Dissertation Proposal on Effectiveness of Internal Growth Strategies
Info: 1989 words (8 pages) Example Dissertation Proposal
Published: 10th Jun 2021
Tagged: BusinessBusiness Strategy
According to Deloitte, most companies pursue an objective of sustainable and continuous growth. They can choose to pursue organic or inorganic growth strategies. Profitable growth creates the basis for long-term competitive advantage and is an essential element in enterprise value creation. Internal growth relies on the capabilities and resources under the control of the firm, and it includes strategies that consist of developing and exploiting those resources and capabilities into launching new products or entering new markets to attain growth. (Kobler, Celner, 2020);
Since the 2008 financial crisis, corporate banks have focused a majority of their attention on protecting their core business against exogenous adverse events, prioritising instead to protect their existing market share in the short-term until more favourable conditions emerged. At this inflexion point, many banks have tried to improve their financial position through a combination of cost management and revenue growth strategies. Still, the outcome has seen volatility in profit margins. In recent years, corporates banks have begun to prioritise growth strategies, but revenue growth has not necessarily led to improved profits. (Kobler, Celner, 2020)
The corporate banking divisions of universal banks are often seen as significant strategic business units and typically only engage in internal growth strategies. As a result, this dissertation will primarily examine internal growth strategies and their effectiveness to firm performance. In contrast to external growth, internal growth strategies require significant resources in the form of time, investment and are intrinsically riskier when compared to external growth strategies. (Aktas et al., 2008; Kemppi et al., 2012).
In brief, both internal and external strategies have advantages and disadvantages regarding the way they influence firm performance. However, since growth is a requirement to satisfy shareholder returns, firms typically pursue different strategies to achieve their profit objectives. It is understood why companies choose external or internal growth strategies; however, what are the effects of these strategies on performance? Does inorganic growth provide superior performance than the organic ones? Or is it the opposite? This research seeks to examine the impact of internal growth strategies on firm performance by examining the growth strategies employed by Barclays Ireland Plc in the decade following the 2008 financial crisis (i.e. 2010-2020)
1.1 Theoretical design of research
This section focuses on outlining what this topic entails and why this research is conducted. Firstly, paragraph 1.1.1 outlines the context of the topic, which is centred on the literature of firms’ growth strategies. Secondly, paragraph 1.1.2 outlines the problem statement and main research objectives to highlight the critical issues from the context. Thirdly, paragraph 1.1.3 outlines the procedures that are required to realise the research objective by providing the research framework. Lastly, in paragraph 1.1.4, the theoretical framework provides primary and sub-research questions.
1.1.1 Research context
The Penrose growth theory distinguishes between internal and external growth. Internal growth refers to growing an enterprise from internal resources such as marketing, R&D and core business operations. It depends on existing resources that can be amplified by employing and training new staff. (Penrose,1959)
External growth, in contrast, involves a firm achieving growth from external resources through strategic alliances or acquisitions of companies in related or unrelated business areas. (Penrose,1959)
External growth strategies allow an enterprise to take advantage of growth opportunities by establishing synergies between resources that are already present in the firm with complementary resources from external firms. External strategies include alliances, M&A, greenfield investments, minority stakes, and partnership (Chen, 2009)
In strategic management literature, these two strategies are mainly examined independently. A large majority of literature examines the motives and the effects of external strategies on large companies and the subsequent financial performance. In contrast, internal growth strategies are less common.
Therefore, matters involving the impact on firm performance of internal growth strategies for large business divisions withing multinational firms still need to be comprehensively examined.
1.1.2 Analysis of Problem
For several decades, distinctive growth strategies were not necessary for banks to grow and expand. In the economic boom periods of the 1990s and for the most of the 2000s, a majority of corporate banks pursued unsystematic growth strategies, had broad appetites for risk and diversified their portfolios without worrying enough about the management of costs or carving out unique positions in the eyes of their customers (Hadley, Nielsen, Olsen & Turner, 2015).
The 2008 financial crisis caused an abrupt shift in focus for many large global corporate banks - from pursuing aggressive uncoordinated growth strategies to survival. In hindsight, while many of the measures utilised to ensure survival during one of the most severe economic downturns in history, the scope of strategies deployed hindered future growth prospects.
According to a Bain Co. report, most corporate banks relied on similar cost rationalising and performance improvement tactics over the five years after the crisis, resulting in the industry’s return on equity dropping by 6% in comparison to levels before the crisis and this trend continued beyond 2014. (see Figure 1).
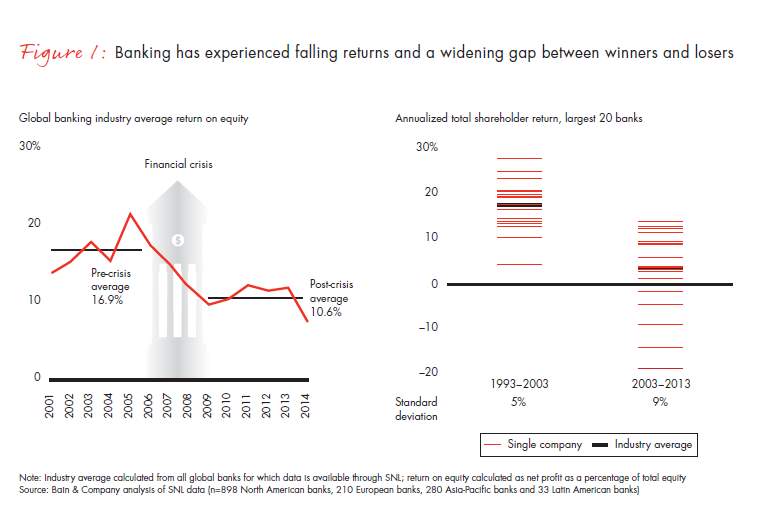
Figure:1: Extent of losses experienced by global corporate banks Source: Bain (The Return of Corporate Strategy in Banking, 2015).
Corporate banks in Europe have experienced stalled growth post the 2008 crisis, with banks’ sources of revenue coming under severe pressure. Several factors in Europe attributed to this stagnation, primarily driven by the combined effects of:
- slowing credit growth amongst consumers and businesses,
- net fee income coming under pressure as a result of increased competition,
- low or negative interest rate environment,
- macroeconomic volatility,
- subdued economic growth across the region and
- a further increasing Know Your Customer (KYC) regulatory requirements.
Further exacerbating the headwinds on revenues are the new digitally based entrants with disruptive business models, which have been attacking large profit pools. These challenger banks have taken significant market share from incumbent banks. In Europe, banks have had to face increased waves of additional regulation which were introduced to ensure stricter and higher capital requirements, reducing banks’ balance sheet leverage. This additional regulation has harmed banking profits.
Conversely, these factors have also created valuable opportunities for banks. Corporate banks with the capabilities of serving large companies can navigate today’s challenging conditions by adjusting to market dislocations, avoiding the impact of negative rates and managing KYC provisions (Miarka, Casalis & Pasque 2020)
Against this backdrop, the new macro and competitive environment mean that banks need to adapt through more disciplined growth strategies. Research indicates that at some banks, what passes for strategy, consists of the pursuit of quarterly profit targets. A long-term growth strategy, in comparison, typically involves enduring some pain over the short term and communicating to shareholders why it takes time to deliver results. (Hadley, Nielsen, Olsen & Turner, 2015).
The choice regarding which internal growth strategies is an essential consideration for corporate banks. Though, there is a limited response from the literature regarding their differential impact on performance (Aktas et al., 2008).
Therefore, this research confronts two main issues: (1) what the growth strategies adopted by Barclays Bank Ireland plc corporate banking unit are, and (2) what the impact of these strategies is on the company’s financial performance.
The aim is to contribute and to increase the strategic management literature regarding growth strategies in corporate banking. Currently, only a few studies compare the impact of internal growth strategies on financial performance within the banking sector. Thus, this research will contribute to the literature by:
- Evaluating how Barclays Bank Ireland Plc develops and implements growth strategies amid a turbulent and uncertain macro environment. Thus, by focusing on a specific business unit, this research will provide meaningful insights to understand the firm’s growth patterns.
- Analysing the impact of identified growth strategies on firm performance.
This analysis will allow us to derive the following objective as it relates to this study:
“Contribution to the strategic management literature, by assessing internal growth strategies adopted by corporate banks within the Irish market, and further assessing their impact on performance.”
1.1.3 Research Framework
This paper will seek to (i) identify the growth strategies as classified in the literature. Also, it will investigate how the literature measures and assesses the impact of these growth strategies on performance. (ii) during the empirical research, data collection concerning the strategies identified, which will take the form of an inductive, qualitative interview conducted in-house, representing an opportunity for general comments about the growth strategies implemented by the management of Barclays Bank. This will provide an opportunity to explore this information using a qualitative approach to establish the performance obtained (iii) Based on the assessment of the data gathered during the empirical research and the study of the literature (iv) conclusions and recommendations will be outlined.
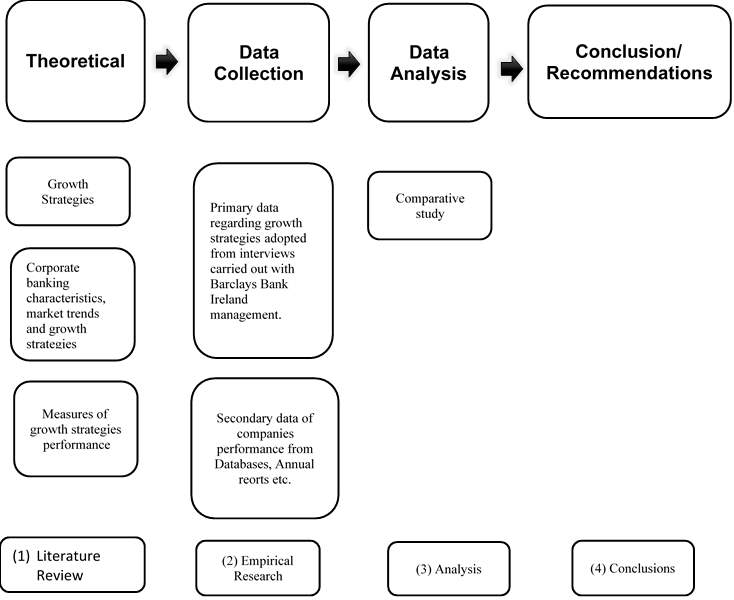
Figure 2: Research framework ‘Growth strategies for corporate banks
1.1.4 Research Questions
The main research question is:
What are the growth strategies implemented in the Barclays Cash Management and Debt (Lending) businesses within corporate banking, and what is the impact of these strategies on their performance?
Sub-questions fr this research will cover:
1. The academic methods and insights regarding growth strategies examined in strategic management literature? Additionally, what are the advantages and disadvantages of an internal growth strategy?
2. What are the characteristics of the Banking industry and what are the industry specific growth strategies and rationales behind these?
3. What are the suitable metrics to measure firm growth and firm performance with regard to growth strategies?
4. What are the differences in the performance of corporate banking firms in Europe based on their growth or expansion strategies? In order to answer to this objective, I will first formulate my hypothesis according to the literature, and test the hypothesis with the empirically collected data.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Business Strategy"
Business strategy is a set of guidelines that sets out how a business should operate and how decisions should be made with regards to achieving its goals. A business strategy should help to guide management and employees in their decision making.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation proposal and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




