Using the SIR Model to Model the Spread of Influenza
Info: 14109 words (56 pages) Dissertation
Published: 12th Oct 2021
Tagged: Biomedical Science
Introduction
Ever since I was young, I was always interested in epidemics. My interest started to arise when I heard about the Ebola outbreak that took place in Africa during 2014. I wondered how such a deadly disease could be so wide-spread in a matter of days, infecting hundreds if not thousands of people. Then, the Zika virus followed in 2015, where cases weren’t noted in just one country but several continents. I found it scary that such deadly viruses could make its way all over the world in days, and I felt that no where was safe. Then, I learned about the Bubonic Plague, or the Black Death, during one of my social studies classes during middle school, where the spread of the disease was so massive and devastating to the European population back then.
I wanted to see how epidemiologists were able to represent the spread of such diseases. I decided that for this investigation, I would model the spread of influenza using the SIR model. Recently in the news, I heard that deaths from influenza were jumped from 12 to 31 in Alberta from December 2017 to January 2018, while the number of hospitalizations from influenza has doubled from 867 to 1,570 reports in the span of 3 weeks. Modelling the spread of influenza would allow me to develop a greater understand on this epidemic and the SIR model as well.
SIR Model
The SIR Model is a model which compares the number of people who are susceptible to a contagious disease, the number of people who have been infected by said disease, and those who are immune or recovered from the disease over a certain period in a closed population. It was first developed by McKendrick and Kermack in 1927 who wanted to explain the rise and fall of the total number of infected persons over the period of an epidemic. The SIR model divides up the total population of the sample size into 3 separate classes. These classes do not intersect (no one can be in two or more classes) and assumes each person has equal susceptibility to contract the disease. The three classes are as follows:
- Susceptible (S) : The majority of the population, it represents the total amount of people who are susceptible to the disease. These individuals have never come in contact with the disease and may include individuals who are passively-immune and have lost their immunity, or newborns who are born from a mother who has never been infected and therefore has not passed down any immunity. Once these individuals have contracted the disease, they are moved to the infected class.
- Infected (I) : This class represents the number of individuals who have contracted the disease. The parasite or virus within them is large enough so that there’s potential that they may pass down the disease to other susceptible individuals, making these individuals infectious. Once these individuals are cured, they move to the resistant class.
- Resistant (R) : These represent the number of individuals who have been infected and recovered from the disease, developing immunity towards it. It also includes the individuals who are naturally immune to the disease and cannot contract it, and individuals who have died from the disease.
The SIR model utilizes several variables to model the spread of an epidemic. First is the independent variable, which is time. The SIR model is used to model the spread of an epidemic over a definite time period, so this time period measured in days would be the independent variable and will be denoted as
t.
The next set of variables would be the dependent variables. The three main dependent variables are used to represent the individuals who are split into the three categories mentioned above. These variables are all a function of time. There is
St, where are the susceptible population,
It,which are the infected population and
Rt,which are the resistant population. These variables will change with time. Since these variables make up the total population, a separate variable,
N, may be used to represent the total population which is the sum of all three classes.
N=St+It+Rt
We may also use take these variables and turn them into fractions of the total population by taking the value of the classes and dividing them by
N.This will represent the same information as the variables above, except it will be more convenient to use fractional values regarding such a large population like Alberta. It is also more convenient to use fractional values in the calculations, so I will be using them during my investigation. Also, since we’re working with fractions, the total population is 1. If we want to see the actual population, we take the decimal value of the fraction and multiply it by the actual total population.
st=StN
it=ItN
rt=RtN
There are also the variables
R0,
γand β.
R0represents the number of people an infectious person will typically infect in a susceptible population, β represents the transmission rate of the disease and
γrepresents the recovery rate from the disease.
γ may be calculated by using another variable D, where D is the duration of the infection in days. The recovery rate of the disease would be calculated with the equation
γ=1D. Since recovery rate is defined as the rate at which the infectious population can recovery, 1/D allows us to see how much of the infectious population will recovery in a day. For example, if the duration of the infection is 5 days, then
γ=15=0.2. This means 20% of the infectious population will recovery everyday.
Β may be calculated if
R0and
γare already known, using the formula
R0=βγ. To calculate β, we simply rearrange the formula so
β=R0• γ. For example, if an infectious person infects on average 2 people in a susceptible population, and the recovery rate is 0.33, then the transmission rate would be:
β=2•0.33=0.66
There are also several assumptions that are used within this model.
Assumptions
- Population size is large and is always constant. No one can join the total population either from birth or immigration. Likewise, no one may leave the total population from emigration or death, whether it be from disease or other causes.
- The population is homogeneous. This means there are no discrepancies within the population in terms of their ability to contract the disease. Each person has an equal chance of contracting the disease from an infectious individual. Each individual also has an equal chance of coming into contact with one another.
- The incubation period of the disease is instantaneous. There is no delay to becoming infectious when an individual contract the disease.
- Once an individual has moves to the resistant class, they are assumed to be resistant to the disease for life.
- There is a fixed portion of the infectious class that recovers per day.
- Infectious individuals spread disease directly. Every time a susceptible individual meets an infectious individual, they become infected.
There are 3 main differential equations used to model the spread of an epidemic in an SIR model. These represent the overall change in the total amount of individuals in each of the classes as time goes on. With the differential equations,
tstarts at 0, and gradually moves up by 1 as time moves on.
Equations
1.
dSdt= -β st it
This represents the change in the number of susceptible individuals per day. Since β represents the transmission rate of the disease,
SIwould have to represent the number of encounters between the susceptible population and the infectious population. Since not every encounter is guaranteed to infect someone, β would represent the chance of an infectious person transmitting the disease over the total amount of encounters, so the equation represents the total number of people infected from this. This value would also be negative as it detracts the infected population from the total susceptible population.
2. dI dt= βstit- γit
This represents the change in the number of infected individuals per day.
βSIrepresents the number of individuals who got infected that day, and
γIrepresents the number of individuals who have recovered from said disease. Since we would need to take away the number of recovered individuals from the total infected population,
yIwould represent the removal of the population from the infected and
βSIwould represent the number of new infected added to the total.
3. dRdt= γit
As mentioned above,
yIrepresents the number of newly recovered individuals from the infectious population. We would add this value to the amount of population that are now immune to the epidemic.
Unfortunately, these differential equations are extremely complicated and tedious to solve in an SIR system. However, I can take an algebraic approach to accommodate. First, I will solve for the numerical value of the differential equations. Then, I will assume these values are the change in the total population of each class and add them to the initial populations to get the populations at that certain day.
Susceptable Formula: st=st-1-βst-1it-1
Infectious Formula: it=it-1+ βst-1it-1- γit-1
Resistant Formula: rt=rt-1+ γit
Since the population remains constant, there should be no net change within each of the processes. Therefore,
dSdt+dIdt+dRdt=0as there is no net change within the population.
Apply the SIR Model to the Influenza epidemic in Alberta
Influenza is a respiratory illness that affects the nose, throat and lungs. It is also very contagious, being spread through the air when someone sneezes, coughs or by simply talking. While anyone can catch influenza at any time, it is most commonly diagnosed in the winter months. Influenza lowers the body’s ability to fight off other infections and may also lead to bacterial infections such as pneumonia, ear or sinus infections, and make chronic illnesses worse. The most notable case of an influenza pandemic would be the Spanish Flu Pandemic of 1917-1918, which infected around 500 million people, and killed around 20-50 million people. Since there were no effective vaccines or medication for this illness, the pandemic spread all around the world being known as one of the worst pandemics ever since the Bubonic Plague.
Though most people who have influenza nowadays usually recover, the disease can cause around 12,000 Canadians to be hospitalized and around 3,500 deaths each year in Canada. Because of this epidemic, the Government of Alberta issued yearly influenza vaccines to the population in hopes of raising the overall immunity. My family always makes me take the yearly vaccine to protect myself from this disease. I never considered influenza a serious threat as I have never been diagnosed with it myself, and I thought the lethality of it was similar to the common cold. However, now that I’ve learned of the severity this illness has had on Canada, it has prompted me to use the SIR model to investigate how this disease could spread throughout Canada.
To model the spread of influenza in Alberta, I will use the influenza records from 2016-2017 to record this. According to Alberta Health Services, during 2016-2017, there have been 4,494 laboratory confirmed cases of influenza with 1,653 Albertans being admitted to hospital and having lab-confirmed influenza. However, there have been 1,171,825 doses of influenza vaccine administered throughout the province, and 64 Albertans having died from influenza. The total population of Alberta during 2017 was 4,286,100 persons as of July 1st. Influenza typically lasts 5-7 days, so I will use 6 days for the duration of influenza to break even. The
R0value for seasonal influenza is 1.28, which is the influenza most commonly found in Alberta.
With this information, I can now define my variables.
As there were 4,494 laboratory confirmed cases of influenza, the total infected population would be
Ii=4,494 ii=4,4944,286,000=1.049•10-3
The resistant population is made up of those who are immune to the infection. Since those who’ve been administered the influenza vaccine are assumed to be immune, and deaths from influenza are also considered under the resistant class, the total resistant population would be
Ri=1,171,825+64=1,171,889 ri=1,171,8894,286,000=0.273423
The total susceptible population would be the remainder of the population aside from the infected and recovered. Thus, the susceptible population would be
Si=4,286,000- 1,171,889-4,494=3,109,617 si=3,109,6174,286,000=0.725529
The recovery rate of influenza, γ, can be calculated by taking the inverse of the duration of influenza, which is 6 days.
γ=16
The transmission rate of the disease,
β, can be calculated by multiplying
R0and
γ.
β=1.28•16=0.2133
I will assume that all these values would be at
t=0. If I wanted to calculate the values at
t=1, then I would use the susceptible formula, infectious formula, and resistant formula stated in my background.
s1=s0-βs0i0=3,109,6174,286,000 – 0.213¯ •3,109,6174,286,000 •4,4944,286,000= 0.725367
i1=i0+ βs0i0- γi0= 4,4944,286,000 +0.213¯ •3,109,6174,286,000 •4,4944,286,000-164,4944,286,000 =9.039•10-4
r1=r0+ γi0= 1,171,8894,286,000 + 164,4944,286,000 =0.273597
As we can see, this is extremely tedious to do by hand. Therefore, I will use Microsoft Excel to process the raw data that will be used for the SIR model.
Figure 1: SIR Model for the Influenza Epidemic in Alberta during 2016-2017 for 100 days
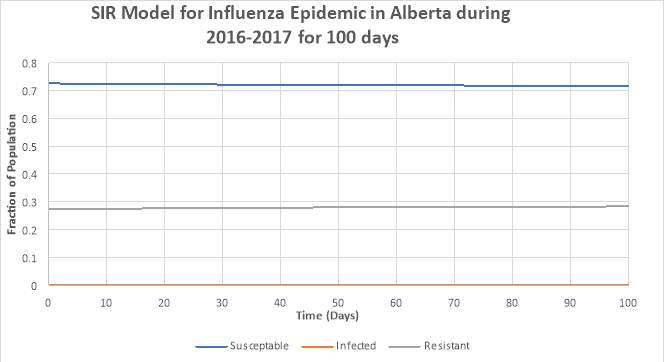
As we see in Figure 1, the influenza epidemic of Alberta is not even deadly at all. While initially, the slopes of the susceptible and infected population change slightly, it balances out at around 50 days to the point where there is no noticeable change. The slope of the infectious population also gradually decreases where it’s approaching 0, with no noticeable rise whatsoever. This means that the influenza epidemic in Alberta will naturally dissipate on its own, holding no threat whatsoever to the general population. In the graph, we can see that as the susceptible population decreased, the resistant population increased, showing an inverse relationship with each other. This makes sense since as the susceptible population get infected, those individuals will eventually recover and move into the resistant population. To be honest, I expected the SIR model of Alberta influenza to show more of an impact. However, due to the limitations of the models and the fact that the infection itself isn’t threatening to the population, it seems fair that this figure shows no significant impact on the total population. After all, there are several vaccinations designed to minimize the spread of influenza, and medicinal technologies today are advanced enough to protect the population from the spread of these diseases.
Unfortunately, this wasn’t enough to draw out the full potential of the SIR Model. The SIR model is designed to model a very infectious pandemic, so a non-life-threatening epidemic such as seasonal influenza isn’t the disease this model is designed for. To draw out the full potential of the SIR model for a better understanding of it, I will model the Spanish Flu pandemic of 1918 for USA.
Spanish Flu Pandemic
The Spanish Flu pandemic of 1918 was a deadly global pandemic which infected around 500 million people worldwide and killed around 20-50 million people. It was first observed in parts of Europe and America before spreading around the rest of the world. It was able to spread so easily since there were no substantial vaccines or medications that could treat this illness, and World War 1 had devastated the living conditions of many families, decreasing overall sanitation and health. The population of the USA in 1918 is estimated to be around 103.2 million, and the Spanish Flu infected around 675,000 Americans.
As there were no immunities developed back then, there are no initial resistant people. The characteristics of the influenza found in the Spanish Flu had similarities to H5N1 influenza, so I will use the attributes of H5N1 for the SIR Model. According to the World Health Organization, H5N1 can last up to 17 days, so γ would equate to
117. The
R0value of H5N1 was determined to be around 2.21 from an article by Ward MP, so β would be 2.21 • (1/17) = 0.13. The values for the SIR model will be illustrated in the table below.
Table 1: Variables used for SIR model of the Spanish Flu in the USA.
| Total Population/Susceptible population | 1,032,000,000 |
| Infected Population | 675,000 |
| Initial Resistant Population | 0 |
| 1/17 or 0.05882 | |
| 0.13 |
Figure 2: SIR Model for the Spanish Flu Pandemic of 1918 in the USA
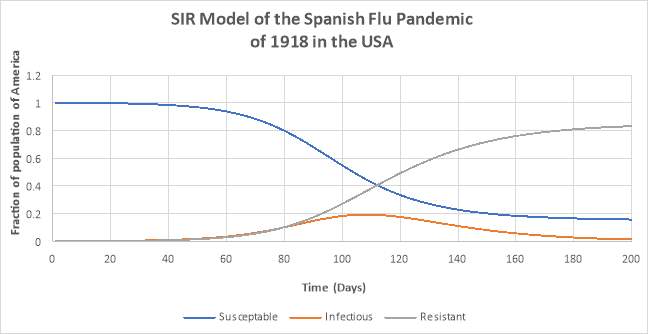
In Figure 2, we see more of a substantial impact within the model. First, the changes in slope are much more prominent now, which allows us to interpret this graph. We see that the susceptible population starts to gradually decrease at around 60 days, and as the infection passes on, there is less than 0.2 of the original susceptible population remaining as the curve starts to level out. This shows how deadly this pandemic truly was, being able to infect a clear majority of the population in only a span of around 150 days. We can see the inverse relationship between susceptible and resistant population being displayed, where as the susceptible population keeps decreasing, the resistant population steadily increases. As for the infectious population, it peaked at around 110 days infecting around 0.2 of the population of the United States. The slope of the infectious population gradually increases throughout days 40-110, most likely representing the interval where the spread of the pandemic started to gain traction. However, the slope of the infectious population gradually decreases after it peaks at 110 days and approaches 0, most likely due to most of the population developing immunity to the disease now (either through recovery of death) and the pandemic having few suitable hosts to infect. In proportion to this decrease, the change in slope of the susceptible and resistant population also start to decrease with their slopes becoming flatter during this interval. It seems the effects of the pandemic start to dissipate at around 180 days, as shown by all 3 of the slopes gradually approaching an equilibrium.
Limitations of this model
While this model is good for showing a general look at how an epidemic could spread, it does not accurately reflect how epidemics spread in real life. First of all, the model assumes that everyone in the population has an equal chance of encountering one another. However, this is simply not true. In the real world, sometimes we encounter the same people everyday while we may not even come in contact with the majority of the rest of the population of all in our lifetime. Second of all, it assumes the population is homogeneous with an equal chance of being infected, which is also not true. In the real world, age is a factor in one’s likelihood of being infected. Children and the elderly are more susceptible to illnesses compared to young adults as their health isn’t as great or developed enough yet to develop natural immunity to general illnesses. Also, health is also a factor in one’s likelihood of being infected, with healthier individuals being less susceptible to illnesses. The third limitation is that it assumes the population remains constant, with no immigration or emigration. In real life however, immigration and emigration happen, where more infected individuals may immigrate into the country or emigrate out of the country, which affects the transmission rate of the epidemic. Deaths are also regarded under the resistant class, which is also not true. Corpses of the infected still carry the virus inside and can still transmit it to the susceptible population. Deaths are also do not solely result from that specific epidemic in the real world, but can include death from age, chronic illness, or other unnatural causes. Other limitations include the assumption that there’s no incubation of the disease where the person is not infectious, and the assumption that there’s permanent immunity after recovery.
Conclusion
The SIR Model allows one to model the spread of an epidemic throughout its lifespan. Throughout this investigation, I was able to model the influenza epidemic in Alberta and the Spanish Flu pandemic of 1918. Both models varied greatly, with the first representing a non-threatening illness that doesn’t make a substantial impact on the populace, and the latter representing a deadly pandemic that took the lives of millions. The SIR Model allowed me to interpret various areas of importance such as the peak of the infectious populace, when the spread of the epidemic was at its maximum, and the lifespan of the epidemic. However, the SIR Model isn’t perfect, but greatly simplifies things with its assumptions. This results in limitations that should be considered when employing the SIR Model.
This investigation has allowed me the develop a greater understanding of how epidemiologists model epidemics, and how illnesses spread in general. I was able to fulfill my interest in learning more about epidemics and learned how to develop a model used by many professional epidemiologists. I was surprised at how simplistic the process of making an SIR Model was, as I thought developing these models would be an extremely complicated task. Through my modelling, I was able to see how deadly and devastating pandemics were in the past, but I was also able to see that modern-day epidemics very threatening to the general populace now with modern-day innovations such as vaccines and medications. I’m glad to learn that I have nothing to fear when it comes to epidemics today, since the medicinal technologies nowadays are advanced enough to prevent these epidemics from mass spreading.
Overall, I was about to broaden my understanding on how epidemics are represented nowadays. I was able to satisfy my curiosity about this topic and learned how to develop a model recognized by many professionals. If I wanted to further investigate this topic, I could investigate other models such as the SEIS and SEIR models where there is an incubation period, or the SIS Model where there is no immunity upon recovery.
Bibliography
Biggerstaff, M., Cauchemez, S., Reed, C., Gambhir, M., & Finelli, L. (2014, September 04). Estimates of the reproduction number for seasonal, pandemic, and zoonotic influenza: a systematic review of the literature. Retrieved March 11, 2018, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25186370
Canada, G. O. (2017, September 27). Population by year, by province and territory (Number). Retrieved March 11, 2018, from http://www.statcan.gc.ca/tables-tableaux/sum-som/l01/cst01/demo02a-eng.htm
Government of Alberta. (n.d.). Influenza. Retrieved March 9, 2018, from https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Alberta/Pages/influenza-symptoms-faqs.aspx
Haran, M. (2009, December). An introduction to models for disease dynamics. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from http://www.unc.edu/~rls/s940/samsidisdyntut.pdf
History.com Staff. (2010). Spanish Flu. Retrieved March 9, 2018, from https://www.history.com/topics/1918-flu-pandemic
Kaufmann, B. (2018, January 12). Flu fatalities spike during cold snap; virus combination ‘wreaking havoc’ in Calgary. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from http://calgaryherald.com/news/local-news/number-of-flu-fatalities-in-alberta-jumps-by-63-in-three-weeks
Modelling Infectious Diseases. (2014, May 03). Retrieved March 8, 2018, from https://ibmathsresources.com/2014/05/17/modelling-infectious-diseases
Nesse, H. (n.d.). SIR Model. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from http://www.public.asu.edu/~hnesse/classes/sir.html?Alpha=1&Beta=0.2&initialI=50&initialR=0&initialS=1000&iters=50
Ng, T. W., Dr. (n.d.). The mathematics of disease – On Modelling Hong Kong’s SARS Outbreak. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from http://hkumath.hku.hk/~ntw/SCNC1001-2004b.pdf
Nykamp, D. Q., & Morrissey, D. P. (n.d.). A discrete SIR infectious disease model. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from https://mathinsight.org/discrete_sir_infectious_disease_model
Publishing, H. H. (2018, January 16). How long does the flu last? Retrieved March 9, 2018, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/how-long-does-the-flu-last
Rodrigues, H. S. (2016). Application of SIR epidemiological model : new trends. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from http://www.naun.org/main/UPress/ami/2016/a262013-075.pdf
Services, A. H. (2017, Oct. & nov.). Past Influenza Seasonal Data. Retrieved March 9, 2018, from https://www.albertahealthservices.ca/influenza/Page14481.aspx
Smith, D., & Moore, L. (n.d.). The SIR Model for Spread of Disease – The Differential Equation Model. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from https://www.maa.org/press/periodicals/loci/joma/the-sir-model-for-spread-of-disease-the-differential-equation-model
The SIR Model for Spread of Disease. (n.d.). Retrieved March 8, 2018, from https://services.math.duke.edu/education/postcalc/sir/sir2.html
U.S. Census Bureau. (2000, June 28). Historic National Population Estimates. Retrieved March 10, 2018, from https://www.census.gov/population/estimates/nation/popclockest.txt
Weisstein, E. W. (n.d.). Kermack-McKendrick Model. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Kermack-McKendrickModel.html
Ward, M. P., Maftei, D., Apostu, C., & Suru, A. (2009, February). Estimation of the basic reproductive number (R0) for epidemic, highly pathogenic avian influenza subtype H5N1 spread. Retrieved March 10, 2018, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18559127
World Health Organization. (2018, January). Influenza (Avian and other zoonotic). Retrieved March 10, 2018, from http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/avian_influenza/en/
Appendix
Table 2: Raw Data for SIR Model of Influenza Epidemic in Alberta during 2016-2017 for 100 days
| Days | st | it | rt | dS/dt | dI/dt | dR/dt |
| 0 | 0.725528931 | 0.00104853 | 0.273422538 | -0.000162291 | -1.2464E-05 | 0.000174755 |
| 1 | 0.72536664 | 0.001036066 | 0.273597294 | -0.000160326 | -1.23518E-05 | 0.000172678 |
| 2 | 0.725206315 | 0.001023714 | 0.273769971 | -0.00015838 | -1.22395E-05 | 0.000170619 |
| 3 | 0.725047935 | 0.001011475 | 0.27394059 | -0.000156452 | -1.21274E-05 | 0.000168579 |
| 4 | 0.724891483 | 0.000999347 | 0.274109169 | -0.000154543 | -1.20153E-05 | 0.000166558 |
| 5 | 0.724736941 | 0.000987332 | 0.274275727 | -0.000152652 | -1.19034E-05 | 0.000164555 |
| 6 | 0.724584289 | 0.000975429 | 0.274440283 | -0.00015078 | -1.17917E-05 | 0.000162571 |
| 7 | 0.724433509 | 0.000963637 | 0.274602854 | -0.000148926 | -1.16801E-05 | 0.000160606 |
| 8 | 0.724284583 | 0.000951957 | 0.27476346 | -0.000147091 | -1.15688E-05 | 0.000158659 |
| 9 | 0.724137492 | 0.000940388 | 0.27492212 | -0.000145274 | -1.14577E-05 | 0.000156731 |
| 10 | 0.723992218 | 0.000928931 | 0.275078851 | -0.000143475 | -1.13469E-05 | 0.000154822 |
| 11 | 0.723848743 | 0.000917584 | 0.275233673 | -0.000141694 | -1.12364E-05 | 0.000152931 |
| 12 | 0.723707049 | 0.000906347 | 0.275386603 | -0.000139932 | -1.11262E-05 | 0.000151058 |
| 13 | 0.723567118 | 0.000895221 | 0.275537661 | -0.000138187 | -1.10163E-05 | 0.000149204 |
| 14 | 0.72342893 | 0.000884205 | 0.275686865 | -0.000136461 | -1.09068E-05 | 0.000147367 |
| 15 | 0.72329247 | 0.000873298 | 0.275834232 | -0.000134752 | -1.07977E-05 | 0.00014555 |
| 16 | 0.723157718 | 0.0008625 | 0.275979782 | -0.000133061 | -1.0689E-05 | 0.00014375 |
| 17 | 0.723024657 | 0.000851811 | 0.276123532 | -0.000131388 | -1.05807E-05 | 0.000141969 |
| 18 | 0.722893269 | 0.000841231 | 0.276265501 | -0.000129732 | -1.04728E-05 | 0.000140205 |
| 19 | 0.722763537 | 0.000830758 | 0.276405706 | -0.000128094 | -1.03655E-05 | 0.00013846 |
| 20 | 0.722635442 | 0.000820392 | 0.276544165 | -0.000126474 | -1.02585E-05 | 0.000136732 |
| 21 | 0.722508969 | 0.000810134 | 0.276680897 | -0.00012487 | -1.01521E-05 | 0.000135022 |
| 22 | 0.722384099 | 0.000799982 | 0.27681592 | -0.000123284 | -1.00462E-05 | 0.00013333 |
| 23 | 0.722260815 | 0.000789935 | 0.27694925 | -0.000121715 | -9.94083E-06 | 0.000131656 |
| 24 | 0.7221391 | 0.000779995 | 0.277080906 | -0.000120163 | -9.83599E-06 | 0.000129999 |
| 25 | 0.722018936 | 0.000770159 | 0.277210905 | -0.000118628 | -9.73169E-06 | 0.00012836 |
| 26 | 0.721900308 | 0.000760427 | 0.277339265 | -0.00011711 | -9.62797E-06 | 0.000126738 |
| 27 | 0.721783199 | 0.000750799 | 0.277466003 | -0.000115608 | -9.52482E-06 | 0.000125133 |
| 28 | 0.72166759 | 0.000741274 | 0.277591136 | -0.000114123 | -9.42227E-06 | 0.000123546 |
| 29 | 0.721553467 | 0.000731852 | 0.277714681 | -0.000112655 | -9.32032E-06 | 0.000121975 |
| 30 | 0.721440812 | 0.000722532 | 0.277836657 | -0.000111203 | -9.21899E-06 | 0.000120422 |
| 31 | 0.721329609 | 0.000713313 | 0.277957079 | -0.000109767 | -9.11829E-06 | 0.000118885 |
| 32 | 0.721219842 | 0.000704194 | 0.278075964 | -0.000108347 | -9.01822E-06 | 0.000117366 |
| 33 | 0.721111494 | 0.000695176 | 0.27819333 | -0.000106944 | -8.91879E-06 | 0.000115863 |
| 34 | 0.72100455 | 0.000686257 | 0.278309192 | -0.000105556 | -8.82003E-06 | 0.000114376 |
| 35 | 0.720898994 | 0.000677437 | 0.278423569 | -0.000104184 | -8.72192E-06 | 0.000112906 |
| 36 | 0.72079481 | 0.000668715 | 0.278536475 | -0.000102828 | -8.62449E-06 | 0.000111453 |
| 37 | 0.720691982 | 0.000660091 | 0.278647927 | -0.000101487 | -8.52774E-06 | 0.000110015 |
| 38 | 0.720590494 | 0.000651563 | 0.278757943 | -0.000100162 | -8.43168E-06 | 0.000108594 |
| 39 | 0.720490332 | 0.000643131 | 0.278866536 | -9.88523E-05 | -8.33631E-06 | 0.000107189 |
| 40 | 0.72039148 | 0.000634795 | 0.278973725 | -9.75575E-05 | -8.24164E-06 | 0.000105799 |
| 41 | 0.720293922 | 0.000626553 | 0.279079524 | -9.62779E-05 | -8.14768E-06 | 0.000104426 |
| 42 | 0.720197645 | 0.000618406 | 0.27918395 | -9.50132E-05 | -8.05443E-06 | 0.000103068 |
| 43 | 0.720102631 | 0.000610351 | 0.279287017 | -9.37633E-05 | -7.96189E-06 | 0.000101725 |
| 44 | 0.720008868 | 0.000602389 | 0.279388743 | -9.25282E-05 | -7.87008E-06 | 0.000100398 |
| 45 | 0.71991634 | 0.000594519 | 0.279489141 | -9.13076E-05 | -7.779E-06 | 9.90866E-05 |
| 46 | 0.719825032 | 0.00058674 | 0.279588227 | -9.01014E-05 | -7.68864E-06 | 9.77901E-05 |
| 47 | 0.719734931 | 0.000579052 | 0.279686017 | -8.89096E-05 | -7.59902E-06 | 9.65086E-05 |
| 48 | 0.719646021 | 0.000571453 | 0.279782526 | -8.7732E-05 | -7.51014E-06 | 9.52421E-05 |
| 49 | 0.719558289 | 0.000563943 | 0.279877768 | -8.65684E-05 | -7.42199E-06 | 9.39904E-05 |
| 50 | 0.719471721 | 0.000556521 | 0.279971759 | -8.54188E-05 | -7.33459E-06 | 9.27534E-05 |
| 51 | 0.719386302 | 0.000549186 | 0.280064512 | -8.42831E-05 | -7.24793E-06 | 9.1531E-05 |
| 52 | 0.719302019 | 0.000541938 | 0.280156043 | -8.3161E-05 | -7.16202E-06 | 9.0323E-05 |
| 53 | 0.719218858 | 0.000534776 | 0.280246366 | -8.20525E-05 | -7.07686E-06 | 8.91293E-05 |
| 54 | 0.719136806 | 0.000527699 | 0.280335495 | -8.09574E-05 | -6.99244E-06 | 8.79499E-05 |
| 55 | 0.719055848 | 0.000520707 | 0.280423445 | -7.98757E-05 | -6.90878E-06 | 8.67845E-05 |
| 56 | 0.718975972 | 0.000513798 | 0.28051023 | -7.88071E-05 | -6.82587E-06 | 8.5633E-05 |
| 57 | 0.718897165 | 0.000506972 | 0.280595863 | -7.77516E-05 | -6.74371E-06 | 8.44953E-05 |
| 59 | 0.718819414 | 0.000500228 | 0.280680358 | -7.67091E-05 | -6.6623E-06 | 8.33714E-05 |
| 60 | 0.718742705 | 0.000493566 | 0.280763729 | -7.56794E-05 | -6.58165E-06 | 8.2261E-05 |
| 61 | 0.718667025 | 0.000486984 | 0.28084599 | -7.46623E-05 | -6.50175E-06 | 8.11641E-05 |
| 62 | 0.718592363 | 0.000480483 | 0.280927154 | -7.36578E-05 | -6.42259E-06 | 8.00804E-05 |
| 63 | 0.718518705 | 0.00047406 | 0.281007235 | -7.26658E-05 | -6.34419E-06 | 7.901E-05 |
| 64 | 0.718446039 | 0.000467716 | 0.281086245 | -7.16861E-05 | -6.26654E-06 | 7.79526E-05 |
| 65 | 0.718374353 | 0.000461449 | 0.281164197 | -7.07186E-05 | -6.18964E-06 | 7.69082E-05 |
| 66 | 0.718303635 | 0.00045526 | 0.281241106 | -6.97631E-05 | -6.11348E-06 | 7.58766E-05 |
| 67 | 0.718233871 | 0.000449146 | 0.281316982 | -6.88196E-05 | -6.03807E-06 | 7.48577E-05 |
| 68 | 0.718165052 | 0.000443108 | 0.28139184 | -6.7888E-05 | -5.9634E-06 | 7.38514E-05 |
| 69 | 0.718097164 | 0.000437145 | 0.281465691 | -6.6968E-05 | -5.88948E-06 | 7.28575E-05 |
| 70 | 0.718030196 | 0.000431255 | 0.281538549 | -6.60596E-05 | -5.81629E-06 | 7.18759E-05 |
| 71 | 0.717964136 | 0.000425439 | 0.281610425 | -6.51626E-05 | -5.74384E-06 | 7.09065E-05 |
| 72 | 0.717898974 | 0.000419695 | 0.281681331 | -6.42771E-05 | -5.67213E-06 | 6.99492E-05 |
| 73 | 0.717834697 | 0.000414023 | 0.28175128 | -6.34027E-05 | -5.60115E-06 | 6.90038E-05 |
| 74 | 0.717771294 | 0.000408422 | 0.281820284 | -6.25394E-05 | -5.5309E-06 | 6.80703E-05 |
| 75 | 0.717708755 | 0.000402891 | 0.281888355 | -6.16871E-05 | -5.46137E-06 | 6.71485E-05 |
| 76 | 0.717647067 | 0.00039743 | 0.281955503 | -6.08457E-05 | -5.39257E-06 | 6.62383E-05 |
| 77 | 0.717586222 | 0.000392037 | 0.282021741 | -6.0015E-05 | -5.32449E-06 | 6.53395E-05 |
| 78 | 0.717526207 | 0.000386713 | 0.282087081 | -5.9195E-05 | -5.25713E-06 | 6.44521E-05 |
| 79 | 0.717467012 | 0.000381455 | 0.282151533 | -5.83854E-05 | -5.19048E-06 | 6.35759E-05 |
| 80 | 0.717408626 | 0.000376265 | 0.282215109 | -5.75863E-05 | -5.12454E-06 | 6.27108E-05 |
| 81 | 0.71735104 | 0.00037114 | 0.28227782 | -5.67974E-05 | -5.0593E-06 | 6.18567E-05 |
| 82 | 0.717294243 | 0.000366081 | 0.282339676 | -5.60187E-05 | -4.99477E-06 | 6.10135E-05 |
| 83 | 0.717238224 | 0.000361086 | 0.28240069 | -5.52501E-05 | -4.93094E-06 | 6.0181E-05 |
| 84 | 0.717182974 | 0.000356155 | 0.282460871 | -5.44914E-05 | -4.8678E-06 | 5.93592E-05 |
| 85 | 0.717128482 | 0.000351288 | 0.28252023 | -5.37426E-05 | -4.80535E-06 | 5.85479E-05 |
| 86 | 0.71707474 | 0.000346482 | 0.282578778 | -5.30034E-05 | -4.74359E-06 | 5.7747E-05 |
| 87 | 0.717021736 | 0.000341739 | 0.282636525 | -5.22739E-05 | -4.68251E-06 | 5.69564E-05 |
| 88 | 0.716969462 | 0.000337056 | 0.282693481 | -5.15539E-05 | -4.62211E-06 | 5.6176E-05 |
| 89 | 0.716917909 | 0.000332434 | 0.282749658 | -5.08433E-05 | -4.56238E-06 | 5.54057E-05 |
| 90 | 0.716867065 | 0.000327872 | 0.282805063 | -5.01419E-05 | -4.50332E-06 | 5.46453E-05 |
| 91 | 0.716816923 | 0.000323368 | 0.282859708 | -4.94498E-05 | -4.44493E-06 | 5.38947E-05 |
| 92 | 0.716767474 | 0.000318923 | 0.282913603 | -4.87667E-05 | -4.3872E-06 | 5.31539E-05 |
| 93 | 0.716718707 | 0.000314536 | 0.282966757 | -4.80926E-05 | -4.33012E-06 | 5.24227E-05 |
| 94 | 0.716670614 | 0.000310206 | 0.28301918 | -4.74273E-05 | -4.27369E-06 | 5.1701E-05 |
| 95 | 0.716623187 | 0.000305932 | 0.283070881 | -4.67708E-05 | -4.21791E-06 | 5.09887E-05 |
| 96 | 0.716576416 | 0.000301714 | 0.283121869 | -4.6123E-05 | -4.16276E-06 | 5.02857E-05 |
| 97 | 0.716530293 | 0.000297552 | 0.283172155 | -4.54837E-05 | -4.10826E-06 | 4.95919E-05 |
| 98 | 0.716484809 | 0.000293443 | 0.283221747 | -4.48529E-05 | -4.05438E-06 | 4.89072E-05 |
| 99 | 0.716439957 | 0.000289389 | 0.283270654 | -4.42304E-05 | -4.00113E-06 | 4.82315E-05 |
| 100 | 0.716395726 | 0.000285388 | 0.283318886 | -4.36161E-05 | -3.94851E-06 | 4.75646E-05 |
Table 3: Raw Data for SIR Model of the Spanish Flu in America
| Days | st | it | rt | dS/dt | dI/dt | dR/dt |
| 1 | 1 | 0.00065407 | 0 | -8.5029E-05 | 4.65544E-05 | 3.84747E-05 |
| 2 | 0.999914971 | 0.000700624 | 3.8475E-05 | -9.1073E-05 | 4.98602E-05 | 4.12132E-05 |
| 3 | 0.999823898 | 0.000750484 | 7.9688E-05 | -9.7546E-05 | 5.33996E-05 | 4.41461E-05 |
| 4 | 0.999726352 | 0.000803884 | 0.00012383 | -0.00010448 | 5.7189E-05 | 4.72873E-05 |
| 5 | 0.999621875 | 0.000861073 | 0.00017112 | -0.0001119 | 6.12458E-05 | 5.06514E-05 |
| 6 | 0.999509978 | 0.000922319 | 0.00022177 | -0.00011984 | 6.55886E-05 | 5.4254E-05 |
| 7 | 0.999390136 | 0.000987907 | 0.00027603 | -0.00012835 | 7.02374E-05 | 5.81122E-05 |
| 8 | 0.999261786 | 0.001058145 | 0.00033414 | -0.00013746 | 7.52135E-05 | 6.22438E-05 |
| 9 | 0.999124329 | 0.001133358 | 0.00039638 | -0.00014721 | 8.05394E-05 | 6.66681E-05 |
| 10 | 0.998977121 | 0.001213898 | 0.00046305 | -0.00015765 | 8.62395E-05 | 7.14058E-05 |
| 11 | 0.998819476 | 0.001300137 | 0.00053446 | -0.00016882 | 9.23397E-05 | 7.64787E-05 |
| 12 | 0.998650657 | 0.001392477 | 0.00061094 | -0.00018078 | 9.88673E-05 | 8.19104E-05 |
| 13 | 0.99846988 | 0.001491344 | 0.00069285 | -0.00019358 | 0.000105852 | 8.77261E-05 |
| 14 | 0.998276302 | 0.001597196 | 0.00078057 | -0.00020728 | 0.000113325 | 9.39527E-05 |
| 15 | 0.998069024 | 0.001710521 | 0.00087452 | -0.00022194 | 0.000121319 | 0.000100619 |
| 16 | 0.997847086 | 0.001831841 | 0.00097514 | -0.00023763 | 0.000129871 | 0.000107755 |
| 17 | 0.997609459 | 0.001961712 | 0.0010829 | -0.00025441 | 0.000139018 | 0.000115395 |
| 18 | 0.997355046 | 0.00210073 | 0.00119829 | -0.00027237 | 0.0001488 | 0.000123572 |
| 19 | 0.997082673 | 0.00224953 | 0.00132187 | -0.00029159 | 0.00015926 | 0.000132325 |
| 20 | 0.996791088 | 0.002408791 | 0.00145419 | -0.00031214 | 0.000170444 | 0.000141694 |
| 21 | 0.99647895 | 0.002579235 | 0.00159588 | -0.00033412 | 0.0001824 | 0.00015172 |
| 22 | 0.99614483 | 0.002761635 | 0.0017476 | -0.00035763 | 0.000195179 | 0.000162449 |
| 23 | 0.995787201 | 0.002956815 | 0.00191005 | -0.00038277 | 0.000208836 | 0.00017393 |
| 24 | 0.995404435 | 0.003165651 | 0.00208398 | -0.00040964 | 0.000223429 | 0.000186215 |
| 25 | 0.994994791 | 0.00338908 | 0.0022702 | -0.00043838 | 0.000239018 | 0.000199358 |
| 26 | 0.994556416 | 0.003628097 | 0.00246956 | -0.00046909 | 0.000255668 | 0.000213417 |
| 27 | 0.994087331 | 0.003883765 | 0.00268297 | -0.0005019 | 0.000273447 | 0.000228457 |
| 28 | 0.993585427 | 0.004157212 | 0.00291143 | -0.00053697 | 0.000292429 | 0.000244542 |
| 29 | 0.993048456 | 0.004449642 | 0.00315597 | -0.00057443 | 0.000312689 | 0.000261744 |
| 30 | 0.992474023 | 0.00476233 | 0.00341772 | -0.00061444 | 0.000334306 | 0.000280137 |
| 31 | 0.99185958 | 0.005096637 | 0.00369785 | -0.00065717 | 0.000357367 | 0.000299802 |
| 32 | 0.991202411 | 0.005454004 | 0.00399766 | -0.00070278 | 0.000381959 | 0.000320824 |
| 33 | 0.990499628 | 0.005835963 | 0.00431848 | -0.00075147 | 0.000408176 | 0.000343292 |
| 34 | 0.98974816 | 0.006244138 | 0.00466177 | -0.00080342 | 0.000436114 | 0.000367302 |
| 35 | 0.988944744 | 0.006680252 | 0.00502907 | -0.00085883 | 0.000465876 | 0.000392956 |
| 36 | 0.988085912 | 0.007146128 | 0.00542203 | -0.00091793 | 0.000497568 | 0.00042036 |
| 37 | 0.987167984 | 0.007643696 | 0.00584239 | -0.00098093 | 0.0005313 | 0.000449629 |
| 38 | 0.986187054 | 0.008174997 | 0.00629202 | -0.00104807 | 0.000567188 | 0.000480882 |
| 39 | 0.985138984 | 0.008742184 | 0.0067729 | -0.00111959 | 0.000605349 | 0.000514246 |
| 40 | 0.984019389 | 0.009347533 | 0.00728715 | -0.00119576 | 0.000645905 | 0.000549855 |
| 41 | 0.982823629 | 0.009993438 | 0.007837 | -0.00127683 | 0.000688983 | 0.000587849 |
| 42 | 0.981546797 | 0.010682421 | 0.00842485 | -0.00136309 | 0.000734711 | 0.000628378 |
| 43 | 0.980183709 | 0.011417132 | 0.00905323 | -0.00145482 | 0.000783219 | 0.000671596 |
| 44 | 0.978728893 | 0.012200351 | 0.00972483 | -0.00155231 | 0.000834641 | 0.000717668 |
| 45 | 0.977176585 | 0.013034992 | 0.01044249 | -0.00165587 | 0.000889109 | 0.000766764 |
| 46 | 0.975520711 | 0.013924101 | 0.01120926 | -0.00176582 | 0.000946758 | 0.000819065 |
| 47 | 0.973754889 | 0.014870859 | 0.01202832 | -0.00188247 | 0.001007718 | 0.000874756 |
| 48 | 0.971872414 | 0.015878577 | 0.01290308 | -0.00200615 | 0.00107212 | 0.000934034 |
| 49 | 0.969866261 | 0.016950697 | 0.01383711 | -0.00213719 | 0.001140088 | 0.0009971 |
| 50 | 0.967729073 | 0.018090785 | 0.01483421 | -0.00227591 | 0.001211743 | 0.001064164 |
| 51 | 0.965453165 | 0.019302528 | 0.01589838 | -0.00242264 | 0.001287196 | 0.001135443 |
| 52 | 0.963030526 | 0.020589725 | 0.01703382 | -0.00257771 | 0.001366549 | 0.00121116 |
| 53 | 0.960452817 | 0.021956274 | 0.01824498 | -0.00274144 | 0.00144989 | 0.001291546 |
| 54 | 0.957711381 | 0.023406164 | 0.01953652 | -0.00291413 | 0.001537292 | 0.001376833 |
| 55 | 0.954797256 | 0.024943456 | 0.02091336 | -0.00309607 | 0.001628811 | 0.001467262 |
| 56 | 0.951701183 | 0.026572267 | 0.02238062 | -0.00328755 | 0.001724477 | 0.001563075 |
| 57 | 0.948413632 | 0.028296744 | 0.02394369 | -0.00348881 | 0.001824298 | 0.001664514 |
| 58 | 0.944924819 | 0.030121042 | 0.02560821 | -0.00370008 | 0.00192825 | 0.001771826 |
| 59 | 0.941224744 | 0.032049291 | 0.02738003 | -0.00392153 | 0.002036274 | 0.001885252 |
| 60 | 0.937303218 | 0.034085565 | 0.02926529 | -0.00415331 | 0.002148273 | 0.002005033 |
| 61 | 0.933149911 | 0.036233838 | 0.03127032 | -0.00439551 | 0.002264106 | 0.002131402 |
| 62 | 0.928754403 | 0.038497944 | 0.03340172 | -0.00464817 | 0.002383583 | 0.002264585 |
| 63 | 0.924106235 | 0.040881527 | 0.03566631 | -0.00491125 | 0.002506458 | 0.002404796 |
| 64 | 0.919194982 | 0.043387985 | 0.0380711 | -0.00518466 | 0.002632428 | 0.002552234 |
| 65 | 0.91401032 | 0.046020413 | 0.04062334 | -0.00546821 | 0.002761124 | 0.002707083 |
| 66 | 0.908542112 | 0.048781537 | 0.04333042 | -0.00576161 | 0.002892108 | 0.002869502 |
| 67 | 0.902780502 | 0.051673645 | 0.04619992 | -0.00606449 | 0.003024869 | 0.003039626 |
| 68 | 0.896716007 | 0.054698513 | 0.04923955 | -0.00637637 | 0.003158815 | 0.00321756 |
| 69 | 0.890339633 | 0.057857328 | 0.05245711 | -0.00669665 | 0.003293275 | 0.003403372 |
| 70 | 0.883642986 | 0.061150603 | 0.05586048 | -0.00702459 | 0.003427495 | 0.003597094 |
| 71 | 0.876618396 | 0.064578098 | 0.05945758 | -0.00735935 | 0.003560634 | 0.003798712 |
| 72 | 0.869259051 | 0.068138732 | 0.06325629 | -0.00769993 | 0.003691767 | 0.004008161 |
| 73 | 0.861559124 | 0.071830498 | 0.06726445 | -0.00804521 | 0.003819885 | 0.004225323 |
| 74 | 0.853513915 | 0.075650384 | 0.07148977 | -0.00839393 | 0.003943903 | 0.004450023 |
| 75 | 0.84511999 | 0.079594286 | 0.07593979 | -0.00874467 | 0.004062657 | 0.004682017 |
| 76 | 0.836375316 | 0.083656943 | 0.08062181 | -0.00909592 | 0.004174922 | 0.004920997 |
| 77 | 0.827279398 | 0.087831865 | 0.08554281 | -0.00944599 | 0.004279414 | 0.00516658 |
| 78 | 0.817833404 | 0.092111279 | 0.09070939 | -0.00979312 | 0.004374808 | 0.005418311 |
| 79 | 0.808040285 | 0.096486087 | 0.0961277 | -0.0101354 | 0.004459752 | 0.005675652 |
| 80 | 0.797904881 | 0.100945838 | 0.10180335 | -0.01047087 | 0.004532883 | 0.00593799 |
| 81 | 0.787434008 | 0.105478721 | 0.10774134 | -0.01079748 | 0.004592849 | 0.006204631 |
| 82 | 0.776636529 | 0.110071569 | 0.11394597 | -0.01111313 | 0.00463833 | 0.006474798 |
| 83 | 0.765523401 | 0.114709899 | 0.12042077 | -0.0114157 | 0.004668063 | 0.006747641 |
| 84 | 0.754107696 | 0.119377963 | 0.12716841 | -0.0117031 | 0.004680866 | 0.007022233 |
| 85 | 0.742404597 | 0.124058829 | 0.13419064 | -0.01197324 | 0.004675662 | 0.007297578 |
| 86 | 0.730431357 | 0.128734491 | 0.14148822 | -0.01222412 | 0.004651505 | 0.007572617 |
| 87 | 0.718207235 | 0.133385996 | 0.14906084 | -0.01245384 | 0.004607607 | 0.007846235 |
| 88 | 0.705753393 | 0.137993603 | 0.15690707 | -0.01266063 | 0.004543358 | 0.008117271 |
| 89 | 0.693092764 | 0.142536961 | 0.16502434 | -0.01284287 | 0.004458347 | 0.008384527 |
| 90 | 0.68024989 | 0.146995308 | 0.17340887 | -0.01299916 | 0.004352378 | 0.008646783 |
| 91 | 0.66725073 | 0.151347685 | 0.18205565 | -0.01312829 | 0.004225486 | 0.008902805 |
| 92 | 0.654122439 | 0.155573171 | 0.19095846 | -0.01322931 | 0.004077944 | 0.009151363 |
| 93 | 0.640893131 | 0.159651116 | 0.20010982 | -0.01330151 | 0.003910267 | 0.009391242 |
| 94 | 0.627591622 | 0.163561383 | 0.20950106 | -0.01334447 | 0.00372321 | 0.009621258 |
| 95 | 0.614247154 | 0.167284593 | 0.21912232 | -0.01335803 | 0.003517761 | 0.00984027 |
| 96 | 0.600889123 | 0.170802354 | 0.22896259 | -0.01334233 | 0.003295129 | 0.010047197 |
| 97 | 0.587546797 | 0.174097483 | 0.23900979 | -0.01329775 | 0.003056726 | 0.010241028 |
| 98 | 0.574249043 | 0.177154209 | 0.24925082 | -0.01322498 | 0.002804147 | 0.010420836 |
| 99 | 0.56102406 | 0.179958355 | 0.25967165 | -0.01312493 | 0.00253914 | 0.010585786 |
| 100 | 0.547899134 | 0.182497496 | 0.27025744 | -0.01299873 | 0.002263582 | 0.010735147 |
| 101 | 0.534900406 | 0.184761077 | 0.28099259 | -0.01284774 | 0.001979442 | 0.010868299 |
| 102 | 0.522052665 | 0.186740519 | 0.29186089 | -0.01267349 | 0.001688754 | 0.010984736 |
| 103 | 0.509379175 | 0.188429273 | 0.30284562 | -0.01247765 | 0.001393578 | 0.011084075 |
| 104 | 0.496901522 | 0.189822851 | 0.3139297 | -0.01226202 | 0.001095974 | 0.01116605 |
| 105 | 0.484639497 | 0.190918826 | 0.32509575 | -0.01202848 | 0.000797965 | 0.011230519 |
| 106 | 0.472611013 | 0.191716791 | 0.33632627 | -0.01177897 | 0.000501512 | 0.011277458 |
| 107 | 0.460832042 | 0.192218303 | 0.34760372 | -0.01151545 | 0.000208487 | 0.011306959 |
| 108 | 0.449316596 | 0.19242679 | 0.35891068 | -0.01123987 | -7.93514E-05 | 0.011319223 |
| 109 | 0.438076725 | 0.192347439 | 0.37022991 | -0.01095418 | -0.000360374 | 0.011314555 |
| 110 | 0.427122543 | 0.191987065 | 0.38154446 | -0.01066026 | -0.000633096 | 0.011293357 |
| 111 | 0.416462283 | 0.191353969 | 0.39283782 | -0.01035992 | -0.000896193 | 0.011256116 |
| 112 | 0.40610236 | 0.190457776 | 0.40409393 | -0.0100549 | -0.001148503 | 0.011203399 |
| 113 | 0.396047464 | 0.189309273 | 0.41529733 | -0.00974681 | -0.00138903 | 0.01113584 |
| 114 | 0.386300655 | 0.187920243 | 0.42643317 | -0.00943718 | -0.001616949 | 0.011054132 |
| 115 | 0.376863472 | 0.186303293 | 0.4374873 | -0.00912742 | -0.001831599 | 0.010959017 |
| 116 | 0.367736055 | 0.184471694 | 0.44844632 | -0.0088188 | -0.00203248 | 0.010851276 |
| 117 | 0.358917258 | 0.182439214 | 0.4592976 | -0.00851248 | -0.002219243 | 0.010731718 |
| 118 | 0.350404783 | 0.180219971 | 0.47002932 | -0.00820949 | -0.002391683 | 0.010601175 |
| 119 | 0.342195291 | 0.177828289 | 0.48063049 | -0.00791076 | -0.002549727 | 0.010460488 |
| 120 | 0.33428453 | 0.175278561 | 0.49109098 | -0.00761708 | -0.002693425 | 0.010310504 |
| 121 | 0.326667452 | 0.172585136 | 0.50140148 | -0.00732913 | -0.002822934 | 0.010152067 |
| 122 | 0.319338319 | 0.169762202 | 0.51155355 | -0.0070475 | -0.002938507 | 0.009986012 |
| 123 | 0.312290814 | 0.166823696 | 0.52153956 | -0.00677268 | -0.003040483 | 0.009813159 |
| 124 | 0.305518138 | 0.163783213 | 0.53135272 | -0.00650504 | -0.00312927 | 0.009634307 |
| 125 | 0.299013101 | 0.160653943 | 0.54098703 | -0.00624489 | -0.00320534 | 0.009450232 |
| 126 | 0.292768209 | 0.157448603 | 0.55043726 | -0.00599247 | -0.00326921 | 0.009261683 |
| 127 | 0.286775736 | 0.154179394 | 0.55969894 | -0.00574794 | -0.003321438 | 0.009069376 |
| 128 | 0.281027798 | 0.150857956 | 0.56876832 | -0.00551139 | -0.003362611 | 0.008873997 |
| 129 | 0.275516411 | 0.147495345 | 0.57764231 | -0.00528286 | -0.003393336 | 0.008676197 |
| 130 | 0.270233551 | 0.144102008 | 0.58631851 | -0.00506236 | -0.003414233 | 0.008476589 |
| 131 | 0.265171195 | 0.140687775 | 0.5947951 | -0.00484982 | -0.003425927 | 0.008275751 |
| 132 | 0.26032137 | 0.137261849 | 0.60307085 | -0.00464519 | -0.003429041 | 0.008074226 |
| 133 | 0.255676185 | 0.133832807 | 0.61114508 | -0.00444832 | -0.003424196 | 0.007872518 |
| 134 | 0.251227863 | 0.130408611 | 0.6190176 | -0.0042591 | -0.003411999 | 0.007671095 |
| 135 | 0.246968767 | 0.126996612 | 0.62668869 | -0.00407735 | -0.003393043 | 0.007470389 |
| 136 | 0.242891422 | 0.123603569 | 0.63415908 | -0.00390289 | -0.003367906 | 0.007270798 |
| 137 | 0.23898853 | 0.120235663 | 0.64142988 | -0.00373554 | -0.003337143 | 0.007072686 |
| 138 | 0.235252987 | 0.11689852 | 0.64850256 | -0.00357509 | -0.003301289 | 0.006876384 |
| 139 | 0.231677893 | 0.113597231 | 0.65537895 | -0.00342134 | -0.003260854 | 0.00668219 |
| 140 | 0.228256557 | 0.110336376 | 0.66206114 | -0.00327405 | -0.003216325 | 0.006490375 |
| 141 | 0.224982507 | 0.107120051 | 0.66855151 | -0.00313302 | -0.003168162 | 0.006301179 |
| 142 | 0.221849489 | 0.10395189 | 0.67485269 | -0.00299802 | -0.003116799 | 0.006114817 |
| 143 | 0.218851471 | 0.10083509 | 0.68096751 | -0.00286883 | -0.003062648 | 0.005931476 |
| 144 | 0.215982643 | 0.097772442 | 0.68689898 | -0.00274523 | -0.003006091 | 0.00575132 |
| 145 | 0.213237414 | 0.094766352 | 0.6926503 | -0.00262701 | -0.002947486 | 0.005574491 |
| 146 | 0.210610409 | 0.091818866 | 0.6982248 | -0.00251394 | -0.002887169 | 0.00540111 |
| 147 | 0.208096467 | 0.088931697 | 0.70362591 | -0.00240583 | -0.002825448 | 0.005231276 |
| 148 | 0.205690639 | 0.086106249 | 0.70885718 | -0.00230246 | -0.002762611 | 0.005065073 |
| 149 | 0.203388177 | 0.083343638 | 0.71392226 | -0.00220364 | -0.002698923 | 0.004902567 |
| 150 | 0.201184532 | 0.080644715 | 0.71882482 | -0.00210918 | -0.002634626 | 0.004743807 |
| 151 | 0.199075351 | 0.07801009 | 0.72356863 | -0.00201889 | -0.002569944 | 0.004588829 |
| 152 | 0.197056466 | 0.075440146 | 0.72815746 | -0.00193258 | -0.00250508 | 0.004437656 |
| 153 | 0.19512389 | 0.072935066 | 0.73259511 | -0.00185008 | -0.002440219 | 0.004290298 |
| 154 | 0.193273812 | 0.070494847 | 0.73688541 | -0.00177123 | -0.002375531 | 0.004146756 |
| 155 | 0.191502587 | 0.068119316 | 0.74103217 | -0.00169585 | -0.002311165 | 0.004007019 |
| 156 | 0.189806733 | 0.065808151 | 0.74503919 | -0.00162381 | -0.00224726 | 0.003871068 |
| 157 | 0.188182925 | 0.063560891 | 0.74891025 | -0.00155494 | -0.002183936 | 0.003738876 |
| 158 | 0.186627986 | 0.061376955 | 0.75264913 | -0.00148911 | -0.002121304 | 0.003610409 |
| 159 | 0.18513888 | 0.059255651 | 0.75625954 | -0.00142617 | -0.002059458 | 0.003485627 |
| 160 | 0.183712712 | 0.057196193 | 0.75974516 | -0.001366 | -0.001998485 | 0.003364482 |
| 161 | 0.182346715 | 0.055197708 | 0.76310965 | -0.00130847 | -0.001938458 | 0.003246924 |
| 162 | 0.181038249 | 0.053259249 | 0.76635657 | -0.00125345 | -0.001879442 | 0.003132897 |
| 163 | 0.179784794 | 0.051379807 | 0.76948947 | -0.00120085 | -0.001821492 | 0.003022342 |
| 164 | 0.178583944 | 0.049558316 | 0.77251181 | -0.00115054 | -0.001764654 | 0.002915195 |
| 165 | 0.177433403 | 0.047793662 | 0.775427 | -0.00110242 | -0.001708967 | 0.002811392 |
| 166 | 0.176330978 | 0.046084695 | 0.7782384 | -0.0010564 | -0.001654464 | 0.002710864 |
| 167 | 0.175274577 | 0.044430232 | 0.78094926 | -0.00101237 | -0.001601169 | 0.002613543 |
| 168 | 0.174262203 | 0.042829062 | 0.7835628 | -0.00097025 | -0.001549103 | 0.002519357 |
| 169 | 0.17329195 | 0.041279959 | 0.78608216 | -0.00092995 | -0.00149828 | 0.002428233 |
| 170 | 0.172361997 | 0.039781679 | 0.78851039 | -0.00089139 | -0.001448708 | 0.002340099 |
| 171 | 0.171470607 | 0.038332971 | 0.79085049 | -0.00085449 | -0.001400394 | 0.002254881 |
| 172 | 0.17061612 | 0.036932577 | 0.79310537 | -0.00081917 | -0.001353336 | 0.002172505 |
| 173 | 0.169796952 | 0.035579241 | 0.79527788 | -0.00078536 | -0.001307534 | 0.002092897 |
| 174 | 0.169011589 | 0.034271706 | 0.79737077 | -0.000753 | -0.001262982 | 0.002015983 |
| 175 | 0.168258588 | 0.033008725 | 0.79938676 | -0.00072202 | -0.00121967 | 0.00194169 |
| 176 | 0.167536568 | 0.031789055 | 0.80132845 | -0.00069236 | -0.001177587 | 0.001869944 |
| 177 | 0.16684421 | 0.030611469 | 0.80319839 | -0.00066396 | -0.00113672 | 0.001800675 |
| 178 | 0.166180255 | 0.029474749 | 0.80499907 | -0.00063676 | -0.001097053 | 0.001733809 |
| 179 | 0.1655435 | 0.028377696 | 0.80673287 | -0.00061071 | -0.00105857 | 0.001669276 |
| 180 | 0.164932793 | 0.027319126 | 0.80840215 | -0.00058576 | -0.001021251 | 0.001607007 |
| 181 | 0.164347036 | 0.026297875 | 0.81000916 | -0.00056186 | -0.000985077 | 0.001546934 |
| 182 | 0.163785179 | 0.025312799 | 0.81155609 | -0.00053896 | -0.000950026 | 0.001488988 |
| 183 | 0.163246217 | 0.024362773 | 0.81304508 | -0.00051703 | -0.000916077 | 0.001433104 |
| 184 | 0.16272919 | 0.023446695 | 0.81447818 | -0.00049601 | -0.000883207 | 0.001379217 |
| 185 | 0.16223318 | 0.022563488 | 0.8158574 | -0.00047587 | -0.000851393 | 0.001327264 |
| 186 | 0.161757309 | 0.021712095 | 0.81718467 | -0.00045657 | -0.00082061 | 0.001277182 |
| 187 | 0.161300738 | 0.020891485 | 0.81846185 | -0.00043808 | -0.000790835 | 0.001228911 |
| 188 | 0.160862662 | 0.020100649 | 0.81969076 | -0.00042035 | -0.000762043 | 0.001182391 |
| 189 | 0.160442314 | 0.019338606 | 0.82087315 | -0.00040335 | -0.00073421 | 0.001137565 |
| 190 | 0.160038959 | 0.018604396 | 0.82201071 | -0.00038707 | -0.000707311 | 0.001094376 |
| 191 | 0.159651894 | 0.017897085 | 0.82310509 | -0.00037145 | -0.00068132 | 0.00105277 |
| 192 | 0.159280444 | 0.017215765 | 0.82415786 | -0.00035648 | -0.000656215 | 0.001012692 |
| 193 | 0.158923967 | 0.01655955 | 0.82517055 | -0.00034212 | -0.000631969 | 0.000974091 |
| 194 | 0.158581845 | 0.015927581 | 0.82614464 | -0.00032836 | -0.000608559 | 0.000936917 |
| 195 | 0.158253487 | 0.015319022 | 0.82708156 | -0.00031516 | -0.000585961 | 0.000901119 |
| 196 | 0.15793833 | 0.014733061 | 0.82798268 | -0.0003025 | -0.000564152 | 0.000866651 |
| 197 | 0.157635831 | 0.014168909 | 0.82884933 | -0.00029036 | -0.000543107 | 0.000833465 |
| 198 | 0.157345472 | 0.013625802 | 0.8296828 | -0.00027871 | -0.000522803 | 0.000801518 |
| 199 | 0.157066758 | 0.013102999 | 0.83048431 | -0.00026755 | -0.000503219 | 0.000770765 |
| 200 | 0.156799212 | 0.012599781 | 0.83125508 | -0.00025683 | -0.000484331 | 0.000741164 |
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Biomedical Science"
Biomedical Science focuses on how cells, organs and systems function in the human body and underpins much of modern medicine. Biomedical Science applies parts of natural and/or formal sciences to help develop advances in healthcare.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




