plays a huge part in the cloud service security. The customers must assure about the security measures of the physical facilities. The security controls include prevention of unauthorised access, prevention from external and natural threats, prevention of malicious activities, equipment security control, prevent supporting utility malfunctions, security of cabling, infrastructure maintenance, provision for data backup, plans for handling equipment failure situations.
- Manage security terms in the service agreement – Cloud computing includes two distinctive parties – service provider and the service customer. So, it is imperative that the security responsibilities of each party be made clear through terms of the contract. Each type of cloud service has different security responsibilities for the customer and the provider. Since the outcome of a security breach could mean a huge financial and reputation loss for the provider and the customer, it is crucial to identify the liabilities of the involved parties explicitly.
- Understand the security requirements of the exit process – Once the customer has terminated the cloud service, the customer’s data should be permanently erased and should not remain with the cloud service provider, no matter where the data might have stored. Also, the provider must allow the customer to retrieve the data in a secure form, ensuring the smooth transition without loss of data.
4. Cloud Computing Requirement
Cloud computing requirement classifies the architecture requirement for various cloud service provider. It is essential for delivering quality services, designing fault tolerance system, load balancing, maintaining privacy and security. Depending on service models the cloud providers and the consumer has a different level of control over the application. Some of the cloud computing requirement briefly described and listed below (Sabahi 2011):
- Selecting cloud service delivery model – Essential physical components such as storage, memory and CPU’s provided with IaaS and web services is used to access the IaaS. Limited control is commonly experienced in SaaS application configuration, as all the application is pre-configured and is ready for use. Platform as Service (PaaS) allows dynamic and scalable web application to deploy. So, security controls can maintain by both cloud provider and customers in both web and browser approach.
- Quality of cloud service – For cloud service implementation, quality is a most associated factor for end users and servicer provider too. The quality of service (QoS) often compared with the performance, reliability, security and Service Level Agreement (SLA’s) of the service provided. Quality assurance helps to measure the quality of service (QoS) used by end users. It emphasises the service provider to monitor the quality and performance of the service.
- Interoperability – Interoperability of cloud service enables flexible integration and migration of cloud services within different cloud service providers regardless of the different API and platforms used. It allows both service provider and enterprise customers for interoperability of application on various cloud infrastructures.
- Fault Tolerance – A system with fault tolerance capability could operate automatically in the event if some failure occurred. This feature allows a system for continuing its operation by self-diagnosis and self-healing of the fault. This mechanism is activated once the error detected in the system.
- Load Balancing – One of the key requirements for any cloud architecture for designing self-balanced system for balancing IT resources. Load balancing mechanism distributes various IT resources such as network, storage, memory for easy and quick access to data from the cloud. We can build stable and dynamic Cloud Computing architecture with load balancing technique.
- Virtualization – Virtualization is the main underlying component for any cloud computing architecture. It allows cloud service provider to virtualize the memory, server, storage and network. It also helps any physical server to migrate to a virtual platform and improves its flexibility and agility.
- User-centric Privacy – User’s data is a sensitive piece of information. Cloud users stored the data on different remote location. It has created the major issue for user’s data privacy. It is a responsibility of cloud service provider for maintaining the privacy of user data. Data integrity and confidentiality can implement by using encryption and compression technology.
- User Trust – Trust is a very much essential requirement for building a strong connection between cloud service provider and users. Trust helps consumer for the adaptation of cloud services. By build confidence, you can create trust in your cloud system. Trust building includes trust establishment, trust evaluation and trust management.
- Security concern – Building Cloud architecture has always been a challenge due to security concern. Data on Cloud could contain detail of customers and business information. Cloud service model like SaaS, PaaS and IaaS has different security measure to consider, and it is very much difficult part to guarantee the security of data. As IaaS is the base to build PaaS and SaaS, but each service module has security issues and risks related factors.
5. Open Security in Cloud Computing
- Data Storage Security – Data privacy and security is an important part of quality cloud service delivery. Most of the cloud services have their data server in the remote site. User’s data on cloud server are frequently accessed and manipulated using the different application. Data modification includes insertion, deletion and update of the data. Sometimes the data are modified through unauthorised access; it can create a challenge for maintaining data security. The data would be safe by implementing the proper authentication and verification method.
- Threats Identification – Before the identification of possible threat could secure or mitigate the system attacks. But, identifying threats comes with various challenges. Identifying the risk factors with security control approach can reduce the threats to the cloud system. There can be multiple threats to cloud computing some threats come from malicious and infected APIs, shared technology, data leakage, etc. It can be the internal or external thread. External threats may be more severe than the internal one.
- Data Integrity in Cloud – Data integration is necessary for a business to gather the valuable information. However, the data must be trustworthy and validated before integration. Authorised parties should only carry the integration. It can protect the cloud integrity and prevents unauthorised modification of the data from the cloud servers.
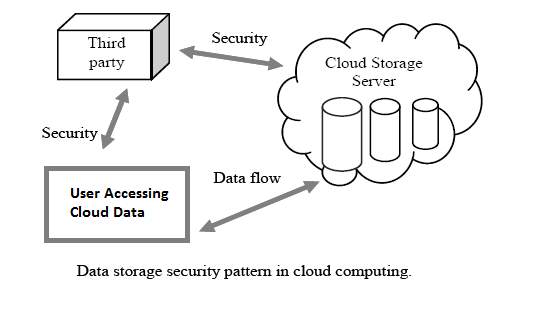
Various approaches can use for data integrity. Integrity can be maintained with the digital signature attached to the data file and also use message authentication code. Data storage protection can also apply during transaction, reduction and other processes in the database.
- Cloud Availability – Cloud Availability ensure the availability of cloud servers to enterprises on demand. Cloud availability also has some of the security objectives, some of them are:
a) Cloud availability ensures the availability of system information.
b) Confidentiality and integrity to maintain the service provided.
c) To maintain authenticated communication between cloud user and server.
6. Security Measures in Cloud
It is now evident fact that security is one of the major concern in cloud computing. Cloud computing has different and some security measures associated with it. Protecting and securing the cloud infrastructure must be ensured by the cloud service provider It is necessary that all the security measure has met their standards to ensure the protection of physical and logical data stored in cloud infrastructure.
Thus, it is essential to make the analysis of security measure in the cloud and is highly required to adopt the security measure in cloud computing environment (Sabahi 2011).
- Threat on Cloud Computing – With the security features available on the architectural design of cloud model, other challenges exist in deploying the cloud services. Some problems may arise due to the unavailability of data control for the real owner of data. There may be possibilities of data leakage due to trust factor on the service provider.
- Cloud Computing Security Analysis – Mostly, security in cloud computing can be implemented with advanced security measure in a centralised data centre. Analysis of the security features can apply to those centralised data. It sometimes such adoption may create a new challenge with the security issue. Security issue may vary on the development models too; public cloud may expose to greater security risk than private one. Data risk are also associated with the location data stored. So, security linked with the application, data transmission and data storage should be properly managed and analysed before cloud service delivery.
- Security Risk & simulation techniques for the security risk – Security risk can associate with people, technology or other physical risks. These all factors can have a persistent threat in a cloud. To minimise these risk, we may need sufficient update of the system and data with latest security update features. However, there can still be chances of risk associated with spooling attack on the business system. This kind of security risk level can be measured with the likelihood incident of scenario occurred.
Evaluating system performance and security issue performed with modelling and simulation technologies. Cloud-based software needs regular testing, and this can be done with various techniques and tools used. It helps to monitor the performance and security risk within the cloud system.
7. The Notorious Nine Cloud Computing Threats
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) on 2013 conducted a survey of cloud expert industry to find the vulnerabilities with the cloud computing and its services delivery. The report also figured out the most recent threats concerned for cloud computing.
With the proper analyses and adoption of above-given security threats, both cloud providers and users can mitigate the risk associated with the system. It also provides for an appropriate and comprehensive guideline to cloud security delivery. The nine most threats that related to cloud security are listed below (Cloud Security Alliance 2013):
- Data Breach – Data breach involves unauthorised access of server data, network or access to the system. It is potentially a security threat. An individual with unauthorised access may engage in stealing and viewing the data which is sensitive, confidential and protected. Cloud service with multitenant services must be designed properly to prevent system data breaches. Data breaches can create a threat to both one and more client’s database in multitenant cloud service.
- Data Loss – Data is a valuable asset for the organisation. A malicious attack on the system sometimes is a root cause of the data loss for the data store. Data might accidentally delete or with environmental catastrophe (fire, flood, earthquake, etc.). Lost encryption key for data protection some time may also be responsible for data loss for cloud clients.
- Hijacking Account or Service traffic – Hijacking methods may involve phishing, inserting software vulnerabilities, fraud, etc. It allows a hijacker to access your account and can manipulate data and information from the system. Avoiding sharing of credential between services and users, installation of the unwanted application and visiting the malicious or phishing site can prevent from hijacking account.
- Insecure Interfaces and APIs – APIs on cloud computing provides an interface to set of cloud software. Without APIs service can’t be delivered to the cloud users. So, security typically depends on the security features of this APIs. Poor APIs may expose risk related to integrity, confidentiality, accountability and availability of the service. Integration of secure appliance to APIs must be secured.
- Denial of Serve (DoS) Attack – It is a most common attack, yet possess high fear to the organisation. Systems attacked with multiple overwhelming traffic flooding to the targeted system resources. It creates unavailability of the service.
- Malicious Insider – Malicious insider is high risk to Cloud Infrastructure (IaaS, PaaS & SaaS). It allows access to the critical system and the data eventually.
- Abuse of Cloud Services – Abuse of cloud service is a major issue for the cloud service providers. However, this may not be the same to as cloud consumer. It is a serious implication to the cloud providers. So, proper legal preparation for ensuring cloud abuse should be implemented and regulated by laws.
- Insufficient Due Diligence – Cloud computing has changed the way the of tradition computing system. Many companies have adopted cloud due to reduced cost, improved security and efficiencies. However moving to the cloud system without measuring unknown risk level can impose various threats to the company.
- Threat with shared technology – Sharing of resources in the cloud computing is an efficient way to scale the available resources. Multitenant architecture is one of the technologies that is practised widely in cloud computing. Shared technology sometimes is dangerous as due to shared component and is vulnerable to entire cloud.
7.1 Outstanding Issues
As we have discussed, the existing security threats on cloud computing. The listed below are the some of the essential strategies for the security threats in the Cloud System (Cloud Security Alliance 2013).
- Retention Policy
- Secure Disposal
- Non-Production Data
- Information Leakage Prevention
- Risk Assessments
- Information Security – Encryption
- Encryption Key Management
- User ID Credentials
- Data Security/Integrity
- Production/Non-Production Environments
- Remote User Multi-Factor Authentication
Solution outline for Information Security – Encryption
Encryption is a vital aspect of cloud computing which deals with the security and privacy of the user data that are in transition or stored somewhere in the cloud environment. The current standard of encryption can be made better by the implementation of fully homomorphic encryption algorithm in cloud computing.
The asymmetric encryption algorithm, RSA algorithm is well and popular approach for many applications. RSA algorithm can be modified to achieve full homomorphic encryption for security in cloud computing. RSA is partially homomorphic cryptosystem because of only the multiplication characteristic of fully homomorphic encryption. The modified RSA algorithm designed such that it will fit fully homomorphic encryption algorithm in cloud computing by developing the additional algorithm to achieve characteristics of the addition of the fully homomorphic encryption (Sha & Zhu 2016).
The modified RSA algorithm helps to strengthen the encryption in cloud computing and protect the integrity of the user’s data.
9. Conclusion
Cloud computing has shaped today’s computing environment with enormous possibilities. However, at the mean time, various cloud service provider and cloud security alliance have analysed the need for increased security in the cloud. Security can be a primary concern for any cloud service provider for its successful implementation. Cloud Infrastructure can be severely affected by security issues. In most of the cloud computing environment, the risk of security and privacy of data compromised. Although there are many real challenges with cloud security, we can also mitigate those risks by adopting proper security measures. Various security measures like advance firewall system, authentication, risk assessment methods, encryption technology, etc. can practice solving the possible security threats (Sabahi 2011).
After reviewing the pieces of literature and research materials, we have summarised the security issue in cloud computing and figured out that reliability, availability and adaptation of the cloud computing services for various business or users. This report also helps to build trust between consumer and cloud service provider.
Reference List
Ahmed, M. & Hossain, M.A. 2014, ‘Cloud Computing and Security Issues in the Cloud’, International Journal of Network Security & Its Applications, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 25-36.
Australian Signals Directorate 2017, Cloud Computing Security Considerations, viewed 12 April 2017, https://www.asd.gov.au/publications/protect/Cloud_Computing_Security_Considerations.pdf>.
Boitnott, J. 2017, What Cloud security is important, but what does it really mean, Venture Beat, viewed 13 April 2017, https://venturebeat.com/2013/07/11/cloud-security-is-important-but-what-does-it-really-mean/>
BakerINFORM 2017, The Importance of Security in the Cloud: Security and Audit, viewed 13 April 2017, http://www.bakerinform.com/home/2016/2/3/the-importance-of-security-in-the-cloud-security-and-audit>
Cloud Security Alliance 2013, The Notorious Nine Cloud Computing Top Threats in 2013, viewed 10 April 2017, https://downloads.cloudsecurityalliance.org/initiatives/top_threats/The_Notorious_Nine_Cloud_Computing_Top_Threats_in_2013.pdf>.
Cloud Standard Customer Council 2015, Security for Cloud Computing Ten Steps to Ensure Success Version 2.0, viewed 11 April 2017, http://www.cloud-council.org/deliverables/CSCC-Security-for-Cloud-Computing-10-Steps-to-Ensure-Success.pdf>.
ENISA 2009, Cloud Computing: Benefits, risks and recommendations for information security, pp. 4-119, viewed 11 April 2017, https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/cloud-computing-risk-assessment>.
Sabahi, F. 2011, ‘Cloud computing security threats and responses’, 2011 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Xi’an, 2011, pp. 245-249.
Jariwala, D. 2017, Understanding the Significance of Cloud Security in Cloud Services, Techstagram, viewed 11 April 2017, http://www.techstagram.com/2013/02/27/significance-of-cloud-security/>.
Microsoft Azure 2017, what is Cloud Computing: A beginner’s guide, viewed 12 April 2017, https://azure.microsoft.com/en-au/overview/what-is-cloud-computing/>.
Padhy, R.P., Patra, M.R. & Satapathy, S.C. 2011, ‘Cloud Computing: Security Issues and Research Challenges’, International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology & Security, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 136-146.
Sha, P. & Zhu, Z. 2016, ‘The modification of RSA algorithm to adapt fully homomorphic encryption algorithm in cloud computing’, 2016 4th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems (CCIS), Beijing, 2016, pp. 388-392.
Rao, R.V. & Selvamani, K. 2015, ‘Data Security Challenges and Its Solutions in Cloud Computing’, Procedia Computer Science, vol. 48, pp. 204-209, viewed 11 April 2017, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050915006808>.
Techopedia 2017, What is Cloud Computing Security, viewed 12 April 2017, https://www.techopedia.com/definition/25114/cloud-computing-security>.
Salesforce Australia 2017, What is Cloud?, viewed 11 April 2017, https://www.salesforce.com/au/cloudcomputing/>.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Computing"
Computing is a term that describes the use of computers to process information. Key aspects of Computing are hardware, software, and processing through algorithms.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




