Processes in Achieving Sustainable Biomimetic Design
Info: 11993 words (48 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
Tagged: BiometricsSustainability
BIO-MIMETICS
A Process of achieving sustainability
ABSTRACT:
Janine M. Benyus in 1997, created a field of subject called Biomimicry (also known as biomimetics) that combined engineering and biology, which made humans again look back into nature for solutions.
Even though Biomimicry is a rather new field of subject it is very likely to have a great impact on our society in the future, as a new way of thinking bringing forward a sustainable solution harmonizing with nature, as a result the solutions in those projects they participate in are moving humanity closer to Nature.
Through biomimicry humans have achieved miracles in Architecture and Design. Buildings have achieved great efficiency in energy by application of biomimicry. Sustainability (in the usage of energy and resources) is a key for satisfying the human needs and comfort. Biomimetic approach to design is seem to be an opportunity to bring nature work into design in a systematic way.
The study explores and analyses the process involved in achieving sustainable biomimetic design from the perspective of 3 main parameters Aesthetics, efficiency and economic. The main aim is define the research to explore the different process involved and how it deals with design factors of projects.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE
- INTRODUCTION…………………………………………………………………1
- Introduction ………………………………………………………………….1
- AIM ……………………………………………………………………………2
- Objective ……………………………………………………………………..2
- Scope …………………………………………………………………………3
- Limitations ……………………………………………………………………3
- Methodology …………………………………………………………………4
- LITERATURE REVIEW …………………………………………………………5
- ARCHITECTURE IN NATURE………………………………………………….6
- Ventilation……………………………………………………………………..6
3.1.1 Termite mound…………………………………………………………6
- Thermoregulation…………………………………………………………….8
- Humming bird’s nest………………………………………………….8
- Weaver bird’s nest……………………………………………………9
- Structure………………………………………………………………………9
- Honey Comb…………………………………………………………..9
- Bird’s Wing……………………………………………………………10
- PROCESS…………………………………………………………………………11
- Principles of Biomimicry……………………………………………………..11
- Approaches to Biomimicry…………………………………………………..13
3.1.1 Problem based approach……………………………………………..13
3.1.2 Solution based approach………………………………………………14
- CASE STUDIES…………………………………………………………………..16
- Primary Case Studies………………………………………………………..16
5.1.1 Lotus Temple………………………………………………………..16
- Secondary Case Studies…………………………………………………….19
- The Eden Project……………………………………………………..19
- Aldar Headquarters……………………………………………………24
- ANALYSIS…………………………………………………………………………27
- CONCLUSION…………………………………………………………………….28
- REFERENCES…………………………………………………………………….29
 List of Figures:
List of Figures:
Figure 1: Formation of Spider Silk
Source: https://veroldin.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/kc3b6ngulc3b3asilkiskirtlar.jpg
Source: https://userscontent2.emaze.com/images/93e5de86-ba04-461c-aa98-8eb96dd4fa9a/7aa5f4d685db2b1991149f8bd41c32ff.jpg
Figure 3:Cross-section of termite mound
Source: https://media.treehugger.com/assets/images/2011/10/termite20mounds.jpg
Figure 5:Humming Bird’s nest adapted to Summer Climate
Figure 6:Humming Bird’s nest adapted to winter climate
Source: https://ssl.c.photoshelter.com/img-get/I0000F19Q_c3ZKmk/t/200/I0000F19Q_c3ZKmk.jpg
Source: https://ak7.picdn.net/shutterstock/videos/4685057/thumb/1.jpg?i10c=img.resize(height:72)
Figure 8:Honey Comb showing Hexagonal Cells
Source: http://www.llafoundation.com/wp-content/uploads/monitoring-beehives-bees.jpg
Figure 9:Anatomy of bird’s wing
Source: http://www.twitt.org/LordsBird02.jpg
Source: http://pubs.sciepub.com/materials/1/2/2/image/fig4.png
Figure 11:Biomimetic Design Process in spiral
Source:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nariman_Lotfi/publication/303587913/figure/fig32/AS:366646561656838@1464426760569/Figure-39-Biology-to-Design-spiral.jpg
Figure 12:Top–down, bottom-up based approach…………………………………14-
Source: http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1110016815001702-gr1.jpg)
Source: http://media2.intoday.in/indiatoday/images/stories/delhi-heritage-2-monuments-1_647_050716084345.jpg
Figure 14:Concept Sketch of Design
Source: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/_O2E3FjX-jK0/TSWGnG269RI/AAAAAAAAAHQ/2pjwC3DUSOo/s1600/sj12-0001.jpg
Figure 15:a)Temple view from Top, b)9 bridges with 9 water bodies
Source:http://2.bp.blogspot.com/_O2E3FjX-jK0/TSWGnG269RI/AAAAAAAAAHQ/2pjwC3DUSOo/s1600/sj12-0001.jpg
Figure 16:Aerial view of Lotus Temple
Source: https://www.holidify.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/lotus-temple.jpg
Figure 17:Eden Project aerial view
Source: http://www.edenproject.com/sites/default/files/ep-t1/HERO-Eden_by_Tamsyn_William_0.jpg
Source: http://edenproject.eu5.org/images/eden%20project%20location-1.jpg
Source: https://revitalizationnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Eden-project-before-65.jpg
Figure 21: Design approach to the site1
Source: https://buildingskins.files.wordpress.com/2010/01/eden-3.jpg
Figure 22:Pentagonal and Hexagonal structure of Radiolaria
Figure 23:Hexagonal Structural members2
Source: http://s.hswstatic.com/gif/eden-63.jpg
Figure 24:Inside view of Eden Project3
Source: http://raredelights.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Eden-Project-11.jpg
Source: http://www.cppwind.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Aldar-HQ.jpg
Source: http://www.vorply.com/media/1087/aldar-headquarters-building-abu-dhabi-seashell-10.jpg
Figure 27:Conceptual Sketches showing a)form, b)Structure resolving5
Source: https://en.wikiarquitectura.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Aldar_boc_concep_2.jpg
Figure 28:Aerial view of Aldar Headquarters6
Source: https://d3sux4fmh2nu8u.cloudfront.net/Pictures/2000x2000fit/2/0/9/1669209_101.jpg
1.1 INTRODUCTION:
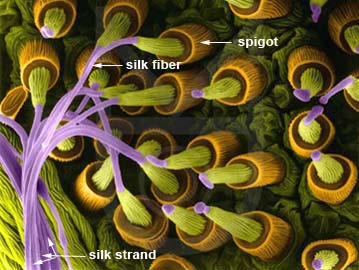 Nature is the most important part of life, without which a human cannot survive. The word Nature is derived from Latin word ‘Natura’ which means birth. Nature is also Conceptually close to word ‘physis’ which refers to System that exits and grows. Accordingly, nature by no means static and is constantly regenerating and transforming itself. What actually Nature can deliver? For Example, Spider web which is strongest fibre ever made in the world. Scientists tried to create the strongest fibre which is still not as strong as spider silk and manufacturing of that fibre results lots of energy usage, pollution etc which spider can produce from the waste left out from the dead insects. In the same way, Fire beetle which is capable of detecting fire from 80 m range. When compared to the scale of detection, it is million times when compared to manmade technologies. (Micheal Pawlyn,2011)
Nature is the most important part of life, without which a human cannot survive. The word Nature is derived from Latin word ‘Natura’ which means birth. Nature is also Conceptually close to word ‘physis’ which refers to System that exits and grows. Accordingly, nature by no means static and is constantly regenerating and transforming itself. What actually Nature can deliver? For Example, Spider web which is strongest fibre ever made in the world. Scientists tried to create the strongest fibre which is still not as strong as spider silk and manufacturing of that fibre results lots of energy usage, pollution etc which spider can produce from the waste left out from the dead insects. In the same way, Fire beetle which is capable of detecting fire from 80 m range. When compared to the scale of detection, it is million times when compared to manmade technologies. (Micheal Pawlyn,2011)

Figure 2: Formation of Spider Silk
Source: https://veroldin.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/kc3b6ngulc3b3asilkiskirtlar.jpg
Figure 1: Fire Beetle
Source:https://userscontent2.emaze.com/images/93e5de86-ba04-461c-aa98-8eb96dd4fa9a/7aa5f4d685db2b1991149f8bd41c32ff.jpg
But the increased population and human scale has unknown consequences for the balance of systems on the species and our own. As the population is being increased, the amount of usage of resources is increased. For shelter and living propose humans started to cut-off trees which resulted in deforestation and also excessive use and wastage of resources. Cities are growing day by day and which results in the depletion of trees, forests (i.e. nature). Because of which so many animal and plant species are under extinction. Over the past million years, so many species are extincted because of humans which result in collapsing the systems of nature. (Climate change (IPCC), 2007)
Nature recycles and reuses most of the resources. In the same way, we should recycle and reuse the materials and natural resources from nature. We can’t regulate everything happening surrounding us, atleast as a person with architecture background, we should design building which will be cost efficient, energy efficient, resource efficient and sustainable design. (Lehni,2001)
Everything in this world is evolving day by day and the process of evolution and resulting adaptations have allowed life to sustain itself for a millennium. Architecture design has grown out of need for shelter and expression and today, the adaptations in building designs and with building technologies and strategies helps us to achieve high levels of comfort in any climate.(Janine M.Benyus, 1997)
Every organism in the world will grow, feed and reproduce. When the species first formed, they might not be in a Sustainable in relation to nature. Over the Last Million years, every living species evolved in its own way according to the climate, living conditions to achieve best sustainable living. While every living species is evolving to have sustainable living system, Imitating natures ideas helps in changing the potential of rate of work, effectivity, comfort, Production etc.(Janine M.Benyus, 1997) But the main question is that architects started inspiring from nature, but how they are achieving the efficiency and sustainability? So the main question which we are focus on is
“What is the process involved in achieving Biomimetic Design?”
1.2 AIM:
The main aim of the research is to look into the process that is involved while imitating biomimetics into architecture for efficient and sustainable design.
1.3 OBJECTIVE:
Every species in this world has been evolving for the past million years and has adopted a system which is efficient and sustainable in according to surroundings and nature. So, by adopting technologies which are developed by imitating nature helps in achieving more efficient and sustainable designs.
- Research on the animal and plant species which are evolved and adapted according to nature.
- Focusing mainly on technologies adapted or inspired from nature.
- Focusing on advantages of adapting Biomimetic in Architecture.
- Concentrating on the different types of process involved in achieving sustainable Biomimetic design.
1.4 SCOPE:
This research will study the architecture of a few selected species from the animal kingdom. The environment and the climatic conditions that they face or live in are of great importance to study their ways of building and understanding the complex set of requirements that they have while building their habitats. The research will try to explore the technologies and structural systems used by those few selected creatures to build their shelters and how they can be incorporated in our architecture for our betterment of human life.
The dissertation will also study a few forms in nature that have been adopted by man and converted into architectural structures will be studied to understand the thought process that the designers had while designing those wonders and what we learn from them for designing such wonders in our future.
1.5 LIMITATIONS:
- There are limited number of built examples which have been inspired from nature and those are too are very limited in Delhi or nearby areas, So the one primary case study is covered, secondary case studies are covered through this research will be very few buildings and through the Secondary sources like journals, internet, publications and documentaries and less on primary observations.
- And the majority of the research and case studies on the technologies and systems used by animal species and plants are mainly through the secondary sources, journals, internet and documentaries etc and less on primary observations.
- The research on the animal species and plants is limited till an extent that is required to examine the form, structure and technologies developed through it.
1.6 METHODOLOGY:
- In the first step, various typologies will be identified from the animal and plant species on the basis of their relevant characteristics. We will concentrate on some of the particular species what they are doing and why they are doing in that way. We will also try to understand the set of requirements and how they are achieving comfortable habitable conditions for themselves.
- We will also concentrate on the solutions thy have achieved in the process of resolving the problems they have faced and the technologies and systems used by them for those habitable space.
- After studying the technologies and systems adopted by these species
in designing and building their habitable spaces, we will try to analyse that how can these technologies and systems can be incorporated or used in architecture for the betterment of life and also for the advancement of our architecture.
- After those studies, we will concentrate on several forms, systems and species in nature that can be adopted by us in our architecture.
- We will then look at few examples which got their inspiration from nature in terms of form, structure or technologies that have been built by man till now and mainly we focus on the design process of achieving that form, structure by inspiring from nature. We will study the various aspects of inspiration in these examples and finally achieving conclusions from the studies.
2.LITERATURE REVIEW:
The biomimetic approach to design is given as a important source of adaption to achieve the main three parameters of building – Aesthetics, efficiency and economy. The main important question is that how to integrate these parameters into buildings. Integrating all these factors in a sustainable, efficient is the difficult part. The most promising source of inspiration for such design solutions is nature. Nature has endless wealth of examples will give humans solutions to all their problems. These study is concerned with some of the design solutions like thermoregulation, water management & drainage, Ventilation and some of the structural systems. If we just started looking at the surroundings, we will experience something new through nature. Architecture has a lot to get from nature. The systems in nature, architecture in animal kingdom and the forms in nature are a great source of inspiration for architects to build in an efficient and economic manner to achieve strength, comfortable living conditions and aesthetic appeal. These books are also confined with some of the design solutions that are adapted and imitated from nature.
Forms and structures found in nature are designed in a efficient manner. They use the minimum amount and provide maximum space and structural strength. These natural forms and shapes area result of adaption to the physical forces over a long period of time so that they respond to these forces in a very efficient manner. The structure of honey comb is such that it requires minimum amount of wax to store honey. The hexagonal cells are arranged in such a way that each wall for two cells and hence the amount of wax used in making a honeycomb is minimized with a good capacity of the honeycomb to hold the honey. Such arrangements can be used for creating spaces for humans. Not only this will reduce the cost of the construction, but also the area required and provide with large amount of usable space.
The achievements that some animals or birds are able to achieve in terms of services are remarkable and have a lot of humans to learn and understand so that they can improve their living conditions and reduce the energy spent in artificially creating comfortable habitable conditions.
In the similar manner, efficiency in maintaining temperature and ambient living conditions is shown by termites in their mounds. Their efficiency in thermoregulation is considered the best one in nature. They can achieve this thermoregulation by means of ventilation and reducing heat gain. Heat gain is reduced by orienting the mound in such a way that minimum amount of sunlight falls on the mound. Similar to the design of their mound as was seen in the eastgate building at Harare where the building maintains temperature by means of ventilation and reduction of heat gain and increased heat loss during the night. The concept is not very difficult to apply in designs today. This will not only reduce the running cost of the building to a great extent but also save a lot of energy spent on thermoregulation of the building. Similarly, on studying the shell structures, it is observed that how beautifully nature integrates for designing of structurers. Making shells of concrete allow us to build large span structures as is evident in a few examples like Lotus Temple, Sydney opera house etc. These structures have a great aesthetic appeal along with structural strength. The use of material is very less in these structures that makes them economic in construction. So with the minimum usage of material, shell structures have high structural strength with a good aesthetic appeal.
3.ARCHITECTURE IN NATURE
 3.1 VENTILATION –
3.1 VENTILATION –
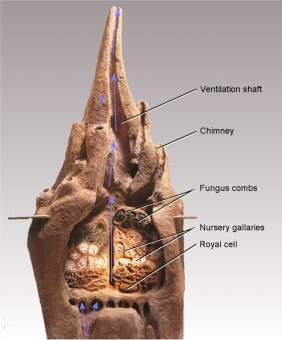
3.1.1 TERMITE MOUND
The natural habitat of termites is the mound that they build which just looks like a pile of dirt from outside. These mounds can go up to 30m diameter and also 10-15m in height. The structure of the mound is very complex which has an outer wall riddled with holes and lots of shafts or tunnels that themselves lead to a series of chimneys that helps in ventilation. The termites live in a hemi-spherical oval nest under the mound.
Figure 3:Cross-section of termite mound
Source: https://media.treehugger.com/assets/images/2011/10/termite20mounds.jpg
 How does the mound dissipate air through its holes or tunnels? Basically, the orientation of these mounds will be in north-south direction so that they have a minimum heat gain from the sun as it faces the sun for very short period of time early in the morning and in the evening. As the sun moves through the sky during the day, the air in the chimneys on the edges of the mound heated up , while the air stays relatively cool in the mound’s big, central chimney. Cool air in the central chimney sinks and Hot air rises up through the outer chimneys. All these ventilation and insulation systems helps in not varying temperature more than 1°C throughout the Year.
How does the mound dissipate air through its holes or tunnels? Basically, the orientation of these mounds will be in north-south direction so that they have a minimum heat gain from the sun as it faces the sun for very short period of time early in the morning and in the evening. As the sun moves through the sky during the day, the air in the chimneys on the edges of the mound heated up , while the air stays relatively cool in the mound’s big, central chimney. Cool air in the central chimney sinks and Hot air rises up through the outer chimneys. All these ventilation and insulation systems helps in not varying temperature more than 1°C throughout the Year.
Figure 4:Termite Mound
Architects and engineers has improved energy efficiency in building by imitating termite mound in their designs. Mick Pearce, a Zimbabwean architect designed the award-winning Eastgate Center in Harare, Zimbabwe imitating termite mound. (Havard,2011)
3.2 THERMOREGULATION –
3.2.1 Nest of Humming Bird
 The amount of heat to be retained or resisted in a shelter is totally a response to the climatic conditions of a place. This can be very clearly seen in the shelters that birds, insects and animals make in different climatic conditions. This control over the climate is achieved by the selection of material to build at times by the orientation of the shelter.
The amount of heat to be retained or resisted in a shelter is totally a response to the climatic conditions of a place. This can be very clearly seen in the shelters that birds, insects and animals make in different climatic conditions. This control over the climate is achieved by the selection of material to build at times by the orientation of the shelter.
 One good example of this is the nest of humming bird that is built in warm and cold regions. The one in warm regions have a shallow nest without a lining of feather that maintains a comparatively low temperature within the structure as compared to outer temperature, whereas in case of the nest of humming bird in cold regions, the nest is deep with thick walls lines with feathers. The feather lining keeps it warm in the inner part as compared to the outside conditions. The absence of feather lining in the one in warm region keeps it cooler inside.(Humming bird nest facts, 2011)
One good example of this is the nest of humming bird that is built in warm and cold regions. The one in warm regions have a shallow nest without a lining of feather that maintains a comparatively low temperature within the structure as compared to outer temperature, whereas in case of the nest of humming bird in cold regions, the nest is deep with thick walls lines with feathers. The feather lining keeps it warm in the inner part as compared to the outside conditions. The absence of feather lining in the one in warm region keeps it cooler inside.(Humming bird nest facts, 2011)
Figure 6:Humming Bird’s nest adapted to winter climate Source: https://i.pinimg.com/736x/a4/42/dd/a442dd01ef45ff33c9bb0857e992e2f2–baby-hummingbirds-hummingbird-nests.jpg
Figure 5:Humming Bird’s nest adapted to Summer Climate, Souce: https://ssl.c.photoshelter.com/img-get/I0000F19Q_c3ZKmk/t/200/I0000F19Q_c3ZKmk.jpg
3.2.2 Weaver bird’s Nest:
Weaver bird is majorly found in the Sub-Saharan Africa, with fewer species in tropical Asia and also in Australia. The nest of this bird shows a striking insulation property. There is a noticeable difference between the temperature of the nest when it occupied and when it’s not occupied. As the birds live in a community, the nest is big in size and has a nest holes. When the holes are occupied, the temperature inside  them is higher than that outside in winters. The nest is majorly occupied majorly in the night and is unoccupied in the day and hence remains warm in the night. The thickness of the wall of the nest is also different indifferent regions depending upon the climatic conditions and requirements of the area. (Avian Reproduction: Nests, 2011)
them is higher than that outside in winters. The nest is majorly occupied majorly in the night and is unoccupied in the day and hence remains warm in the night. The thickness of the wall of the nest is also different indifferent regions depending upon the climatic conditions and requirements of the area. (Avian Reproduction: Nests, 2011)
Figure 7:Weaver Bird’s nest,
Source: https://ak7.picdn.net/shutterstock/videos/4685057/thumb/1.jpg?i10c=img.resize(height:72)
3.3 STRUCTURE –
3.3.1 Honey comb
 Honey bees live in large family groups called colony that may have to 80,000 individual bees. A honey comb is the central structure I the colony of honey bees and is made up of wax.
Honey bees live in large family groups called colony that may have to 80,000 individual bees. A honey comb is the central structure I the colony of honey bees and is made up of wax.
Figure 8:Honey Comb showing Hexagonal Cells Source: http://www.llafoundation.com/wp-content/uploads/monitoring-beehives-bees.jpg
This honey comb is made up of hexagonal wax chambers or cells that vary in size according to the purpose that they fulfil. The walls of these cells are made up of wax secreted by the abdominal gland of the bees. The wax is secreted as flakes that is then chewed and moulded into hexagonal cells. These cells are storage for honey and are home for immature bees. The shape of these cells is the most efficient shape as it contains the maximum amount of honey consuming minimum amount of be wax and the energy for construction.
This is one good example and that shows that all forms and structures in nature are governed by physical laws that try to achieve maximum efficiency through the use of minimum energy. Some of the designer imitated the hexagonal cells as a roof structure and have achieved incredible spans with efficient structure system.(Honey Bee, 2011)
3.3.2 Birds wings:
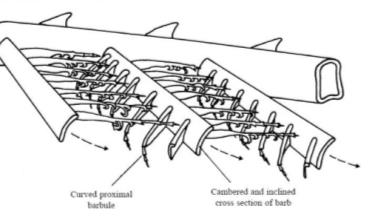
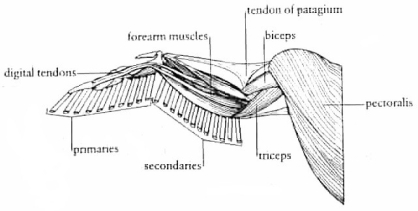 Birds has very impressive wing system which is really dense and is very light weight. And the birds body shape is developed aerodynamically to fly easily in the air. The downward force which they can create with wings is greater than the gravitational force applying on the body. Due to the very light wings, some of the birds can fly for hours continuously without any rest. What made the so lightweight? The primaries and the secondary structure members to which the feather lies are hollow which helps in reducing weight but as they were placed very densely it is providing strength to the wings. (Micheal Pawlyn, 2007)
Birds has very impressive wing system which is really dense and is very light weight. And the birds body shape is developed aerodynamically to fly easily in the air. The downward force which they can create with wings is greater than the gravitational force applying on the body. Due to the very light wings, some of the birds can fly for hours continuously without any rest. What made the so lightweight? The primaries and the secondary structure members to which the feather lies are hollow which helps in reducing weight but as they were placed very densely it is providing strength to the wings. (Micheal Pawlyn, 2007)
Figure 10:Anatomy of bird’s wing
Source: http://www.twitt.org/LordsBird02.jpg
Figure 9:Section of wing
Source: http://pubs.sciepub.com/materials/1/2/2/image/fig4.png
4. PROCESS:
4.1 Principle of Biomimicry:
| Principles | Example | Example of How Human use this to solve Problem |
| Nature runs on sunlight | Leaves use the sunlight for photosynthesis. | Humans are mimicking how plants process sunlight in order to one day split water into clean-burning fuels. This helps eliminate the problem of pollution-causing energy production. |
| Nature uses only the energy it needs | Leaves fall from a tree and are turned into nutrients for the tree | A business decides to locate its waste recovery facilities close to the facility where waste is produced, to eliminate the need to transport the waste a great distance. |
| Nature fits form to function | Vulture wings | The Wright brothers analysed vulture wings to come up their designs for airplanes. This solved the problem of figuring out how to design planes. |
| Nature recycles everything | Oak-hickory forests | Closed-loop manufacturing – a manufacturing plant that runs on sunlight and reuses all its waste. This eliminates waste material. |
| Nature rewards cooperation | Old field succession | Do-nothing farming – method that sows rice, barley, and clover together in one field, so they grow in each other’s shade. This eliminates the need for possibly hazardous fertilizer (and eliminates the need to weed). |
| Nature banks on diversity | Red-wood forest | Industrial eco-parks – Co-located industries work in a food chain, consuming each other’s waste. This eliminates waste from several industries, at one time. |
| Nature demands local expertise | Native grazers (native animals that naturally migrate as they graze) | Holistic ranching mimics the way that native animals graze. This allows grassland to naturally recover, preventing it from becoming unusable |
| Nature curbs excesses from within | Forest fires clear out space for new healthy growth | Natural selection forestry |
| Nature taps the power of limits | Plants in a given environment thrive within the range of temperatures of that region. | Architects design a Building without overdesigning – that is, they don’t design a home in a moderate climate for extreme temperature conditions. This results in the use of less building material. |
(Janine M.Benyus, 1997)(NatureMapping, 2008)
4.2 Approaches to Biomimicry:
4.2.1 Problem Based Approach:
The approach where designers look to the living world for solution requires designers to identify problems and biologists to then match these to organisms that have solved similar issues. This approach is effectively led by designers identifying initial goals of design.
Carl hastrich, Design strategist who is practicing Biomimicry for a long time suggested they represent the process in the spiral that would be visually understandable to designers.
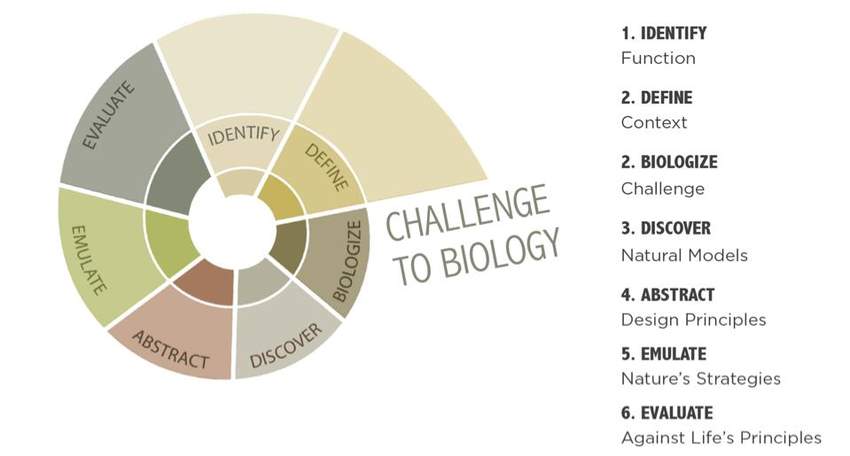
Figure 11:Biomimetic Design Process in spiral
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nariman_Lotfi/publication/303587913/figure/fig32/AS:366646561656838@1464426760569/Figure-39-Biology-to-Design-spiral.jpg
(Biomimicry guild, 2007)
Researchers have defined this approach through 6 definite steps:
- Step 1: Problem Definition
- Step 2: Reframe the problem
- Step 3: Biological Solution research
- Step 4: Define the biological Solution
- Step 5: Practical Extraction
- Step 6: Principle Application
(Micheal Helms, Swaroop S. Vattam and Ashok K.Geol, 2009)
4.2.2 Solution Based Approach:
When the Biological knowledge influences human design, the collaborative design process is initially dependant on people having knowledge influences human design, the collaborative design process is initially depandant on people having knowlwdgeof relevant biological or ecological research rahre than on determined human design problems.
An advantage of this approach therefore is that biology may influnce human in ways that might be outside a predetermined design problem, resulting in previously onthought of technologies or systems or even approaches to design solutions.
 Researchers have defined thid approach too similarly through 7 definite steps:
Researchers have defined thid approach too similarly through 7 definite steps:
- Steps 1: Biological solution Identification. Here, designers start with particular biological solution in mind
- Step 2: Define the Biological Solution
- Step 3: Principle extraction
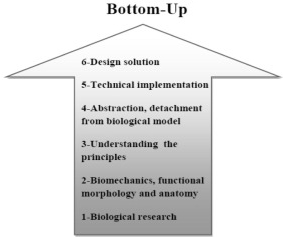 Step 4: Reframe the Solution, In this case, reframing forces designers to think in erms of how Human might view the usefulness of the biological function bieng achieved.
Step 4: Reframe the Solution, In this case, reframing forces designers to think in erms of how Human might view the usefulness of the biological function bieng achieved.- Step 5:Problem search, whereas search in the biological domain includes search through some finite space of documented biological solutions, problem search may include Defining entirely new problems.
Figure 12:Top-down, bottom-up based approach
Source: http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1110016815001702-gr1.jpg
- Step 6: Problem definition
- Step 7: Principle application (Biomimicry guild, 2007)
5. CASE STUDIES:
5.1Primary Case Studies
5.1.1 Baha ‘I’ Temple
Architect: Fariborz Sahba
Architecture Style: Expressionist architecture
Location: New Delhi
Inspiration: Lotus Flower
Main Contractor: Larsen & Toubro Limited
Structural Engineer: Flint & Neill Partnership
Period of Construction: 1978 – 1986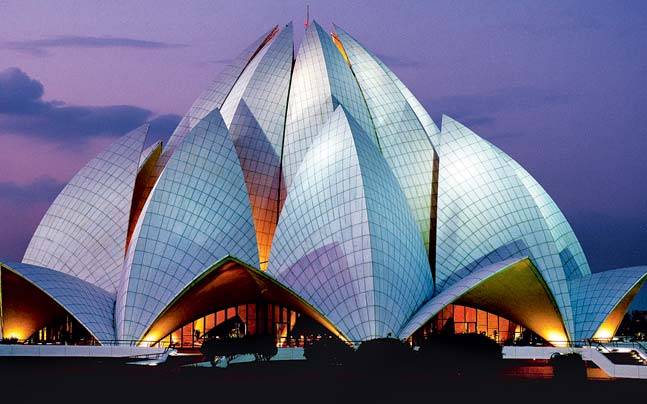 
Source: http://media2.intoday.in/indiatoday/images/stories/delhi-heritage-2-monuments-1_647_050716084345.jpg
The Baha ‘I’ Temple also known as The Lotus Temple is the mother temple of the Baha ‘I’ religion in the Indian Sub-continent.
Design Approach: Problem based Approach
- Step 1: Problem Definition
- In this project, the design itself is a problem. The project is to design Baha ‘I’ temple which should act as a temple for all religions.
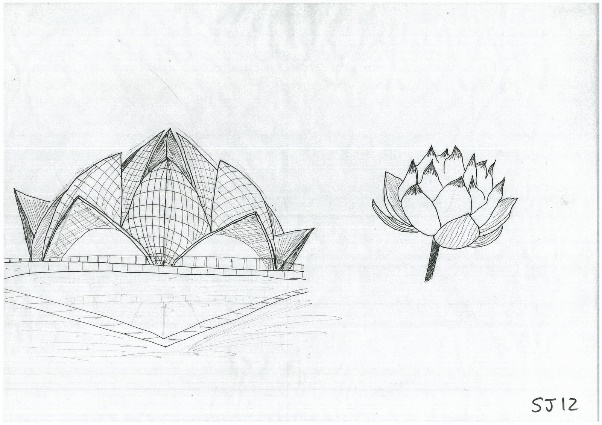 Step 2: Reframe the problem
Step 2: Reframe the problem
- The challenge for the architect, Fariborz Sahba was to have a concept that would be acceptable to the people of all religions and also would fit into the Indian context. (National spiritual assembly of baha ‘I if India,2011)
Figure 14:Concept Sketch of Design
Source: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/_O2E3FjX-jK0/TSWGnG269RI/AAAAAAAAAHQ/2pjwC3DUSOo/s1600/sj12-0001.jpg
- Step 3: Biological Solution research
- With some research, architect Faroborz Sahba came up with the concept of lotus flower for his design because of its importance in Hindu religion and also Buddhists. Lotus flower is choosed, as it is also the national flower of India.(National spiritual assembly of baha ‘I of India,2011)
 Step 4: Define the biological Solution
Step 4: Define the biological Solution
Figure 15:a)Temple view from Top, b)9 bridges with 9 water bodies
Source: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/_O2E3FjX-jK0/TSWGnG269RI/AAAAAAAAAHQ/2pjwC3DUSOo/s1600/sj12-0001.jpg
- Conceptually flower symbolizes purity, holiness.
- The temple looks like a Lotus flower surrounded by leaves afloat on water.
- The building is in the form of a lotus flower which has three layers of petals with nine petals in each layer. (National spiritual assembly of baha ‘I of India,2011)
- Step 5: Practical Extraction
- The lotus flower structure with 9 inner petals and 9 outer petals with 27 petals in total surrounded by gardens and 9 water bodies makes it look like as it is floating on water. (National spiritual assembly of baha ‘I if India,2011)
- Step 6: Principle Application
- Like the form, the structure of the temple too has been inspired from the nature. The structure of the building is inspired from the shells.
- The structure consists of 27 giant marble petals. The structure can be entered through nine bridges which are running over the nine ponds leading the nine entrances.
- The inner nine petals form nine entrances to the worship hall. These petals are separated at top which slightly looks like a bud. The opening is covered with glass which allows natural light.
- The shells of the inner petals are supported by 9 radial beams mainly resting on the arches. (National spiritual assembly of baha ‘I if India,2011)

Figure 16:Aerial view of Lotus Temple
Source: https://www.holidify.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/lotus-temple.jpg
5.2Secondary Case Studies
5.2.1 The Eden Project
Architect: Nicolas Grimshaw
Biologist: Julian Vincent
Location: Bodelva, U.K
Inspiration: J.Baldwin’s Pillow Dome
Period of Construction: 1998 – 2001
Main Contractor: McAlpine JV
Landscape Designers: Greysmith Associates
Structural Engineer: Anthony Hunt and Associates
Service Engineer: Arup
Design Approach: Problem based Approach
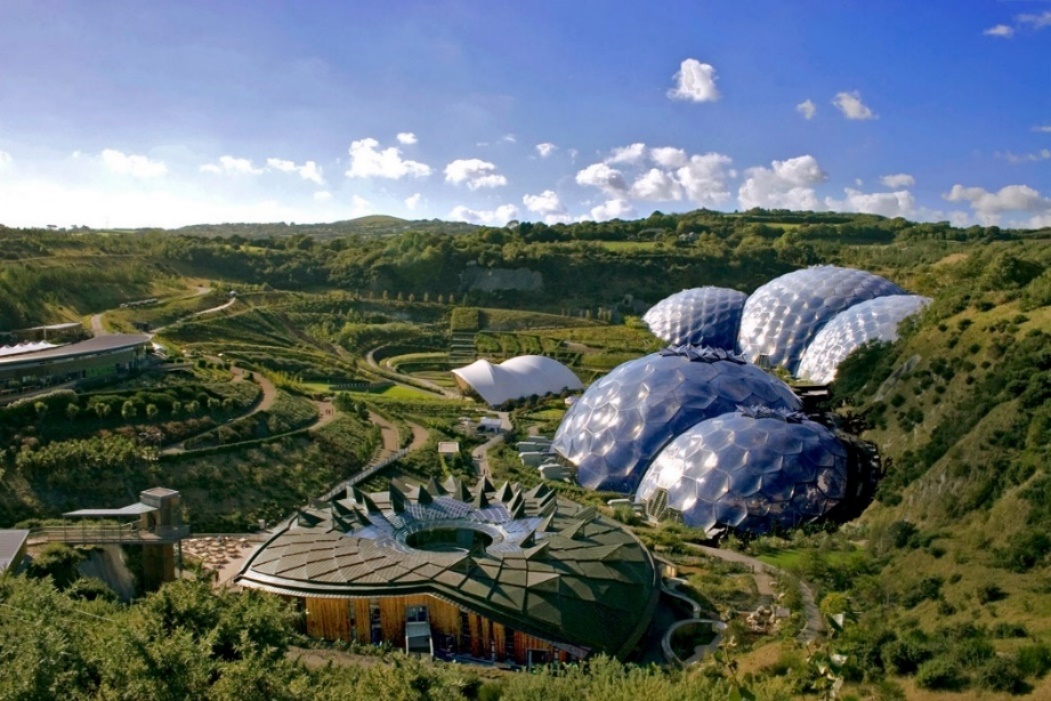

Figure 17:Eden Project aerial view
Source: http://www.edenproject.com/sites/default/files/ep-t1/HERO-Eden_by_Tamsyn_William_0.jpg
- Step 1: Problem Definition
 Defining the problem: The problem which they have already facing before conceptual design is even decided is the site. Site is too irregular and has very steep contours in which they have to design for Biome.
Defining the problem: The problem which they have already facing before conceptual design is even decided is the site. Site is too irregular and has very steep contours in which they have to design for Biome.
Figure 18:Site Topography
Source: http://edenproject.eu5.org/images/eden%20project%20location-1.jpg
- Step 2: Reframe the problem
 The problem which architects normally faced is to create the form which will work good enough for that topography.
The problem which architects normally faced is to create the form which will work good enough for that topography.
- Step 3: Biological Solution research
- With the help of Biologist Julian Vincent, Architects started research for a form from nature which has tendency to adjust according to the surface of the surroundings.
Figure 19: Site Topography
Source: https://revitalizationnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Eden-project-before-65.jpg
- Step 4: Define the biological Solution
 After researching, the basic primary concept they achieved for the form is ‘SOAP BUBBLE’
After researching, the basic primary concept they achieved for the form is ‘SOAP BUBBLE’
- Step 5: Practical Extraction
- Started developing with the concept of Soap Bubble, designers started resolving with respect to the site. What is the final design they are achieving through the site? Structure that is going to resist the structure?
Figure 20:Form of Bubbles
 Structure Approach: Problem based approach
Structure Approach: Problem based approach
- Step 1: Problem Definition
- Defining the Problem: The main primary problem is that they have to solve the structure for Soap Bubble Concept.
Figure 21: Design approach to the site
Source: https://buildingskins.files.wordpress.com/2010/01/eden-3.jpg
- Step 2: Reframe the problem
- For a place like Biome where trees and plants grow inside a building there should be adequate amount of Natural light inside the building.
- Step 3: Biological Solution Research
- Designers started researching for the structural element which can be adjusted and can be increase the shape with less structural members.
- Step 4: Define the Biological Solution
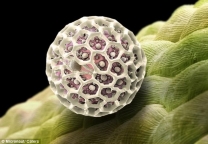 Finally, with the help of Biologist Julian Vincent, they thought of imitating structure of Pollen grain and Radiolaria which has 3d hexagonal and pentagonal structure.
Finally, with the help of Biologist Julian Vincent, they thought of imitating structure of Pollen grain and Radiolaria which has 3d hexagonal and pentagonal structure.
Figure 22:Pentagonal and Hexagonal structure of Radiolaria
- Step 5: Practical Extraction
 The next thing they have concentrated on maximizing the size of Hexagon and to do that they have find an alternative to glass, which is really limited In terms of its unit sizes. And in Nature there are lots of examples of very efficient structures
The next thing they have concentrated on maximizing the size of Hexagon and to do that they have find an alternative to glass, which is really limited In terms of its unit sizes. And in Nature there are lots of examples of very efficient structures  based on pressurized membranes. So, they came up with material alternative ETFE which is high strength polymer. They have started putting that in 3 layers, welded it around the edge and then inflated it. The interesting part in this material is that we can make In units which will be roughly seven times the size of glass, and it is only 1% of the weight of double-glazing. Through this they have factor of 100 saving. By integrating these, they have achieved so much indirectly. Due to the less usage of steel, with less steel they are getting more sunlight in which meant that they didn’t have to put as much extra heat in winter and with less overall weight in superstructure there were big savings in the foundations. (sustainablebuild)
based on pressurized membranes. So, they came up with material alternative ETFE which is high strength polymer. They have started putting that in 3 layers, welded it around the edge and then inflated it. The interesting part in this material is that we can make In units which will be roughly seven times the size of glass, and it is only 1% of the weight of double-glazing. Through this they have factor of 100 saving. By integrating these, they have achieved so much indirectly. Due to the less usage of steel, with less steel they are getting more sunlight in which meant that they didn’t have to put as much extra heat in winter and with less overall weight in superstructure there were big savings in the foundations. (sustainablebuild)
Figure 23:Hexagonal Structural members
- Step 6: Principle application
- They have resolved the structure accordingly with respect to form. They used ETFE which will allow natural light and it is too lightweight when compared to glass. By using ETFE material in place of glass, they have achieved span 7 times when compared to the glass with steel structure. (Stefin, 2011)
- Step 6: Principle Application
- They have already the created the form with respect to site through Soap Bubble. The Steel Structure with ETFE panels used for large span and efficient lighting with the help of Pollen Grains and Radiolaria.
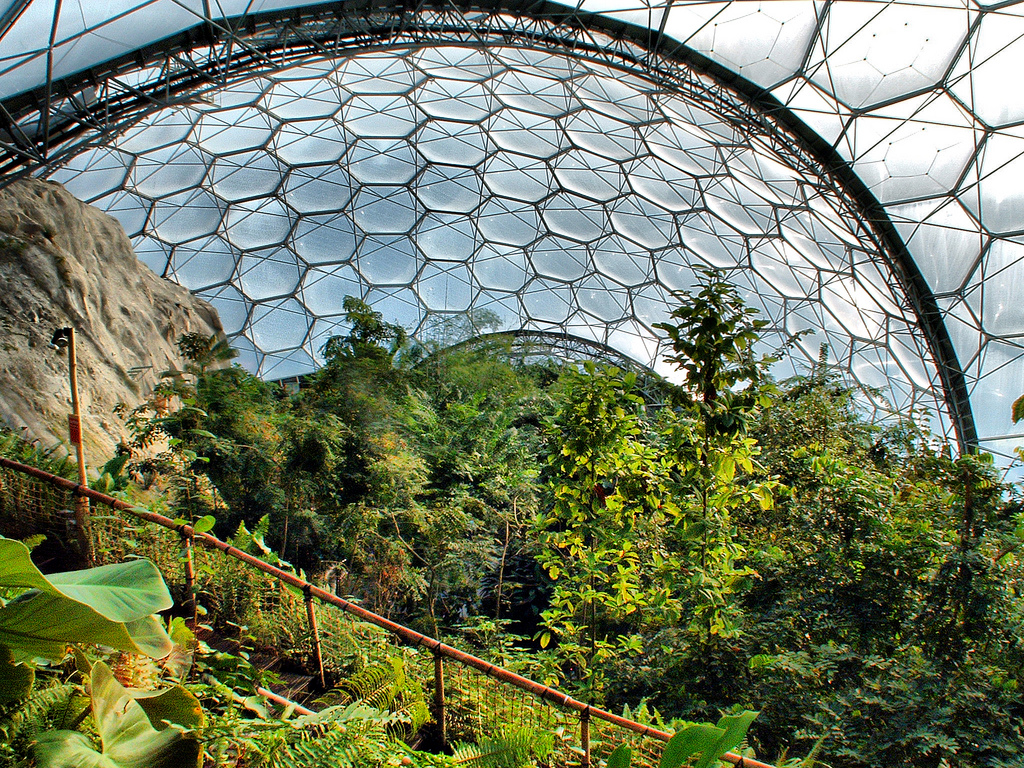

Figure 24:Inside view of Eden Project
Source: http://raredelights.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Eden-Project-11.jpg
At the end of the project they have worked out that the weight of superstructure is actually less than the weight of air inside the building. Eden project is one of the good example showing how the ideas of biology can lead to radical increase in resource efficiency delivering the same function but only with a fraction of the resource input. (suatainablebuild)
5.2.2 Aldar Headquarters:
Architect: MZ Architects ( Marwan Zgheib)
Contractor: ALDAR Liang O’Rourke
 Owner: ALDAR Properties
Owner: ALDAR Properties
Location: Abu Dhabi- United Arab Emirates
Inspiration: Clam Shell
Floor Area: 61,900 sq.m
Height: 110m
Started Design: 2005
Project Completion: 2010
Awards: Best Futuristic Design
Design Approach: Solution based Approach
- Step 1: Solution Identification
- The main requirement of the client is to create an iconic commercial building.
 Architect wants to create a design which should have some relation to Abu Dhabi and simple iconic structure. (wikiarquitectura)
Architect wants to create a design which should have some relation to Abu Dhabi and simple iconic structure. (wikiarquitectura)
- Step 2: Biological Solution
- Designers are inspired by the clam shell which has the deep meaning of maritime heritage of Abu Dhabi. (wikiarquitectura)
- Step 3: Principle extraction
- Architect imagined 2 giant curved circular walls came together representing the shell. (wikiarquitectura)
- Step 4: Reframe the Solution
- Architect Marwan Zgheib enthusiasm for the project resulted a clear goal to create simple, bold and iconic structure. They want design visibly so powerful and fit into the iconic skyscrapers of Abu dhabi and also like a shell
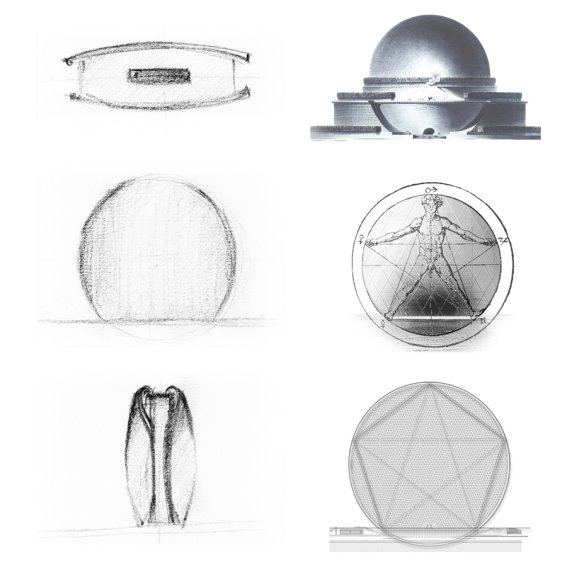 with a pearl resting on the edge of beach. (wikiarquitectura)
with a pearl resting on the edge of beach. (wikiarquitectura)
Figure 27:Conceptual Sketches showing a)form, b)Structure resolving
Source: https://en.wikiarquitectura.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Aldar_boc_concep_2.jpg
- Step 5: Problem search
- The main problem in implementing the design is the structure. They have to make the design stand.
- To make the circular building stand, they have inspired from the cosmic body of human in pentagon inscribed in a circle. (wikiarquitectura)
- Step 6: Problem definition
- The place where base of the pentagon resides on circle are the points where building is going to touch the ground. (wikiarquitectura)
- The circular facades is achieved by using toroidal geometry with triangulated glass panels to achieve perfect circle in the elevation.
- Step 7: Principle application
 The slabs are cantilevered 25 m from the central core. To support the slabs, internal structure and facade, design team developed a complex diamond shaped steel grid structural system called Diagrid. (wikiarquitectura)
The slabs are cantilevered 25 m from the central core. To support the slabs, internal structure and facade, design team developed a complex diamond shaped steel grid structural system called Diagrid. (wikiarquitectura)
Figure 28:Aerial view of Aldar Headquarters Source: https://d3sux4fmh2nu8u.cloudfront.net/Pictures/2000x2000fit/2/0/9/1669209_101.jpg
- Finally, they have achieved iconic structural with well lit natural day lighting and wide view to the beach on one side and to the city on other side.
6. ANALYSIS OF CASE STUDIES
| Baha ‘I’ Temple | The Eden Project | Aldar Headquarters | |
| Building type | Temple | Biome- Visitors Place | Office, commercial |
| Design Inspiration | Lotus Flower | Bubble | Clam Shell |
| Structure Inspiration | Shell Structures | Radiolaria, Pollen grains | Human with Pentagram |
| Approach | Problem based | Problem based | Solution based |
| Design Driven Factor | Centre for all religions | Site Conditions | Iconic Structure |
| Structure System | Steel formwork, concrete shells cladded with marble | Hexagonal steel structure with ETFE roofing panels. | Diagrid structure with triangulated glass panels. |
| Parameters achieved | Aesthetics and efficient | Aesthetics, economic and efficiency | Iconic, economic and efficient |
Whatever the project is, whatever the approach is, Biomimeic design will achieve main 3 important parameters of the building- Aetheticity, economic and efficiency.
7. CONCLUSIONS
Biomimetic architecture is a contemporary philosophy of architecture that seeks solutions for sustainability in nature, not by replicating the natural forms, but by understanding the rules governing those forms.
Buildings are always judged on three main parameters – aesthetics, efficiency and economy. Most of the buildings do not stand well in all the parameters stated. So, the question is that how can these parameters can be integrated in a building. To achieve these parameters, we need innovative thought process and efficient source of inspiration for design. The best source of inspirations for design solutions is nature. Nature has endless source of examples where humans can learn and improve their living conditions.
Forms and structures in nature are designed in a very efficient manner. They use minimum amount of material and provide maximum space and structural strength. The natural forms and shapes are result of adaptation to the physical forces over a long period of time, so that they respond to these forces in a very efficient manner.
Imitating from nature and integrating into design just don’t give us the efficiency, process involved in imitating and integrating takes the major part. Starting from the Site study, we will find pros and cons. Sometimes we can neglect cons, they might be negligible part in context of design. But sometimes cons are major part, which we have start our design in the process of resolving those problems. This is where we will see the type of approach involved problem based or solution based. In case of solution based, they will what should be their final factor which they should achieve i.e. efficiency or aesthetics and process of design conceptualization starts in achieving the desired solution. Architects might follow whatever process they want but finally if the parameters they are trying to achieve are same, then they are going to face the same factors. Final design product may not be same but the level of efficiency might be almost same.
Bibliography:
- Dessertation: (unpublished)
- Augustine.J.T – “Sustainability: Lessons from Biomimicry”
Dessertation, S.P.A., 2011
- Anuj Kandelwal – “Nature Inspired Architecture”
Dessertation, S.P.A., 2012
- Books :
- Ilaria Mazzoleni – “Architecture Follows Nature”, 2013
Biomimetic Principles for Innovative Design
- Petur Om Amarson – “Biomimicry”, New Technology,. 2011
- Articles and Blogs (from internet):
- Mohed Sabry Aziz, Amr Y. El sheriff, 2016, “Biomimicry- as an approach for bio inspired structure with aid of Computation”, viewed 12th June 2017, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s1110016815001702
- Stephanie Vierra,2016, “Biomimicry-Designing to Model Nature”, viewed 12th June 2017,https://www.wbdg.org/resources/biomimicry-designing-model-nature
- Cesar A. Cruz, 2012, “Wright‘s Organic Architecture”, viewed 14th June 2017,< https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=3&ved=0ahUKEwiDyNaC8tvUAhXJqo8KHWAlAwQQFgguMAI&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.cloud-cuckoo.net%2Fjournal1996-2013%2Finhalt%2Fde%2Fheft%2Fausgaben%2F112%2FBeitraege%2F2.2%2520%2520%2520Cruz.pdf&usg=AFQjCNE8EYJWRAyou-T0Mw7QYAI7i05MDQ>
- Ingrid de Pauw, Prabhu Kandachar, Elvin Karana, David Peck, Renee Wever, 2010, “Nature Inspired Design-Strategies towards Sustainability”, viewed 7th June 2017, http://s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/idealco-dev/publications/original/9/Nature-Inspired%20Design_Thesis_Ingrid%20de%20Pauw_pdf.pdf?1448552970
- Gertie Goddard, 2016, “Biomimetic Design-10 examples of nature inspiring technology”, viewed 10th June 2017, https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwjsmYj-_dvUAhXEM48KHT4pCKQQFggtMAE&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencefocus.com%2Farticle%2Fnature%2Fbiomimetic-design-how-nature-inspires-modern-technology&usg=AFQjCNHjU1P453WfP6XXL2gHTSpkHYZtZg
- Audrey Ryan, SOM Foundation Structural Engineering Traveling Fellowship, 2015, “Bio inspiration in structures”, viewed 15th June 2017,< https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwjL-O-Tg9zUAhWJLY8KHVBpA0cQFggoMAA&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.somfoundation.som.com%2Frepository%2Ffiles%2Fsubmissions%2Faudrey.ryan_.portfolio.pdf&usg=AFQjCNFqi6GZllICy_c2_4-xGecsHQ27hA>
- Lidia Badarnah, 2017, “Form Follows Environment-Biomimetic approach to building design for environmental adaptation”, viewed 12th June 2017, < https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwidoJ2RhNzUAhWBrY8KHYziA6wQFggqMAE&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.mdpi.com%2F2075-5309%2F7%2F2%2F40%2Fpdf&usg=AFQjCNGiLgsUocSybkkL4bXmd-4O5kOJCQ>
- Elsevier, “Architectonic and functional quality of buildings”, viewed 11th June 2017, < https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwiZ5eenhdzUAhUJPo8KHQpnAKYQFggoMAA&url=http%3A%2F%2Fv5.books.elsevier.com%2Fbookscat%2Fsamples%2F9780750664578%2F9780750664578.PDF&usg=AFQjCNHBRl27pkyY9bScLyW52pi1gUIUrw>
- Michelle Douglas, “ Nine incredible buildings inspired from Nature”, viewed 30th September 2017,<
http://www.bbc.com/earth/story/20150913-nine-incredible-buildings-inspired-by-nature>
- Micheal J.Maglic, “ Using Nature as Model for Design”, viewed 27th September 2017, <
http://www.schorarworks.Umass.edu/theses/871>
- Lidia Badarnah, “Form Follows Environment: Biomimetic Approches to Building envelope Design for Environmental Adaptation” <
http://www.mdpi.com/2075-5309/7/2/40/htm>
- Websites:
- https://asknature.org/?s=&page=3&hFR%5Bpost_type_label%5D%5B0%5D=Inspired%20Ideas&is_v=1#.WUPYIJCGPIU
- https://www.treehugger.com/green-architecture/biomimicry-architecture-michael-pawlyn-book-review.html
- https://www.nature.org/ourinitiatives/regions/northamerica/nature-inspires-art.xml
- https://architizer.com/blog/biomimicry-binet-som/
- https://www.livescience.com/3191-spookfish-world-strangest-eyes.html
- https://vimeo.com/86659369
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biomimetic_architecture
- https://en.wikiarquitectura.com/building/aldar-headquarters-building/
- https://www.greenmatch.co.uk/blog/2015/01/the-eden-project-uk-s-energy-revolution
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Sustainability"
Sustainability generally relates to humanity living in a way that is not damaging to the environment, ensuring harmony between civilisation and the Earth's biosphere.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




