Impact of the Corporate Culture on its Hybrid Strategy: Starbucks
Info: 13528 words (54 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
The impact of the corporate culture on its hybrid strategy using a new evaluation system: A study of Starbucks’ new hybrid strategy
Table of Contents
Existing evaluation system of corporate culture and limitations
Focus and objectives of the research question
New hybrid strategy of Starbucks
Critical analysis and improvements
Limitation and improvement (Ideal research design)
Appendix 3: Questionnaire data outcome
Introduction and motivation
Why choose Starbucks?
In order to adapt the rapid changes nowadays, more and more corporate change their management strategic into hybrid strategy. Starbucks is one of the most successful corporate which adapt the new strategy well in a well short time. Starbucks is a famous coffee chain that can be found all over the world, becoming one of the leaders of coffee industry (Burns, 2014). However, Starbucks’ success is not only simply relying on its high-quality coffee, but also its unique experiential marketing strategy (Plog, 2005). And Starbucks remained this differentiation strategy, an experiential marketing strategy, until the time of economic recession (Allison, 2010).
Starbucks adopted a new strategy that combined differentiation strategy and cost leadership strategy together, making efforts to reduce business costs while maintaining differentiation (Allison, 2010).
The past studies suggested that Starbucks’ corporate culture played a supporting role for its strategy (Allison, 2010). However, when Starbucks took a strategic transformation, what impact its current corporate culture on its strategy was a research-worthy question.
Existing evaluation system of corporate culture and limitations
As scholars conducted deeper research on evaluation of corporate culture construction and they combined qualitative and quantitative research together, making evaluation more intuitive and effective, some of the most well-known examples included Denison Organizational Culture Model (Kokina & Ostrovska, 2014). The Denison Organizational Culture Model summed up the four characteristics of organizational culture: adaptability, mission, involvement and consistency (Denison, Haaland, & Goelzer, 2003).
However, the disadvantage of this model is that it only focuses on single corporate strategy and fails to take the impact of culture on strategic transformation and change into account (Jaskyte, 2010). There are lots of researches and evaluation systems have been established to assess the impact of corporate culture on a single strategy, but there are not many studies on the impact of corporate culture on a hybrid strategy and no evaluation system been developed to evaluate this (Jaskyte, 2010). An improved evaluation system of corporate culture is designed, which is beneficial to companies with new hybrid strategy and which is planning to change as well.
Focus and objectives of the research question
Through the analysis of this research report, it can help Starbucks to understand the impact of its corporate culture on its new strategy by using new-designed evaluation system of corporate culture. It can also bring forward recommendations for other companies that are ready to take strategic transformation on how to reshape their corporate culture to help themselves to complete their strategic transformation smoothly.
Corporate culture and corporate strategy play an important role in an enterprise’s management (Malekzadeh & Nahavandi, 1987). At the same time, corporate culture has a great influence on corporate strategy. As a method to gain competitive advantage, corporate culture of an enterprise’s will be different in different strategic development process. Therefore, when an enterprise makes a strategic choice, it must consider cultural factors to consider whether the two match with each other well, so as to realize the objectives and achieve the vision of the company’s (Mohindru & Chander, 2010).Considering from the perspective of implementation of strategy, corporate culture not only serves the implementation of corporate strategy, but also restricts the implementation of corporate strategy. In the process of an enterprise’s cultural transformation, it should identify that in the existing culture, which aspects are advantageous for new strategy and the advantageous aspects should be reserved; which will form resistance and should be abandoned, so as to realize the enterprise’s smooth cultural transformation from the old to the new, as well as the effective implementation of the strategy. Therefore, the replacement and coordination of old and new cultures in an enterprise is the guarantee of success of implementing a strategy (Han, 2012). The study of this thesis on the impact of Starbucks’ corporate culture on its strategy has great significance in reality.
Literature review
The literature review is about relevant literature, carrying out a critical analysis towards the literature.
New hybrid strategy of Starbucks
There are three basic competitive strategies, which including cost leadership strategy, differentiation strategy and focus strategy (Porter, 1980). Traditionally, companies always choose one of the strategies as their dominant strategy (Porter, 1980), but Proff also points out that, as competitive environment changes and technology develops, it is difficult for enterprises to make a profit via adopting a single strategy while taking two strategies simultaneously is feasibility (Proff, 2000). In particular, cost leadership strategy and differentiation strategy have been adopted by many enterprises at the same time and achieved good results (Proff, 2000).
Facing the blow of the recession, Starbucks has decided to implement strategic transformation to separate itself from the dilemma, it adopted a new strategy that combined differentiation strategy and cost leadership strategy together (Allison, 2010).
Critical analysis and improvements
There are lots of researches and evaluation systems have been established to assess the impact of corporate culture on a single strategy, but there are not many studies on the impact of corporate culture on a hybrid strategy and no evaluation system been developed to evaluate this.
Moreover, the above studies explored the impact of corporate culture on corporate strategy from the point of view of either the company management or basic-level staffs. However, both corporate culture and corporate strategy have an impact on management and employees of an enterprise simultaneously, and the ways for staff sand management to deal with problems are different.
According to the characteristics of this dissertation, as well as the disadvantage of the above-mentioned existing evaluation system, a new evaluation system in this study is formed of six aspects: adaptability, mission, participatory and consistency and leadership style. Notice that this article would analyze the result from both basic-level staffs and management to explore the impact of Starbucks’ corporate culture on its corporate strategy.
Summary
Starbucks’ past success was linked with its successful strategy and appropriate corporate culture. Its corporate culture has played a huge role in the support of its corporate strategy. In order to cope with the hit arising from the economic crisis, Starbucks adopts a hybrid strategy. Whether Starbucks’ corporate culture can play a supporting role for its hybrid strategy is still a problem that is worthy of study.
The rest of dissertation is through collecting first-hand information (Questionnaire and Interview) to summarize Starbucks today’s characteristics of corporate culture and corporate strategy, based on this to discuss the impact of Starbucks’ corporate culture on its corporate strategy.
Theory/conceptual model
On the basis of previous studies, there are not many studies on the impact of corporate culture on a hybrid strategy and no evaluation system been developed to evaluate this (Jaskyte, 2010). An improved evaluation system of corporate culture is designed, which is beneficial to companies with new hybrid strategy and which is planning to change as well.
an evaluation system is established newly to evaluate the impact of the corporate culture on its hybrid strategy. A new evaluation system is designed in accordance with relevant conclusions of the literature review of this dissertation, it is mainly from six aspects to evaluate Starbucks’ corporate culture, namely, adaptability, mission, involvement and consistency, leadership style.
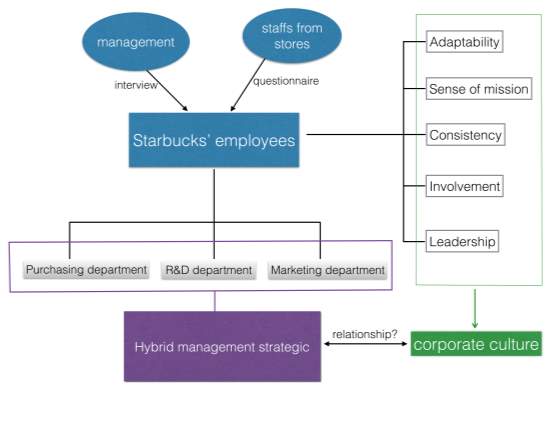
The model is made up of two part: interview and questionnaire. In order to explore the impact of corporate culture on corporate strategy from the point of view of either the company management or basic-level staffs, the quantitative data was obtained mainly through carrying out a questionnaire towards Starbucks’ employees. The qualitative data was acquired by interviewing management of Starbucks’ stores since they are more familiar with the corporate’s strategy than employees, they are better able to understand the advantages, effect as well as worries of the current strategies.
Also, as Starbucks is using both cost leadership strategy and differentiation strategy to manage different departments, the interview and questionnaire need to be carried out in three different departments to ensure most type of employees’ opinion have been included.
After processing data and summarizing the results for both interview and questionnaire, the corporate culture’s impact on corporate strategy will be carried out. And the relationship between corporate culture and hybrid corporate strategy can be summarized, which will help more companies to evaluate their corporate culture when changing into hybrid strategy.
The specific contents of the questionnaire are shown in Appendix 1 while the specific interview are shown in Appendix 2.
Methods
Actual research design
Questionnaire
For Starbucks, the Chinese market has now become the second largest market in the United States after Starbucks. In China, Starbucks is also facing fierce competition in the market from Costa. Starbucks’ strategy in China reflects Starbucks’ new hybrid management strategic thinking. This study selected Starbucks coffeehouses in China as the research objects. The questionnaire is divided into four parts. The first part recounts the purpose of the questionnaire, the second part aims to understand the staff’s opinions about Starbucks’ corporate culture. The third part shows the respondents’ personal background information. The fourth part expresses thanks to the respondents. All answers to the questions are expressed in the form of Likert-scale method.
In this study, 100 questionnaires were sent out and 91 were taken back eventually, of which 86 were effective questionnaires, the recovery rate and effective rate of questionnaires achieved 91% and 94.50%, which was consistent with the requirements of research design.
Findings of the questionnaire showed that among the respondents of the questionnaire from Starbucks, there were 48 male respondents and 42 female respondents. 38 respondents were 18-30 years old. 34 respondents were 30-40 years old, 14 respondents were more than 40 years old. 28 people were from purchasing department, 22 people were from R&D department and 36 people belonged to marketing department. It could be learned from the above data that objects of the questionnaire included staff of various age levels and they were from different departments of Starbucks, so the demographic data was distributed evenly. Thus it could be determined that the perspective of the objects of the questionnaire could represent the perspective of most of Starbucks’ staff’s and the results have certain representativeness (Creswell, 2013).
Moreover, in this study, the statistical tool for processing the data gathered from the questionnaire is SPSS16.0. Statistical processing of data was mainly carried out via two steps. The first step was testing the reliability and validity of the questionnaire and reliability test was implemented by the method of inter-item consistency (Creswell, 2013). Using SPSS to calculate Cronbach’s α, α> 0.6, indicating that the reliability of the questionnaire was qualified (Creswell, 2013). It made use of expert method to test the content validity of the questionnaire (Creswell, 2013). The second step was using analysis of variance to evaluate Starbucks’ corporate culture according to the data results, all data was expressed by means ± standard deviation (± S) (Creswell, 2013). The information collected in the interviews was analyzed by AHP (The analytic hierarchy process), carrying out an in-depth analysis about the nature, influencing factors and intrinsic relationship of Starbucks’ strategic decisions and corporate culture. And all the data processing is shown in Appendix 3.
Interview
By making use of personal relationship, before carrying out the formal interviews, the author of this thesis contacted with relevant personnel of Starbucks’ six stores in Guangzhou via telephone and e-mail to explain the purpose and significance of this study, the personnel showed that they would like to accept the interview. The interview objects included two managers from purchasing department, two managers from R&D department and two managers from marketing department. The interview was carried out by use Skype. The interview of each time was carried out by using the mode of semi-structural interview, through open questions to guide the interviewees. Before starting, the interviewer first stated the purpose of carrying out this interview, interpreting how the contents of these interviews would be used and committing that the interview content, as well as all information related to the companies would not be disclosed for any commercial purposes, they would be strictly used for academic purposes only. The time for each interview was controlled in one hour. After interviewing, the interviewees were asked to provide detailed information about how long have they work in Starbucks, position and other general background information.
Limitation and improvement (Ideal research design)
A successful completion of an interview needs specially trained interviewers with highly skilled techniques. The researchers in this interview may be inadequate in their interview skills (Cooper, Schindler, & Sun, 2003).
To explain the acquired data also requires skill and experience of a high level, limited to the author’s research level and experience, the information obtained cannot be analyzed fully (Creswell, 2013).
In this paper, the sample size is 100, as an empirical research, the samples size may not be large enough to affect the representativeness of the research results (Bryman, 2006).
Results and discussion
Adaptability
Interview
- In terms of your department, compared with the previous strategy, does the current strategy change? What measures does your department take to cope with the change?
Managers of the three departments all expressed that their strategies have changed a lot, in the past, they adopted differentiation strategy, now they also paid attention to cost control in the process of management.
The manager of purchasing department mentioned that their department’s important business was the procurement of raw materials, in the past, what the department emphasized most was the quality of the material and they paid less attention to the price of raw materials, and now they also attached great importance to fluctuations in the price of raw materials, their job was to buy the raw materials with the most preferential prices under the premise of guaranteeing a good quality.
The managers of R & D department and marketing department said that they made use of differentiation strategy in the past, through a variety of ways to understand and meet the potential needs of customers’, they were through marketing to arouse customers’ potential demand, by innovation, improving the speed of introducing new products to the market and the development of new products to meet customers’ demand. And now the strategy has also had some changes, it paid attention to cost control on the basis of meeting consumers’ demand, the specific measures included store decoration, introduction of instant coffee products and so on.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire results showed that, employees of the three department all approved of and adapted to the hybrid strategy, they were competent for their current work after the enterprise’s strategic transformation, proving that Starbucks’ staff has a strong ability to adapt. A large number of studies have showed that strategic transformation of an enterprise’s often leads to the conflict between the enterprise’s new strategy and its original corporate culture (Lumpkin, Droege, & Dess, 2002). As culture of each enterprise’s has its own characteristics, it is the result of organizational memory, once it forms, it is not easy to be changed, it has a very strong inertia (Lumpkin, Droege, & Dess, 2002). However, if the original corporate culture itself has a strong adaptability, which is advantageous to the reduction of the conflict between corporate culture and the new strategy to help with the enterprise’s smooth strategic transformation. Thus Starbucks’ corporate culture has a strong adaptability, which can help with the enterprise’s strategic transformation from the original differentiation strategy to a hybrid strategy.
Sense of mission
Interview
- In order to achieve your department’s strategy, what measures does your department take to improve the staff’s sense of mission?
The managers of the R&D department and the marketing department said that for employees of the department, they accepted training of several weeks about how to be a barista and learned a thorough understanding of the core concept of Starbucks’. It is these training that makes the employees understand Starbucks’ corporate culture and traditions, making them be able to transmit Starbucks’ ‘legendary service’ to customers. In addition, the employees also accepted specific work training continuously, so as to ensure that they have the ability to provide consumers with services of a high quality, which allowed every staff of the department to have the most professional knowledge and dedicated service attitude to win the trust of customers’.
The manager of the purchasing department expressed that for employees of the department, they were first through training to enable the employees to understand Starbucks’ development course and values. Then, through professional training, it made the staff have relevant professional skills, including appraisal of raw material, selection of suppliers, techniques of storage of coffee bean and so on. As far as their department is concerned, their department’s mission is to provide raw materials of a high quality, which relates to the enterprise’s reputation and social image. Therefore, for a long time, in training its employees, it has emphasized that in the selection of raw materials, employees should ensure the quality of raw materials in transportation, storage and other aspects. Now, it also pays attention to price, requiring that in the premise of assuring a good quality, it should buy raw materials with the most preferential prices.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire results showed, first of all, employees of the three departments all thought that they understood the enterprise’s tradition, history culture well. Secondly, employees of the three departments have expressed their willingness to participate in the training organized by the enterprise, showing that the employees were willing to improve their ability for the enterprise’s development, which was also a manifestation of the employees’ having a sense of mission. Finally, the questionnaire results showed that, employees of the three departments all believed that their colleagues have a high working enthusiasm and the employees were willing to work long time in Starbucks. These results represented that staff of the three departments of Starbucks’ have a strong sense of mission. Corporate culture of a high sense of mission is very important for enterprises which adopt cost leadership strategy and differentiated strategy. For an enterprise which adopts cost leadership strategy, the core of its business is to make every attempt to reduce costs, if its staff have a high sense of mission, they are able to link their own interests with the long-term interests of the enterprise’s, therefore in the process of work, they can effectively help the enterprise to reduce the cost of the enterprise’s, for example, taking the initiative to reduce raw material and energy consumption and so on (Lumpkin, Droege, & Dess, 2002).Considering an enterprise with differentiation strategy, it usually upholds service-oriented, customer first philosophy, staff with a high degree of sense of mission will strain every nerve to serve every customer, creating the products that meet consumers’ demand well (Lumpkin, Droege, & Dess, 2002).
Consistency
Interview
- In order to achieve your department’s strategy, what measures does your department take to improve the staff’s consistency?
Considering the methods to enhance cohesion, Starbucks’ managers of the R&D department and the marketing department said that they implemented people-oriented management, the specific practice included reasonable formulation of employees’ working time, respecting employees, treating every employee fairly. In this way, employees worked with more enthusiasm. At the same time, it also developed a reasonable management system, a reasonable salary system to offer fair rewards and penalties. In addition, they were also through continuous training to improve the overall quality of the staff, so that employees adapted to the needs of the enterprise’s changeable development. Through training, it improved the staff’s occupation quality, moral, psychological quality and so on, when the enterprise faced dilemma, the staff were able to ride out the storm together with the enterprise, increasing the cohesion of the company.
The leader of the purchasing department mentioned that they were through salary management to improve the cohesion. For outstanding staff, they were given pecuniary reward, and when a worker saw that what he gained was proportional to what he paid for the enterprise, he would have a kind of trust for the enterprise. This trust is conducive to mobilize the employees’ enthusiasm, initiative to enhance an enterprise’s cohesive affinity.
Questionnaire
Denison, Stephanie and Paulo (Denison, Haaland, & Goelzer, 2003)analyzed that consistency is usually used to test whether a company has a strong and cohesive internal culture. Enterprise cohesion refers to the state of the unity of all the staff of an enterprise, enterprise cohesion belongs to category of corporate culture, it determines the morale of an enterprise’s employees’ and affects employees’ mental state at work (Denison, Haaland, & Goelzer, 2003).Generally, enterprise cohesion includes the following factors: the degree of all staff’s identity for the common goals or leaders of an enterprise, the degree of an enterprise’s interior harmony (Denison, Haaland, & Goelzer, 2003). It could be seen from the findings of the questionnaire that employees of Starbucks’ three department have a high degree of identity for its enterprise goals and its leaders, at the same time, its internal team cooperation ability was relatively high, showing that Starbucks has a high cohesion. It could be found from the interview that Starbucks’ R&D department and marketing department were through humanized management, reasonable compensation system and training to improve enterprise cohesion, and its purchasing department was mainly through compensation system to improve enterprise cohesion.
Both cost leadership strategy and differentiation strategy need enterprises with highly cohesive culture. In an enterprise which conducts cost leadership strategy, it is through the establishment of target cost management to connect cost with employees’ compensation so as to enhance the enterprise’s internal cohesion, which can let employees take the initiative to reduce cost to enable various specific measures, methods and requirements for reducing cost to be implemented and applied successfully, so as to realize cost leadership strategy (Lumpkin, Droege, & Dess, 2002).In terms of an enterprise which adopts differentiation strategy, it is through giving workers certain autonomy, respect for the views of staff’s, helping with employees’ making progress to improve enterprise cohesion, so as to improve employees’ innovation ability to help the enterprise to realize differentiation strategy (Lumpkin, Droege, & Dess, 2002). Thus although Starbucks’ these three departments established a culture with a high cohesion in different ways, the corporate culture with a high cohesion played the role in promoting the achievement of their strategies.
Involvement
Interview
The manager of Starbucks’ purchasing department responded that the communication with staff was mainly a top-down communication, the main modes of communication were: meetings, interviews, written report, etc.
The managers of the R&D department and the marketing department showed that their communication with employees was a two-way communication, they passed on the company’s top advice timely to employees and they would listen to the views of staff’s to provide timely feedback, encouraging organizational communication between members as well as the members’ involvement in management and decision-making, they paid 48 attentions to mobilize staff’s work enthusiasm. They commonly used meetings, written reports, Christmas parties, Thanksgiving festival activities for communication with the staff to enhance team cohesion. Through the organization of travel, it promoted a harmonious relationship among employees.
Questionnaire
The findings of the questionnaire also confirmed the results of the interview, employees of the three departments were willing to communicate with leaders of their departments through a formal way of communication, and they all believed that their formal communication achieved a good result. However, although employees of the purchasing department still hoped to communicate with leaders through informal communication ways, they thought that the informal communication of their department failed to achieve ideal results. Staff of the R&D department and the marketing department was willing to through informal communication ways to communicate with their leaders, they considered that the informal communication effectiveness of their department is comparatively good. Employees of the R&D department and the marketing department were more willing to participate in management and bring forward suggestions than staff of the purchasing department, indicating that to compare staff from the R&D department and the marketing department with staff from the purchasing department, the former’s degree of involvement was higher.
Style of leadership
Interview
- In order to achieve your department’s strategy, what style of leadership does your department adopt?
The manager of the purchasing department said that in general, they put forward specific mission requirements for employees or suppliers, they made clear to staff that what their standard was and what they hoped to get from employees. If the employees did a good job, their bonus would be enhanced, if the staff did not reach the required standards, the bonus would be reduced accordingly.
Management of the R&D department and the marketing department mentioned that he did not make all decisions, some decisions at work were decided by the employees and the management commonly. In terms of staff’s work, it was not required to conform to a united standard, employees were allowed to have their own ideas, in addition to bonus, members were praised in public for doing a good job.
Questionnaire
In this paper, the questionnaire results confirmed the results of interview, firstly, staff of the purchasing department less participated in decision-making of the department, nor did them decide some details of their work. Their rational proposals have not been given sufficient attention. Secondly, staff of the R&D department and the marketing department could participate in the organization’s decision making, at the same time, they have the right to decide details of their work, their rational proposals were also able to get attention. Corporate culture of centralized leadership emphasizes the roles of organizational rules and disciplines, making use of command to conduct leadership. In this way, leadership of a higher efficiency is beneficial to improving efficiency and saving cost, which is in line with the requirements of cost leading strategy of the purchasing department’s, but this style of leadership is not conducive to encourage employees’ intrinsic motivation (Cameron & Quinn, 2005) (An, Yom, & Ruggiero, 2011).While the corporate culture of power equilibrium leadership focuses on the use of methods of dialogue, inspiration, discussion and various kinds of incentive methods to stimulate staff’s inherent power, making subordinates sincerely understand and accept the intention of leaders to consciously to achieve specific leadership goals, which is beneficial to encouraging innovation and in line with the requirements of the R&D department’s and the marketing department’s differentiation strategy (Lumpkin, Droege, & Dess, 2002) (Cameron & Quinn, 2005).
Conclusion
First of all, in order to achieve their own strategies, different department use different strategy which leading to a situation same corporate have various corporate culture. The product R&D department and marketing department adopted the style of power equilibrium leadership. The purchasing department used a centralized leadership. Then, to achieve their own strategies, Starbucks’ departments took different measures, which showed the characteristics of different corporate culture construction. Starbucks’ departments have a high adaptability, consistency, involvement, sense of mission and recognition. But it should be noted that although the corporate cultures of Starbucks’ different departments showed the same characteristics, the styles of different departments’ corporate culture construction are different. The R & D and marketing departments’ corporate culture construction has the characteristics of flexibility, while the purchasing department’s corporate cultural construction has the characteristics of rigidness. For example, the purchasing department was mainly through the way of formal communication to improve employees’ involvement, the R & D and marketing departments were through formal and informal communication ways to improve employees’ involvement.
Through the study in this thesis it can be found that, not only corporate strategies can be hybrid, corporate cultures can also be hybrid, two different kinds of corporate cultures can also coexist in a same corporate according to the need of the corporate strategy and it can serve the strategy well (Spanos, Zaralis, & Lioukas, 2004). It proved that Starbucks’ current hybrid corporate culture has a positive significance for its hybrid strategy. Therefore, the relationship between Starbucks’ corporate culture and their corporate strategy is interesting. Starbucks’ hybrid strategy makes a hybrid type of corporate culture, while hybrid corporate culture helps the employee to smoothly adapt Starbucks’s hybrid strategy.
Reference
Allison, M. (2010, May 16). Starbucks has a new growth strategy — more revenue with lower costs. Retrieved March 18, 2017, from The Seattle Times: http://www.seattletimes.com/business/starbucks-has-a-new-growth-strategy-8212-more-revenue-with-lower-costs/
An, J.-Y., Yom, Y.-H., & Ruggiero, J. S. (2011). Organizational culture, quality of work life, and organizational effectiveness in Korean university hospitals. Journal of Transcultural Nursing , 22 (1), 22-30.
Bryman, A. (2006). Integrating quantitative and qualitative research: how is it done? Qualitative research , 6 (1), 97-113.
Burns, S. (2014, December 17). Top 10: Global Coffee Shop Chains. Retrieved March 19, 2017, from Business Review Europe: http://www.businessrevieweurope.eu/leadership/340/Top-10:-Global-Coffee-Shop-Chains
Cameron, K. S., & Quinn, R. E. (2005). Diagnosing and changing organizational culture: Based on the competing values framework. John Wiley & Sons.
Cooper, D. R., Schindler, P. S., & Sun, J. (2003). Business research methods.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. New York: Sage publications.
Denison, D. R., Haaland, S., & Goelzer, P. (2003). Corporate culture and organizational effectiveness: Is there a similar pattern around the world? In D. R. Denison, S. Haaland, P. Goelzer, J. S. Osland, M. Li, & M. E. Mendenhall (Eds.), Advances in global leadership (3rd Edition ed., Vol. 3, pp. 205-227). Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Garza, G. (2010). The history of Starbucks. Catalogs.com , 7.
Gopalakrishna, P., & Subramanian, R. (2001). Revisiting the Pure versus Hybrid Dilemma: Porter’s Generic Strategies in Developing Economy. Journal of Global Marketing , 15 (2), 61-79.
Han, H. (2012). The relationship among corporate culture, strategic orientation, and financial performance. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly , 53 (3), 207-219.
Jaskyte, K. (2010). An exploratory examination of correlates of organizational culture. Administration in social work , 34 (5), 423-441.
Kim, E., Nam, D.-i., & Stimpert, J. L. (2004). TESTING THE APPLICABILITY OF PORTER’S GENERIC STRATEGIES IN THE DIGITAL AGE: A STUDY OF KOREAN CYBER MALLS. Journal of Business Strategies , 21 (1), 19-45.
Kokina, I., & Ostrovska, I. (2014). THE ANALYSIS OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE WITH THE DENISON MODEL (The Case Study of Latvian Municipality). European Scientific Journal, ESJ , 9 (10), 362-368.
Lumpkin, G., Droege, S. B., & Dess, G. G. (2002). E-Commerce Strategies: Achieving Sustainable Competitive Advantage and Avoiding Pitfalls. Organizational Dynamics , 30 (4), 325-340.
Malekzadeh, A. R., & Nahavandi, A. (1987). The Fit Between Strategy and Culture in Mergers. In Academy of Management Proceedings (pp. 41-45). Academy of Management.
Mohindru, A., & Chander, S. (2010). Diversification Strategy and Corporate Performance in India: An Empirical Investigation. Asia Pacific Business Review , 6 (3), 124-137.
Plog, S. C. (2005). Starbucks: More than a cup of coffee. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly , 46 (2), 284-287.
Porter, M. E. (1980). Techniques for analyzing industries and competitors. Competitive Strategy , 297-449.
Proff, H. (2000). Hybrid strategies as a strategic challenge—the case of the German automotive industry. Omega , 28 (5), 541-553.
Saunders, M. N. (2011). Research methods for business students (5th Edition ed.). Pearson Education India.
Spanos, Y. E., Zaralis, G., & Lioukas, S. (2004). Strategy and industry effects on profitability: evidence from Greece. Strategic management journal , 25 (2), 139-165.
Yuan, Y.-H., & Wu, C. (2008). Relationships among experiential marketing, experiential value, and customer satisfaction. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research , 32 (3), 387-410.
Appendix 1: Questionnaire
Dear participant!
I am a university student who is implementing a research report about ‘the impact of the corporate culture on its hybrid strategy using a new evaluation system: A study of Starbucks’ new hybrid strategy’
I will be very appreciated if you are willing to take 15mins to complete the following questionnaire.
Your questionnaire will be submitted anonymously and it will only use for academic purpose. Thank you very much for your time!
Please tick the options that best represent your opinions.
Part I Corporate culture
Part II Background Information
| Gender | Male | Female |
| □ | □ |
| Age | 18-30 | 30-40 | Above 40 |
| □ | □ | □ |
| Department | Purchasing Department | R&D Department | Marketing Department |
| □ | □ | □ |
Thank for your cooperation!
Appendix 2: Interview Outline
Question 1: In terms of your department, compared with the previous strategy, does the current strategy change? What measures does your department take to cope with the change?
Question 2: In order to achieve your department’s strategy, what measures does your department take to improve the staff’s sense of mission?
Question 3: In order to achieve your department’s strategy, what measures does your department take to improve the staff’s consistency?
Question 4: In order to achieve your department’s strategy, what measures does your department take to improve the staff’s involvement?
Question 5: In order to achieve your department’s strategy, what style of leadership does your department adopt?
Appendix 3: Questionnaire data outcome
Adaptability
Questionnaire
You totally agree with your company’s changes in its business strategy, do you agree?
To analyze the questionnaires completed by staff from Starbucks’ three departments: purchasing department, R&D department and marketing department, their scores showed that the purchasing department scored 4±0.3418, the R&D department scored 4±0.4821, the marketing department scored 4±0.5487. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis and it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (P>0), showing that staff of the three departments all approved of their companies’ changes in its business strategy.
Table 1 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N
|

MEAN
|

Std. Deviation
|
| Purchasing Department | 28 | 4 | .3418 |
| R&D Department | 
22 |

4 |

.4821 |
| Marketing Department | 
36
|

4
|

.5487
|
You adapt to your company’s changes in business strategies, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.2672, the R&D department scored 4±0.3244, the marketing department scored 4±0.6890. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (P>0), showing that staff of the three departments all thought that they adapted to their companies’ changes in business strategies.
Table 2 Descriptive

GROUP |
 
N |

MEAN |

Std. Deviation |

Purchasing Department |
 
28 |

4 |

.2672 |
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .3244 |
| Marketing Department | 36 | 4 | .6890 |
You are qualified for your current work, do you agree?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.0198, the R&D department scored 4±0.0225, the marketing department scored 4±0.3587. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, the data showed p=1>0.05, indicating that there was no significant difference among the three groups, showing that staff of the three departments all thought that they were qualified for their current work.
Table 3 Descriptive
| GROUP |  
N |
MEAN | 
Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department |  
28 |
4 | 
.0198 |
| R&D Department |  
22
|
4 | 
.0225
|
| Marketing Department | 36
|
4 | .3587 |
Sense of mission
Questionnaire
You know Starbucks’ tradition, history and culture well, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0. 2412, the R&D department scored 4±0. 3556, the marketing department scored 4±0. 2178. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (p>0). It showed that staff of the three departments all understood Starbucks’ tradition, history and culture well.
Table 4 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N |

MEAN |

Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 
28
|

4 |

.2412 |
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .3556 |
| Marketing Department | 
36
|
4 | .2178 |
You understand your company’s current status well, do you agree?
The purchasing department scored 4±0. 2339, the R&D department scored 4±0. 2179, the marketing department scored 4±0. 2254. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (p>0), it showed that staff of the three departments all understood the company’s current status well.
Table 5 Descriptive
| GROUP | N | MEAN | Std. Deviation | |||||
| Purchasing Department | 
28 |

4 |

.2339 |
|||||
| R&D Department | 
22 |

4 |

.2179 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||||
| Marketing Department | 36
|
4
|
.2254
|
|||||
Your colleagues are active at work, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0. 1314, the R&D department scored 4±0. 2560, the marketing department scored 4±0.3214. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis and found out p=0>0.05, indicating that there was no significant difference among the three groups, it represented that staff of the three departments all agreed that their colleagues have a high enthusiasm at work.
Table 6 Descriptive

GROUP
|

N
|
MEAN | Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 28 | 4 | .1314 |

R&D Department
|

22
|
4 | .2560 |
| Marketing Department | 36
|
4
|
.3214
|
You are willing to participate in your company’s training activities, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.1790, the R&D department scored 4±0.2711, the marketing department scored 4±0.2109. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (p>0), it showed that staff of the three departments were all willing to participate in their companies’ training activities
Table 7 Descriptive
| GROUP | N | MEAN | Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 28 | 4 | .1790 |
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .2711 |
| Marketing Department | 36 | 4 | .2109 |
Consistency
Questionnaire
You identify with Starbucks’ enterprise goals, do you agree?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.2561, the R&D department scored 4±0.1398, the marketing department scored 4±0.1451. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis and it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (P>0), showing that staff of the three departments all identified with Starbucks’ enterprise goals.
Table 8 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N
|

MEAN
|
Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 28 | 4 | .2561 |
| R&D Department | 
22
|

4
|
.1398 |
| Marketing Department | 36
|
4
|
.1451 |
The instructions of your management can be executed smoothly by your colleagues, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0. .6567, the R&D department scored 4±0. 8991, the marketing department scored 4±0. 3347. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (p>0). It proved that staff of the three departments all believed that the instructions of their management can be executed smoothly by their colleagues.
Table 9 Descriptive

GROUP |
N | MEAN | Std. Deviation |

Purchasing Department |
28 | 4 | .6567 |

R&D Department |
22 | 4 | .8991 |
| Marketing Department
|
36 | 4 | .3347 |
Members of the team of your department cooperate with each other well, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.3257, the R&D department scored 4±0.2724, the marketing department scored 4±0.2156. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, it showed no significant difference among the three groups (p>0), indicating that members of the three departments all believed that the staff of their team cooperated with each other well.
| GROUP | N | MEAN | Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department |  
28 |

4 |

.3257 |
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .2724 |
| Marketing Department | 36 | 4 | .2156 |
Table 10 Descriptive
Involvement
Questionnaire
You are willing to communicate with your managers through formal channels, such as meetings, written communication, interviews, etc., do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.3418, the R&D department scored 4±0.2821, the marketing department scored 4±0.1487. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis and it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (p>0), it showed that staff of the three departments were willing to communicate with their managers through formal channels.
Table 11 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N |
MEAN | Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 
28
|
4
|
.3418
|
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .2821 |
| Marketing Department | 
36
|

4
|

.1487
|
You are willing to communicate with your managers through informal channels, such as parties or tourism organized by your company, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.1667, the R&D department scored 4±0.2179, the marketing department scored 4±0.1567. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis and it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (P>0), it showed that staff of the three departments were willing to communicate with their managers through informal channels.
Table 12 Descriptive
| GROUP | N |  
MEAN |

Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 28 |  
4
|

.1667
|
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .2179 |
| Marketing Department | 36 |  
4 |

.1567 |
You are satisfied with effect of Starbucks’ formal communication, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 4±0.1121, the R&D department scored 4±0.2475, the marketing department scored 4±0.1879. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis and it indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups (p>0), it showed that staff of the three departments were all satisfied with effect of Starbucks’ formal communication.
Table 13 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N |
MEAN | Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 
28
|
4 | .1121 |
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .2475 |
| Marketing Department | 
36
|

4
|

.1879
|
You are satisfied with effect of Starbucks’ informal communication, do you agree with that?
The purchasing department scored 3±0.2467, the R&D department scored 4±0.4356, the marketing department scored 4±0.3978. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, to compare the R&D department and the marketing department, it showed no significant difference (p>0), and there was significant difference between the purchasing department and the other two departments (p<0), showing that staff of the R&D department and the marketing department were satisfied with effect of Starbucks’ informal communication and staff of the purchasing department did not feel the same way.
Table 14 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N |
MEAN | 
Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 
28
|
3 | 
.2467
|
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .4356 |
| Marketing Department | 
36 |
4 | 
.3978 |
You would like to participate in management and put forward a proposal, do you agree?
The purchasing department scored 3±0.1269, the R&D department scored 4±0.3176, the marketing department scored 4±0.2543. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, there was no significant difference between the R&D department and the marketing department (p>0), to compare the purchasing department with the other two departments, it showed a significant difference (p<0), showing that staff of the R&D department and the marketing department were more willing to participate in management and put forward a proposal than staff of the purchasing department.
Table 15 Descriptive

GROUP |

N |

MEAN |

Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 
28 |
3 | .1269 |
| R&D Department | 
22
|
4 | .3176 |
| Marketing Department | 36
|
4 | .2543 |
Style of leadership
Questionnaire
You can participate in the organization’s internal decision-making, do you agree?
The purchasing department scored 3±0.2218, the R&D department scored 4±0.3455, the marketing department scored 4±0.2112. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, there was no significant difference between the R&D department and the marketing department (p>0), to compare the purchasing department with the other two departments, it showed a significant difference (p<0), showing that staff of the other two departments participated in the organization’s internal decision-making more than the staff of the purchasing department.
Table 16 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N |
MEAN | 
Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 
28
|
3
|

.2218 |
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .3455 |
| Marketing Department | 
36
|

4
|
.2112 |
You have the right to decide some details of your work, such as the progress of work, clothing and so on, do you agree?
The purchasing department scored 2±0.8778, the R&D department scored 4±0.1441, the marketing department scored 4±0.2333. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, there was no significant difference between the R&D department and the marketing department (p>0), to compare the purchasing department with the other two departments, it showed a significant difference (p<0), showing that staff of the other two departments have more right that staff of the purchasing department in determining some details of their work.
Table 17 Descriptive
| GROUP | N |  
MEAN
|
Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 28 | 2 | .8778 |
| R&D Department | 22 |  
4 |
.1441 |
| Marketing Department | 36 |  
4
|
.2333 |
Staff’s rational proposals are valued by the management, do you agree?
The purchasing department scored 3±0.1531, the R&D department scored 4±0.2890, the marketing department scored 4±0.1247. Making use of SPSS to conduct variance analysis, there was no significant difference between the R&D department and the marketing department (p>0), to compare the purchasing department with the other two departments, it showed a significant difference (p<0), showing that staff of the other two departments thought that their advice was valued and the staff from the purchasing department considered that their advice has not been valued.
Table 18 Descriptive
| GROUP | 
N |
MEAN | 
Std. Deviation |
| Purchasing Department | 
28
|
3 | 
.1531
|
| R&D Department | 22 | 4 | .2890 |
| Marketing Department | 
36
|
4
|

.1247 |
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Business Analysis"
Business Analysis is a research discipline that looks to identify business needs and recommend solutions to problems within a business. Providing solutions to identified problems enables change management and may include changes to things such as systems, process, organisational structure etc.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:

 Strongly disagree Strongly disagree
Strongly disagree Strongly disagree


